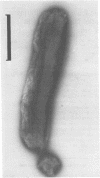
Abstract
Analysis of nucleated cell size in a minicell-producing strain of Escherichia coli and in its parental strain shows that the two distributions are considerably different. A model is proposed to account for this difference. The model states that: (i) in the mutant population, the cell poles are available as potential division sites in addition to the normally located division sites; (ii) the probability of a division occurring at any of the potential division sites is equal; and (iii) only enough “division factor” arises at each unit cell doubling to permit a single division. This factor is utilized entirely in the formation of a single septum. Thus, the occurrence of a polar division with the production of an anucleate minicell (which occurs only in the mutant strain) prevents the occurrence of a non-polar division, with the result that the average nucleated cell length is increased in minicell-producing strains. The model has been used to construct a theoretical population, and a number of parameters of the real and theoretical populations have been compared. The two populations are very similar in all of the parameters measured.
Full text
PDF
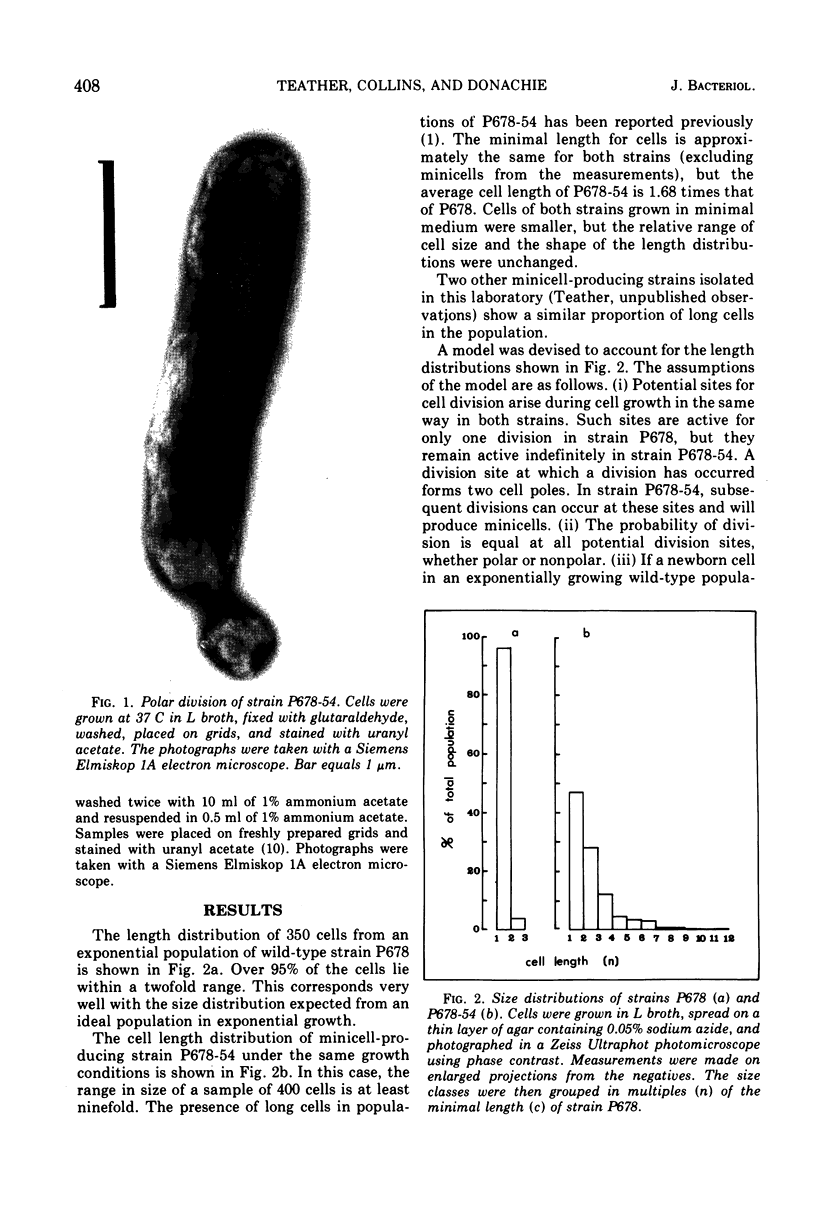
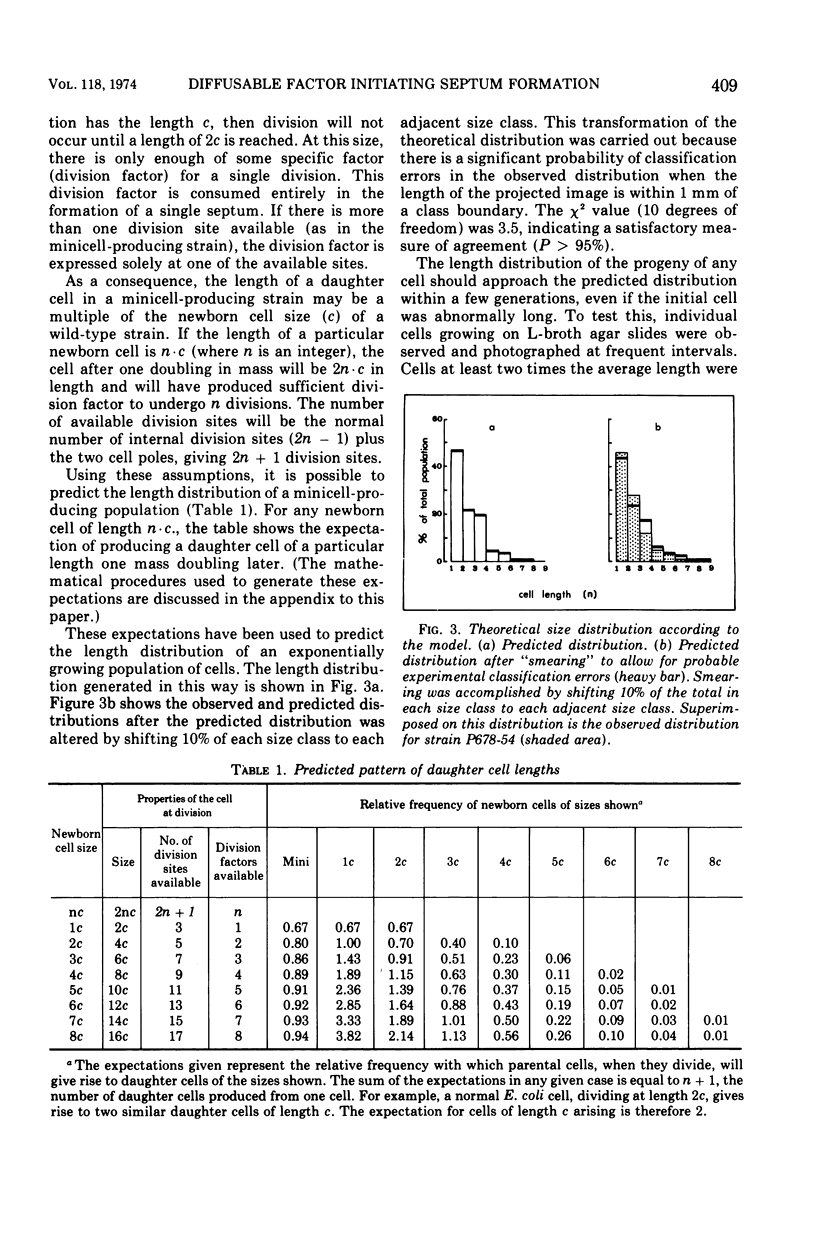
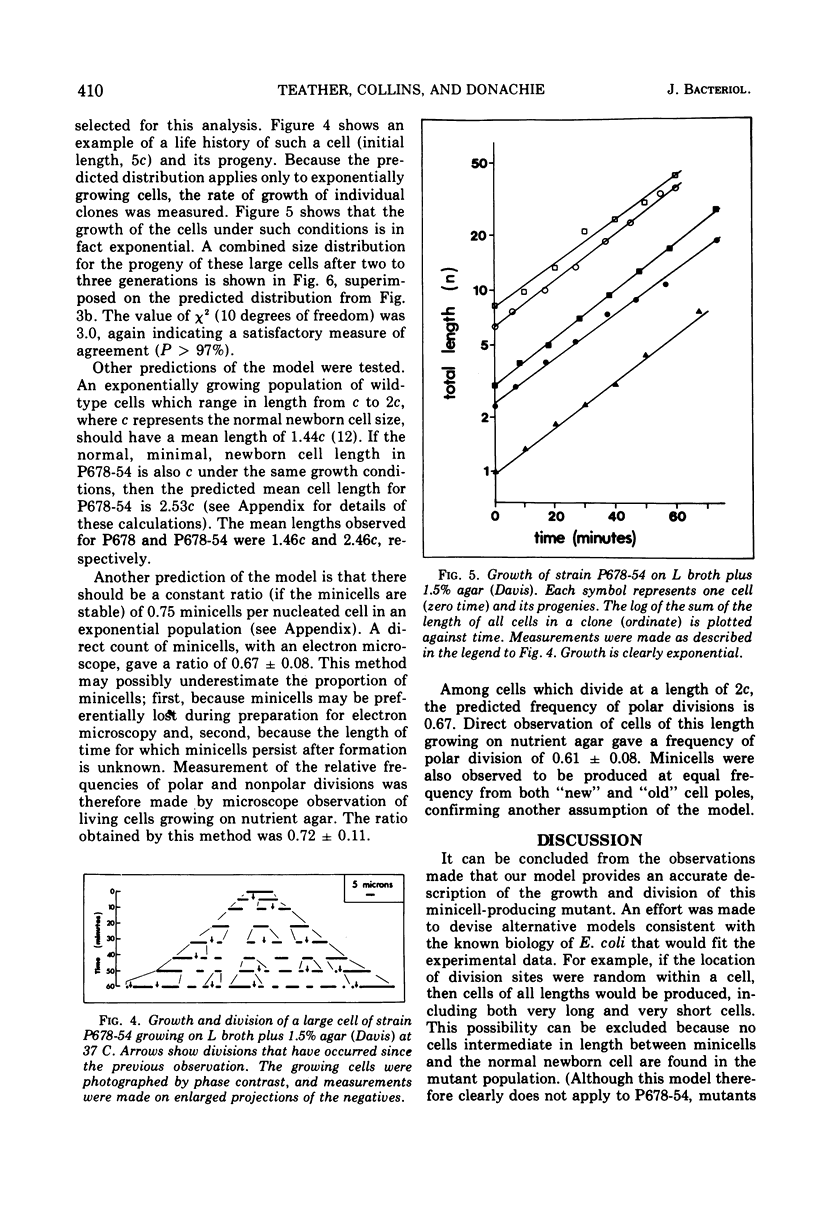


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adler H. I., Fisher W. D., Cohen A., Hardigree A. A. MINIATURE escherichia coli CELLS DEFICIENT IN DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Feb;57(2):321–326. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.2.321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COLLINS J. F., RICHMOND M. H. Rate of growth of Bacillus cereus between divisions. J Gen Microbiol. 1962 Apr;28:15–33. doi: 10.1099/00221287-28-1-15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark D. J. The regulation of DNA replication and cell division in E. coli B-r. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1968;33:823–838. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1968.033.01.094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donachie W. D., Begg K. J. Growth of the bacterial cell. Nature. 1970 Sep 19;227(5264):1220–1224. doi: 10.1038/2271220a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donachie W. D. Control of cell division in Escherichia coli: experiments with thymine starvation. J Bacteriol. 1969 Oct;100(1):260–268. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.1.260-268.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones N. C., Donachie W. D. Chromosome replication, transcription and control of cell division in Escherichia coli. Nat New Biol. 1973 May 23;243(125):100–103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POWELL E. O. Growth rate and generation time of bacteria, with special reference to continuous culture. J Gen Microbiol. 1956 Dec;15(3):492–511. doi: 10.1099/00221287-15-3-492. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierucci O., Helmstetter C. E. Chromosome replication, protein synthesis and cell division in Escherichia coli. Fed Proc. 1969 Nov-Dec;28(6):1755–1760. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryter A., Hirota Y., Jacob F. DNA-membrane complex and nuclear segregation in bacteria. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1968;33:669–676. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1968.033.01.076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]