Abstract
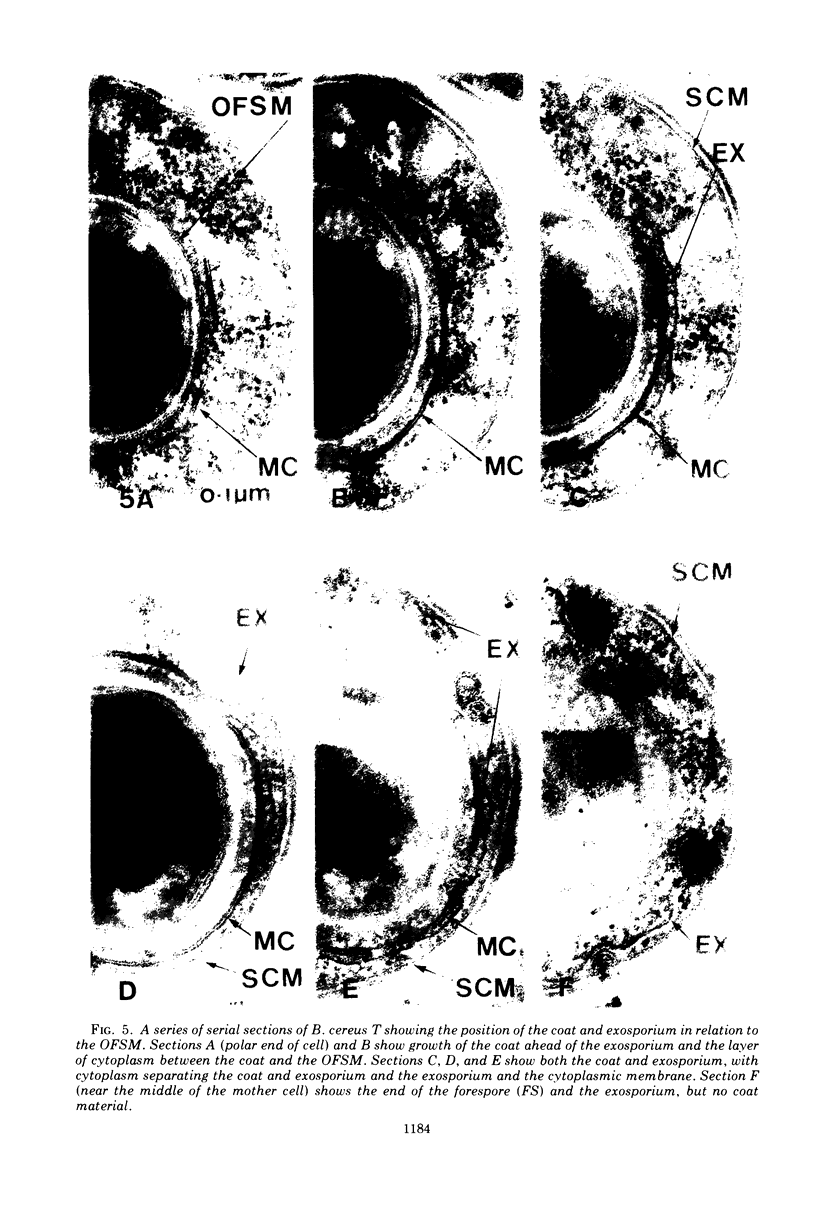
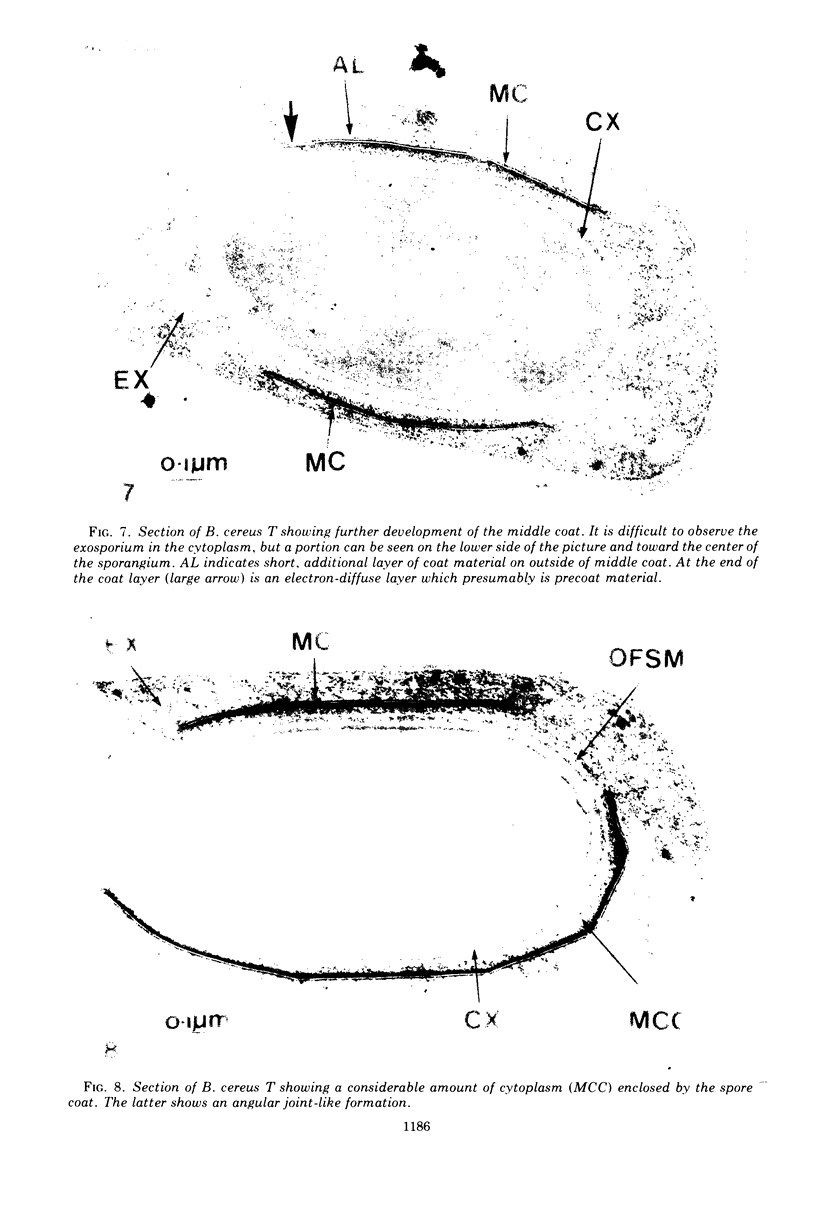
The exosporium of Bacillus cereus T was first observed as a small lamella in the cytoplasm in proximity to the outer forespore membrane (OFSM) near the middle of the sporangium. Serial sections, various staining methods, and enzyme treatments failed to show any connections between the small lamella and the OFSM. The advancing edge of the exosporium moved toward the polar end of the cell until the spore was completely enveloped. The middle coat was formed between the exosporium and the OFSM from a three-layered single plate or “belt,” consisting of two electron-dense layers separated by an electron-transparent layer. This “belt,” usually first observed toward the center of the sporangium, developed without changing thickness or appearance over the surface of the forespore. Between the middle coat and the OFSM, a layer of cytoplasm about 50-nm thick was enclosed by the developing coat; this became the inner coat. Electron-dense material was deposited on the outer surface of the middle coat to form the outer coat.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baillie A., Thomson R. O., Batty I., Walker P. D. Some preliminary observations on the location of esterases in Bacillus cereus. J Appl Bacteriol. 1967 Aug;30(2):312–316. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1967.tb00302.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellar D. J., Lundgren D. G. Fine structure of sporulation in Bacillus cereus grown in a chemically defined medium. J Bacteriol. 1966 Dec;92(6):1748–1764. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.6.1748-1764.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freer J. H., Levinson H. S. Fine structure of Bacillus megaterium during microcycle sporogenesis. J Bacteriol. 1967 Aug;94(2):441–457. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.2.441-457.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GERHARDT P., RIBI E. ULTRASTRUCTURE OF THE EXOSPORIUM ENVELOPING SPORES OF BACILLUS CEREUS. J Bacteriol. 1964 Dec;88:1774–1789. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.6.1774-1789.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon R. A., Murrell W. G. Simple method of detecting spore septum formation and synchrony of sporulation. J Bacteriol. 1967 Jan;93(1):495–496. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.1.495-496.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoo T., Conti S. F. Ultrastructural changes associated with activation and germination of Bacillus cereus T spores. J Bacteriol. 1971 Jan;105(1):361–368. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.1.361-368.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoeniger J. F., Stuart P. F., Holt S. C. Cytology of spore formation in Clostridium perfringens. J Bacteriol. 1968 Nov;96(5):1818–1834. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.5.1818-1834.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLENBERGER E., RYTER A., SECHAUD J. Electron microscope study of DNA-containing plasms. II. Vegetative and mature phage DNA as compared with normal bacterial nucleoids in different physiological states. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1958 Nov 25;4(6):671–678. doi: 10.1083/jcb.4.6.671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OHYE D. F., MURRELL W. G. Formation and structure of the spore of Bacillus coagulans. J Cell Biol. 1962 Jul;14:111–123. doi: 10.1083/jcb.14.1.111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBINOW C. F. Observations on the structure of Bacillus spores. J Gen Microbiol. 1951 Aug;5(3):439–457. doi: 10.1099/00221287-5-3-439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santo L. M., Hohl H. R., Frank H. A. Ultrastructure of putrefactive anaerobe 3679h during sporulation. J Bacteriol. 1969 Sep;99(3):824–833. doi: 10.1128/jb.99.3.824-833.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spudich J. A. Symposium on bacterial spores: 3. Biochemical studies of spore core and coat protein synthesis. J Appl Bacteriol. 1970 Mar;33(1):25–33. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1970.tb05231.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAKAGI A., KAWATA T., YAMAMOTO S., KUBO T., OKITA S. Electron microscopic studies on ultrathin sections of spores of Clostridium tetani and Clostridium histolyticum, with special reference to sporulation and spore germination process. Jpn J Microbiol. 1960 Apr;4:137–155. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1960.tb00162.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takagi A., Nakamura K., Ueda M. Electron microscope studies of the intracytoplasmic membrane system in Clostridium tetani and Clostridium botulinum. Jpn J Microbiol. 1965 Sep;9(3):131–143. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1965.tb00282.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker P. D., Baillie A. Structure of Bacillus stearothermophilus: an electron microscope study. J Appl Bacteriol. 1968 Mar;31(1):108–113. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1968.tb00346.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker P. D., Baillie A., Thomson R. O., Batty I. The use of ferritin labelled antibodies in the location of spore and vegetative antigens of Bacillus cereus. J Appl Bacteriol. 1966 Dec;29(3):512–518. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1966.tb03502.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker P. D. Symposium on bacterial spores: I. Cytology of spore formation and germination. J Appl Bacteriol. 1970 Mar;33(1):1–12. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1970.tb05229.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wegner K. W. Easy and accurate collection of thin serial sections by means of a grid support. Mikroskopie. 1971 Dec;27(9):289–293. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YOUNG I. E., JAMES P. C. Chemical and morphological studies of bacterial spore formation. IV. The development of spore refractility. J Cell Biol. 1962 Jan;12:115–133. doi: 10.1083/jcb.12.1.115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]