Abstract
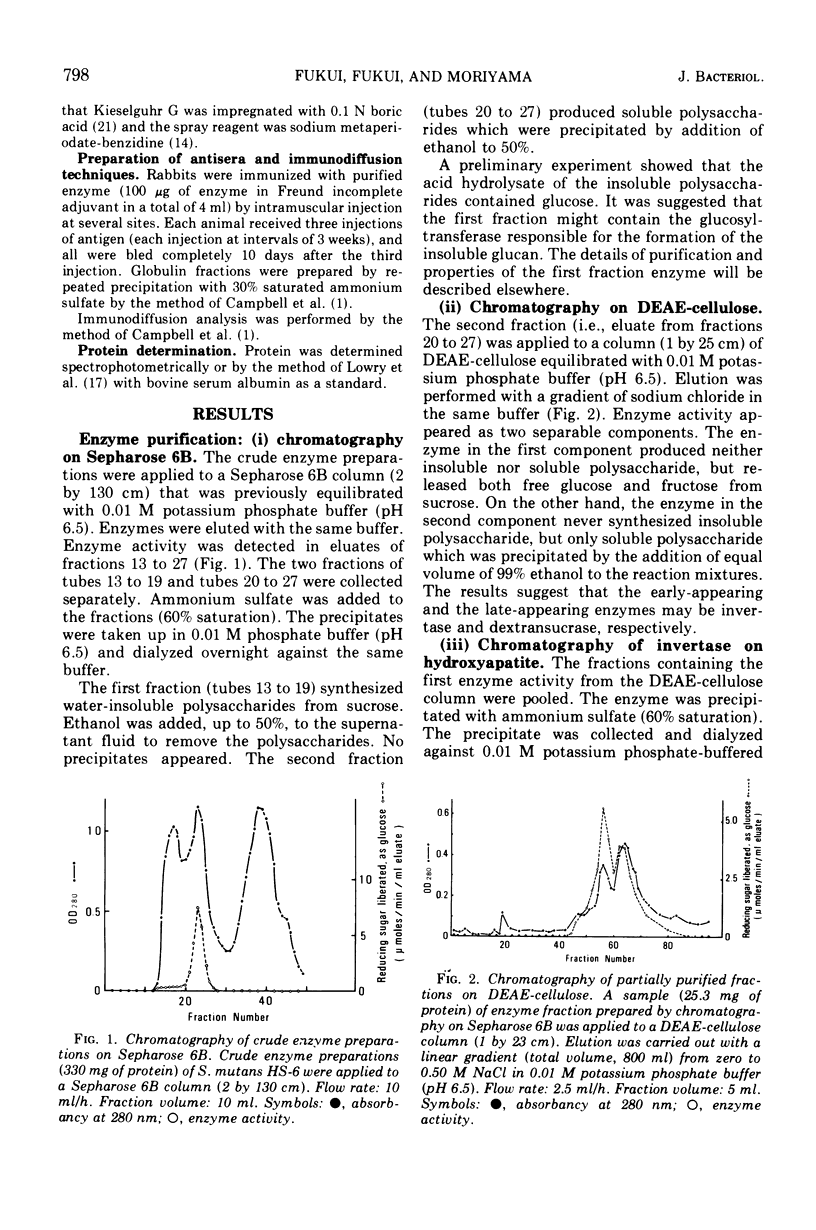
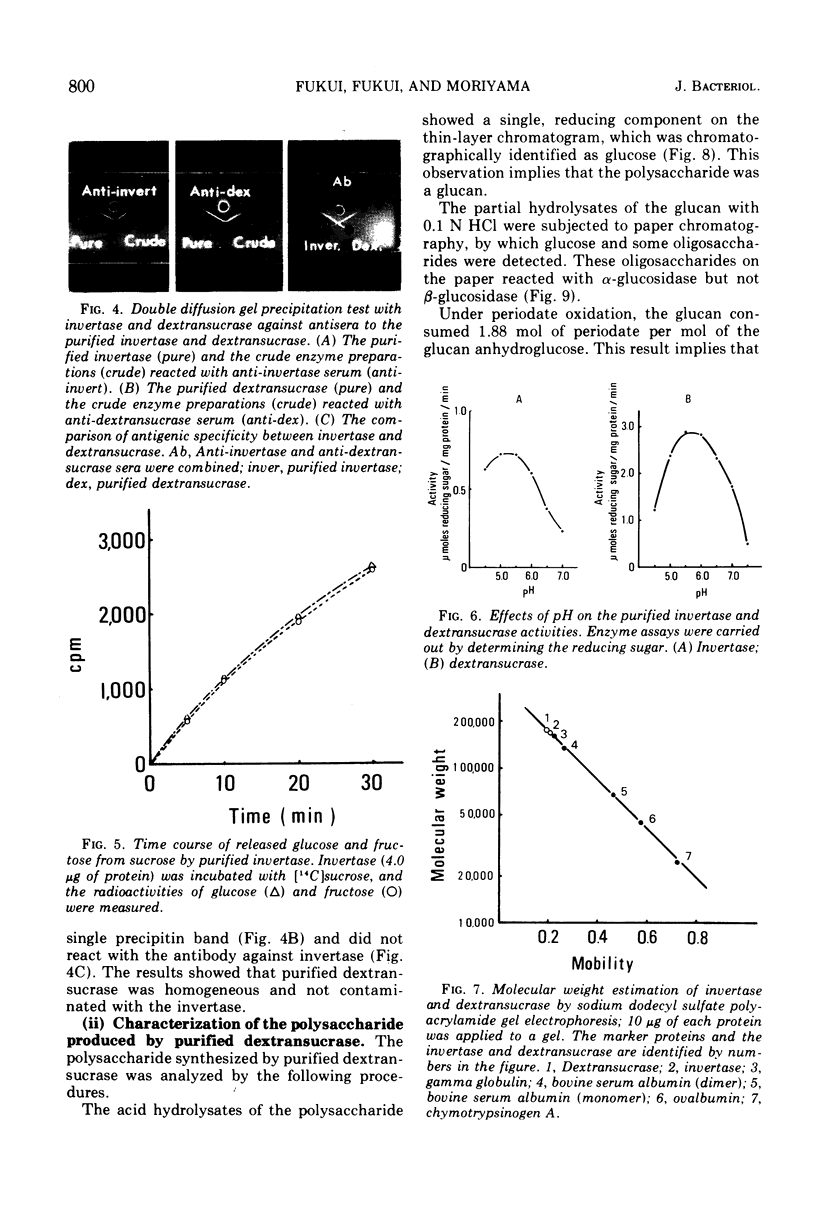
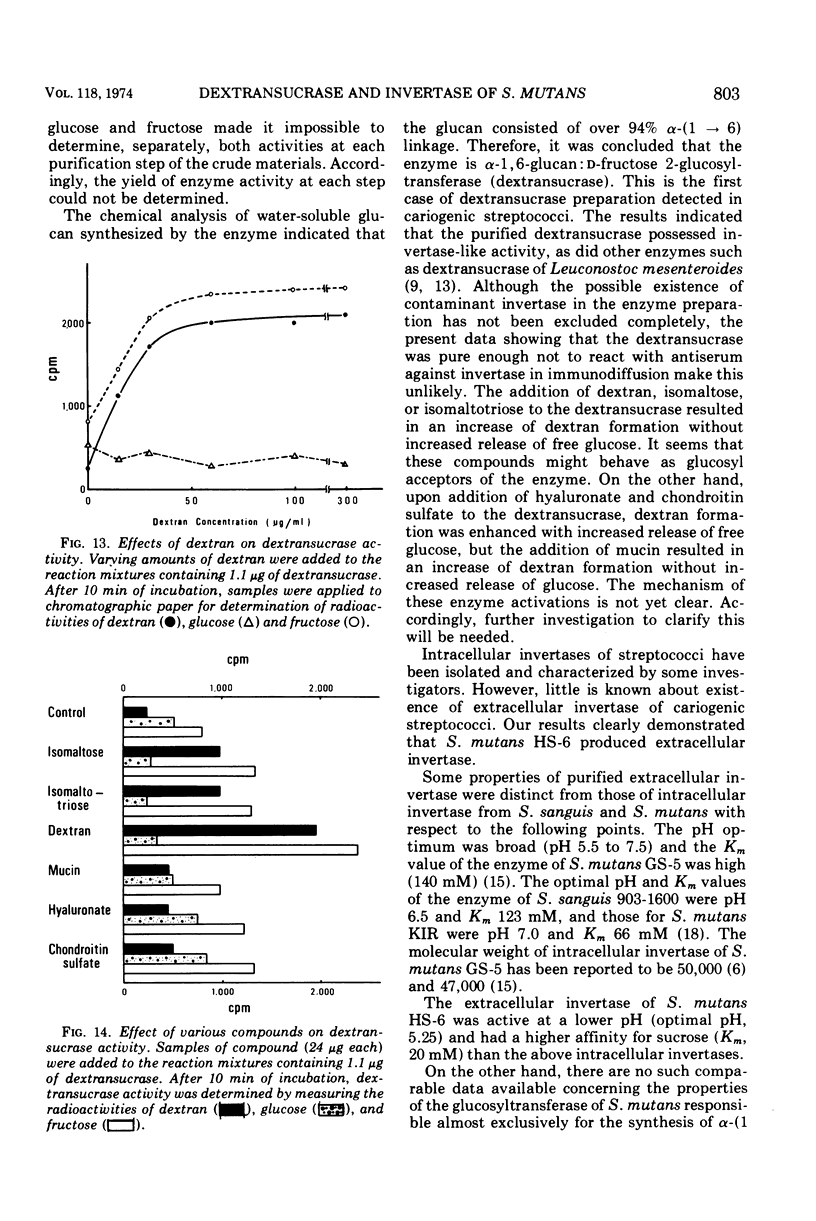
Invertase (β-d-fructofuranoside fructohydrolase, EC 3.2.1.26) and dextransucrase (α-1, 6-glucan: d-fructose 2-glucosyltransferase, EC 2.4.1.5) were purified from the culture fluids of Streptococcus mutans by chromatography on Sepharose 6B and diethylaminoethyl-cellulose followed by treatment with hydroxyapatite. Each of the enzyme preparations gave a single band when analyzed by either polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis or immunodiffusion. The antigenic determinant of invertase was different from that of dextransucrase on immunodiffusion. The pH optima were 5.25 for invertase and 5.75 for dextransucrase, and the Km values were 20 mM for invertase and 2.0 mM for dextransucrase. The molecular weights determined by sodium dodecyl sulfate gel electrophoresis were 160,000 for invertase and 170,000 for dextransucrase. The data obtained suggest that the dextransucrase had dextran-synthesizing activity and invertase-like activity.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Carlsson J., Newbrun E., Krasse B. Purification and properties of dextransucrase from Streptococcus sanguis. Arch Oral Biol. 1969 May;14(5):469–478. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(69)90140-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FITZGERALD R. J., KEYES P. H. Demonstration of the etiologic role of streptococci in experimental caries in the hamster. J Am Dent Assoc. 1960 Jul;61:9–19. doi: 10.14219/jada.archive.1960.0138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOODMAN A., WEIL R. M., STERN K. G. On the mechanism of dextran formation; chromatographic studies with C14-labeled sugars. J Biol Chem. 1955 Dec;217(2):977–985. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. J., Banghart S. B. Synthesis of extracellular dextran by cariogenic bacteria and its presence in human dental plaque. Arch Oral Biol. 1967 Jan;12(1):11–23. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(67)90137-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. J., Nygaard M. Synthesis of insoluble dextran and its significance in the formation of gelatinous deposits by plaque-forming streptococci. Arch Oral Biol. 1968 Oct;13(10):1249–1262. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(68)90081-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. J. Presence of an invertase-like enzyme and a sucrose permeation system in strains of Streptococcus mutans. Caries Res. 1972;6(2):122–131. doi: 10.1159/000259784. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guggenheim B., König K. G., Herzog E., Mühlemann H. R. The cariogenicity of different dietary carbohydrates tested on rats in relative gnotobiosis with a Streptococcus producing extracellular polysaccharide. Helv Odontol Acta. 1966 Oct;10(2):101–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guggenheim B., Newbrun E. Extracellular glucosyltransferase activity of an HS strain of Streptococcus mutans. Helv Odontol Acta. 1969 Oct;13(2):84–97. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guggenheim B., Schroeder H. E. Biochemical and morphological aspects of extracellular polysaccharides produced by cariogenic streptococci. Helv Odontol Acta. 1967 Oct;11(2):131–152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HJERTEN S., LEVIN O., TISELIUS A. Protein chromatography on calcium phosphate columns. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1956 Nov;65(1):132–155. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(56)90183-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOEPSELL H. J., TSUCHIYA H. M., HELLMAN N. N., KAZENKO A., HOFFMAN C. A., SHARPE E. S., JACKSON R. W. Enzymatic synthesis of dextran; acceptor specificity and chain initiation. J Biol Chem. 1953 Feb;200(2):793–801. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuramitsu H. K. Characterization of invertase activity from cariogenic Streptococcus mutans. J Bacteriol. 1973 Sep;115(3):1003–1010. doi: 10.1128/jb.115.3.1003-1010.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MONTGOMERY R., WU Y. C., LEE Y. C. PERIODATE OXIDATION OF GLYCOPEPTIDES FROM OVALBUMIN. Biochemistry. 1965 Mar;4:578–587. doi: 10.1021/bi00879a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCabe M. M., Smith E. E., Cowman R. A. Invertase activity in Streptococcus mutans and Streptococcus sanguis. Arch Oral Biol. 1973 Apr;18(4):525–531. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(73)90073-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAZUR J. H., KLEPPE K. THE OXIDATION OF GLUCOSE AND RELATED COMPOUNDS BY GLUCOSE OXIDASE FROM ASPERGILLUS NIGER. Biochemistry. 1964 Apr;3:578–583. doi: 10.1021/bi00892a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]








