Abstract
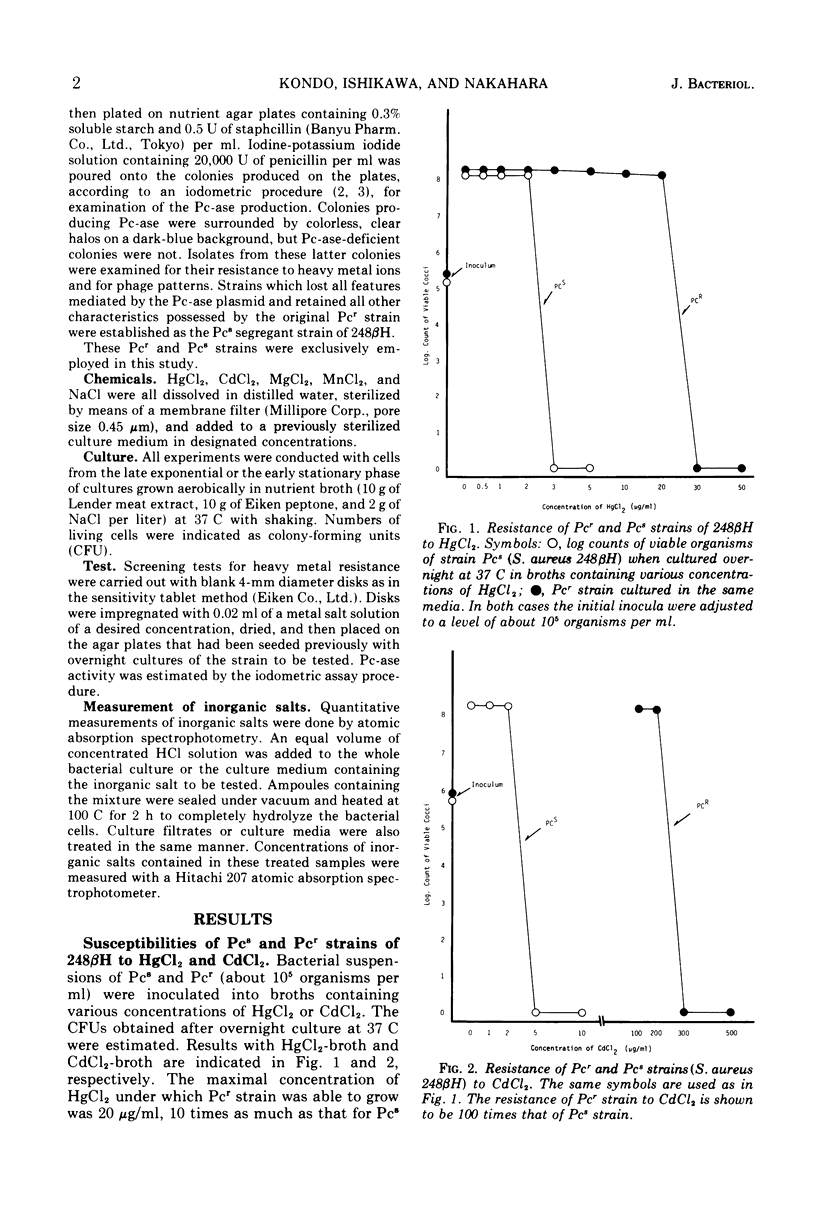
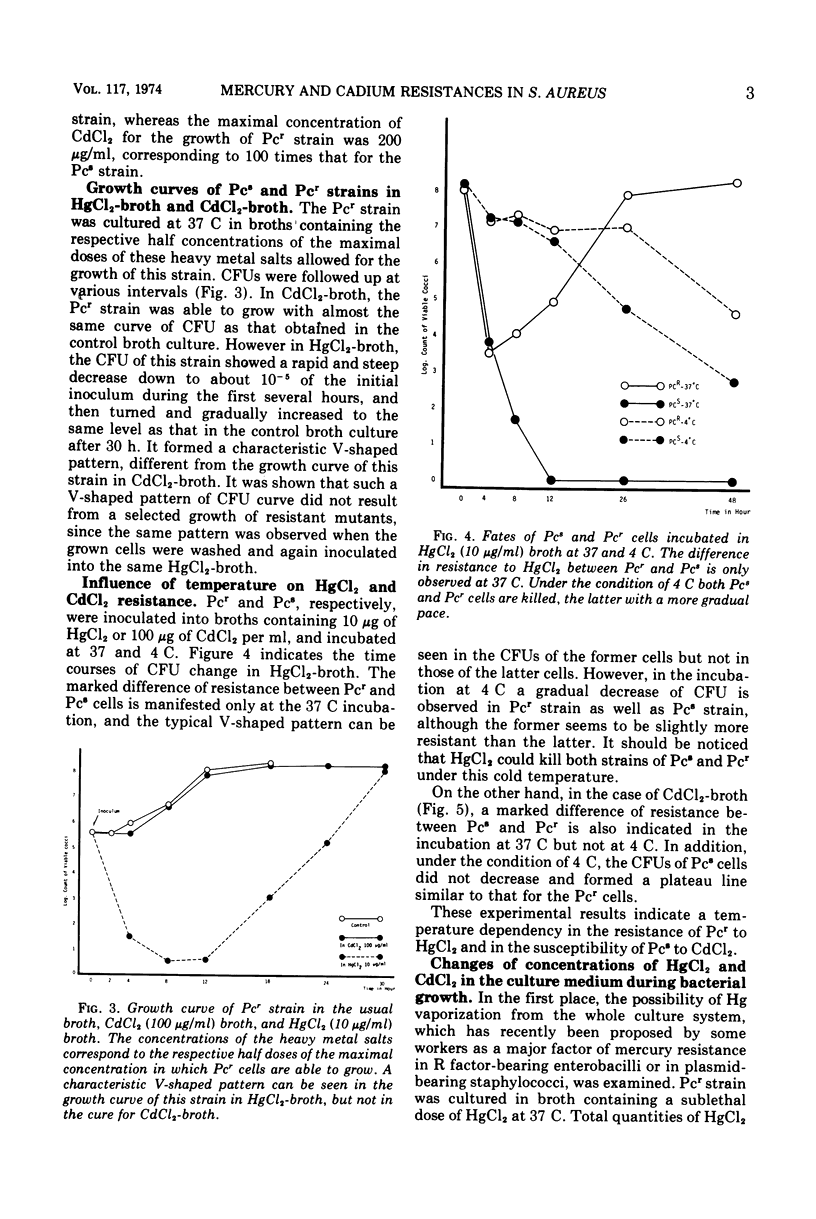
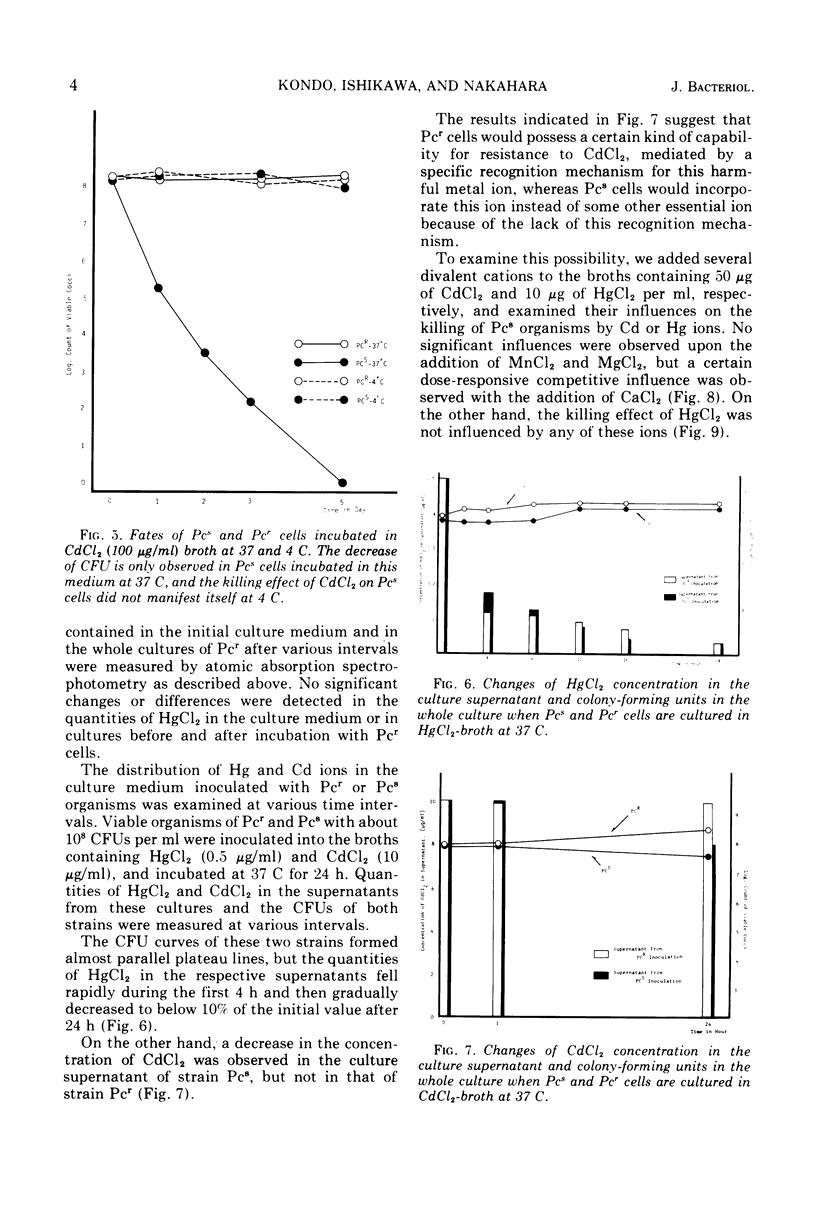
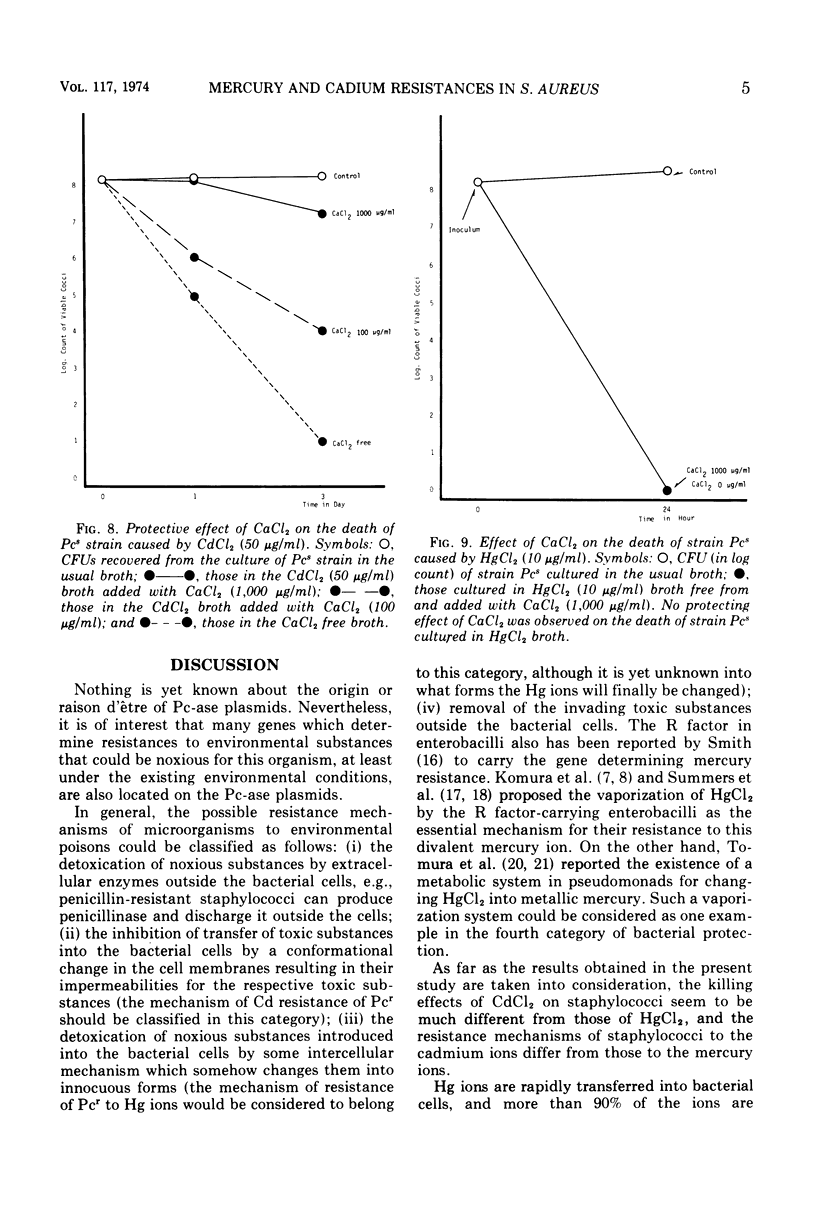
Resistance of Staphylococcus aureus mediated by the penicillinase (Pc-ase) plasmid to divalent metal ions of Hg and Cd was found to be controlled by different mechanisms. The Hg resistance of the Pc-ase plasmid-carrying organisms is based upon a process of changing the ion incorporated in the cell into a somewhat innocuous form. This process is independent of temperature and seems to be controlled by an inducible enzyme. The killing effect of Hg salts was not influenced by the coexistence of other di- or monovalent ions such as MgCl2, CaCl2, MnCl2, and NaCl. No vaporization of Hg, which explains the resistance mechanism such as that proposed by Komura et al. for R factor-mediated Hg resistance in enterobacilli, was found in the case of Hg resistance in staphylococci. On the other hand, the resistance to Cd ion is mediated by some protective mechanism to retain the ion outside the cell. Pc-sensitive organisms not carrying the Pc-ase plasmid incorporate Cd ions into the cells, whereas the Pc-ase plasmid-carrying organisms do not. The incorporation of this ion is temperature dependent and does not take place at 4 C. When incubated with this ion at 4 C, Pc-sensitive organisms as well as Pc-resistant organisms are also able to show a resistance. The addition of CaCl2 could eliminate the killing effect of CdCl2 with a dose-effective response.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CSANYI V. A modified iodometric method of penicillinase assay. Acta Physiol Acad Sci Hung. 1961;18:261–263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chopra I. Decreased uptake of cadmium by a resistant strain of Staphylococcus aureus. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Oct;63(2):265–267. doi: 10.1099/00221287-63-2-265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper R. G., Brown G. W., Vesey B. V. Iodometric detection of staphylococcal penicillinase in clinical microbiology. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1966 Dec;44(6):715–717. doi: 10.1038/icb.1966.70. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emmerson B. T. "Ouch-ouch" disease: the osteomalacia of cadmium nephropathy. Ann Intern Med. 1970 Nov;73(5):854–855. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-73-5-854. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLETCHER M. J., FLUHARTY A. L., SANADIDR On the mechanism of oxidative phosphorylation. V. Effect of arsenite and cadmium ion in mitochondrial fragments. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Jul 2;60:425–427. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90424-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirayama K., Takahashi H. Studies on the treatment for methyl mercury poisoning "lowering of the methyl mercury content in the poisoned animal brain". Kumamoto Med J. 1970 Jun 30;23(2):56–64. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komura I., Funaba T., Izaki K. Mechanism of mercuric chloride resistance in microorganisms. II. NADPH-dependent reduction of mercuric chloride and vaporization of mercury from mercuric chloride by a multiple drug resistant strain of Escherichia coli. J Biochem. 1971 Dec;70(6):895–901. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a129719. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komura I., Izaki K. Mechanism of mercuric chloride resistance in microorganisms. I. Vaporization of a mercury compound from mercuric chloride by multiple drug resistant strains of Escherichia coli. J Biochem. 1971 Dec;70(6):885–893. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a129718. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondo I., Masuda S., Kimura K., Kurosaka K., Hasegawa N. Effects of intrarenal inoculation of Staphylococcus aureus on mice. Infect Immun. 1971 Aug;4(2):103–109. doi: 10.1128/iai.4.2.103-109.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MITSUHASHI S., MORIMURA M., KONO K., OSHIMA H. ELIMINATION OF DRUG RESISTANCE OF STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS BY TREATMENT WITH ACRIFLAVINE. J Bacteriol. 1963 Jul;86:162–164. doi: 10.1128/jb.86.1.162-164.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick R. P., Roth C. Plasmid-linked resistance to inorganic salts in Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1968 Apr;95(4):1335–1342. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.4.1335-1342.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RICHMOND M. H., JOHN M. CO-TRANSDUCTION BY A STAPHYLOCOCCAL PHAGE OF THE GENES RESPONSIBLE FOR PENICILLINASE SYNTHESIS AND RESISTANCE TO MERCURY SALTS. Nature. 1964 Jun 27;202:1360–1361. doi: 10.1038/2021360a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh K., Nath R. Studies on the identification of the cadmium-binding protein in rat testis. Biochem J. 1972 Jun;128(1):48P–49P. doi: 10.1042/bj1280048pd. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. H. R factors mediate resistance to mercury, nickel, and cobalt. Science. 1967 May 26;156(3778):1114–1116. doi: 10.1126/science.156.3778.1114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers A. O., Lewis E. Volatilization of mercuric chloride by mercury-resistant plasmid-bearing strains of Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1973 Feb;113(2):1070–1072. doi: 10.1128/jb.113.2.1070-1072.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers A. O., Silver S. Mercury resistance in a plasmid-bearing strain of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1972 Dec;112(3):1228–1236. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.3.1228-1236.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takizawa Y., Kosaka T., Sugai R., Sasagawa I., Sekiguchi C. Studies on the cause of the Niigata episode of Minamata disease outbreak. Acta Med Biol (Niigata) 1972 Mar;19(3):193–206. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonomura K., Kanzaki F. The reductive decomposition of organic mercurials by cell-free extract of a mercury-resistant pseudomonad. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Jun 17;184(1):227–229. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(69)90124-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonomura K., Maeda K., Futai F., Nakagami T., Yamada M. Stimulative vaporization of phenylmercuric acetate by mercury-resistant bacteria. Nature. 1968 Feb 17;217(5129):644–646. doi: 10.1038/217644b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuchiya K. Causation of Ouch-Ouch Disease (Itai-Itai Byõ)--an introductory review. I. Nature of the disease. Keio J Med. 1969 Dec;18(4):181–194. doi: 10.2302/kjm.18.181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuchiya K. Causation of Ouch-Ouch Disease (Itai-Itai Byõ)--an introductory review. II. Epidemiology and evaluation. Keio J Med. 1969 Dec;18(4):195–211. doi: 10.2302/kjm.18.195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuchiya K. Epidemic of mercury poisoning in the Agano River area--an introductory review. Keio J Med. 1969 Dec;18(4):213–227. doi: 10.2302/kjm.18.213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasserman R. H., Corradino R. A., Taylor A. N. Vitamin D-dependent calcium-binding protein. Purification and some properties. J Biol Chem. 1968 Jul 25;243(14):3978–3986. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


