Abstract
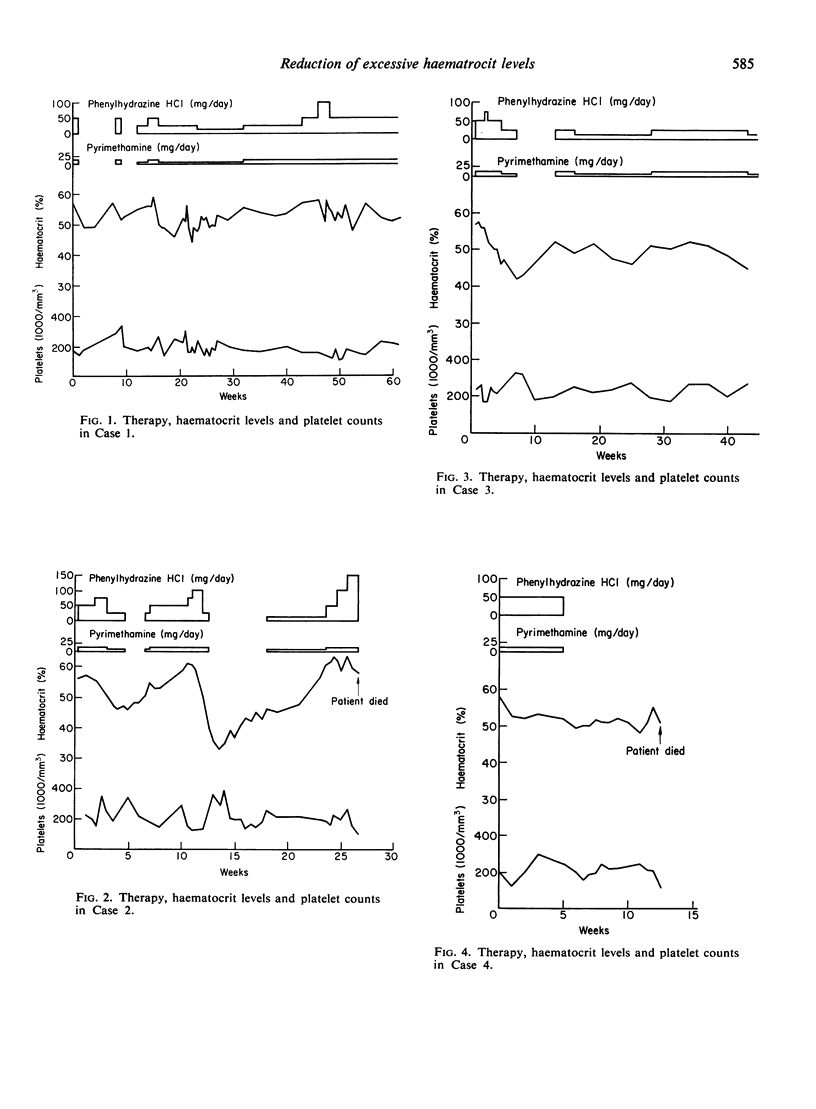
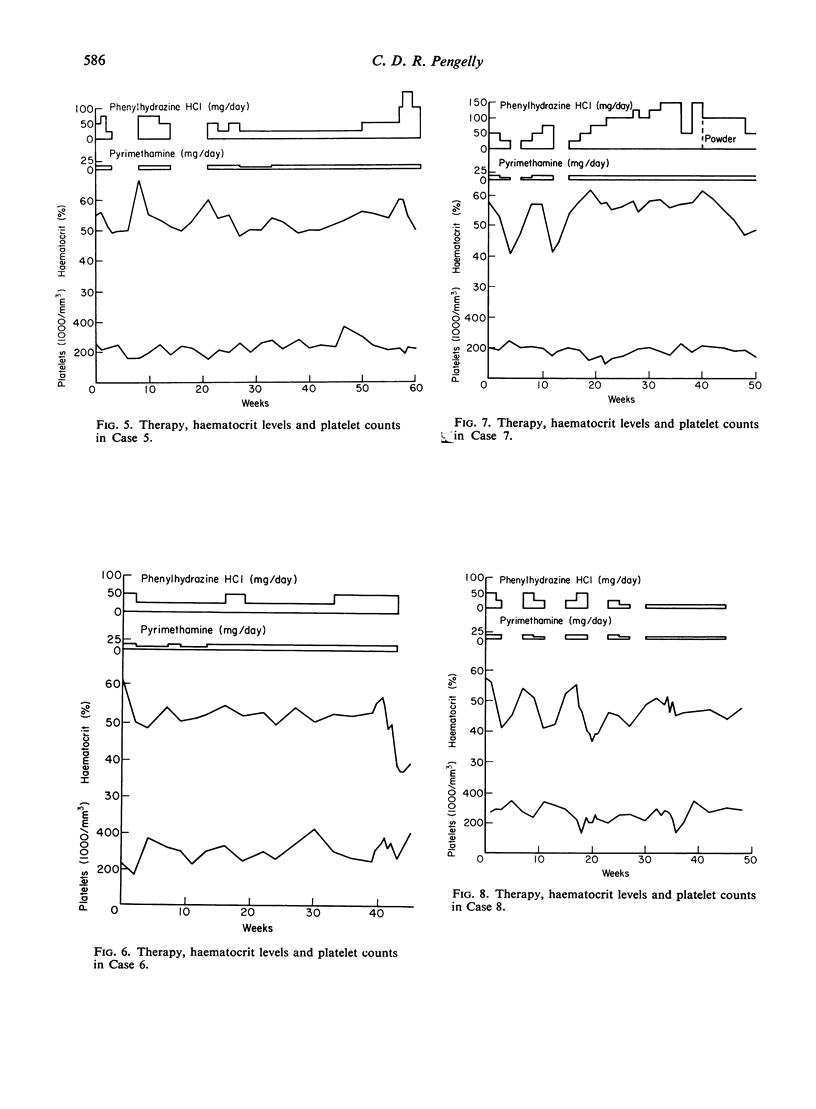
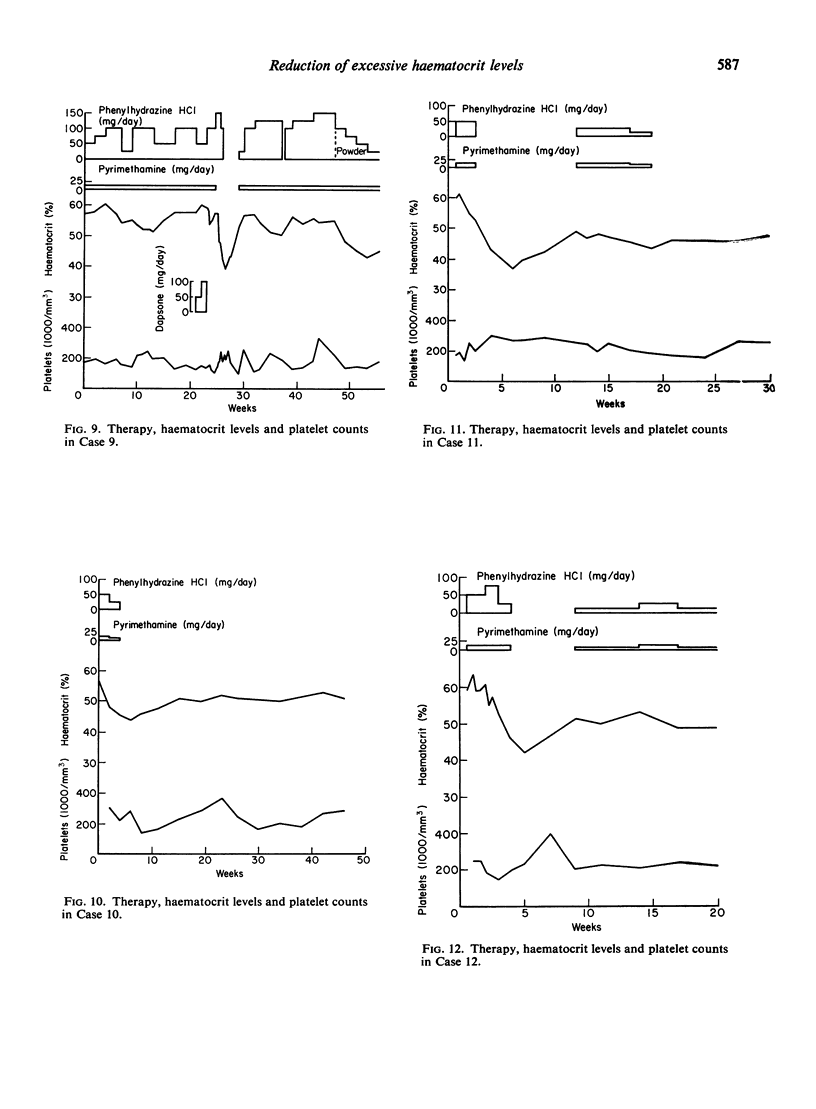
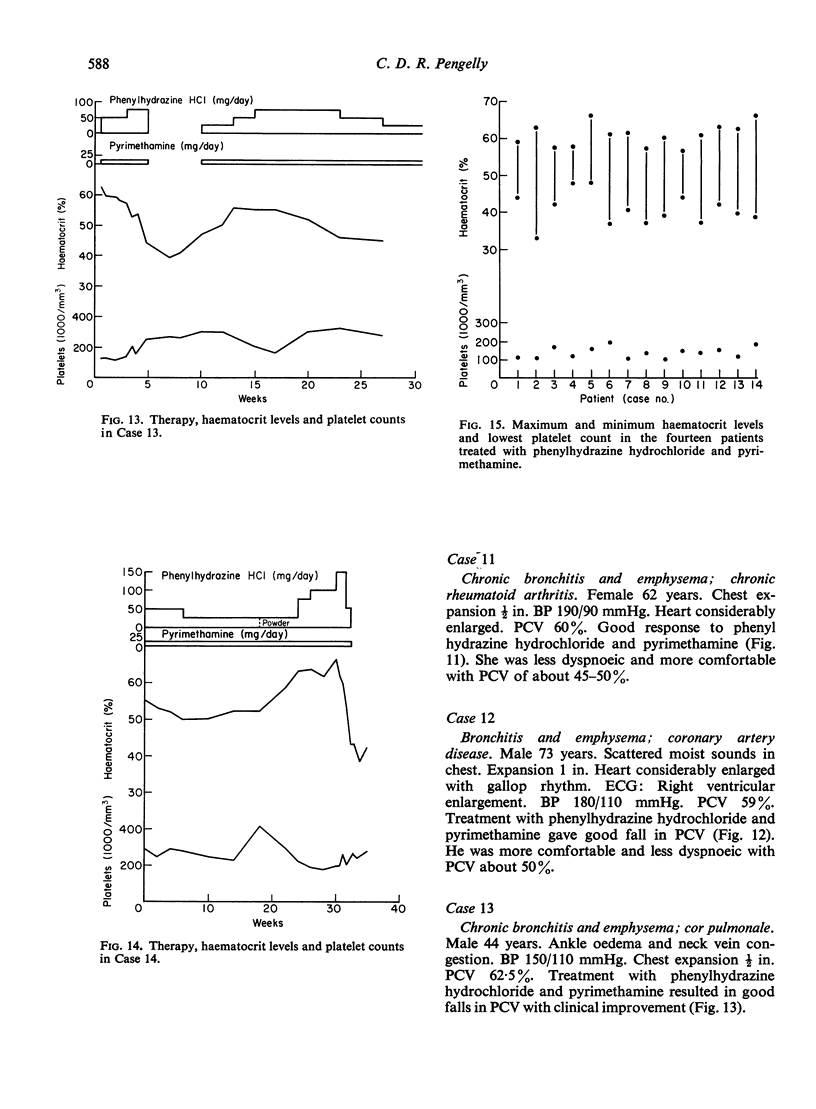
A series of fourteen patients with polycythaemia due to hypoxic lung disease has been treated with a combination of phenylhydrazine hydrochloride and pyrimethamine to reduce the haematocrit level, with doses usually of up to 100 mg/day (and rarely up to 150 mg/day) of the former and never more than 12·5 mg/day of the latter.
Successful reduction of the haematocrit level was achieved in every case without any significant thrombocytopenia, the lowest level ever occurring being 100,000 platelets/mm3 in two patients.
All the patients were improved symptomatically.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CHAMBERLAIN D. A., MILLARD F. J. THE TREATMENT OF PLYCYTHAEMIA A/CHAMBERLAIN DA, MILLARD FJ: THE TREATMENT OF POLYCYTHAEMIA SECONDARY TO HYPOXIC LUNG DISEASE BY CONTINUOUS OXYGEN ADMINISTRATION. Q J Med. 1963 Oct;32:341–350. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cumming R. L., Goldberg A., Morrow J., Smith J. A. Effect of phenylhydrazine-induced haemolysis on the urinary excretion of iron after desferrioxamine. Lancet. 1967 Jan 14;1(7481):71–74. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(67)92473-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOLLISON P. L., VEALL N. The use of the isotope 51Cr as a label for red cells. Br J Haematol. 1955 Jan;1(1):62–74. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1955.tb05489.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PENGELLY C. D. DAPSONE-INDUCED HAEMOLYSIS. Br Med J. 1963 Sep 14;2(5358):662–664. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5358.662. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pengelly C. D. Reduction of haematocrit and red-blood-cell volume in patients with polycythaemia secondary to hypoxic lung disease by dapsone and pyrimethamine. Lancet. 1966 Dec 24;2(7478):1381–1386. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(66)90421-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


