Abstract
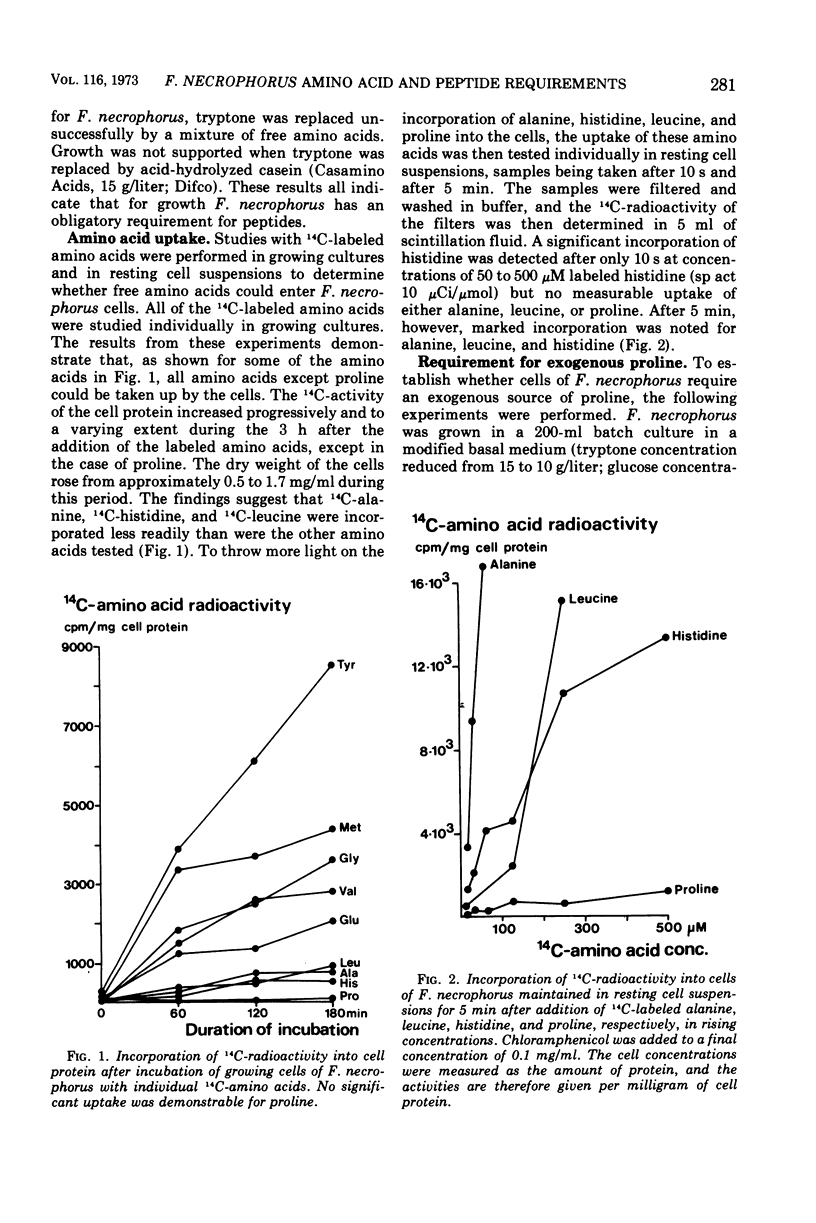
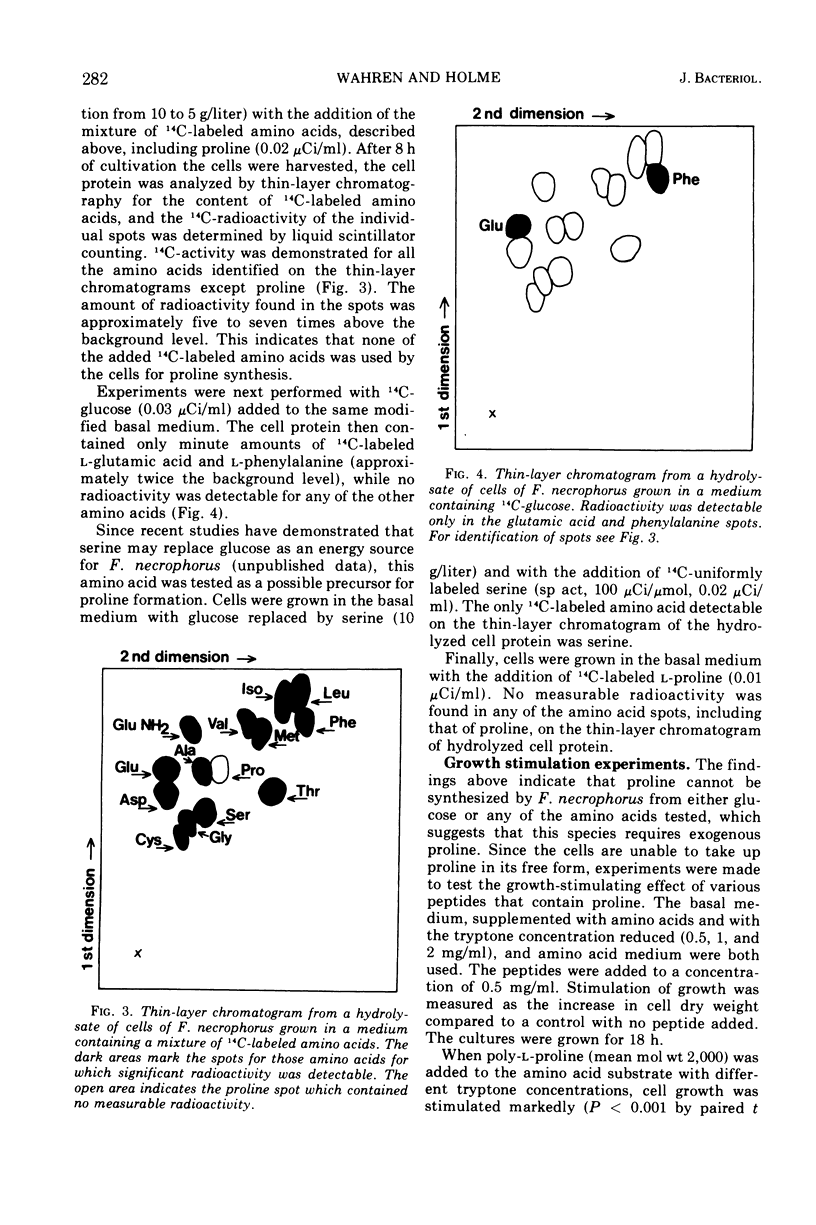
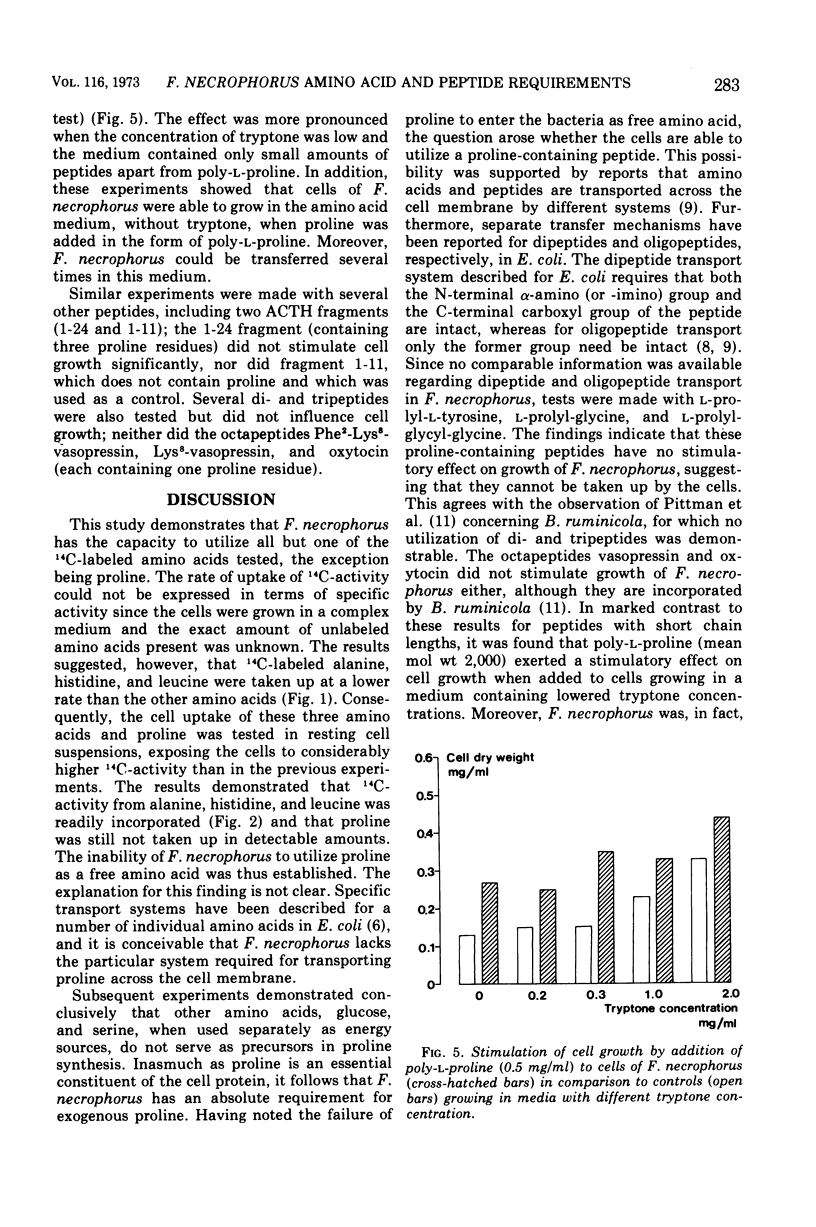
Uptake of individual amino acids and peptides by Fusiformis necrophorus was studied in growing cultures and resting cell suspensions. The cells were able to incorporate 16 of 17 14C-labeled amino acids into cell protein, the exception being proline. Proline could neither be formed by the cells from any of the other tested amino acids nor be synthesized from glucose or serine when these were used as energy sources. The addition of di- and tripeptides, the octapeptides vasopressin and oxytocin, and the poly (24) peptide ACTH did not stimulate cell growth, but a marked stimulatory effect was noted after the addition of poly-l-proline (mean molecular weight 2,000). It is concluded that cells of F. necrophorus (i) possess transport systems for most amino acids but not for proline, (ii) are dependent on exogenous proline in the form of proline-containing peptides for growth, and (iii) may be cultivated in a defined amino acid medium provided the proline requirement is met by the addition of a proline-containing peptide.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BRITTEN R. J., McCLURE F. T. The amino acid pool in Escherichia coli. Bacteriol Rev. 1962 Sep;26:292–335. doi: 10.1128/br.26.3.292-335.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heathcote J. G., Davies D. M., Haworth C. Analysis of free amino acid pools in fungal mycelia. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Feb;23(2):349–353. doi: 10.1128/am.23.2.349-353.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heathcote J. G., Haworth C. An improved technique for the analysis of amino acids and related compounds on thin layers of cellulose. II. The quantitative determination of amino acids in protein hydrolysates. J Chromatogr. 1969 Aug 5;43(1):84–92. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(00)99169-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin E. C. The genetics of bacterial transport systems. Annu Rev Genet. 1970;4:225–262. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.04.120170.001301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PITTMAN K. A., BRYANT M. P. PEPTIDES AND OTHER NITROGEN SOURCES FOR GROWTH OF BACTEROIDES RUMINICOLA. J Bacteriol. 1964 Aug;88:401–410. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.2.401-410.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne J. W. The utilization of prolyl peptides by Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1971 Jun;123(2):255–260. doi: 10.1042/bj1230255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pittman K. A., Lakshmanan S., Bryant M. P. Oligopeptide uptake by Bacteroides ruminicola. J Bacteriol. 1967 May;93(5):1499–1508. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.5.1499-1508.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sussman A. J., Gilvarg C. Peptide transport and metabolism in bacteria. Annu Rev Biochem. 1971;40:397–408. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.40.070171.002145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahren A., Berholm K., Holme T. Formation of proteolytic activity in continuous culture of Sphaerophorus necrophorus. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1971;79(3):391–398. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1971.tb00078.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahren A., Gibbons R. J. Amino acid fermentation by Bacteroides melaninogenicus. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1970;36(1):149–159. doi: 10.1007/BF02069017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahren A., Holme T. Growth of Bacteroidaceae in stirred fermentors. Appl Microbiol. 1969 Aug;18(2):235–239. doi: 10.1128/am.18.2.235-239.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


