Abstract
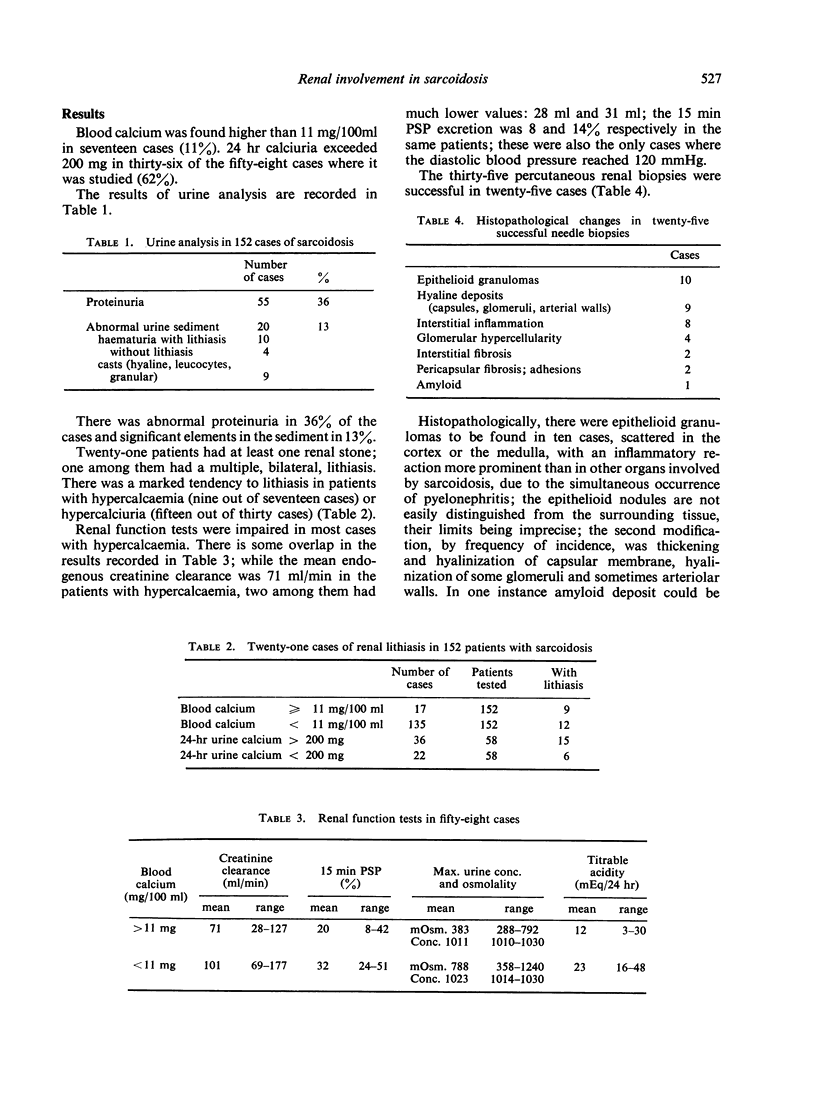
Among 152 sarcoidosis patients, 11% had hypercalcaemia, 62% had hypercalciuria and 13·8% had at least one renal stone. Impairment of renal function was mostly conspicuous in patients with hypercalcaemia. Twenty-five successful percutaneous renal biopsies were performed. Epithelioid granulomas were seen in ten cases, with inflammatory reaction more prominent than in other organs involved by sarcoidosis, due to simultaneous pyelonephritis. Thickening and hyalinization of capsular membrane and glomeruli as well as arterial walls were frequently encountered. Amyloid deposits could be seen in one case with chronic lung infection. Histopathological changes specific of sarcoidosis are related to an abnormal amount of serum gammaglobulins and calciuria exceeding 200 mg in 24 hr, which seem to be the best tests of involvement by the disease.
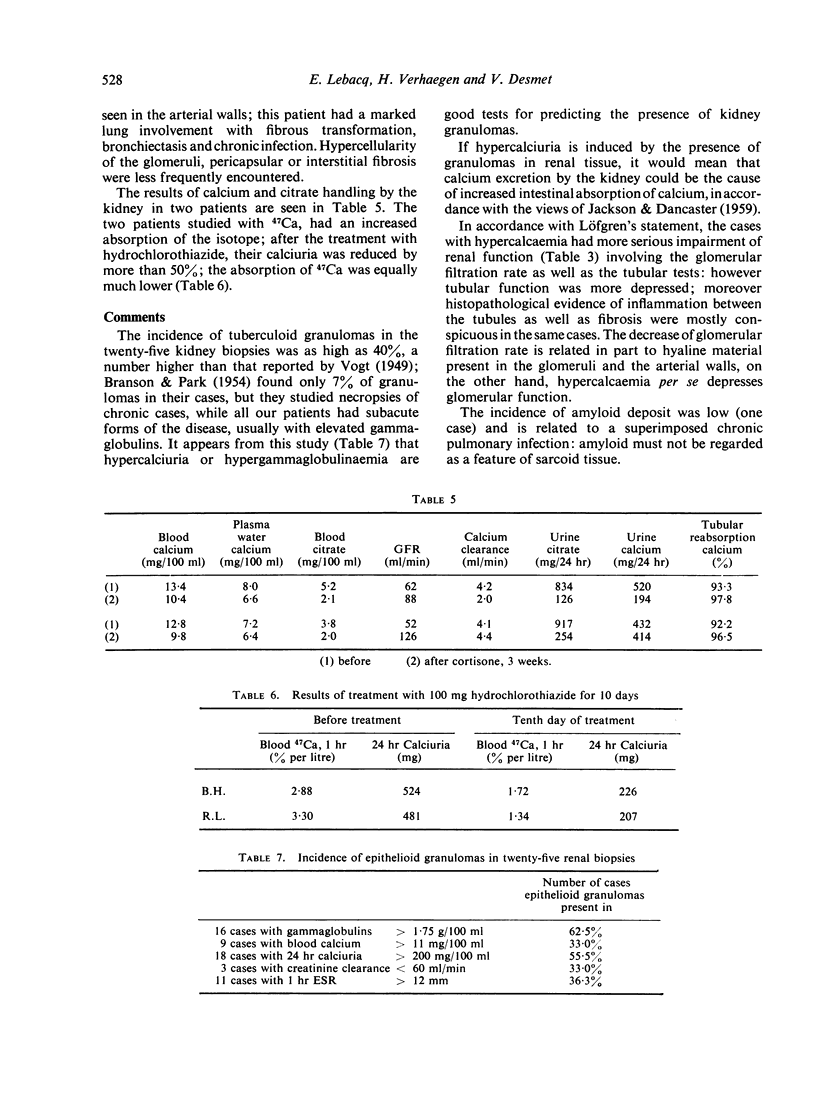
Tubular reabsorption of calcium was low in two patients with hypercalciuria, which was corrected after corticosteroid treatment.
High intestinal calcium absorption was lowered after hydrochlorothiazide had decreased urine calcium.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AVIOLI L. V., MCDONALD J. E., SINGER R. A., HENNEMAN P. H. A NEW ORAL ISOTOPIC TEST OF CALCIUM ABSORPTION. J Clin Invest. 1965 Jan;44:128–139. doi: 10.1172/JCI105119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOYCE W. H., KING J. S., Jr Effects of high calcium intakes on urine in human beings. Fed Proc. 1959 Dec;18:1102–1111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRANSON J. H., PARK J. H. Sarcoidosishepatic involvement: presentation of a case with fatal liver involvement; including autopsy findings and review of the evidence for sarcoid involvement of the liver as found in the literature. Ann Intern Med. 1954 Jan;40(1):111–145. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-40-1-111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coburn J. W., Hobbs C., Johnston G. S., Richert J. H., Shinaberger J. H., Rosen S. Granulomatous sarcoid nephritis. Am J Med. 1967 Feb;42(2):273–283. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(67)90025-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIGGINS B. A., NASSIM J. R., COLLINS J., HILB A. THE EFFECT OF BENDROFLUAZIDE ON URINE CALCIUM EXCRETION. Clin Sci. 1964 Dec;27:457–462. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKINSON A. The relation between citric acid and calcium metabolism with particular reference to primary hyper-parathyroidism and idiopathic hypercalciuria. Clin Sci. 1963 Apr;24:167–178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JACKSON W. P., DANCASTER C. A consideration of the hypercalciuria in sarcoidosis, idiopathic hypercalciuria, and that produced by vitamin D; a new suggestion regarding calcium metabolism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1959 Jun;19(6):658–680. doi: 10.1210/jcem-19-6-658. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEECH M. K. Generalized sarcoidosis with renal involvement. Proc R Soc Med. 1951 Aug;44(8):728–729. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOFGREN S., SNELLMAN B., LINDGREN A. G. Renal complications in sarcoidosis; functional and biopsy studies. Acta Med Scand. 1957 Dec 12;159(4):295–305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LONGCOPE W. T., FREIMAN D. G. A study of sarcoidosis; based on a combined investigation of 160 cases including 30 autopsies from The Johns Hopkins Hospital and Massachusetts General Hospital. Medicine (Baltimore) 1952 Feb;31(1):1–132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OGILVIE R. I., KAYE M., MOORE S. GRANULOMATOUS SARCOID DISEASE OF THE KIDNEY. Ann Intern Med. 1964 Oct;61:711–715. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-61-4-711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RICKER W., CLARK M. Sarcoidosis; a clinicopathologic review of 300 cases, including 22 autopsies. Am J Clin Pathol. 1949 Aug;19(8):725–749. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/19.8.725. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSE G. A. The relative importance of the ionized and complexed fractions of calcium in human plasma in control of the urine calcium. Proc R Soc Med. 1959 May;52(5):347–349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEITZ H., JAWORSKI Z. F. EFFECT OF HYDROCHLOROTHIAZIDE ON SERUM AND URINARY CALCIUM AND URINARY CITRATE. Can Med Assoc J. 1964 Feb 8;90:414–420. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TEILUM G. Allergic hyperglobulinosis and hyalinosis (paramyloidosis) in the reticulo-endothelial system in Boeck's sarcoid and other conditions; a morphologic immunity reaction. Am J Pathol. 1948 Mar;24(2):389–407. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



