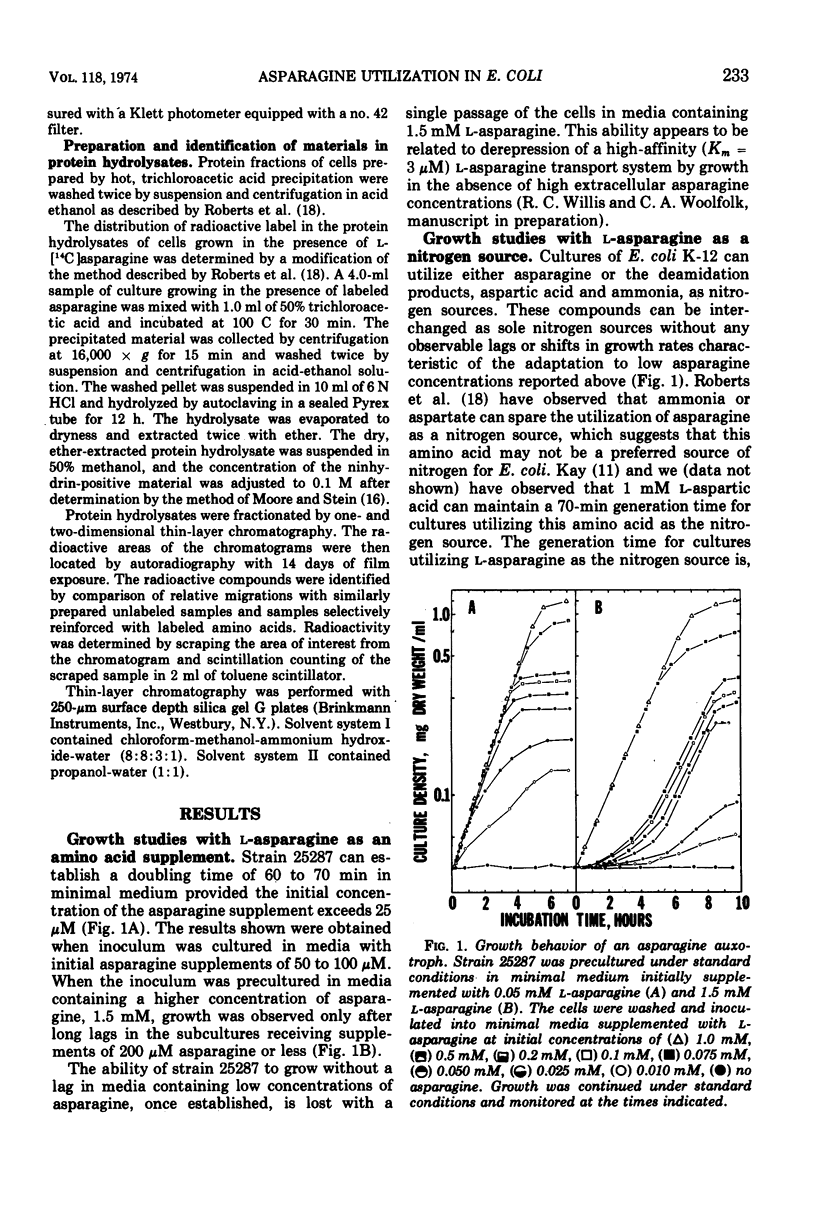
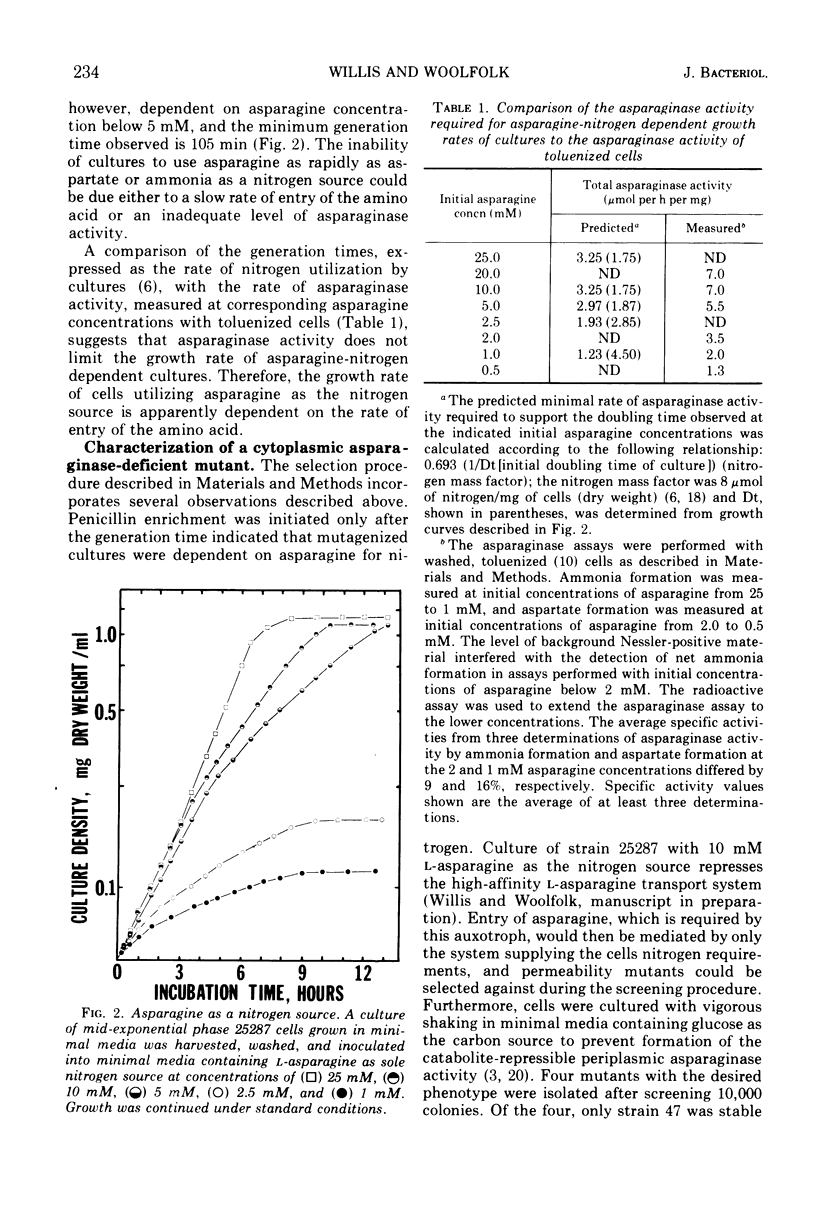
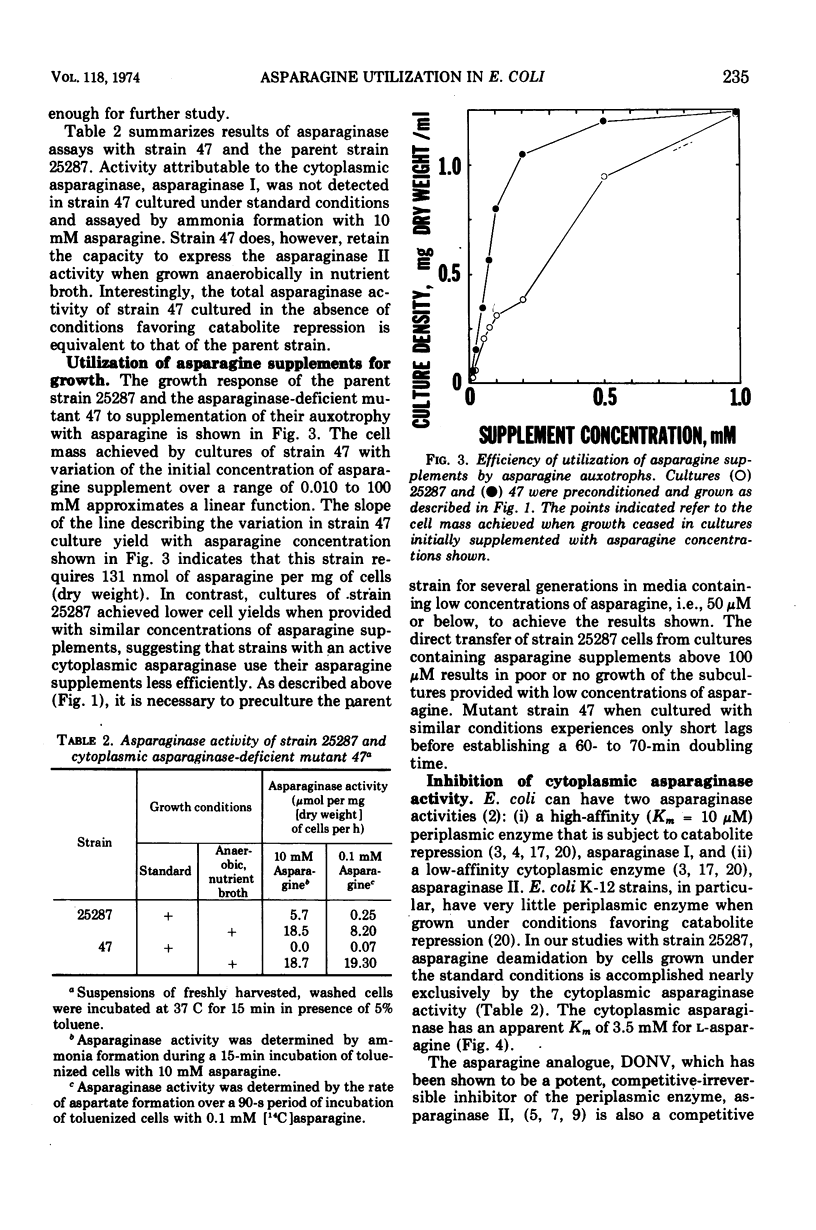
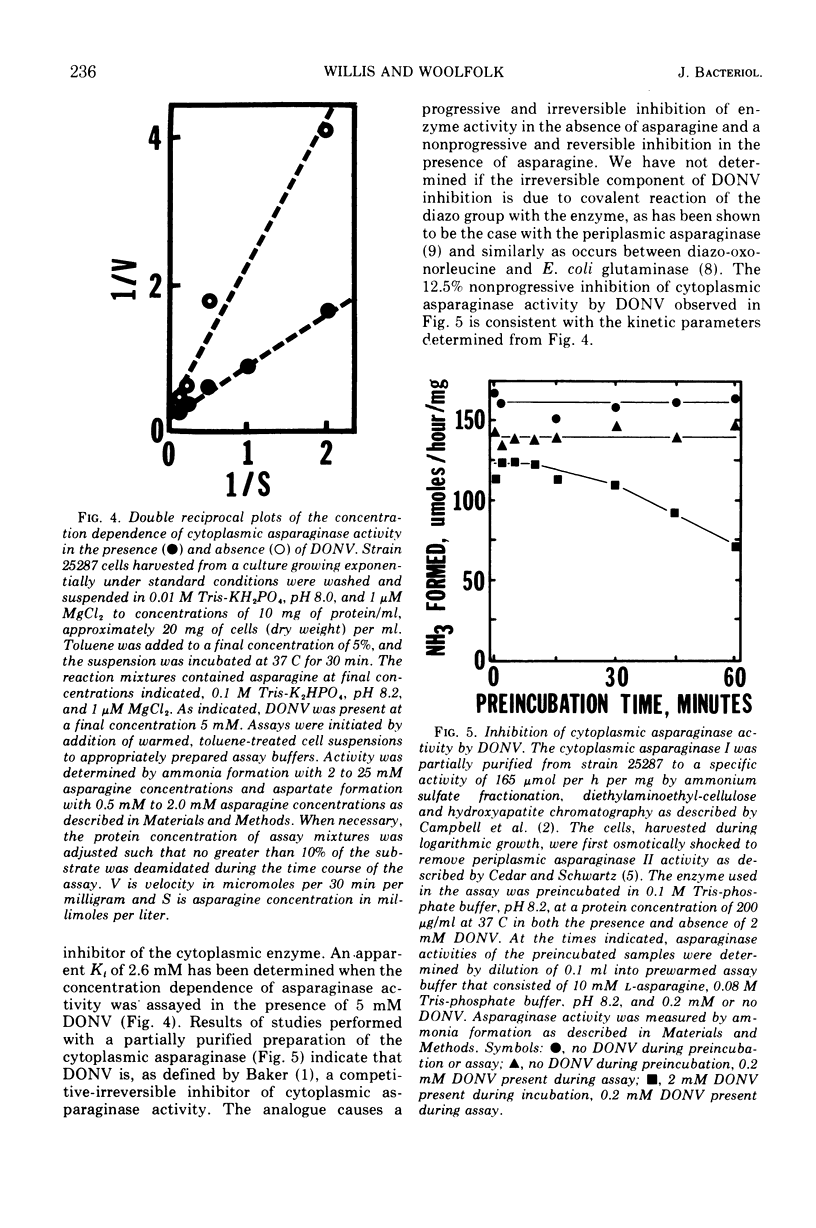
Abstract
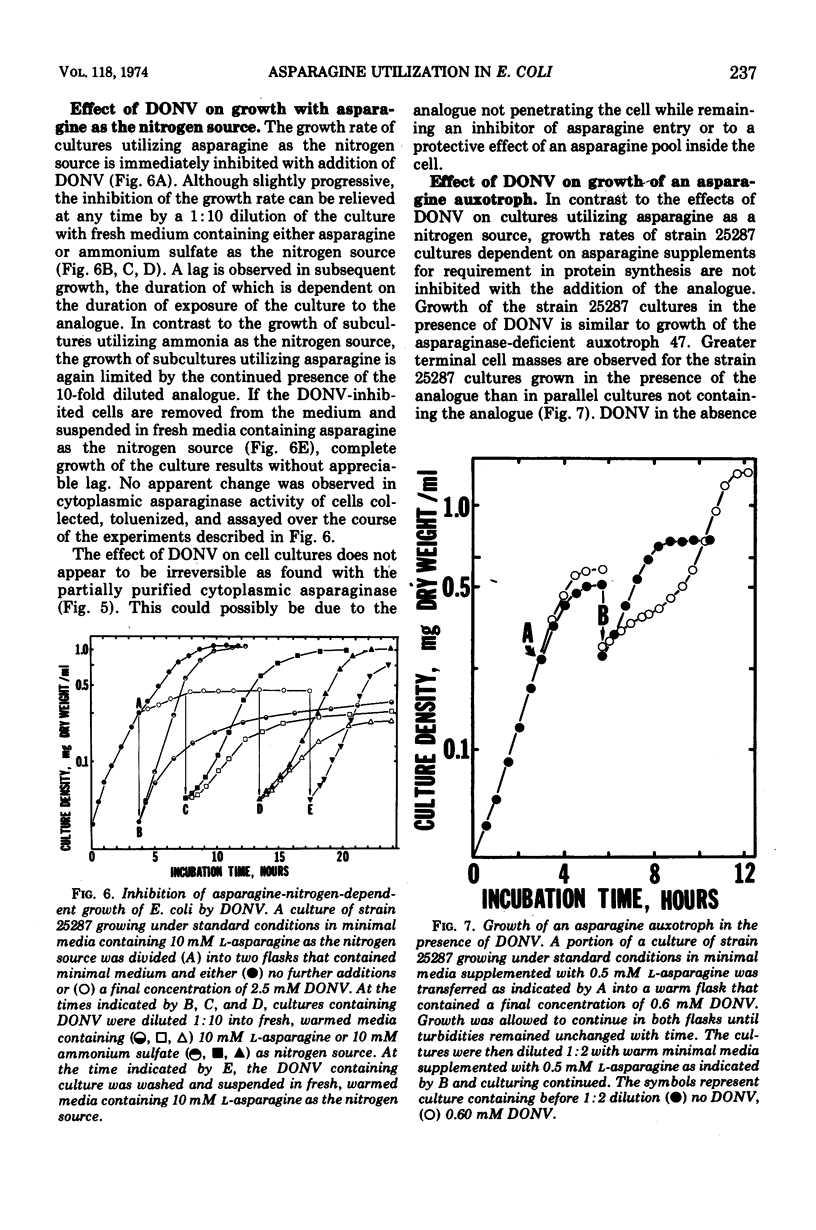
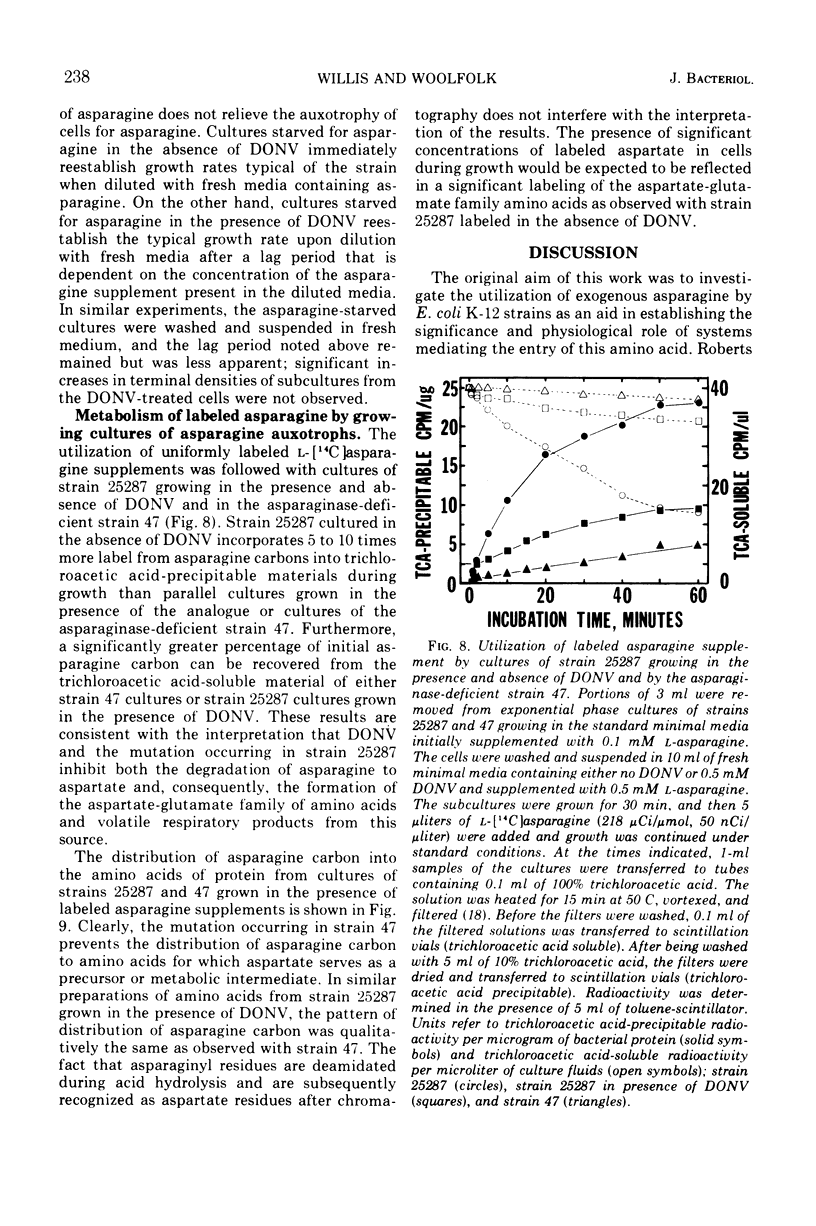
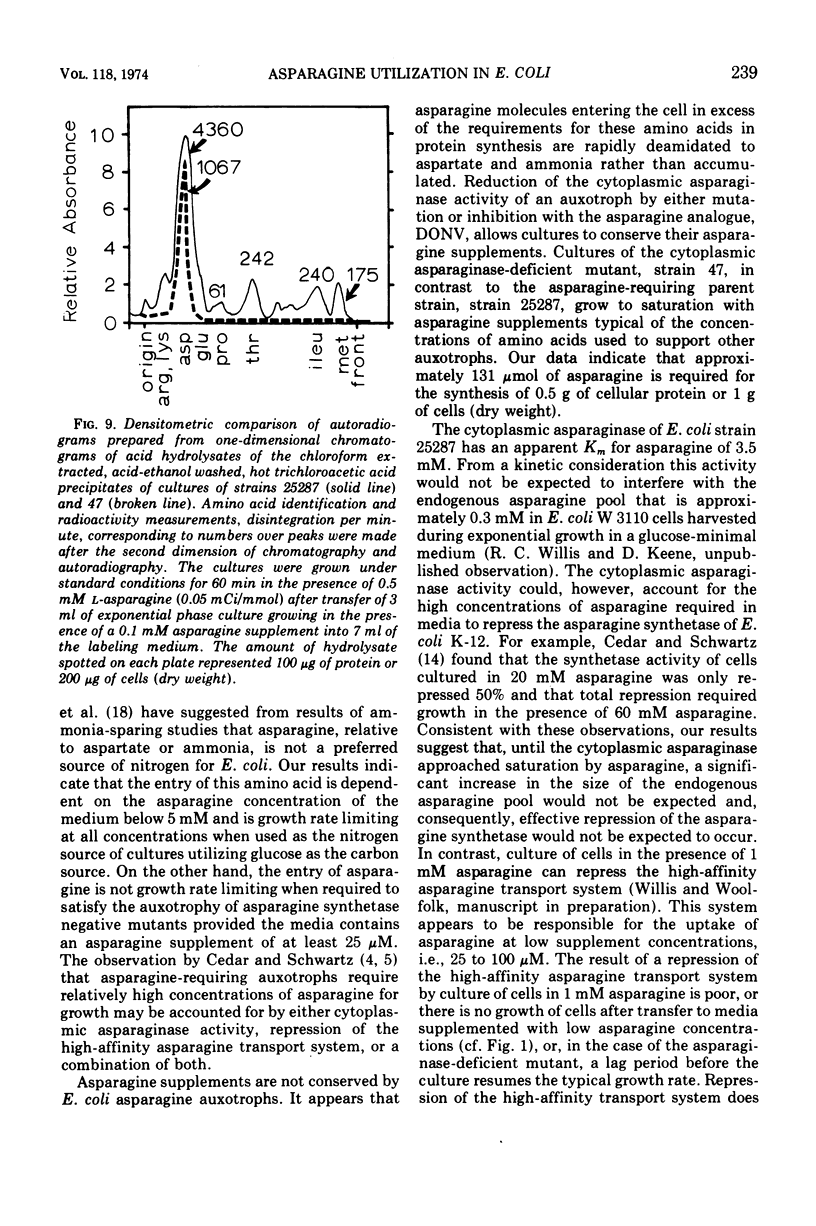
Asparagine-requiring auxotrophs of Escherichia coli K-12 that have an active cytoplasmic asparaginase do not conserve asparagine supplements for use in protein synthesis. Asparagine molecules entering the cell in excess of the pool required for use of this amino acid in protein synthesis are rapidly degraded rather than accumulated. Supplements are conserved when asparagine degradation is inhibited by the asparagine analogue 5-diazo-4-oxo-l-norvaline (DONV) or mutation to cytoplasmic asparaginase deficiency. A strain deficient in cytoplasmic asparaginase required approximately 260 μmol of asparagine for the synthesis of 1 g of cellular protein. The cytoplasmic asparaginase (asparaginase I) is required for growth of cells when asparagine is the nitrogen source. This enzyme has an apparent Km for l-asparagine of 3.5 mM, and asparaginase activity is competitively inhibited by DONV with an apparent Ki of 2 mM. The analogue provides a time-dependent, irreversible inhibition of cytoplasmic asparaginase activity in the absence of asparagine.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Campbell H. A., Mashburn L. T., Boyse E. A., Old L. J. Two L-asparaginases from Escherichia coli B. Their separation, purification, and antitumor activity. Biochemistry. 1967 Mar;6(3):721–730. doi: 10.1021/bi00855a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cedar H., Schwartz J. H. Localization of the two-L-asparaginases in anaerobically grown Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1967 Aug 25;242(16):3753–3755. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cedar H., Schwartz J. H. Production of L-asparaginase II by Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1968 Dec;96(6):2043–2048. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.6.2043-2048.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cedar H., Schwartz J. H. The asparagine synthetase of Escherhic coli. I. Biosynthetic role of the enzyme, purification, and characterization of the reaction products. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 10;244(15):4112–4121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank L., Hopkins I. Sodium-stimulated transport of glutamate in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1969 Oct;100(1):329–336. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.1.329-336.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handschumacher R. E., Bates C. J., Chang P. K., Andrews A. T., Fischer G. A. 5-Diazo-4-oxo-L-norvaline: reactive asparagine analog with biological specificity. Science. 1968 Jul 5;161(3836):62–63. doi: 10.1126/science.161.3836.62. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartman S. C. Glutaminase of Escherichia coli. I. Purification and general catalytic properties. J Biol Chem. 1968 Mar 10;243(5):853–863. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson R. C., Handschumacher R. E. Escherichia coli L-asparaginase. Catalytic activity and subunit nature. Biochemistry. 1970 Sep 1;9(18):3585–3590. doi: 10.1021/bi00820a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson R. W., DeMoss J. A. Effects of toluene on Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1965 Nov;90(5):1420–1425. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.5.1420-1425.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay W. W. Two aspartate transport systems in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1971 Dec 10;246(23):7373–7382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUBIN M., KESSEL D. H., BUDREAU A., GROSS J. D. The isolation of bacterial mutants defective in amino acid transport. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 Aug 26;42:535–538. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)90836-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MONOD J., COHEN-BAZIRE G., COHN M. Sur la biosynthèse de la beta-galactosidase (lactase) chez Escherichia coli; la spécificité de l'induction. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1951 Nov;7(4):585–599. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(51)90072-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOORE S., STEIN W. H. A modified ninhydrin reagent for the photometric determination of amino acids and related compounds. J Biol Chem. 1954 Dec;211(2):907–913. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts J., Burson G., Hill J. M. New procedures for purification of L-asparaginase with high yield from Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jun;95(6):2117–2123. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.6.2117-2123.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SALIVAR W. O., TZAGOLOFF H., PRATT D. SOME PHYSICAL-CHEMICAL AND BIOLOGICAL PROPERTIES OF THE ROD-SHAPED COLIPHAGE M13. Virology. 1964 Nov;24:359–371. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(64)90173-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz J. H., Reeves J. Y., Broome J. D. Two L-asparaginases from E. coli and their action against tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Nov;56(5):1516–1519. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.5.1516. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WITKIN E. M. Time, temperature, and protein synthesis: a study of ultraviolet-induced mutation in bacteria. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1956;21:123–140. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1956.021.01.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


