Abstract
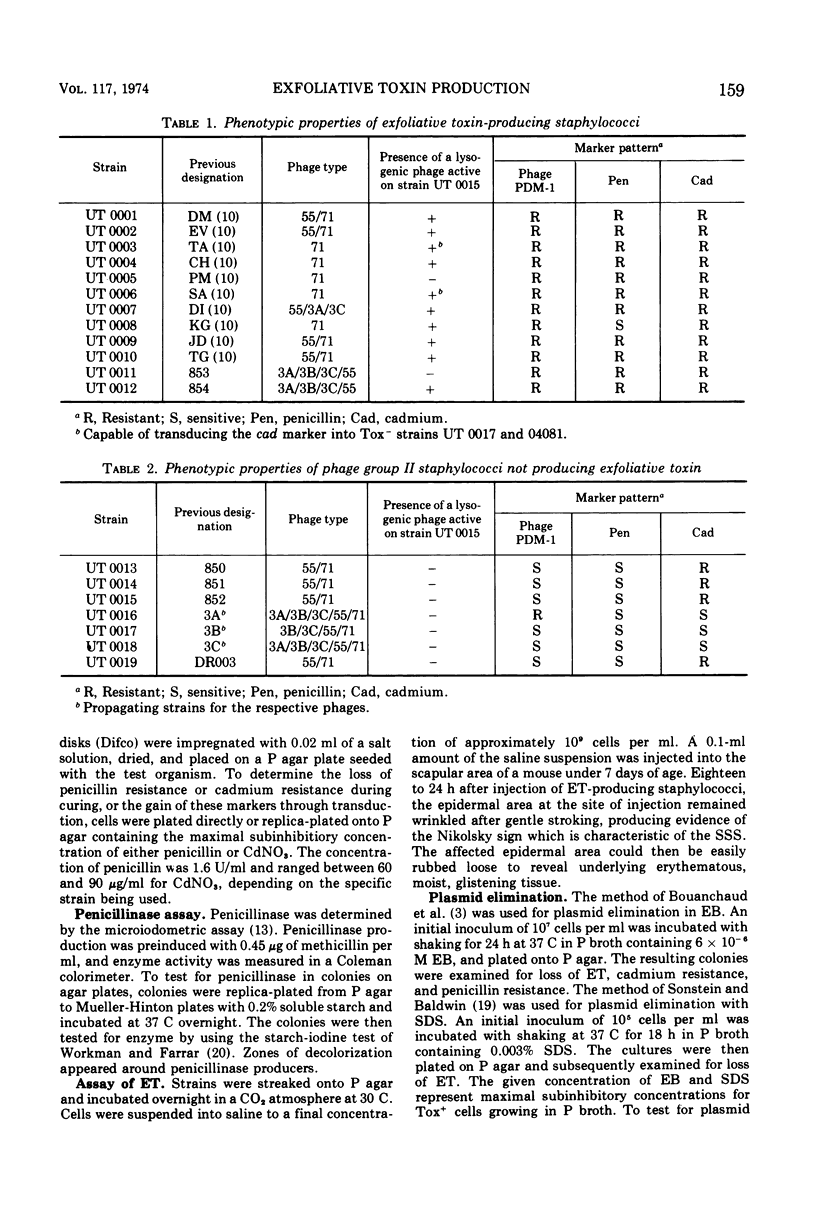
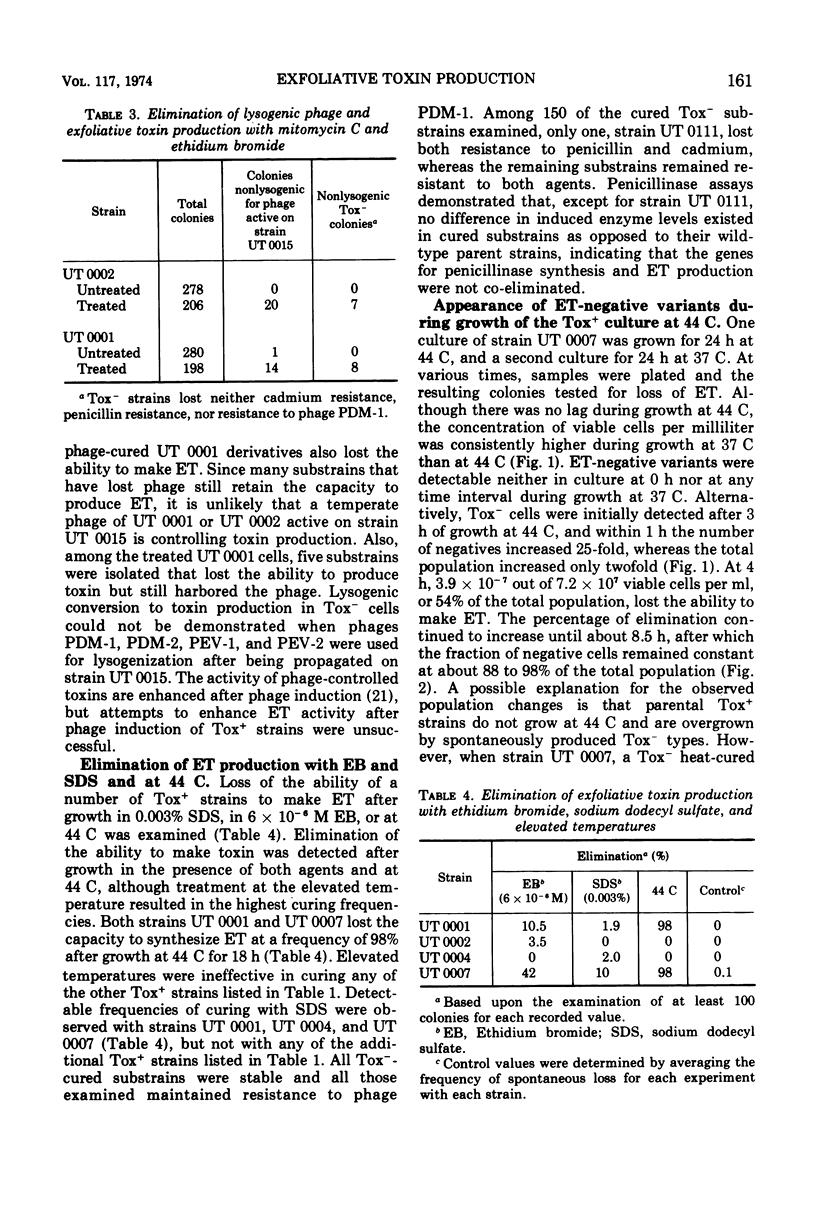
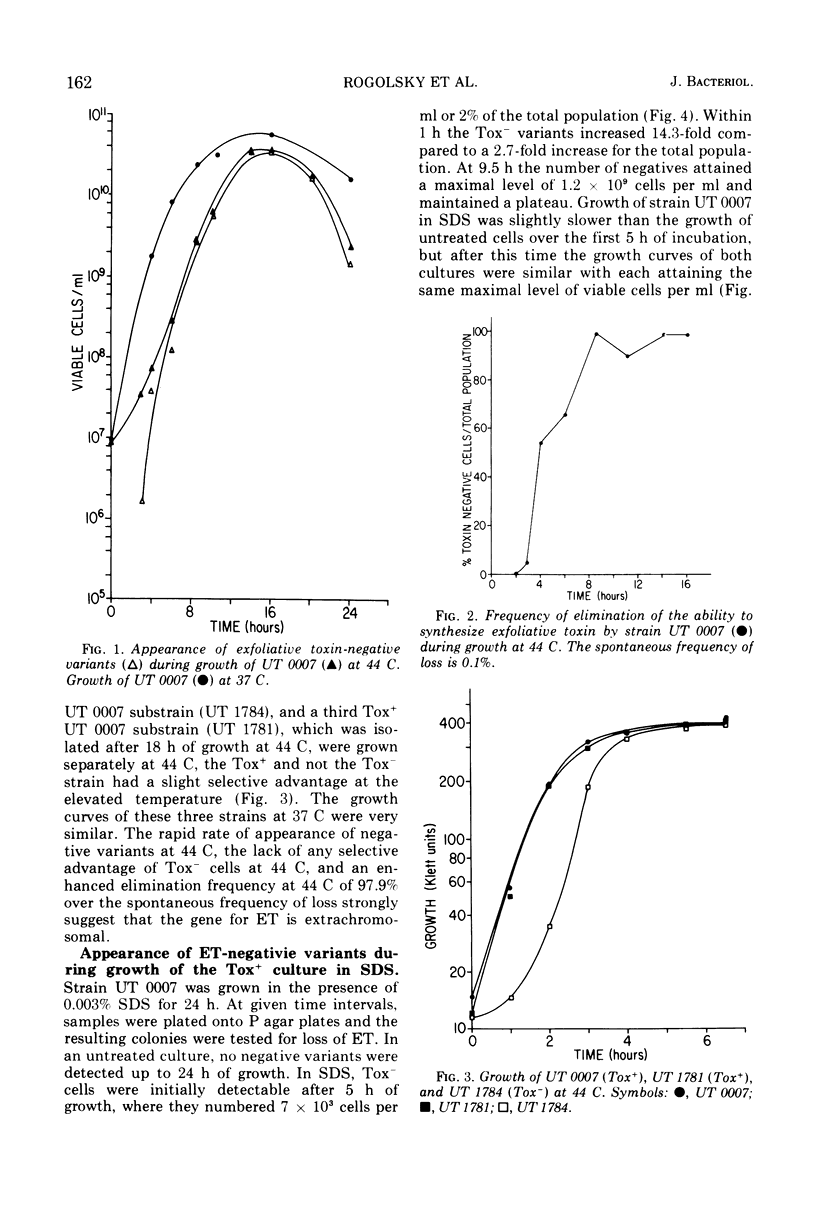
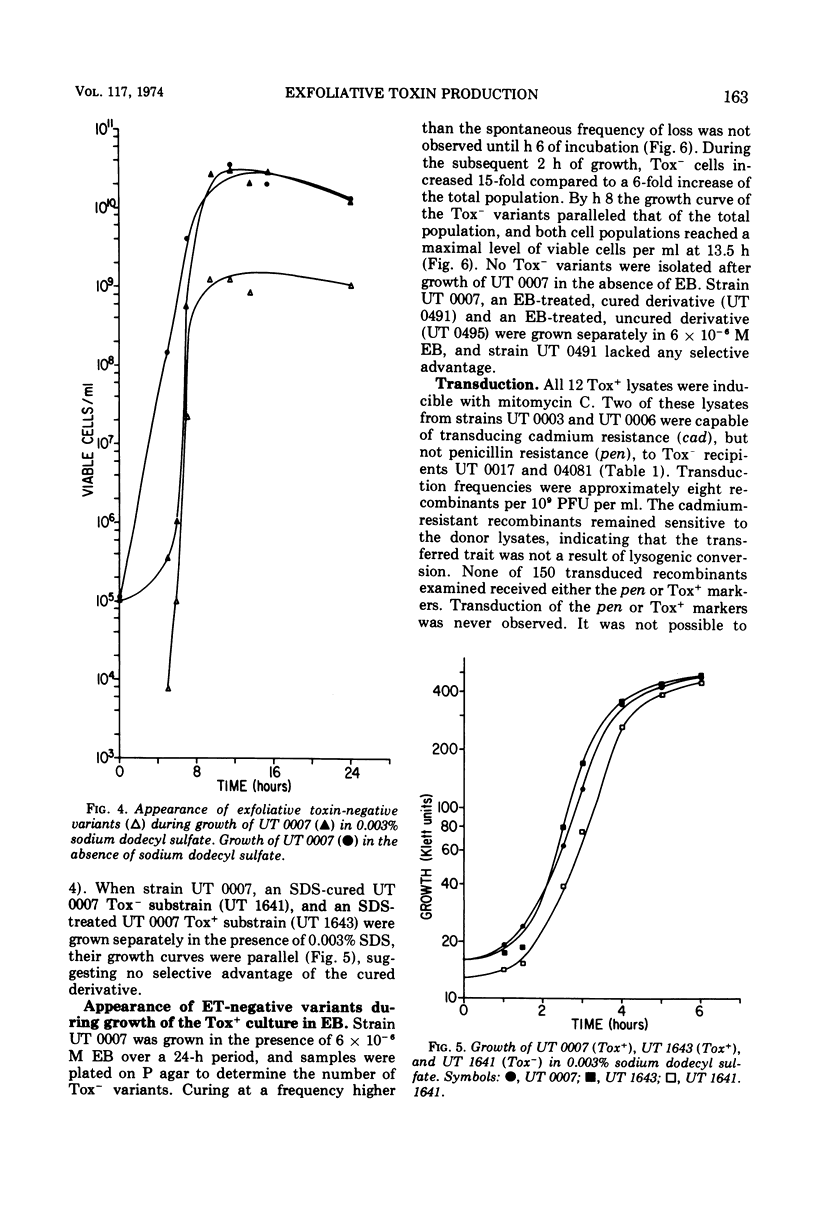
Phage group II Staphylococcus aureus has been identified as the etiological agent of the staphylococcal scaleded skin syndrome. The development of an animal model system permitted fulfillment of Koch's postulates and recognition of exfoliative toxin (ET) as being responsible for some of the clinical manifestations of this syndrome. Initial studies directed toward associating a lysogenic phage with the genetic control of ET synthesis failed to support this hypothesis. Growth of two Tox+ strains at 44 C was more effective than growth in ethidium bromide or sodium dodecyl sulfate in eliminating the ability to produce ET. The early and rapid accumulation of ET-negative (Tox−) variants during growth of strain UT 0007 at 44 C, the lack of any selective advantage of the Tox− variants over Tox+ cells during growth at 44 C, and an enhanced elimination frequency at 44 C of 97.9% over the spontaneous frequency of loss strongly suggest that the gene for ET synthesis is extrachromosomal. Additional evidence suggests that this gene is located on a plasmid which is not associated with genes for penicillinase synthesis and cadmium resistance. Two Tox+ strains harbored lysogenic phage capable of transducing cadmium resistance, but not penicillin resistance, to specific Tox− recipients.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BAUER A. W., PERRY D. M., KIRBY W. M. Single-disk antibiotic-sensitivity testing of staphylococci; an analysis of technique and results. AMA Arch Intern Med. 1959 Aug;104(2):208–216. doi: 10.1001/archinte.1959.00270080034004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLAIR J. E., CARR M. Lysogeny in staphylococci. J Bacteriol. 1961 Dec;82:984–993. doi: 10.1128/jb.82.6.984-993.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouanchaud D. H., Scavizzi M. R., Chabbert Y. A. Elimination by ethidium bromide of antibiotic resistance in enterobacteria and staphylococci. J Gen Microbiol. 1968 Dec;54(3):417–425. doi: 10.1099/00221287-54-3-417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dornbusch K., Hallander H. O., Löfquist F. Extrachromosomal control of methicillin resistance and toxin production in Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1969 May;98(2):351–358. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.2.351-358.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friend P. L., Slade M. D. Characteristics of group A streptococcal bacteriophages. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jul;92(1):148–154. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.1.148-154.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREEN S. M. Mercury sensitivity of staphylococci. J Clin Pathol. 1962 May;15:249–251. doi: 10.1136/jcp.15.3.249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapral F. A., Miller M. M. Product of Staphylococcus aureus responsible for the scalded-skin syndrome. Infect Immun. 1971 Nov;4(5):541–545. doi: 10.1128/iai.4.5.541-545.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence P. J., Rogolsky M., Hanh V. T. Binding of radioactive benzylpenicillin to sporulating Bacillus cultures: chemistry and fluctuations in specific binding capacity. J Bacteriol. 1971 Nov;108(2):662–667. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.2.662-667.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAY J. W., HOUGHTON R. H., PERRET C. J. THE EFFECT OF GROWTH AT ELEVATED TEMPERATURES ON SOME HERITABLE PROPERTIES OF STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS. J Gen Microbiol. 1964 Nov;37:157–169. doi: 10.1099/00221287-37-2-157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melish M. E., Glasgow L. A. Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome: the expanded clinical syndrome. J Pediatr. 1971 Jun;78(6):958–967. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(71)80425-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melish M. E., Glasgow L. A. The staphylococcal scalded-skin syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1970 May 14;282(20):1114–1119. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197005142822002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melish M. E., Glasgow L. A., Turner M. D. The staphylococcal scalded-skin syndrome: isolation and partial characterization of the exfoliative toxin. J Infect Dis. 1972 Feb;125(2):129–140. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.2.129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NOVICK R. P. Micro-iodometric assay for penicillinase. Biochem J. 1962 May;83:236–240. doi: 10.1042/bj0830236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick R. P., Bouanchaud D. The problems of drug-resistant pathogenic bacteria. Extrachromosomal nature of drug resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1971 Jun 11;182:279–294. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1971.tb30664.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick R. P., Roth C. Plasmid-linked resistance to inorganic salts in Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1968 Apr;95(4):1335–1342. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.4.1335-1342.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin S. J., Rosenblum E. D. Effects of ethidium bromide on growth and on loss of the penicillinase plasmid of Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1971 Dec;108(3):1200–1204. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.3.1200-1204.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEAMAN E., TARMY E., MARMUR J. INDUCIBLE PHAGES OF BACILLUS SUBTILIS. Biochemistry. 1964 May;3:607–613. doi: 10.1021/bi00893a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonstein S. A., Baldwin J. N. Loss of the penicillinase plasmid after treatment of Staphylococcus aureus with sodium dodecyl sulfate. J Bacteriol. 1972 Jan;109(1):262–265. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.1.262-265.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Workman R. G., Farrar W. E., Jr Activity of penicillinase in Staphylococcus aureus as studied by the iodometric method. J Infect Dis. 1970 Apr;121(4):433–437. doi: 10.1093/infdis/121.4.433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zabriskie J. B. Viral-induced bacterial toxins. Annu Rev Med. 1966;17:337–350. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.17.020166.002005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



