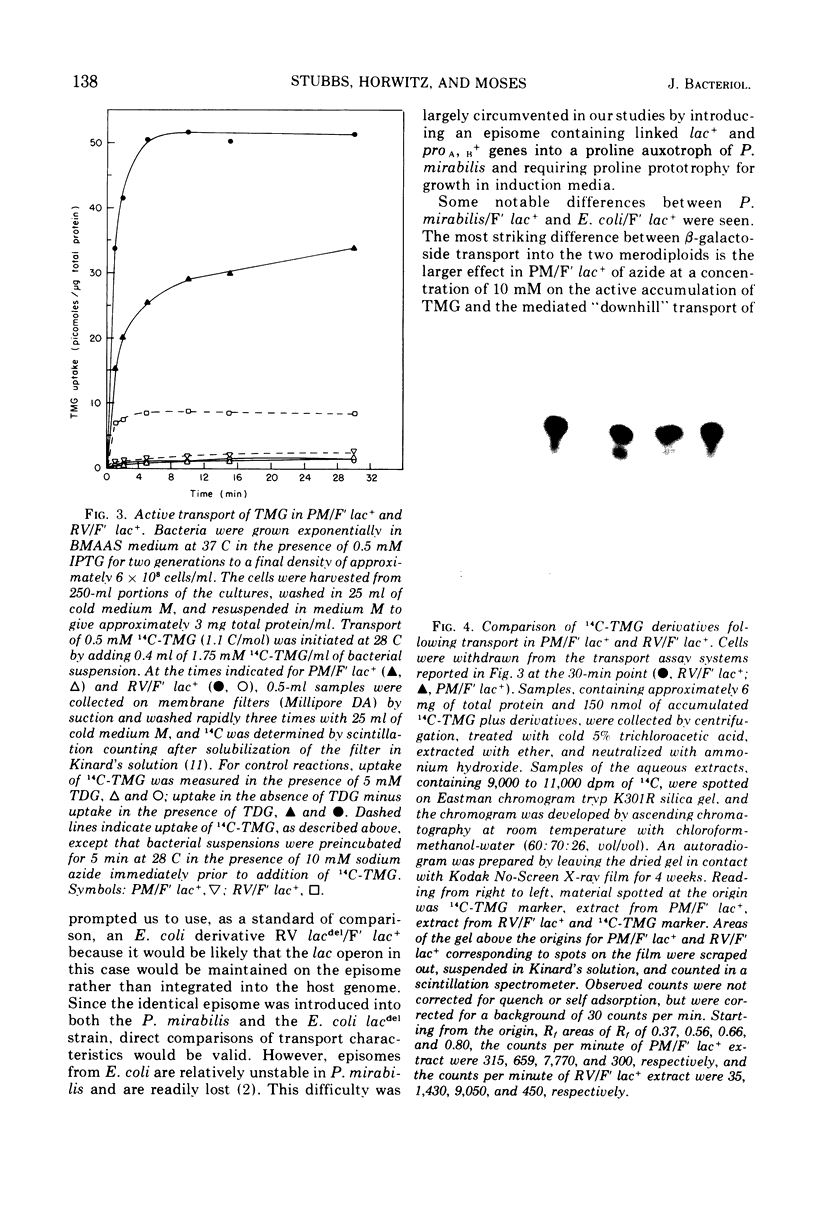
Abstract
Merodiploid derivatives bearing an F-linked lac operon (i+, o+, z+, y+, a+) from Escherichia coli were prepared from a Proteus mirabilis strain unable to utilize lactose and from a lac deletion strain of E. coli. A suitable growth medium was found in which the episomal element in the P. mirabilis derivative was sufficiently stable to allow induction of the episome-borne lac operon and thus to permit a comparison of the activities and properties of E. coli lac products in the intracellular environments of P. mirabilis and E. coli. In both derivatives the episomal lac operon was shown to be repressed in the absence of inducer. Kinetics of induction with gratuitous inducer (isopropyl-1-thio-β-d-galactoside) were similar for both β-galactosidase activity (β-d-galactoside galactohydrolase, EC 3.4.1.23) and β-galactoside transport activity in both derivatives, although the ratio of galactoside transport to β-galactosidase activity was approximately 1.6-fold higher in the E. coli derivative. Comparison of β-galactosidase and M-protein (lac y gene product)-specific activities indicated coordinate expression of the induced lac operon in both derivatives. Quantitatively, the maximal β-galactosidase specific activity was two or three times higher for the E. coli derivative. A significant sodium azide inhibition (65% inhibition by 10 mM sodium azide) of lactose permease-mediated transport of o-nitrophenyl-β-galactoside from an outside region of high concentration to an inside region of very low concentration (“downhill transport”) was observed for the P. mirabilis derivative. Identical conditions for the E. coli derivative yielded only about 15% inhibition. Active transport of thiomethyl-β-galactoside was similar for both derivatives, the major difference being that active transport was more sensitive to azide poisoning in the P. mirabilis derivative. Preliminary examination of the thiomethyl-β-galactoside derivatives following active transport did not demonstrate the accumulation of a phosphorylated product in either strain but did reveal an unidentified derivative present in the P. mirabilis merodiploid extract which was not detectable in the E. coli merodiploid.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BUTTIN G., COHEN G. N., MONOD J., RICKENBERG H. V. La galactoside-perméase d'Escherichia coli. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1956 Dec;91(6):829–857. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein W. Transposition of the lac region of Escherichia coli. IV. Escape from repression in bacteriophage-carried lac genes. J Mol Biol. 1967 Dec 28;30(3):529–543. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90366-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FALKOW S., WOHLHIETER J. A., CITARELLA R. V., BARON L. S. TRANSFER OF EPISOMIC ELEMENTS TO PROTEUS. I. TRANSFER OF F-LINKED CHROMOSOMAL DETERMINANTS. J Bacteriol. 1964 Jan;87:209–219. doi: 10.1128/jb.87.1.209-219.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox C. F. A lipid requirement for induction of lactose transport in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Jul;63(3):850–855. doi: 10.1073/pnas.63.3.850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox C. F., Carter J. R., Kennedy E. P. GENETIC CONTROL OF THE MEMBRANE PROTEIN COMPONENT OF THE LACTOSE TRANSPORT SYSTEM OF Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Mar;57(3):698–705. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.3.698. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERZENBERG L. A. Studies on the induction of beta-galactosidase in a cryptic strain of Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1959 Feb;31(2):525–538. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(59)90029-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu C. C., Fox C. F. Induction of the lactose transport system in a lipid-synthesis-defective mutant of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1970 Aug;103(2):410–416. doi: 10.1128/jb.103.2.410-416.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JACOB F., MONOD J. Genetic regulatory mechanisms in the synthesis of proteins. J Mol Biol. 1961 Jun;3:318–356. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(61)80072-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOCH A. L. THE ROLE OF PERMEASE IN TRANSPORT. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Jan 27;79:177–200. doi: 10.1016/0926-6577(64)90050-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kashket E. R., Wilson T. H. Isolation and properties of mutants of Escherichia coli with increased phosphorylations of thiomethyl-beta-galactoside. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969;193(2):294–307. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(69)90190-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch A. L. Energy expenditure is obligatory for the downhill transport of galactosides. J Mol Biol. 1971 Aug 14;59(3):447–459. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90309-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIN E. C., LERNER S. A., JORGENSEN S. E. A method for isolating constitutive mutants for carbohydrate-catabolizing enzymes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Jul 2;60:422–424. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90423-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARDEE A. B., PRESTIDGE L. S. The initial kinetics of enzyme induction. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1961 Apr 29;49:77–88. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(61)90871-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar S. Properties and regulation of the beta-D-galactosidase in Shigella dysenteriae and in Escherichia coli-Shigella dysenteriae hybrids. J Bacteriol. 1966 Apr;91(4):1477–1488. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.4.1477-1488.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stubbs J. D., Stubbs E. A. Influences of various amino acids on tryptophan-mediated control of the tryptophan biosynthetic enzymes in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1971 Dec;108(3):1181–1191. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.3.1181-1191.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson G., Fox C. F. Biogenesis of microbial transport systems: evidnce for coupled incorporation of newly synthesized lipids and proteins into membrane. J Mol Biol. 1971 Jan 14;55(1):49–60. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90280-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler H. H., Wilson T. H. The role of energy coupling in the transport of beta-galactosides by Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1966 May 25;241(10):2200–2211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]