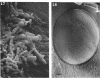
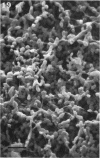
Abstract
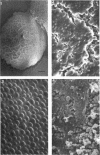
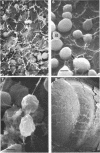
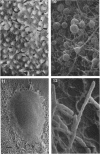
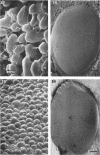
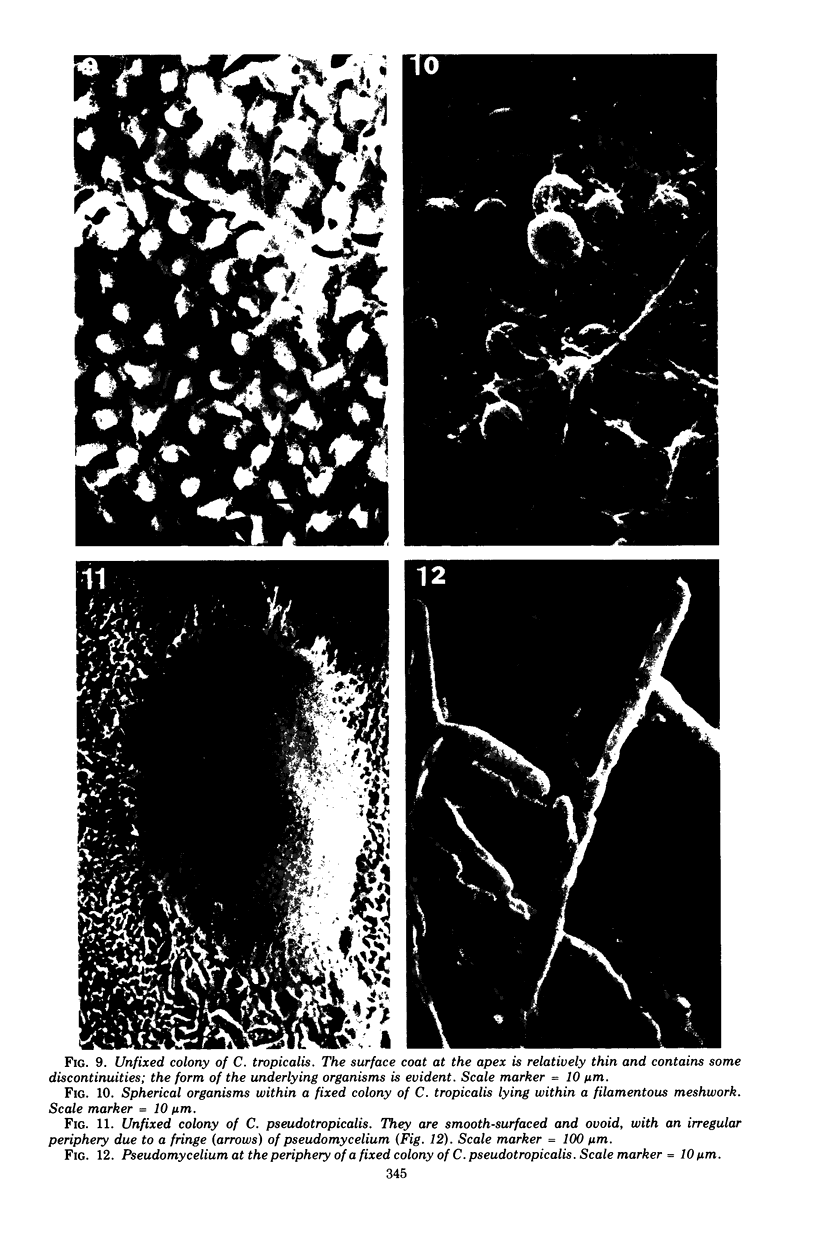
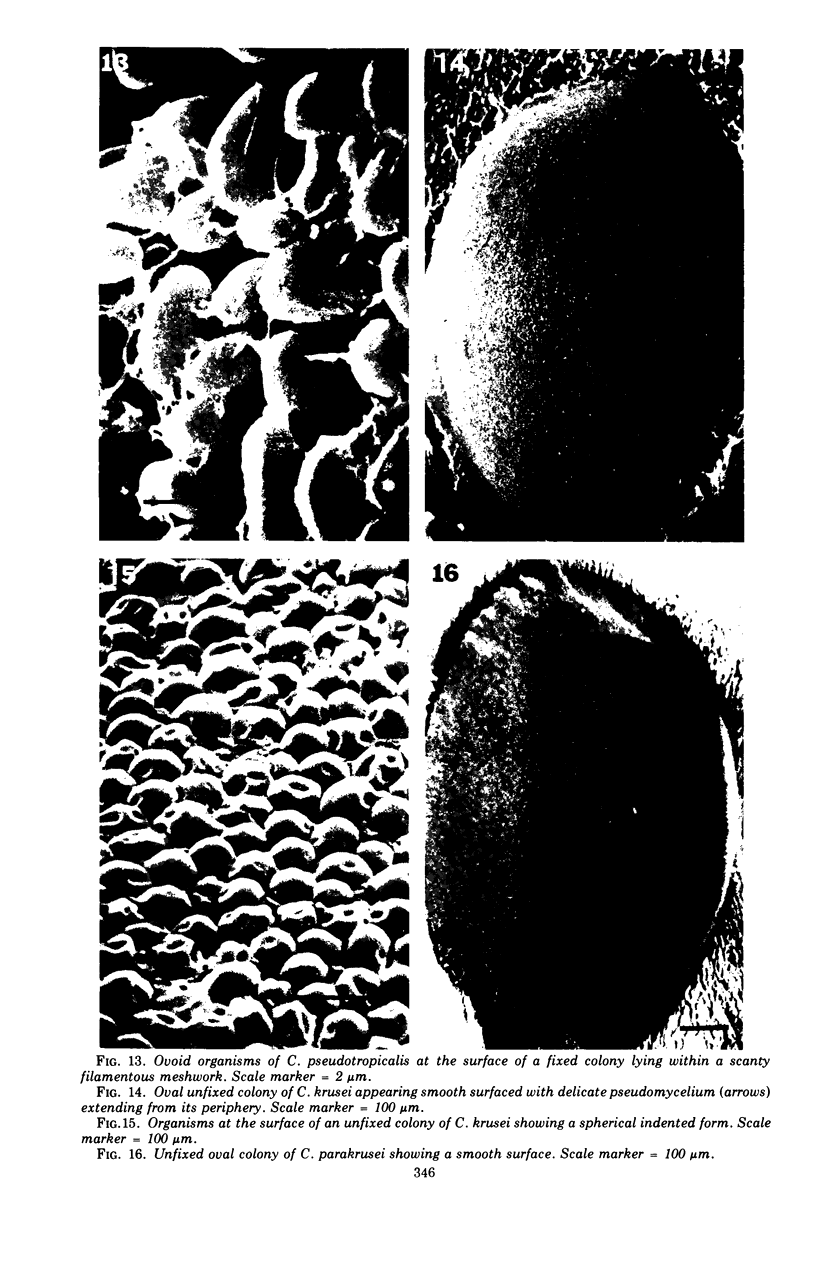
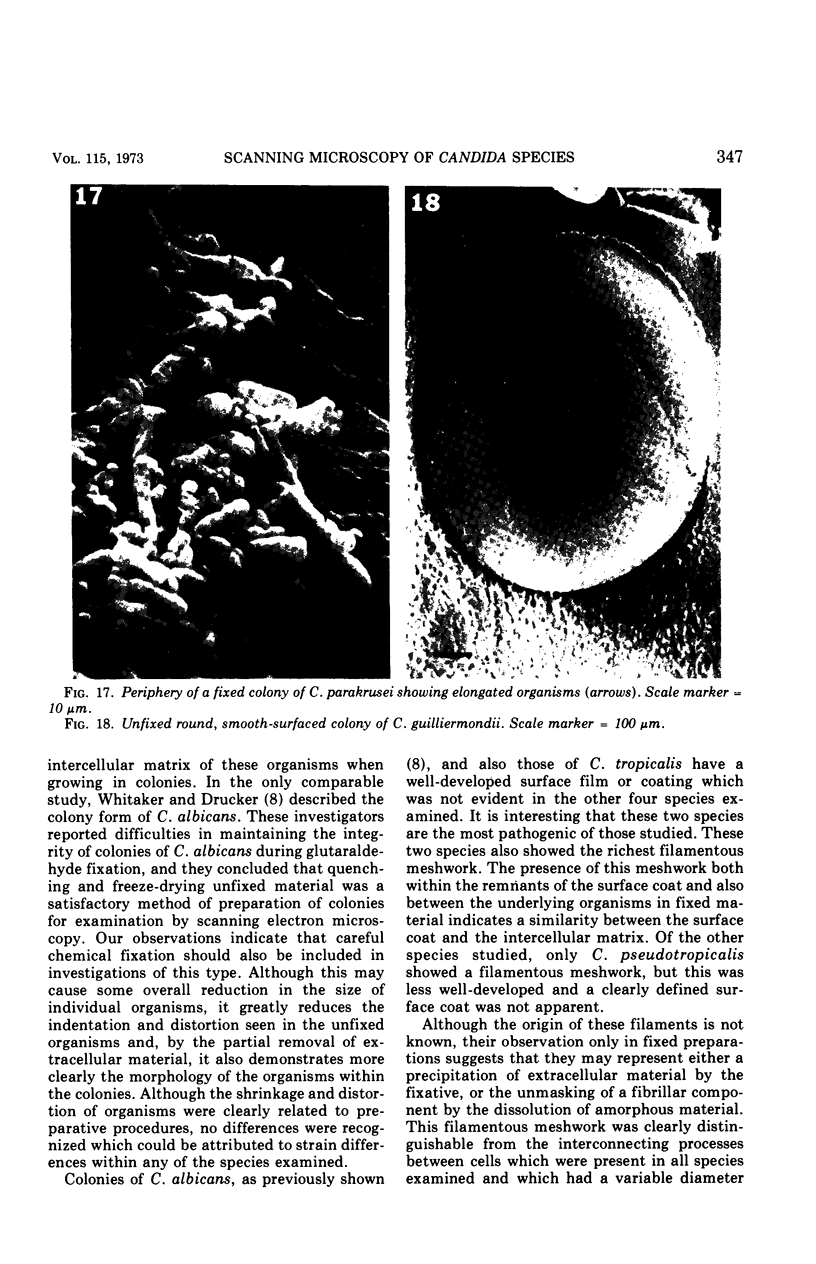
Thirty strains of six species of Candida isolated from patients were cultured for 60 h on Sabouraud agar, freeze-dried, and examined with a scanning electron microscope. The colonies were circular (Candida albicans, C. guilliermondii) or oval (C. tropicalis, C. pseudotropicalis, C. krusei, C. parakrusei) in outline, and those of C. pseudotropicalis and C. krusei had an irregular outline due to a peripheral pseudomycelium. The morphology of individual microorganisms was examined at the margins and apex of those species which lacked a surface coat (C. pseudotropicalis, C. krusei, C. parakrusei, C. guilliermondii), and through cracks in the surface coating of those which showed a surface coat (C. albicans, C. tropicalis). All species showed buds, bud scars, and interconnecting intercellular processes, but were generally spherical (C. albicans, C. tropicalis) or ovoid (C. pseudotropicalis, C. krusei, C. parakrusei, C. guilliermondii) in fixed preparations. In unfixed material, individual organisms were almost invariably indented. Fixation with 3% glutaraldehyde and washing before freeze-drying caused partial removal of the surface coating of colonies of C. albicans and C. tropicalis, which persisted only as irregular sheets or as a filamentous meshwork. This filamentous meshwork was also present among the organisms of colonies of C. albicans, C. tropicalis, and C. pseudotropicalis. It is concluded that these filaments represent the precipitation or unmasking of some component of the intercellular matrix of these organisms.
Full text
PDF
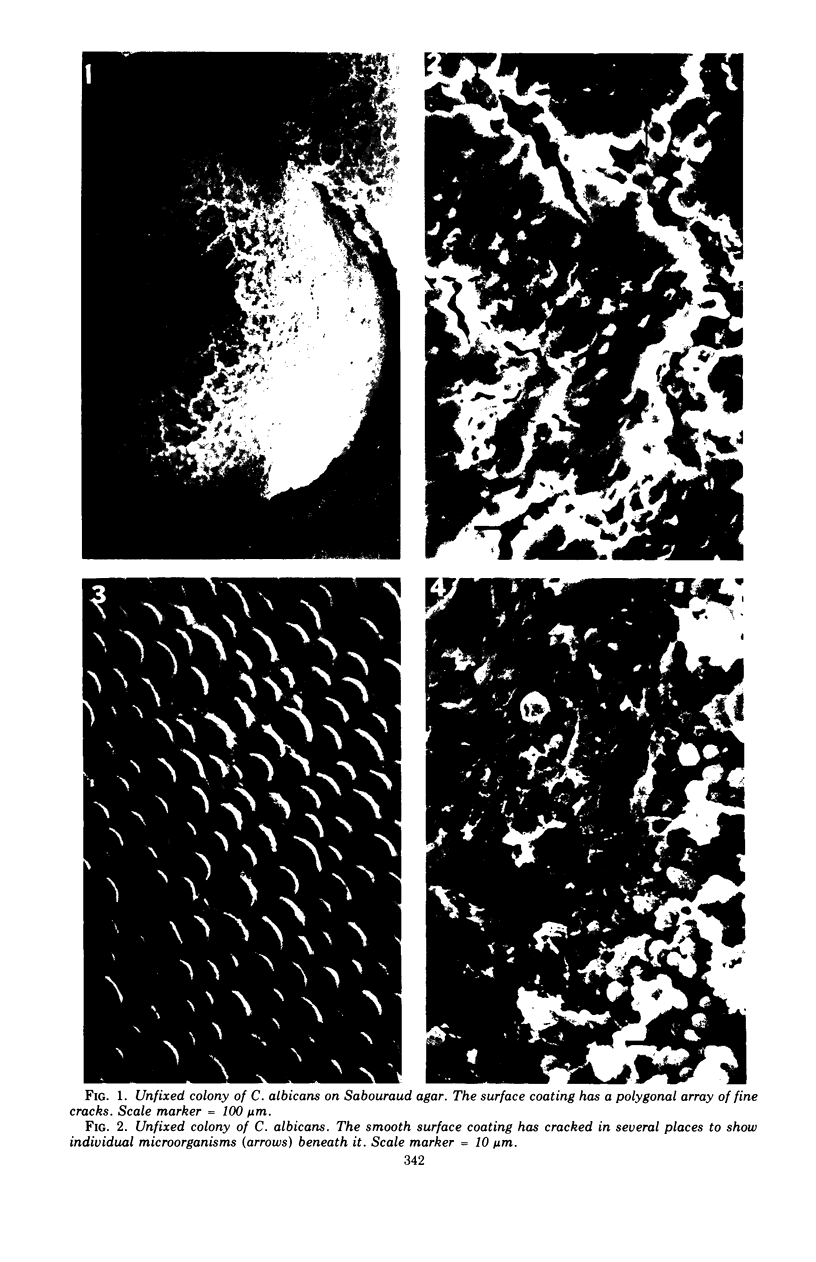

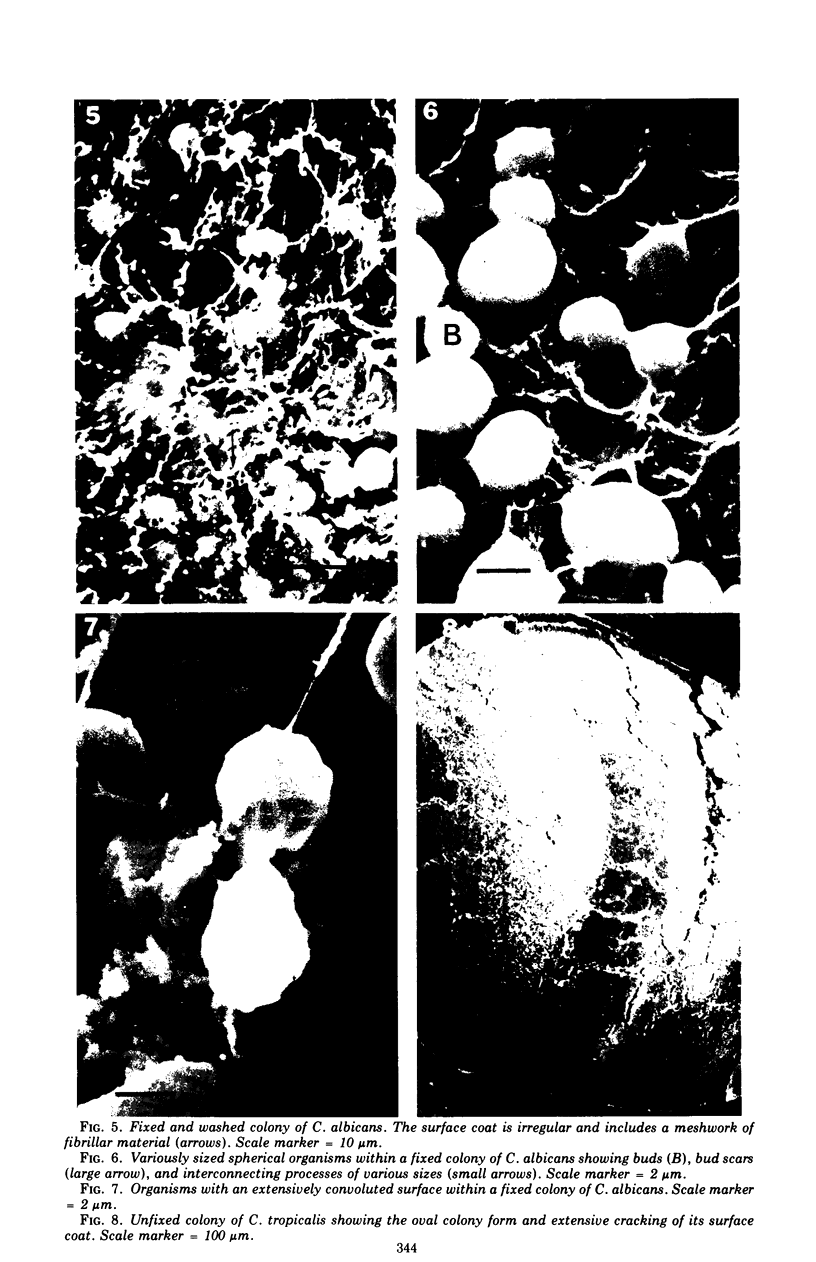

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barnes W. G., Flesher A., Berger A. E., Arnold J. D. Scanning electron microscopic studies of Candida albicans. J Bacteriol. 1971 Apr;106(1):276–280. doi: 10.1128/jb.106.1.276-280.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bulla L. A., St Julian G., Rhodes R. A., Hesseltine C. W. Scanning electron and phase-contrast microscopy of bacterial spores. Appl Microbiol. 1969 Sep;18(3):490–495. doi: 10.1128/am.18.3.490-495.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito Y., Nozawa Y., Suzuki H., Setoguti T. Surface structure of dermatophytes as seen by the scanning electron microscope. Sabouraudia. 1970 Feb;7(4):270–272. doi: 10.1080/00362177085190501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klainer A. S., Betsch C. J. Scanning-beam electron microscopy of selected microorganisms. J Infect Dis. 1970 Mar;121(3):339–343. doi: 10.1093/infdis/121.3.339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montes L. F., Patrick T. A., Martin S. A., Smith M. Ultrastructure of blastospores of Candida albicans after permanganate fixation. J Invest Dermatol. 1965 Sep;45(3):227–232. doi: 10.1038/jid.1965.121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy J. A., Campbell L. L. Surface features of Bacillus polymyxa spores as revealed by scanning electron microscopy. J Bacteriol. 1969 May;98(2):737–743. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.2.737-743.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittaker D. K., Drucker D. B. Scanning electron microscopy of intact colonies of microorganisms. J Bacteriol. 1970 Nov;104(2):902–909. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.2.902-909.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams S. T., Davies F. L. Use of scanning electron microscope for the examination of actinomycetes. J Gen Microbiol. 1967 Aug;48(2):171–177. doi: 10.1099/00221287-48-2-171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]