Abstract
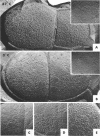
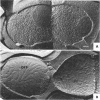
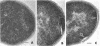
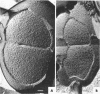
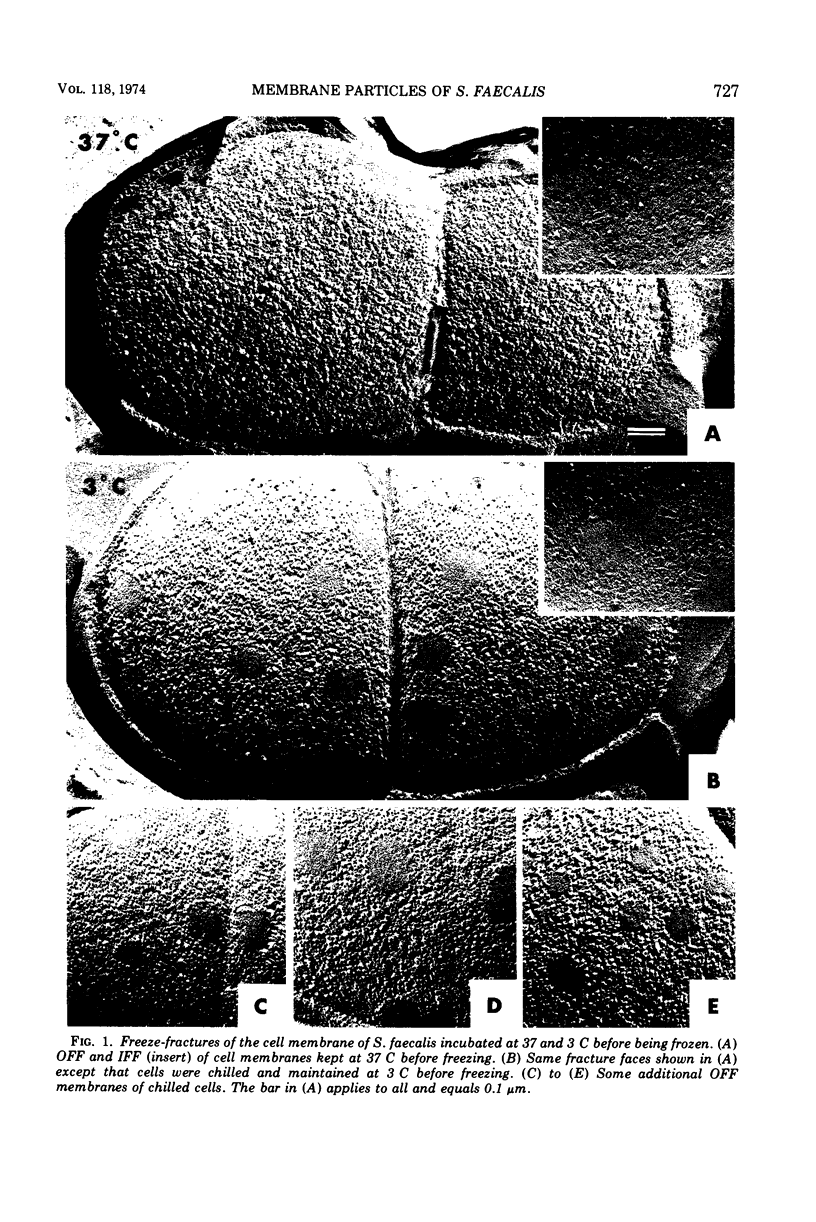
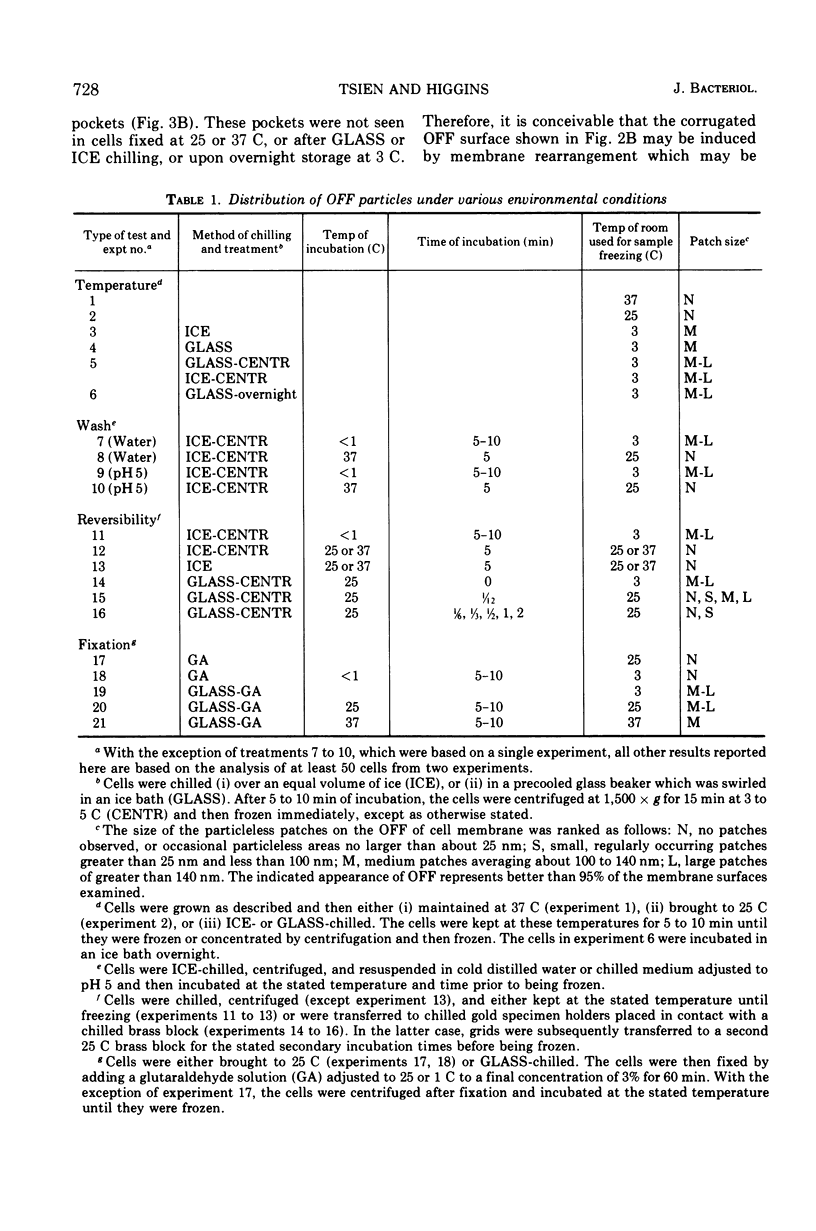
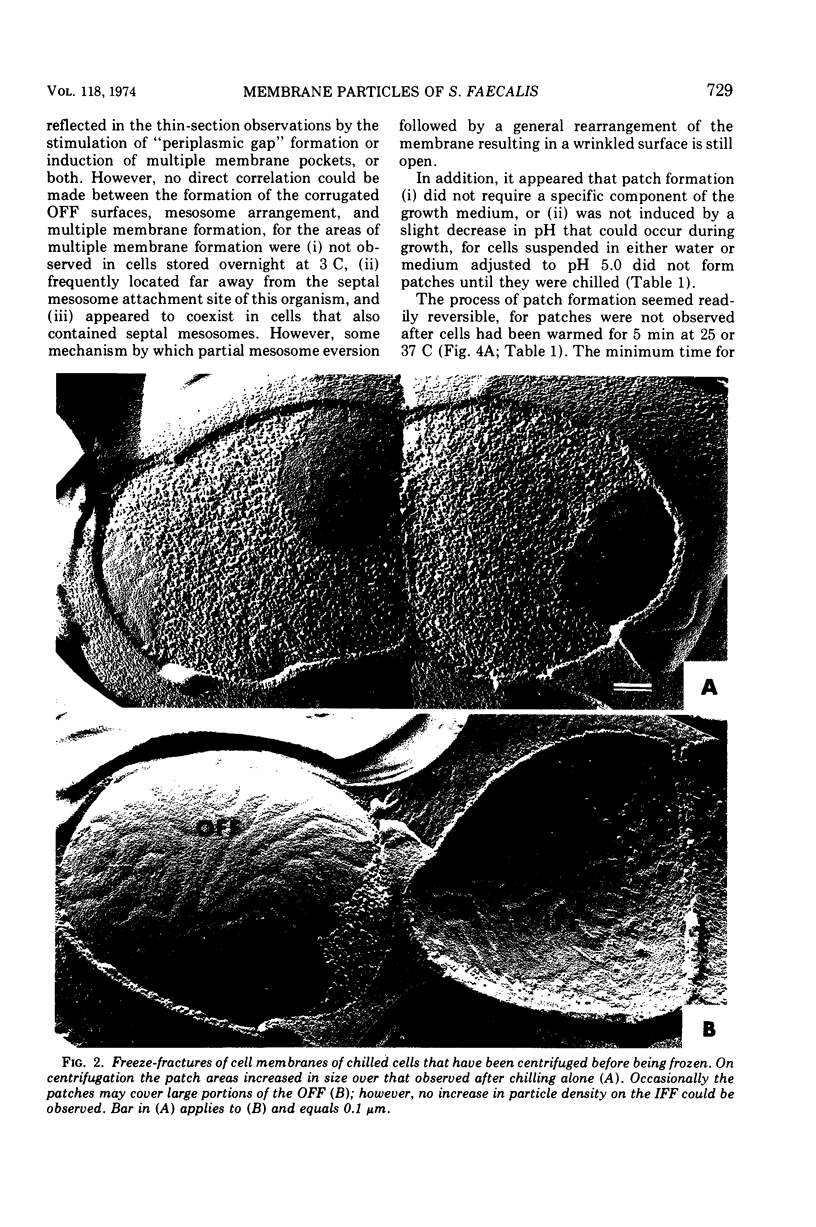
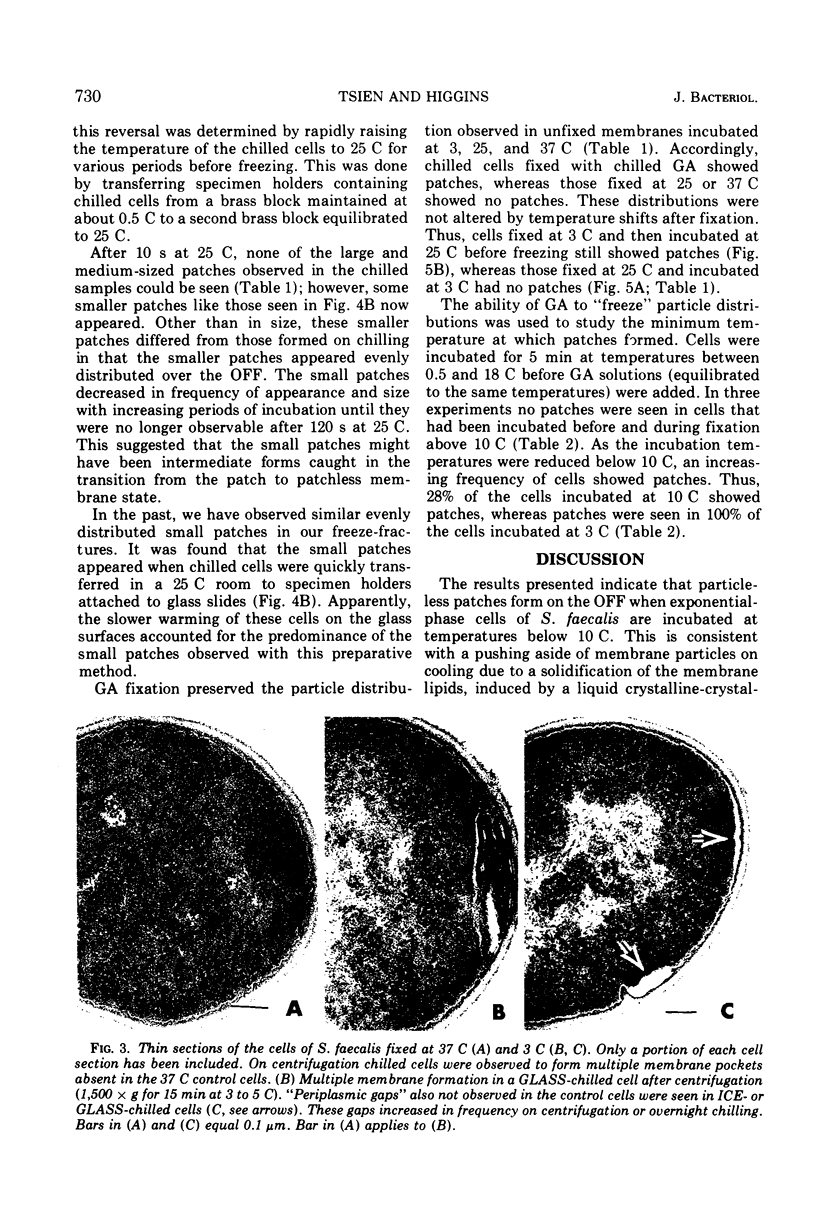
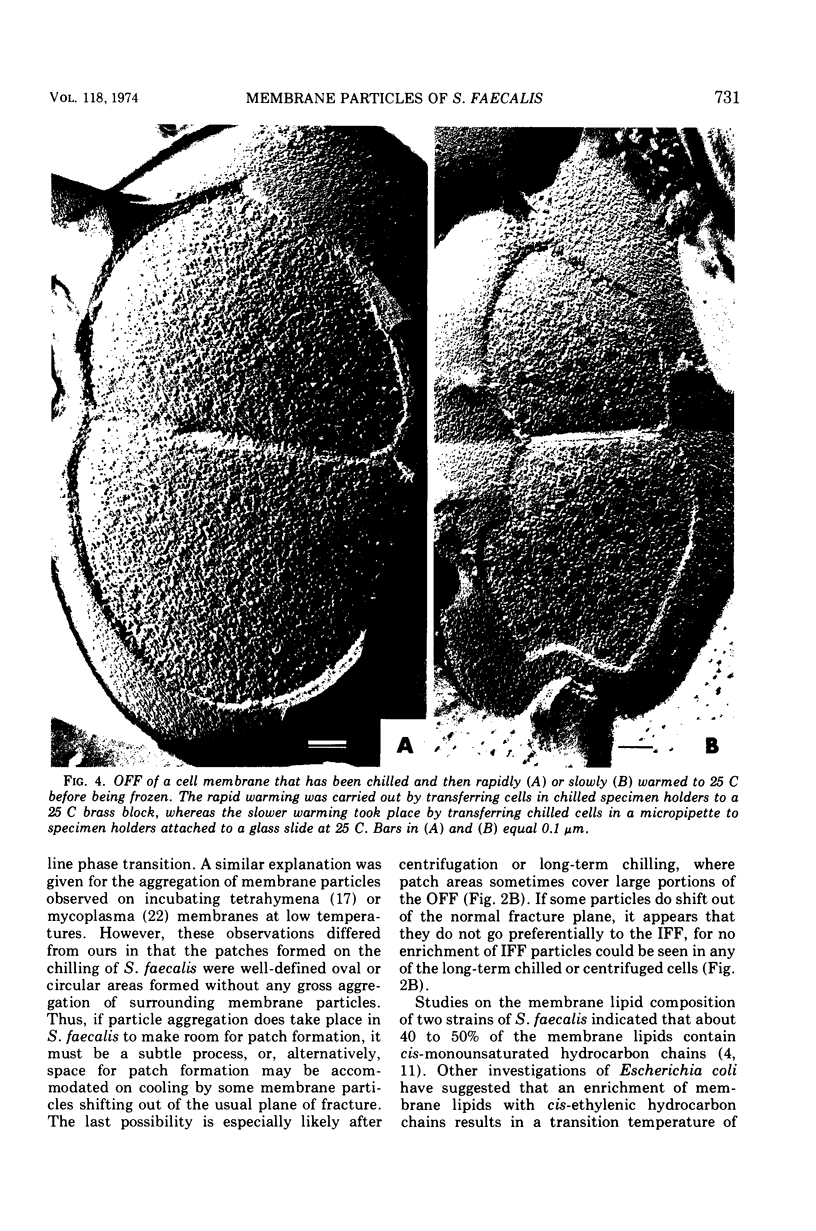
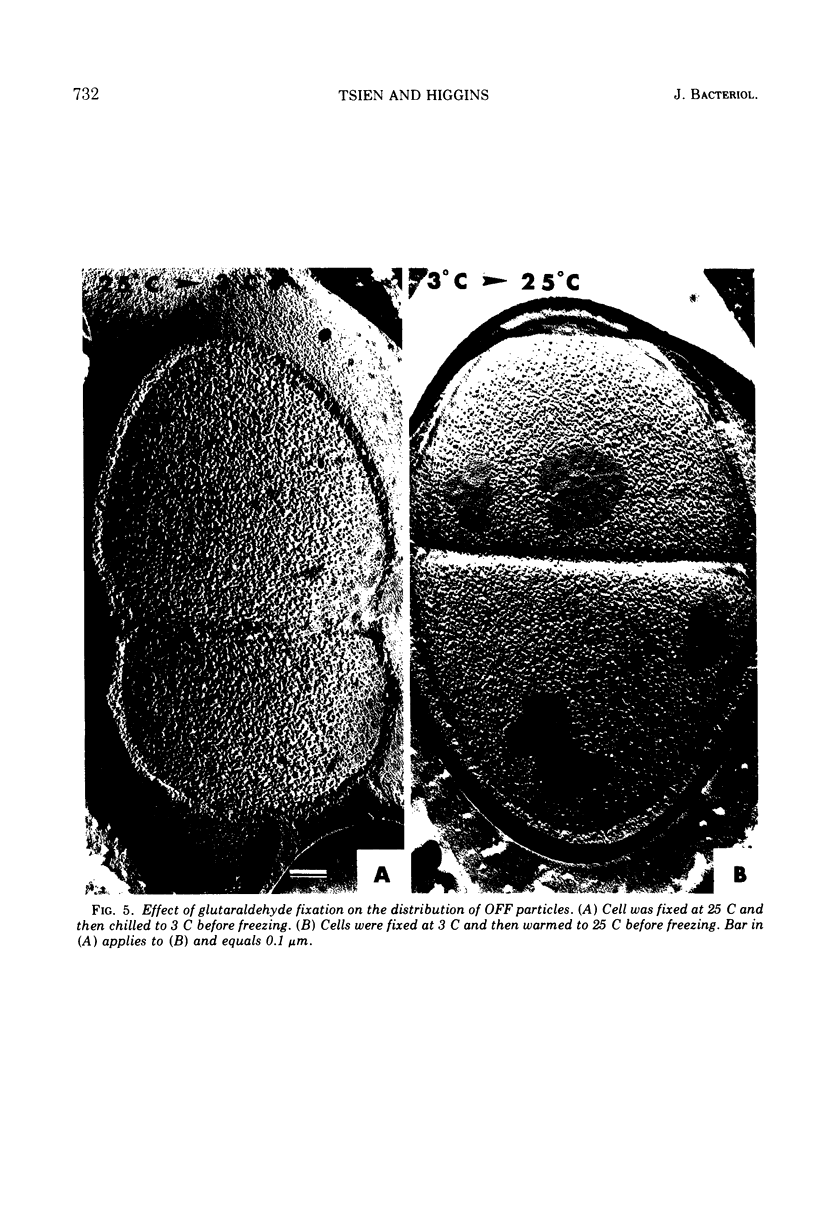
When cells of Streptococcus faecalis ATCC 9790 were incubated at temperatures above 10 C before being frozen for freeze-fracture, a random distribution of particles was observed on the outer fracture face of the freeze-cleaved cell membrane. However, when cells were incubated below 10 C before freezing, particleless patches were seen on this membrane surface. The size of the patches produced on chilling could be increased by centrifugation or by storing the chilled cells overnight at about 3 C. Patch formation appeared readily reversible, since the medium and large patches that formed on chilling could not be observed in cells warmed for 10 s at 25 C. However, during the transition from the patch to patchless state, smaller patches not seen in the chilled cells were observed. This suggested that the smaller patches might have been intermediate forms produced by the fragmentation of larger patches on warming.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bayer M. E., Remsen C. C. Structure of Escherichia coli after freeze-etching. J Bacteriol. 1970 Jan;101(1):304–313. doi: 10.1128/jb.101.1.304-313.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esfahani M., Limbrick A. R., Knutton S., Oka T., Wakil S. J. The molecular organization of lipids in the membrane of Escherichia coli: phase transitions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Dec;68(12):3180–3184. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.12.3180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiil A., Branton D. Changes in the plasma membrane of Escherichia coli during magnesium starvation. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jun;98(3):1320–1327. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.3.1320-1327.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt S. C., Leadbetter E. R. Comparative ultrastructure of selected aerobic spore-forming bacteria: a freeze-etching study. Bacteriol Rev. 1969 Jun;33(2):346–378. doi: 10.1128/br.33.2.346-378.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nanninga N. Structural features of mesosomes (chondrioids) of Bacillu subtilis after freeze-etching. J Cell Biol. 1968 Nov;39(2):251–263. doi: 10.1083/jcb.39.2.251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overath P., Träuble H. Phase transitions in cells, membranes, and lipids of Escherichia coli. Detection by fluorescent probes, light scattering, and dilatometry. Biochemistry. 1973 Jul 3;12(14):2625–2634. doi: 10.1021/bi00738a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pieringer R. A., Ambron R. T. A method for the specific labeling of the glycerol in glyceride-containing lipids of Streptococcus faecalis ATCC 9790. J Lipid Res. 1973 May;14(3):370–372. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinto da Silva P., Branton D. Membrane intercalated particles: the plasma membrane as a planar fluid domain. Chem Phys Lipids. 1972 May;8(4):265–278. doi: 10.1016/0009-3084(72)90054-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinto da Silva P., Branton D. Membrane splitting in freeze-ethching. Covalently bound ferritin as a membrane marker. J Cell Biol. 1970 Jun;45(3):598–605. doi: 10.1083/jcb.45.3.598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinto da Silva P. Translational mobility of the membrane intercalated particles of human erythrocyte ghosts. pH-dependent, reversible aggregation. J Cell Biol. 1972 Jun;53(3):777–787. doi: 10.1083/jcb.53.3.777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remsen C., Lundgren D. G. Electron microscopy of the cell envelope of Ferrobacillus ferrooxidans prepared by freeze-etching and chemical fixation techniques. J Bacteriol. 1966 Dec;92(6):1765–1771. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.6.1765-1771.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speth V., Wunderlich F. Membranes of Tetrahymena. II. Direct visualization of reversible transitions in biomembrane structure induced by temperature. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Feb 16;291(3):621–628. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90467-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tillack T. W., Marchesi V. T. Demonstration of the outer surface of freeze-etched red blood cell membranes. J Cell Biol. 1970 Jun;45(3):649–653. doi: 10.1083/jcb.45.3.649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tourtellotte M. E., Zupnik J. S. Freeze-fractured Acholeplasma laidlawii membranes: nature of particles observed. Science. 1973 Jan 5;179(4068):84–86. doi: 10.1126/science.179.4068.84. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Träuble H. Phase transitions in lipids. Biomembranes. 1972;3:197–227. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-0961-1_14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukagoshi N., Fox C. F. Transport system assembly and the mobility of membrane lipids in Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1973 Jul 17;12(15):2822–2829. doi: 10.1021/bi00739a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verkleij A. J., Ververgaert P. H., van Deenen L. L., Elbers P. F. Phase transitions of phospholipid bilayers and membranes of Acholeplasma laidlawii B visualized by freeze fracturing electron microscopy. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Nov 2;288(2):326–332. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90253-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]