Abstract
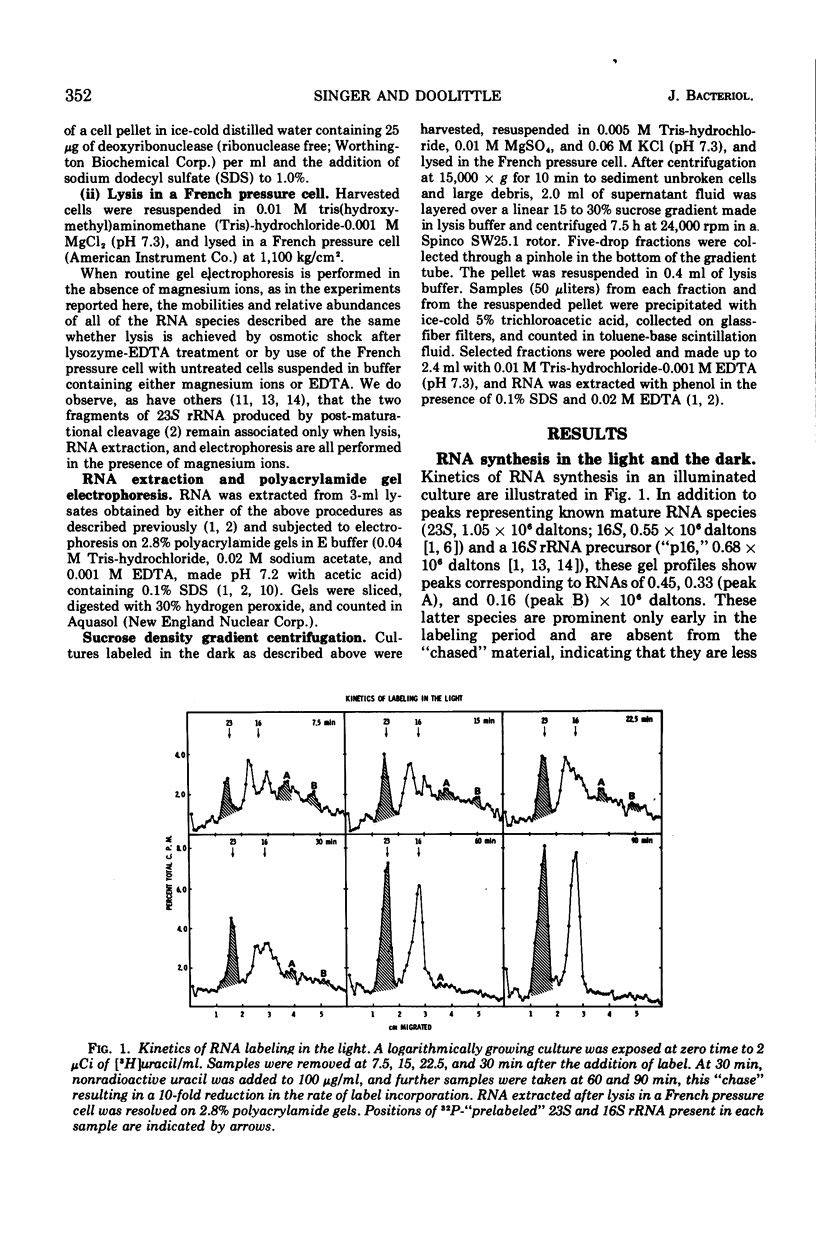
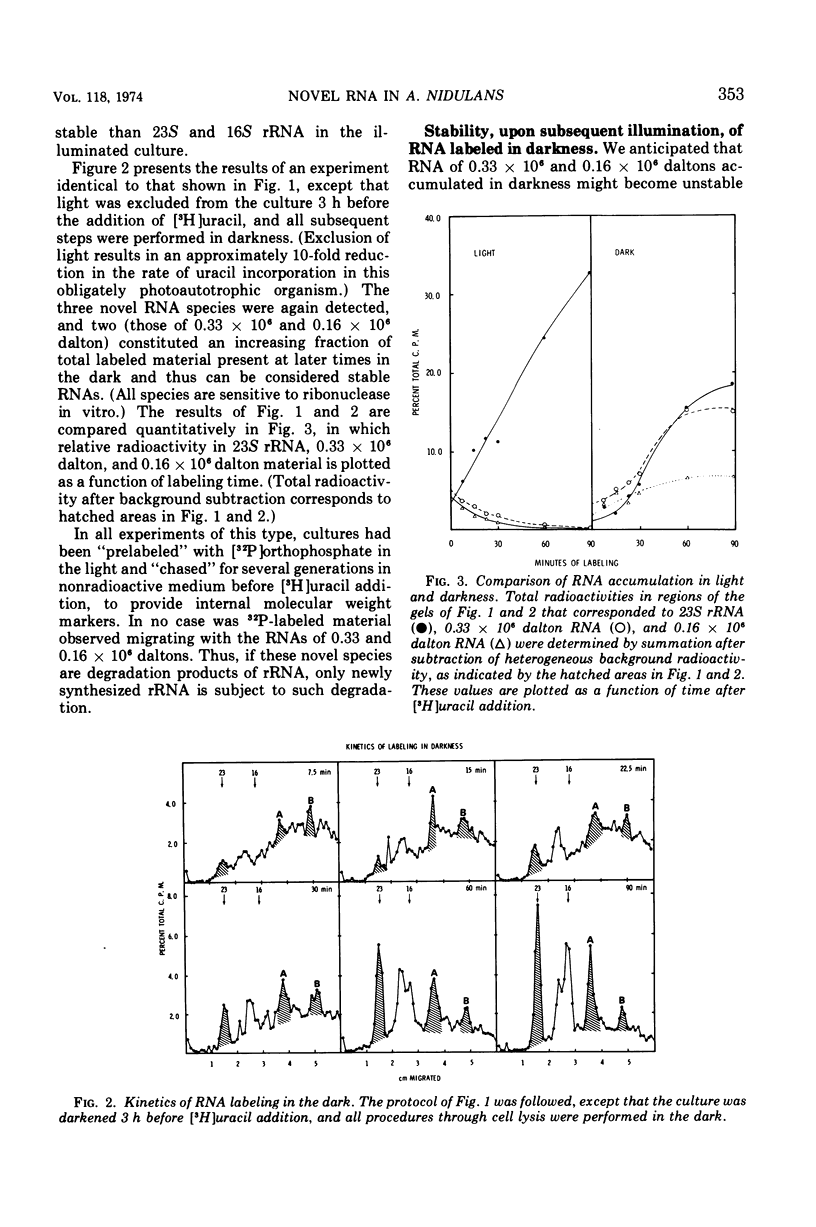
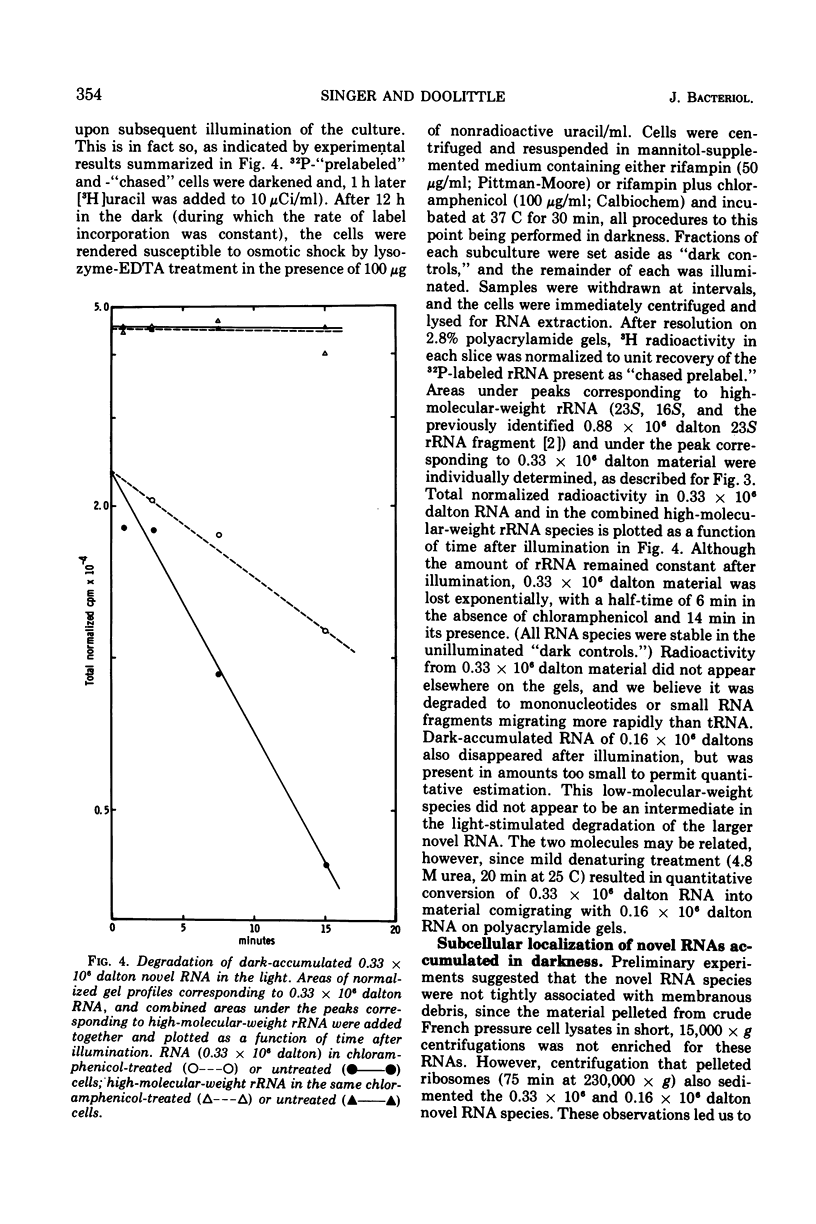
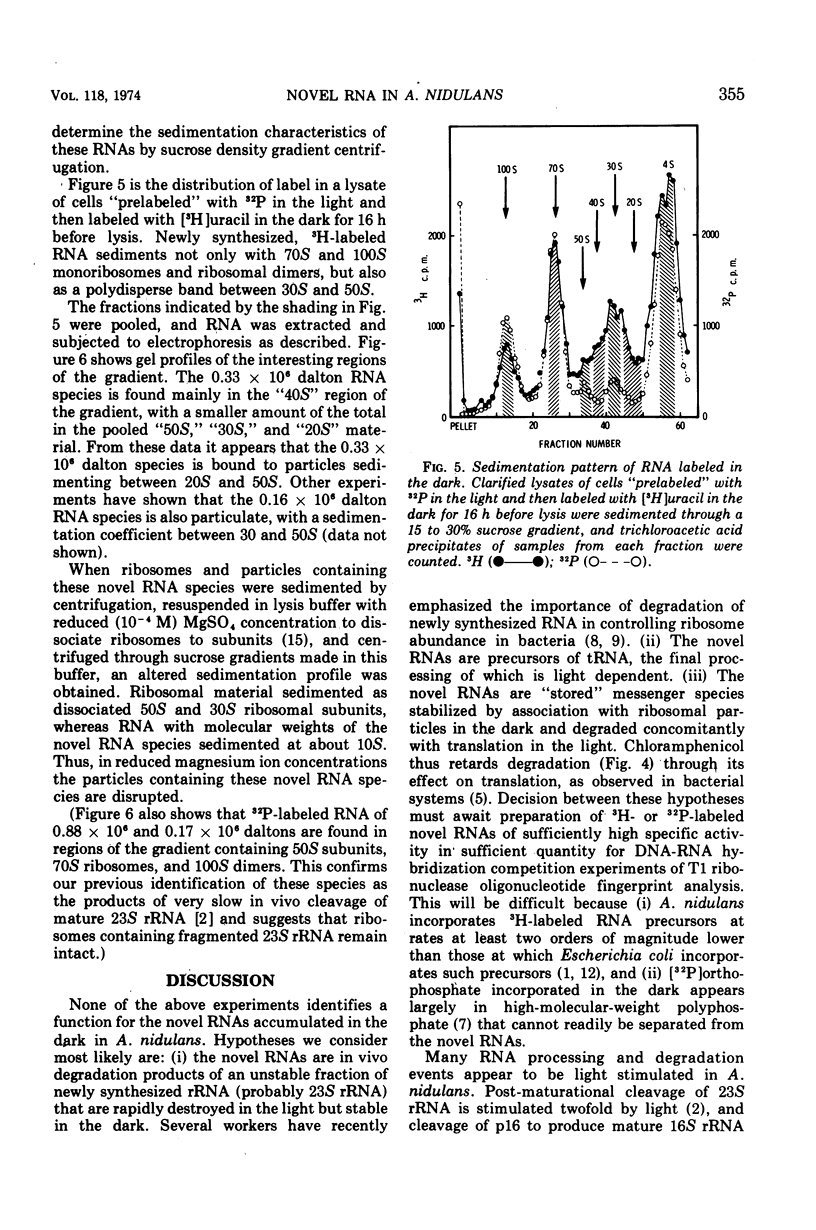
In the dark, the obligately photoautotrophic blue-green alga Anacystis nidulans accumulates large relative amounts of two novel stable ribonucleic acid species (RNAs). These species are also made in illuminated cells but are unstable in them. When darkened cells are reilluminated, these RNAs are rapidly degraded; degradation is inhibited by chloramphenicol. Upon denaturation with heat or urea, one novel species (0.33 × 106 daltons) dissociates into two fragments that comigrate with the second novel species (0.16 × 106 daltons) on polyacrylamide gels. Both RNAs are associated with particles sedimenting between 30S and 50S through sucrose gradients and are removed from these particles at low magnesium concentration. The function(s) of these RNAs remains unknown.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Doolittle W. F. Postmaturational cleavage of 23s ribosomal ribonucleic acid and its metabolic control in the blue-green alga Anacystis nidulans. J Bacteriol. 1973 Mar;113(3):1256–1263. doi: 10.1128/jb.113.3.1256-1263.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doolittle W. F. Ribosomal ribonucleic acid synthesis and maturation in the blue-green alga Anacystis nidulans. J Bacteriol. 1972 Aug;111(2):316–324. doi: 10.1128/jb.111.2.316-324.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loening U. E. Molecular weights of ribosomal RNA in relation to evolution. J Mol Biol. 1968 Dec;38(3):355–365. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90391-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niemeyer R., Richter G. Schnellmarkierte Polyphosphate und Metaphosphate bei der Glaualge Anacystis niculans. Arch Mikrobiol. 1969;69(1):54–59. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norris T. E., Koch A. L. Effect of growth rate on the relative rates of synthesis of messenger, ribosomal and transfer RNA in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1972 Mar 14;64(3):633–649. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90088-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pace B., Peterson R. L., Pace N. R. Formation of all stable RNA species in Escherichia coli by posttranscriptional modification. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Apr;65(4):1097–1104. doi: 10.1073/pnas.65.4.1097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pace N. R. Structure and synthesis of the ribosomal ribonucleic acid of prokaryotes. Bacteriol Rev. 1973 Dec;37(4):562–603. doi: 10.1128/br.37.4.562-603.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne P. I., Dyer T. A. Characterization of the ribosomal ribonucleic acids of blue-green algae. Arch Mikrobiol. 1972;87(1):29–40. doi: 10.1007/BF00424776. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pigott G. H., Carr N. G. The assimilation of nucleic acid precursors by intact cells and protoplasts of the blue-green alga anacystis nidulans. Arch Mikrobiol. 1971;79(1):1–6. doi: 10.1007/BF00412035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seitz U., Seitz U. Biosynthese der ribosomalen RNS bei der blaugrünen Alge Anacystis nidulans. Arch Mikrobiol. 1973;90(3):213–222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szalay A., Munsche D., Wolligiehn R., Parthier B. Ribosomal ribonucleic acid and ribosomal precursor ribonucleic acid in Anacystis nidulans. Biochem J. 1972 Aug;129(1):135–140. doi: 10.1042/bj1290135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



