Abstract
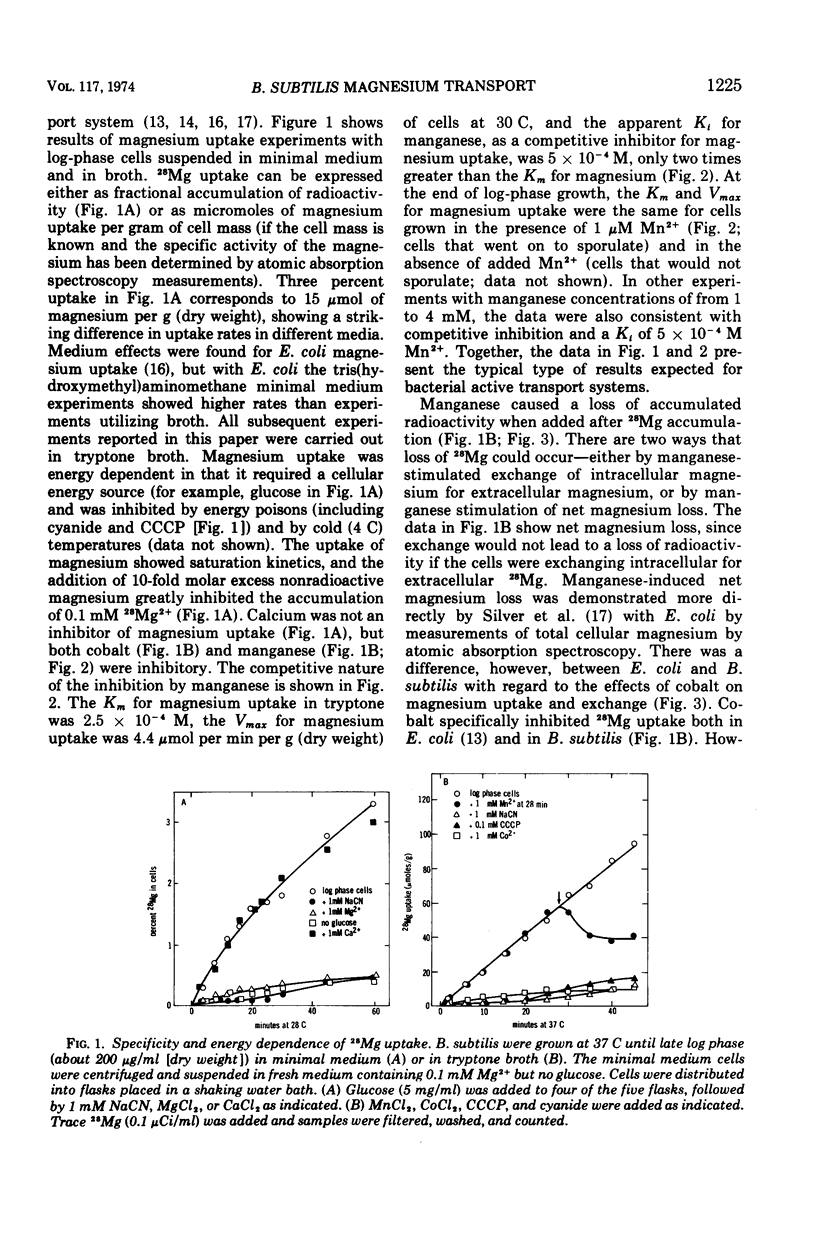
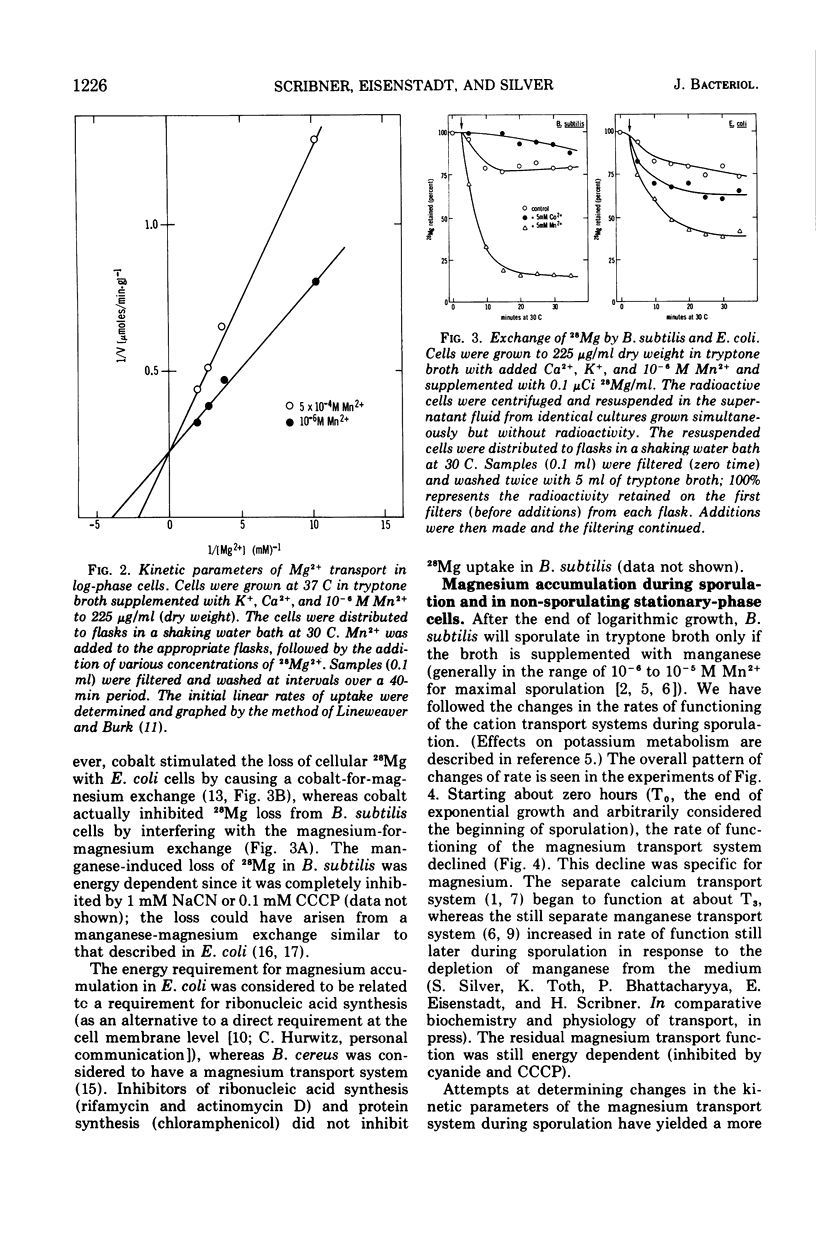
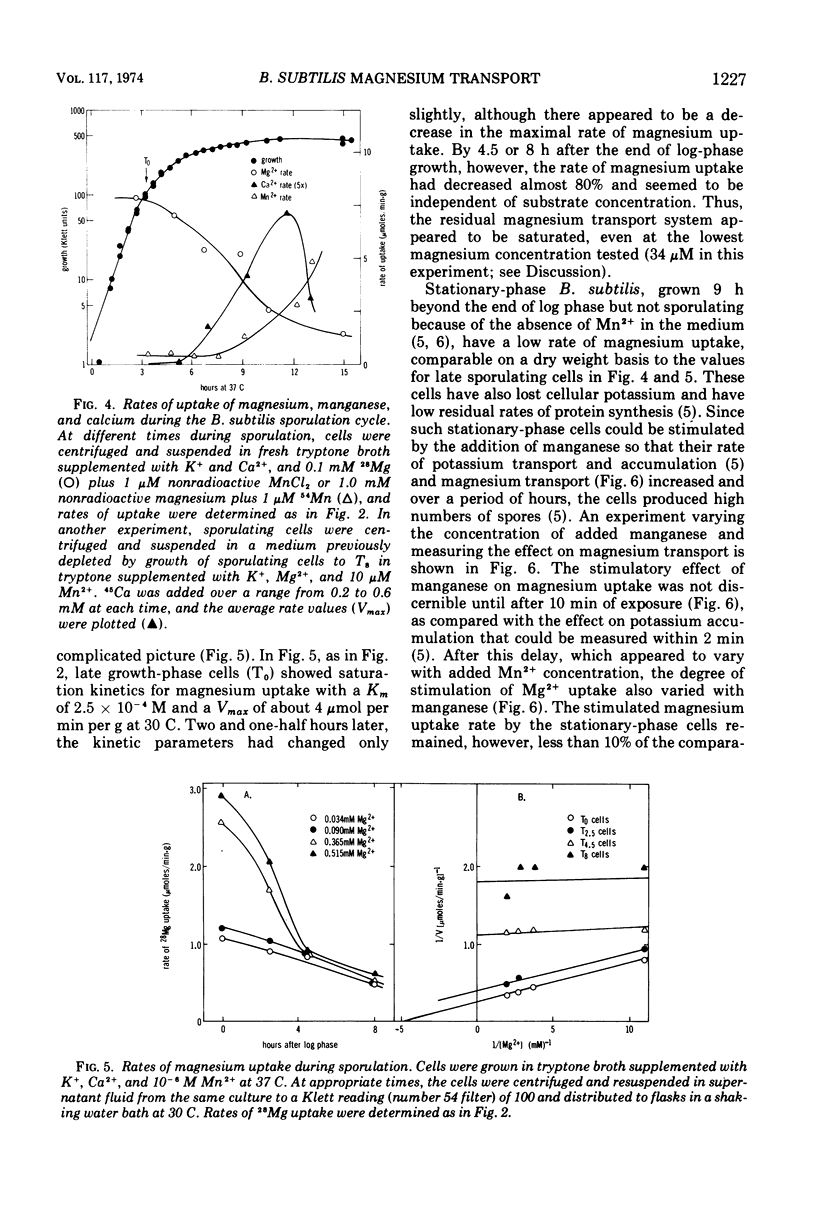
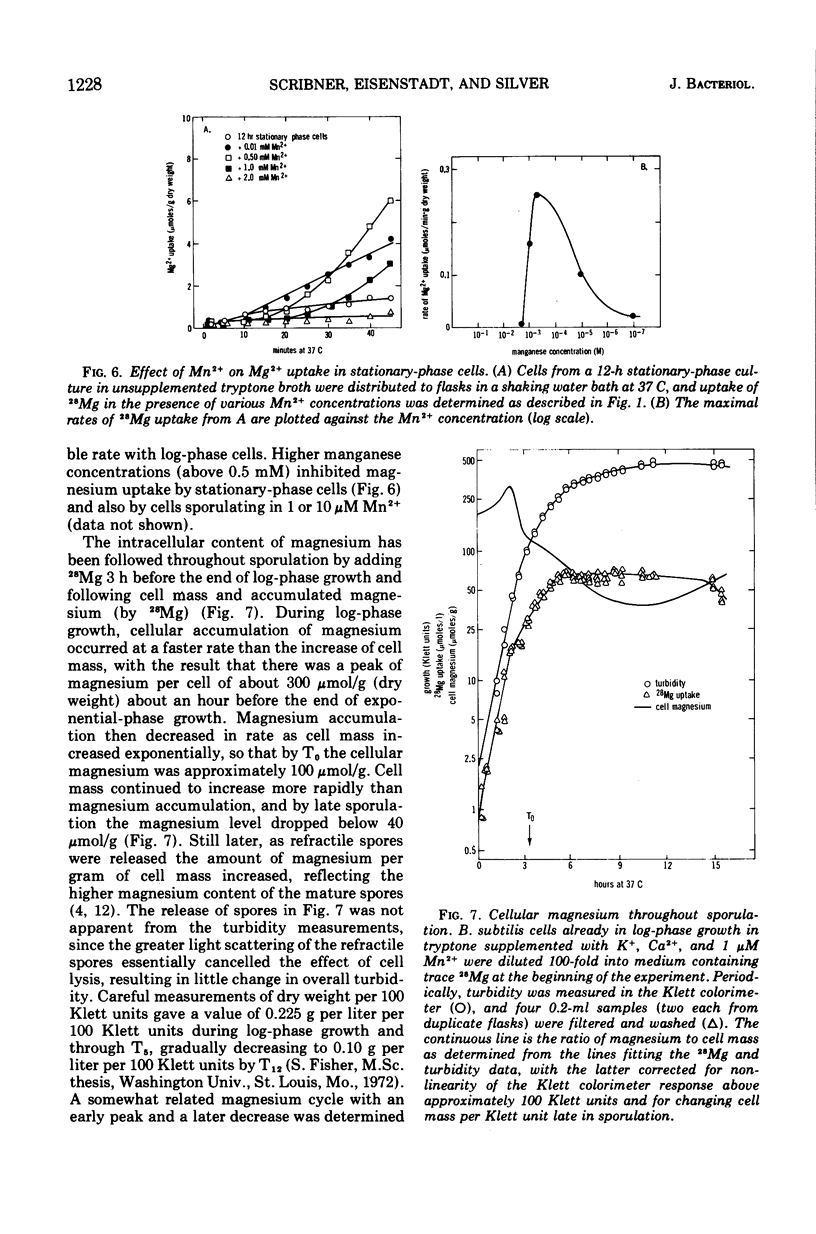
The active transport of magnesium by cells of Bacillus subtilis strain W23 occurs by a highly specific transport system (Mg2+ is favored over Mn2+, Co2+, or Ca2+) that is energy dependent (i.e., glucose is required in minimal medium and the system is inhibited by cyanide and m-chlorophenyl carbonylcyanidehydrazone). The rate of magnesium uptake by log-phase B. subtilis cells follows saturation kinetics with a Km of 2.5 × 10−4 M and a Vmax of 4.4 μmol per min per g (dry weight) at 30 C. Manganese is a competitive inhibitor showing a Ki of 5 × 10−4 M. During sporulation the rate of magnesium transport declines. This decline in rate is specific for the magnesium system as the manganese and calcium transport rates increase. The residual magnesium transport function in sporulating cells shows both an altered Km and an altered Vmax. The magnesium content of late sporulating cells is also lower than that for log-phase cells.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CHARNEY J., FISHER W. P., HEGARTY C. P. Managanese as an essential element for sporulation in the genus Bacillus. J Bacteriol. 1951 Aug;62(2):145–148. doi: 10.1128/jb.62.2.145-148.1951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clausen T. Measurement of 32P activity in a liquid scintillation counter without the use of scintillator. Anal Biochem. 1968 Jan;22(1):70–73. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(68)90260-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenstadt E., Fisher S., Der C. L., Silver S. Manganese transport in Bacillus subtilis W23 during growth and sporulation. J Bacteriol. 1973 Mar;113(3):1363–1372. doi: 10.1128/jb.113.3.1363-1372.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenstadt E. Potassium content during growth and sporulation in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1972 Oct;112(1):264–267. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.1.264-267.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher S., Buxbaum L., Toth K., Eisenstadt E., Silver S. Regulation of manganese accumulation and exchange in Bacillus subtilis W23. J Bacteriol. 1973 Mar;113(3):1373–1380. doi: 10.1128/jb.113.3.1373-1380.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurwitz C., Rosano C. L. The intracellular concentration of bound and unbound magnesium ions in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1967 Aug 25;242(16):3719–3722. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson D. L., Kennedy E. P. Magnesium transport in Escherichia coli. Inhibition by cobaltous ion. J Biol Chem. 1971 May 10;246(9):3042–3049. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson D. L., Kennedy E. P. Transport of magnesium by a repressible and a nonrepressible system in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 May;69(5):1091–1093. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.5.1091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt G. B., Rosano C. L., Hurwitz C. Evidence for a magnesium pump in Bacillus cereus T. J Bacteriol. 1971 Jan;105(1):150–155. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.1.150-155.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver S., Clark D. Magnesium transport in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1971 Feb 10;246(3):569–576. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver S., Johnseine P., Whitney E., Clark D. Manganese-resistant mutants of Escherichia coli: physiological and genetic studies. J Bacteriol. 1972 Apr;110(1):186–195. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.1.186-195.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spizizen J. TRANSFORMATION OF BIOCHEMICALLY DEFICIENT STRAINS OF BACILLUS SUBTILIS BY DEOXYRIBONUCLEATE. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1958 Oct 15;44(10):1072–1078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.44.10.1072. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb M. The mechanism of acquired resistance to Co2+ and Ni2+ in Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Nov 24;222(2):440–446. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(70)90134-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willecke K., Gries E. M., Oehr P. Coupled transport of citrate and magnesium in Bacillus subtilis. J Biol Chem. 1973 Feb 10;248(3):807–814. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



