Abstract
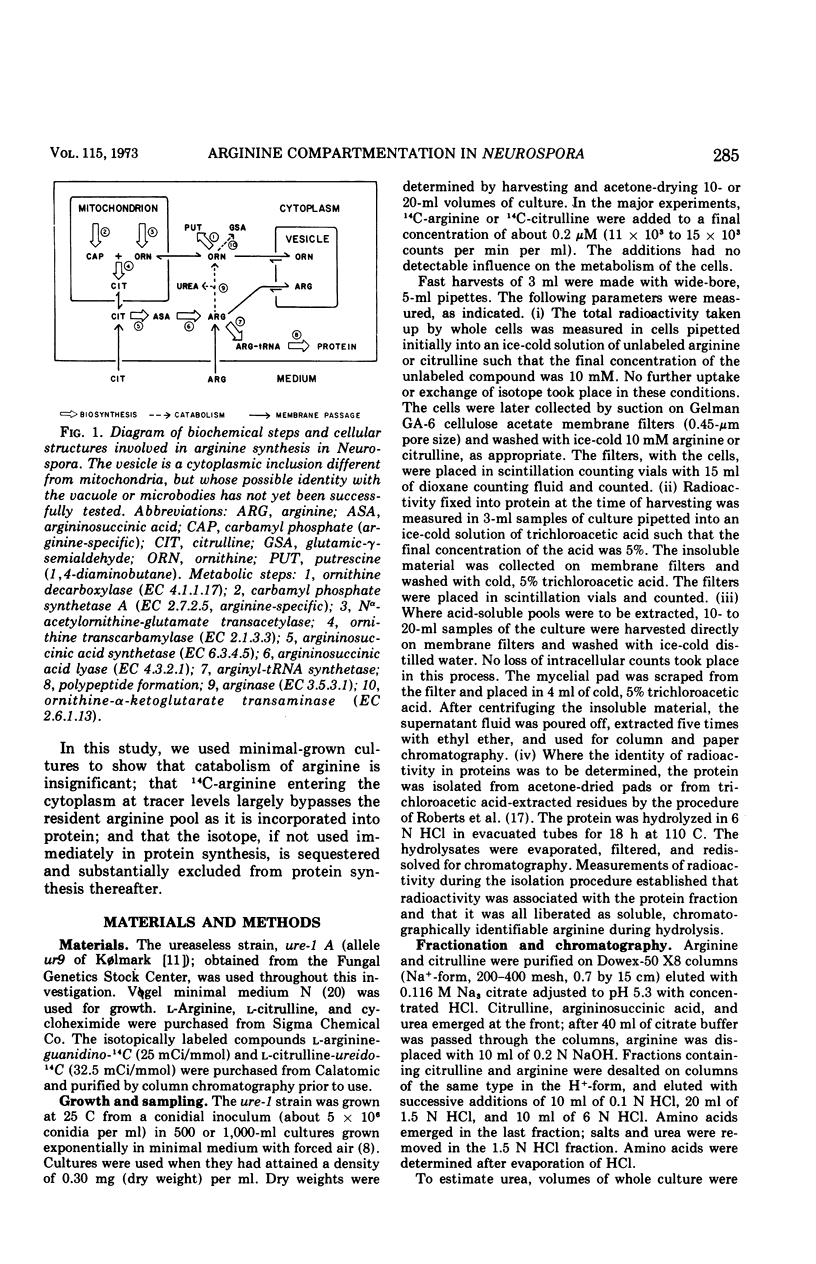
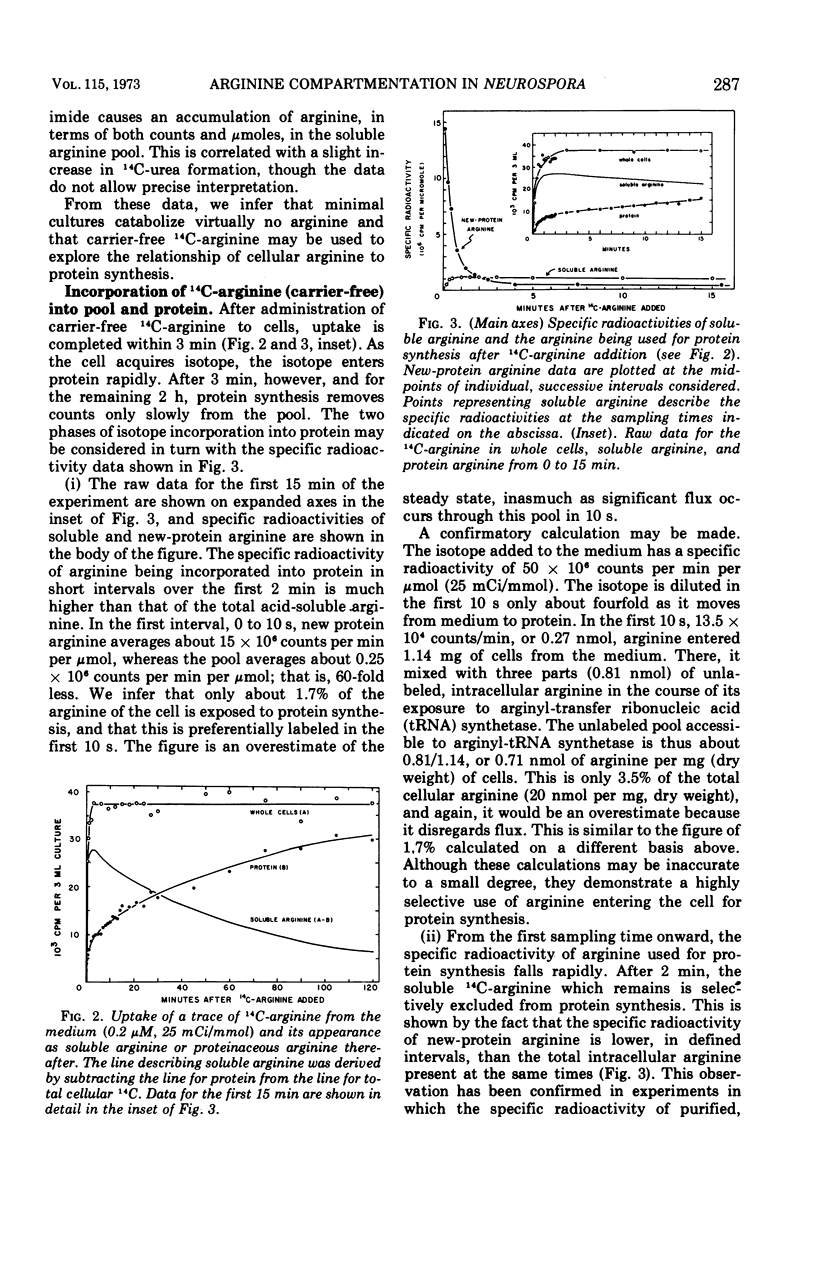
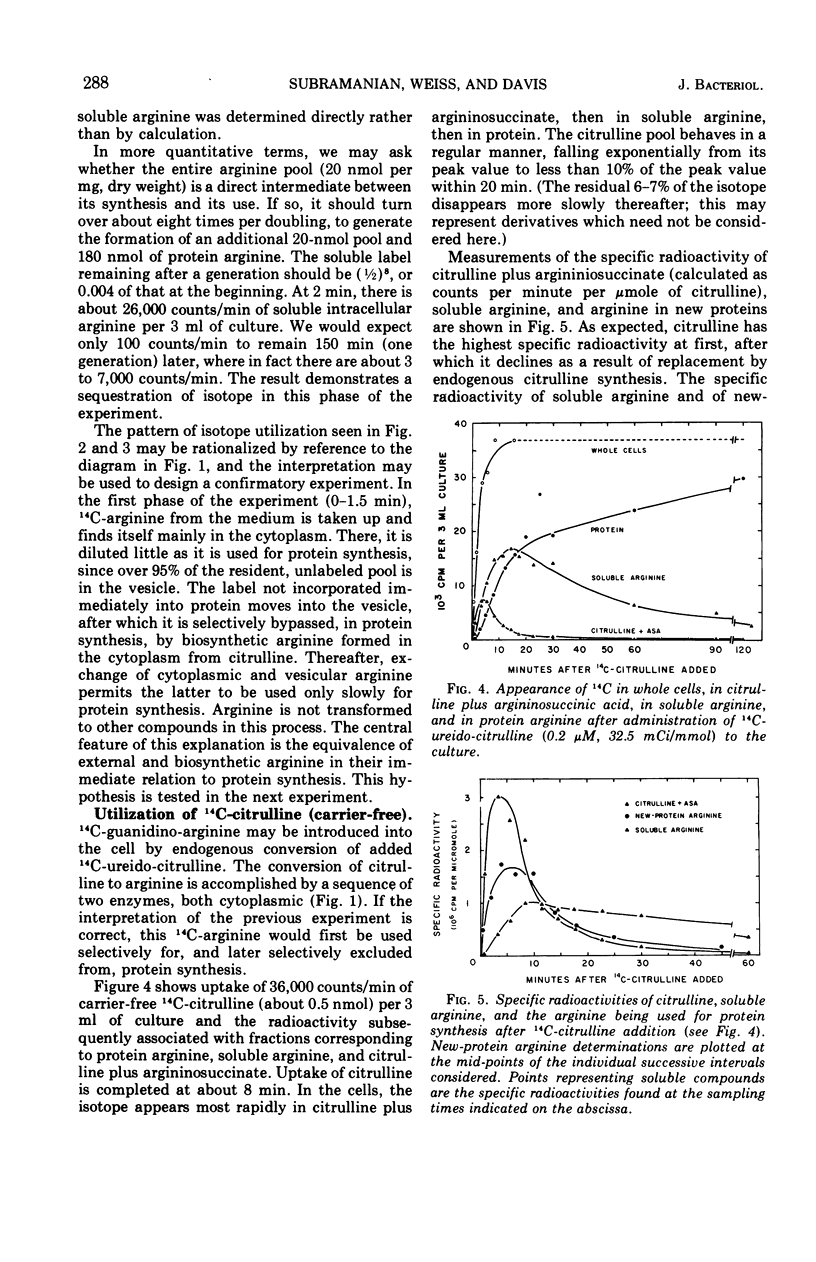
The fate of very low amounts of 14C-arginine derived from the medium or from biosynthesis was studied in Neurospora cells grown in minimal medium. In both cases, the label enters the cytoplasm, where it is very briefly used with high efficiency for protein synthesis without mixing with the bulk of the large, endogenous pool of 12C-arginine. The soluble 14C-arginine which is not used for protein synthesis is sequestered in a vesicle with the bulk of the endogenous arginine pool. After this time, it is selectively excluded from use in protein synthesis except by exchange with cytoplasmic arginine. The data suggest that in vivo, the non-organellar cytoplasm contains less than 5% of the soluble, cellular arginine. The cellular organization of Neurospora described here also prevents the catabolism of arginine. Our results are discussed in relation to previous work on amino acid pools of other eukaryotic systems.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bernhardt S. A., Davis R. H. Carbamoyl phosphate compartmentation in Neurospora: histochemical localization of aspartate and ornithine transcarbamoylases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jul;69(7):1868–1872. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.7.1868. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COWIE D. B., BOLTON E. T. The use of metabolic pools of purine compounds for nucleic acid synthesis in yeast. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1957 Aug;25(2):292–298. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(57)90471-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COWIE D. B., McCLURE F. T. Metabolic pools and the synthesis of macromolecules. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1959 Jan;31(1):236–245. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(59)90460-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COWIE D. B., WALTON B. P. Kinetics of formation and utilization of metabolic pools in the biosynthesis of protein and nucleic acid. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1956 Aug;21(2):211–226. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(56)90001-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CROKAERT R., SCHRAM E. Dosage des N-carbamoyldérivés d'acides aminés par la diacétylmonoxime. Bull Soc Chim Biol (Paris) 1958;40(7-8):1093–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. H., Lawless M. B., Port L. A. Arginaseless Neurospora: genetics, physiology, and polyamine synthesis. J Bacteriol. 1970 May;102(2):299–305. doi: 10.1128/jb.102.2.299-305.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. H. Sources of urea in Neurospora. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Aug 14;215(2):412–414. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(70)90042-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALVORSON H. O., COHEN G. N. Incorporation des amino-acides endogènes et exogènes dans les protéines de la levure. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1958 Jul;95(1):73–87. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HESS J., KITO E., MARTIN R. P., VAN PILSUM J. F. Determination of creatine, creatinine, arginine, guanidinoacetic acid, guanidine, and methylguanidine in biological fluids. J Biol Chem. 1956 Sep;222(1):225–235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KORITZ S. B., COHEN P. P. Colorimetric determination of carbamylamino acids and related compounds. J Biol Chem. 1954 Jul;209(1):145–150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolmark H. G. Genetic studies of urease mutants in Neurospora crassa. Mutat Res. 1969 Jul-Aug;8(1):51–63. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(69)90140-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MATCHETT W. H., DEMOSS J. A. PHYSIOLOGICAL CHANNELING OF TRYPTOPHAN IN NEUROSPORA CRASSA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Apr 4;86:91–99. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(64)90162-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mora J., Tarrab R., Bojalil L. F. On the structure and function of different arginases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Apr 12;118(1):206–209. doi: 10.1016/s0926-6593(66)80161-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mortimore G. E., Woodside K. H., Henry J. E. Compartmentation of free valine and its relation to protein turnover in perfused rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1972 May 10;247(9):2776–2784. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SLAYMAN C. W., TATUM E. L. POTASSIUM TRANSPORT IN NEUROSPORA. I. INTRACELLULAR SODIUM AND POTASSIUM CONCENTRATIONS, AND CATION REQUIREMENTS FOR GROWTH. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Nov 29;88:578–592. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZALOKAR M. Kinetics of amino acid uptake and protein synthesis in Neurospora. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1961 Jan 29;46:423–432. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(61)90573-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


