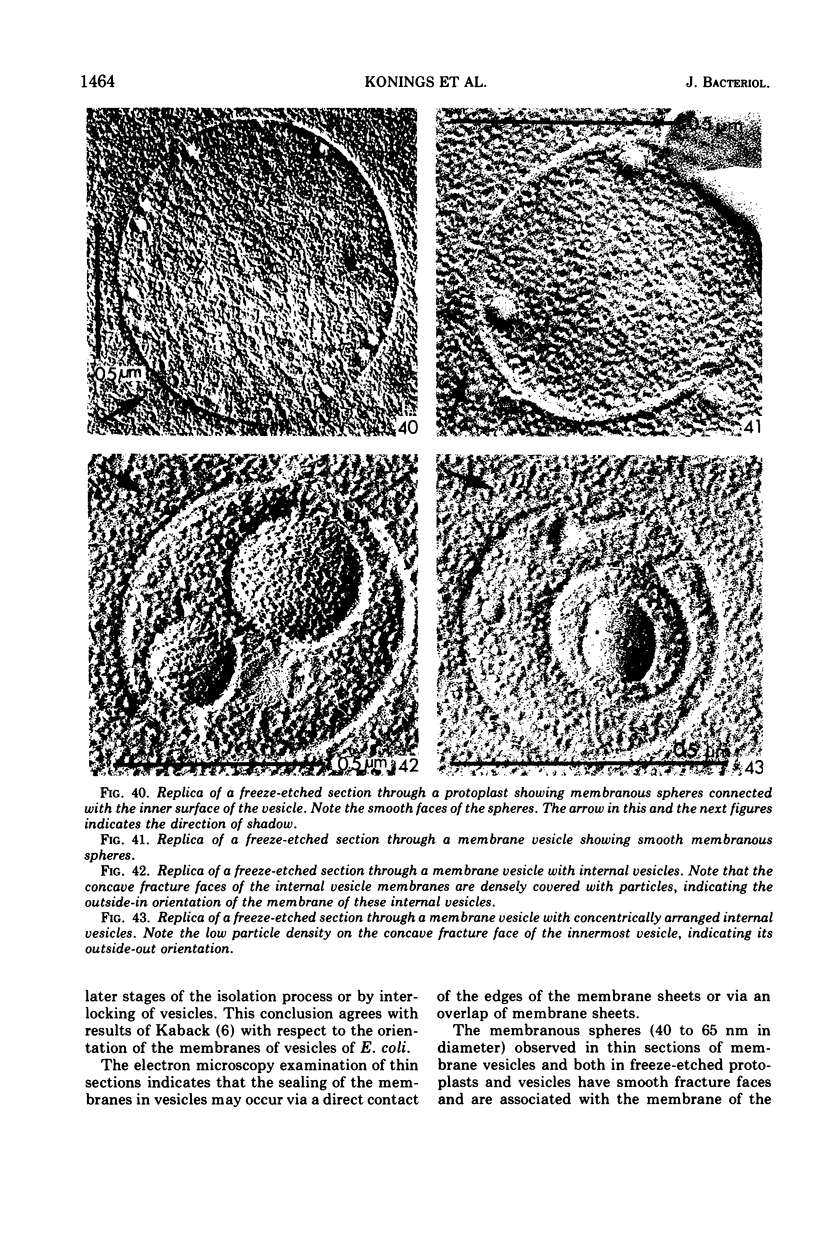
Abstract
A rapid procedure for the isolation of membrane vesicles of Bacillus subtilis is described that minimizes the action of proteolytic enzymes, excreted by this organism, on the membrane proteins. The membrane vesicles obtained have, in addition to a low endogenous respiration rate, a low endogenous activity for transport of amino acids and carboxylic acids. In the presence of the electron donor, ascorbate-phenazine methosulfate, the transport activities for these compounds were comparable to the activities of intact cells. In addition, these activities were retained for a prolonged period of time. Electron microscopy examination of thin sections of the vesicles showed that the preparation consisted almost exclusively of membrane vesicles which were not contaminated with other cell components. The membrane vesicles, which are six to seven times smaller in diameter than protoplasts, often enclosed smaller vesicles. Freeze-etching of intact cells, protoplasts, and membrane vesicles showed that the orientation of the membrane of the vesicles was identical to the orientation of the plasma membrane in intact cells and protoplasts. This also held for the majority of the membranes of the enclosed vesicles, only 15% having the opposite orientation.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Branton D. Fracture faces of frozen membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 May;55(5):1048–1056. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.5.1048. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietz G. W. Dehydrogenase activity involved in the uptake of glucose 6-phosphate by a bacterial membrane system. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jul 25;247(14):4561–4565. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiil A., Branton D. Changes in the plasma membrane of Escherichia coli during magnesium starvation. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jun;98(3):1320–1327. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.3.1320-1327.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt S. C., Leadbetter E. R. Comparative ultrastructure of selected aerobic spore-forming bacteria: a freeze-etching study. Bacteriol Rev. 1969 Jun;33(2):346–378. doi: 10.1128/br.33.2.346-378.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLENBERGER E., RYTER A., SECHAUD J. Electron microscope study of DNA-containing plasms. II. Vegetative and mature phage DNA as compared with normal bacterial nucleoids in different physiological states. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1958 Nov 25;4(6):671–678. doi: 10.1083/jcb.4.6.671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaback H. R. Transport across isolated bacterial cytoplasmic membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Aug 4;265(3):367–416. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(72)90014-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirk R. G., Ginzburg M. Ultrastructure of two species of halobacterium. J Ultrastruct Res. 1972 Oct;41(1):80–94. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(72)90040-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konings W. N., Barnes E. M., Jr, Kaback H. R. Mechanisms of active transport in isolated membrane vesicles. 2. The coupling of reduced phenazine methosulfate to the concentrative uptake of beta-galactosides and amino acids. J Biol Chem. 1971 Oct 10;246(19):5857–5861. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konings W. N., Freese E. Amino acid transport in membrane vesicles of Bacillus subtilis. J Biol Chem. 1972 Apr 25;247(8):2408–2418. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOOR H. DIE GEFRIER-FIXATION LEBENDER ZELLEN UND IHRE ANWENDUNG IN DER ELEKTRONENMIKROSKOPIE. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1964 Apr 28;62:546–580. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matile P., Moor H., Mühlethaler K. Isolation and properties of the plasmalemma in yeast. Arch Mikrobiol. 1967;58(3):201–211. doi: 10.1007/BF00408804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matin A., Konings W. N. Transport of lactate and succinate by membrane vesicles of Escherichia coli, Bacillus subtilis and a pseudomonas species. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Apr 2;34(1):58–67. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02728.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer H. W., Winkelmann H. Die Gefrierätzung und die Struktur biologischer Membranen. Protoplasma. 1969;68(3):253–270. doi: 10.1007/BF01251613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mota J. S., Silva M. T., Guerra F. C. Variations in the membranes of Streptococcus faecalis related to different cultural conditions. Arch Mikrobiol. 1972;83(4):293–302. doi: 10.1007/BF00425241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munoz E., Freer J. H., Ellar D. J., Salton M. R. Membrane-associated ATPase activity from Micrococcus lysodeikticus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Apr 29;150(3):531–533. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(68)90156-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinto da Silva P., Branton D. Membrane splitting in freeze-ethching. Covalently bound ferritin as a membrane marker. J Cell Biol. 1970 Jun;45(3):598–605. doi: 10.1083/jcb.45.3.598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS E. S. The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:208–212. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remsen C. C. Fine structure of the mesosome and nucleoid in frozen-etched Bacillus subtilis. Arch Mikrobiol. 1968;61(1):40–47. doi: 10.1007/BF00704290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remsen C. C. The fine structure of frozen-etched Bacillus cereus spores. Arch Mikrobiol. 1966 Sep 8;54(3):266–275. doi: 10.1007/BF00408999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remsen C. C., Valois F. W., Watson S. W. Fine structure of the cytomembranes of Nitrosocystis oceanus. J Bacteriol. 1967 Aug;94(2):422–433. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.2.422-433.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryter A., Frehel C., Ferrandes B. Comportement des mésosomes lors de l'attaque de Bacillus subtilis par le lysozyme en milieu hyper- ou hypotonique. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1967 Oct 23;265(17):1259–1262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sleytr U. B. Fracture faces in intact cells and protoplasts of Bacillus stearothermophilus. A study by conventional freeze-etching and freeze-etching of corresponding fracture moieties. Protoplasma. 1970;71(3):295–312. doi: 10.1007/BF01279638. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sleytr U., Adam H., Klaushofer H. Die Feinstruktur der Zellwand und Cytoplasmamembran von Clostridium nigrificans, dargestellt mit Hilfe der Gefrierätz- und Ultradünnschnittechnik. Arch Mikrobiol. 1969;66(1):40–58. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sleytr U. Die Gefrierätzung korrespondierender Bruchhälften: ein neuer Weg zur Aufklärung von Membranstrukturen. Protoplasma. 1970;70(1):101–117. doi: 10.1007/BF01276845. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sleytr U. Gefrierätzung verschiedener Stämme von Bacillus sphaericus. Arch Mikrobiol. 1970;72(3):238–251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sleytr U., Krebs B. Protoplastenbildung und Interpretation des Gefrierätzbildes der Membranstrukturen bei Clostridium nigrificans. Arch Mikrobiol. 1971;77(4):377–389. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tillack T. W., Marchesi V. T. Demonstration of the outer surface of freeze-etched red blood cell membranes. J Cell Biol. 1970 Jun;45(3):649–653. doi: 10.1083/jcb.45.3.649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein R. S., Koo V. M. Penetration of red cell membranes by some membrane-associated particles. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1968 Jun;128(2):353–357. doi: 10.3181/00379727-128-33013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]