Abstract
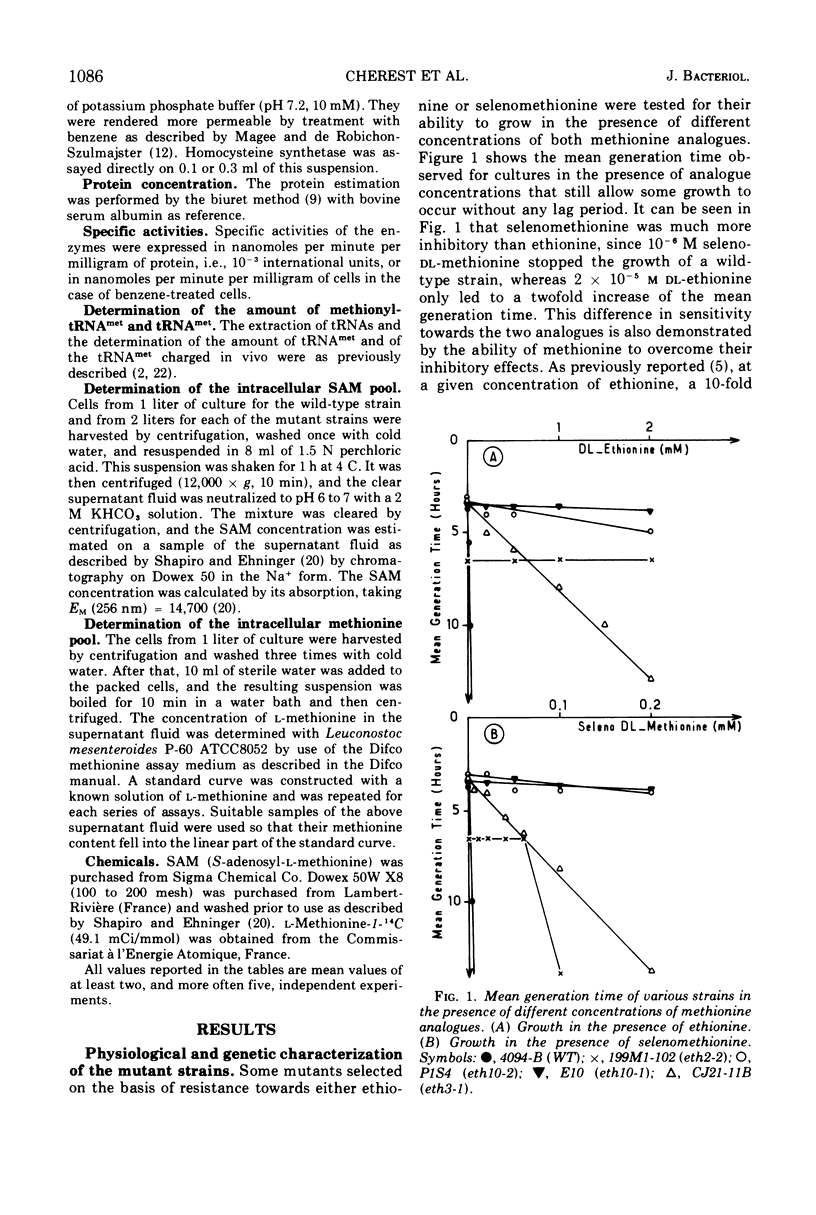
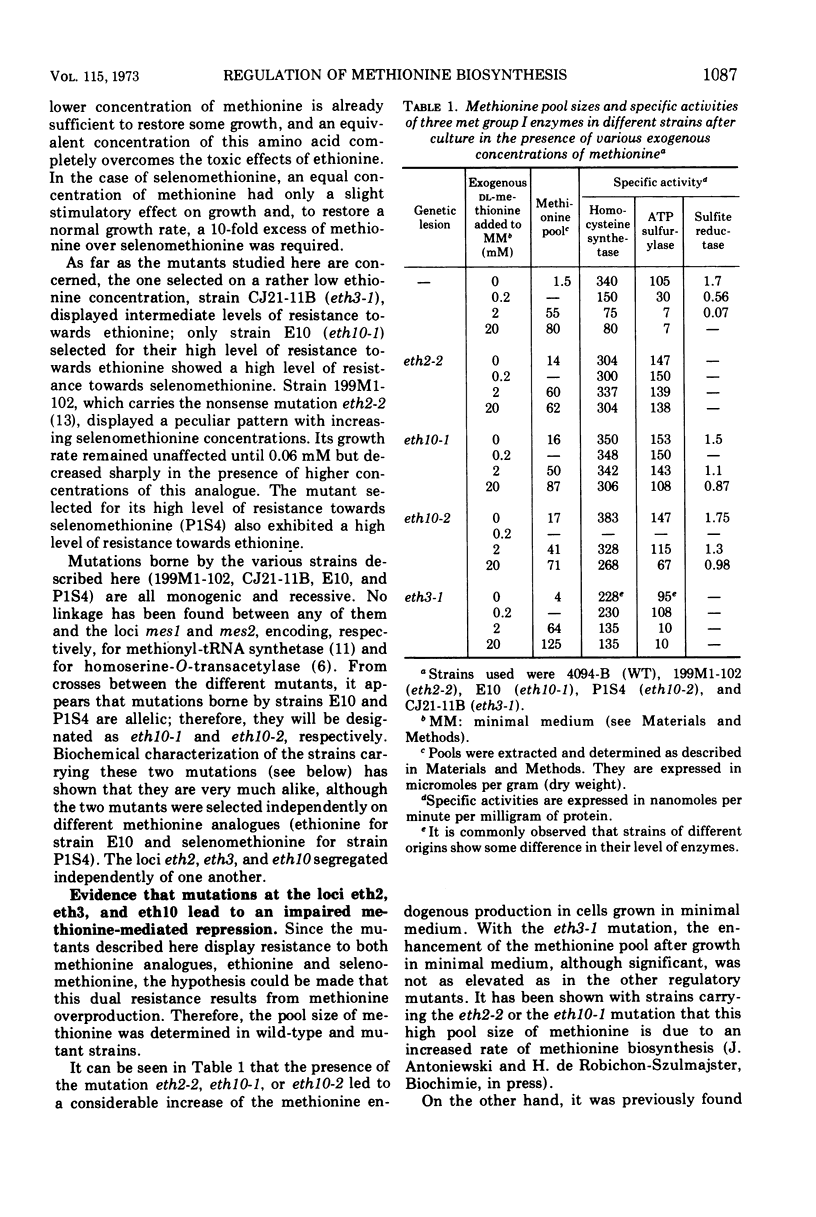
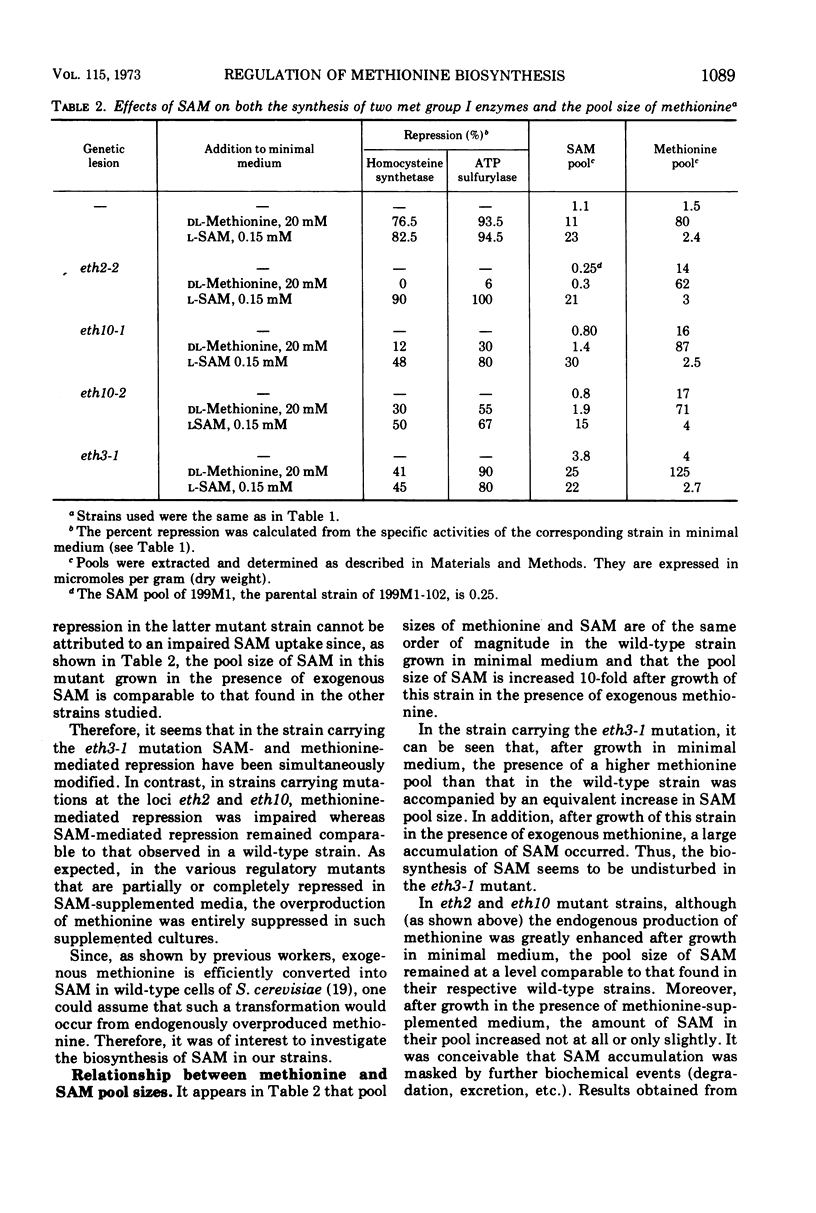
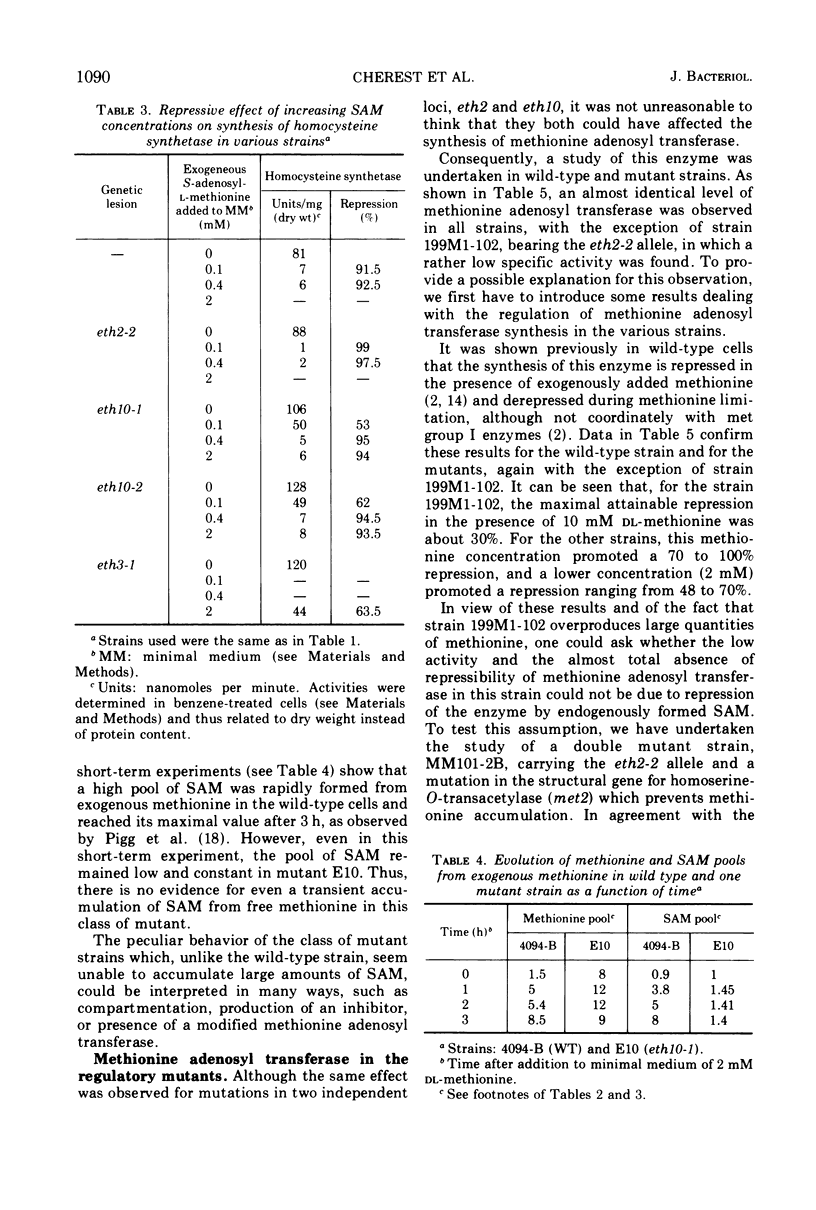
The effects of mutations occurring at three independent loci, eth2, eth3, and eth10, were studied on the basis of several criteria: level of resistance towards two methionine analogues (ethionine and selenomethionine), pool sizes of free methionine and S-adenosyl methionine (SAM) under different growth conditions, and susceptibility towards methionine-mediated repression and SAM-mediated repression of some enzymes involved in methionine biosynthesis (met group I enzymes). It was shown that: (i) the level of resistance towards both methionine analogues roughly correlates with the amount of methionine accumulated in the pool; (ii) the repressibility of met group I enzymes by exogenous methionine is either abolished or greatly lowered, depending upon the mutation studied; (iii) the repressibility of the same enzymes by exogenous SAM remains, in at least three mutants studied, close to that observed in a wild-type strain; (iv) the accumulation of SAM does not occur in the most extreme mutants either from endogenously overproduced or from exogenously supplied methionine: (v) the two methionine-activating enzymes, methionyl-transfer ribonucleic acid (tRNA) synthetase and methionine adenosyl transferase, do not seem modified in any of the mutants presented here; and (vi) the amount of tRNAmet and its level of charging are alike in all strains. Thus, the three recessive mutations presented here affect methionine-mediated repression, both at the level of overall methionine biosynthesis which results in its accumulation in the pool, and at the level of the synthesis of met group I enzymes. The implications of these findings are discussed.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cherest H., Eichler F., Robichon-Szulmajster H. Genetic and regulatory aspects of methionine biosynthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jan;97(1):328–336. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.1.328-336.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherest H., Surdin-Kerjan Y., Antoniewski J., Robichon-Szulmajster H. S-adenosyl methionine-mediated repression of methionine biosynthetic enzymes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1973 Jun;114(3):928–933. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.3.928-933.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherest H., Surdin-Kerjan Y., Robichon-Szulmajster H. Methionine-mediated repression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: a pleiotropic regulatory system involving methionyl transfer ribonucleic acid and the product of gene eth2. J Bacteriol. 1971 Jun;106(3):758–772. doi: 10.1128/jb.106.3.758-772.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou T. C., Lombardini J. B. A rapid assay procedure for ATP:L-methionine adenosyltransferase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Aug 28;276(2):399–406. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(72)91000-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEVITO P. C., DREYFUSS J. METABOLIC REGULATION OF ADENOSINE TRIPHOSPHATE SULFURYLASE IN YEAST. J Bacteriol. 1964 Nov;88:1341–1348. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.5.1341-1348.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GALZY P., SLONIMSKI P. P. Evolution de la constitution enzymatique de la levure cultivée sur acide lactique ou sur glucose comme seule source de carbone. C R Hebd Seances Acad Sci. 1957 Dec 23;245(26):2556–2558. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kredich N. M., Tomkins G. M. The enzymic synthesis of L-cysteine in Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium. J Biol Chem. 1966 Nov 10;241(21):4955–4965. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magee P. T., Robichon-Szulmajster H. The regulation of isoleucine-valine biosynthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. 3. Properties and regulation of the activity of acetohydroxyacid synthetase. Eur J Biochem. 1968 Feb;3(4):507–511. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1967.tb19560.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masselot M., Robichon-Szulmajster H. Nonsense mutation in the regulatory gene ETH2 involved in methionine biosynthesis in Saccharomyces cervisiae. Genetics. 1972 Aug;71(4):535–550. doi: 10.1093/genetics/71.4.535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin C. S., Hartwell L. H. A mutant of yeast with a defective methionyl-tRNA synthetase. Genetics. 1969 Mar;61(3):557–566. doi: 10.1093/genetics/61.3.557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mertz J. E., Spence K. D. Methionine adenosyltransferase and ethionine resistance in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1972 Sep;111(3):778–783. doi: 10.1128/jb.111.3.778-783.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murgola E. J., Adelberg E. A. Mutants of Escherichia coli K-12 with an altered glutamyl-transfer ribonucleic acid synthetase. J Bacteriol. 1970 Jul;103(1):178–183. doi: 10.1128/jb.103.1.178-183.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murgola E. J., Adelberg E. A. Streptomycin-suppressible lethal mutations in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1970 Jul;103(1):20–26. doi: 10.1128/jb.103.1.20-26.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagai S., Flavin M. Acetylhomoserine. An intermediate in the fungal biosynthesis of methionine. J Biol Chem. 1967 Sep 10;242(17):3884–3895. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PIGG C. J., SORSOLI W. A., PARKS L. W. INDUCTION OF THE METHIONINE-ACTIVATING ENZYME IN SACCHAROMYCES CEREVISIAE. J Bacteriol. 1964 Apr;87:920–923. doi: 10.1128/jb.87.4.920-923.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robichon-Szulmajster H., Cherest H. Regulation of homoserine O-transacetylase, first step in methionine biosyntheis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Jul 21;28(2):256–262. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(67)90438-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robichon-Szulmajster H., Cherest H. Résistance a l'éthionine chez Saccharomyces cerevisiae. II. Etude physiologique. Genetics. 1966 Oct;54(4):993–1006. doi: 10.1093/genetics/54.4.993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHLENK F., DEPALMA R. E. The formation of S-adenosylmethionine in yeast. J Biol Chem. 1957 Dec;229(2):1037–1050. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SIEGEL L. M. A DIRECT MICRODETERMINATION FOR SULFIDE. Anal Biochem. 1965 Apr;11:126–132. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(65)90051-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro S. K., Ehninger D. J. Methods for the analysis and preparation of adenosylmethionine and adenosylhomocysteine. Anal Biochem. 1966 May;15(2):323–333. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(66)90038-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surdin-Kerjan Y., Cherest H., Robichon-Szulmajster H. Relationship between methionyl transfer ribonucleic acid cellular content and synthesis of methionine enzymes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1973 Mar;113(3):1156–1160. doi: 10.1128/jb.113.3.1156-1160.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILSON L. G., BANDURSKI R. S. Enzymatic reactions involving sulfate, sulfite, selenate, and molybdate. J Biol Chem. 1958 Oct;233(4):975–981. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiebers J. L., Garner H. R. Acyl derivatives of homoserine as substrates for homocysteine synthesis in Neurospora crassa, yeast, and Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1967 Dec 10;242(23):5644–5649. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



