Abstract
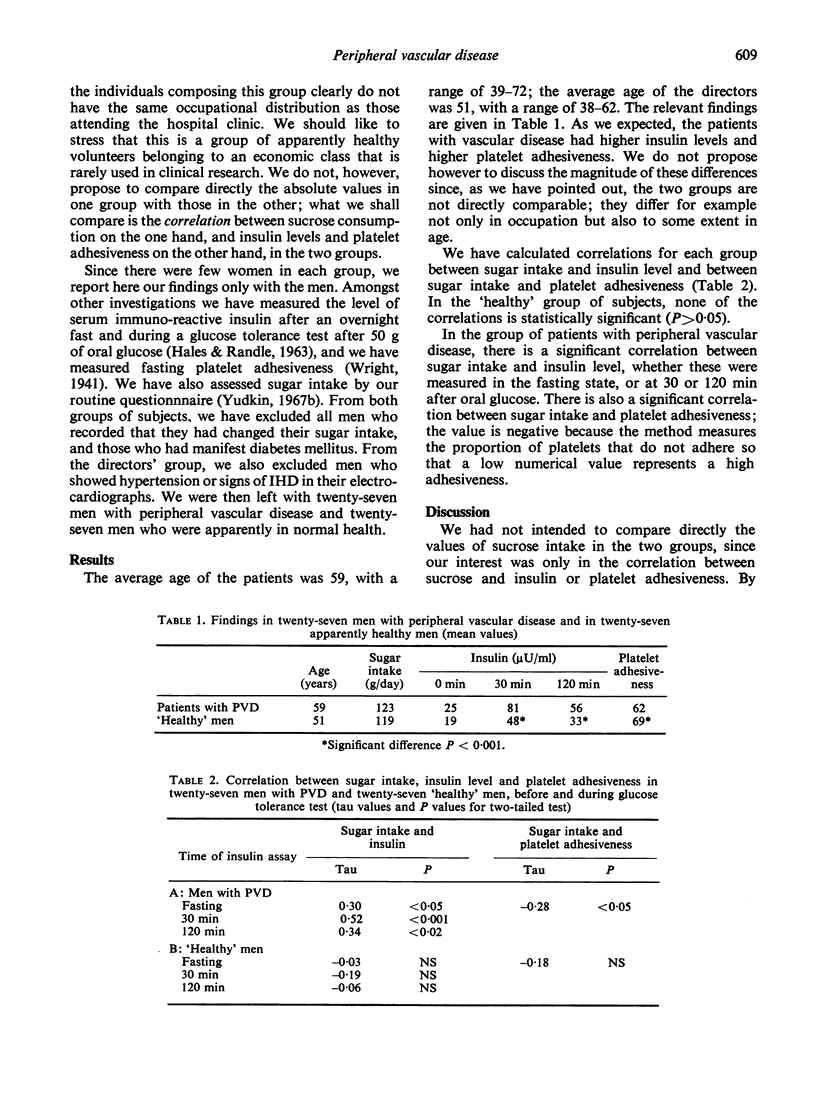
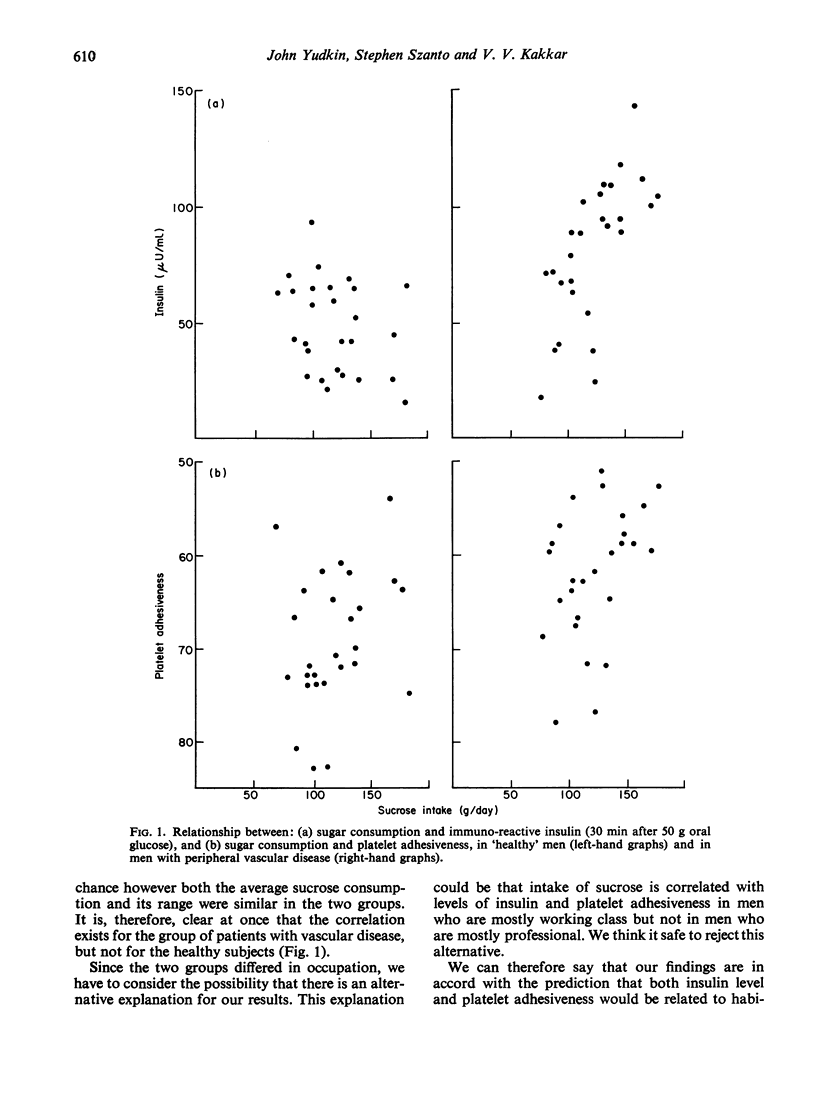
Both the level of serum insulin and the adhesiveness of platelets are correlated with sucrose intake in men with peripheral vascular disease. These correlations do not exist in men who have no signs or symptoms of the disease, or of predisposing conditions such as hypertension.
The results support the suggestion of Szanto & Yudkin (1969) that an habitual high intake of sugar raises the insulin level in some individuals but not all, and that these individuals are susceptible to the effect of sucrose in producing occlusive arterial disease.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- HALES C. N., RANDLE P. J. Immunoassay of insulin with insulin-antibody precipitate. Biochem J. 1963 Jul;88:137–146. doi: 10.1042/bj0880137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szanto S., Yudkin J. The effect of dietary sucrose on blood lipids, serum insulin, platelet adhesiveness and body weight in human volunteers. Postgrad Med J. 1969 Sep;45(527):602–607. doi: 10.1136/pgmj.45.527.602. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YUDKIN J., RODDY J. LEVELS OF DIETARY SUCROSE IN PATIENTS WITH OCCLUSIVE ATHEROSCLEROTIC DISEASE. Lancet. 1964 Jul 4;2(7349):6–8. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(64)90003-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


