Abstract
Undecyl acetate esterase has been purified from Pseudomonas cepacia grown on the methyl ketone, 2-tridecanone. The Km for undecyl acetate was 2.3 × 10−2 M. Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis indicated that two esterase bands were being recovered during purification. These bands were separated by preparative polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Molecular weights were estimated to be approximately 34,500 by several methods. Molecular sieve polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis indicated that the two esterases had the same molecular weight but different charge, which is indicative of isoenzymes.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALDRIDGE W. N. Serum esterases. I. Two types of esterase (A and B) hydrolysing p-nitrophenyl acetate, propionate and butyrate, and a method for their determination. Biochem J. 1953 Jan;53(1):110–117. doi: 10.1042/bj0530110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baboolal R. A study of the enzyme patterns of some oral filamentous bacteria by starch gel electrophoresis. Arch Oral Biol. 1972 Apr;17(4):691–700. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(72)90195-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballard R. W., Palleroni N. J., Doudoroff M., Stanier R. Y., Mandel M. Taxonomy of the aerobic pseudomonads: Pseudomonas cepacia, P. marginata, P. alliicola and P. caryophylli. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Feb;60(2):199–214. doi: 10.1099/00221287-60-2-199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baptist J. N., Shaw C. R., Mandel M. Comparative zone electrophoresis of enzymes of Pseudomonas solanacearum and Pseudomonas cepacia. J Bacteriol. 1971 Nov;108(2):799–803. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.2.799-803.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dulaney J. T., Touster O. The solubilization and gel electrophoresis of membrane enzymes by use of detergents. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Jan 6;196(1):29–34. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(70)90162-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forney F. W., Markovetz A. J. An enzyme system for aliphatic methyl ketone oxidation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Sep 24;37(1):31–38. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90876-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forney F. W., Markovetz A. J., Kallio R. E. Bacterial oxidation of 2-tridecanone to 1-undecanol. J Bacteriol. 1967 Feb;93(2):649–655. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.2.649-655.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forney F. W., Markovetz A. J. Oxidative degradation of methyl ketones. II. Chemical pathway for degradation of 2-tridecanone by Pseudomonas multivorans and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1968 Oct;96(4):1055–1064. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.4.1055-1064.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forney F. W., Markovetz A. J. Subterminal oxidation of aliphatic hydrocarbons. J Bacteriol. 1970 Apr;102(1):281–282. doi: 10.1128/jb.102.1.281-282.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forney F. W., Markovetz A. J. The biology of methyl ketones. J Lipid Res. 1971 Jul;12(4):383–395. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke R. G., Berry J. A. Taxonomic application of isozyme patterns produced with disc electrophoresis of some myxomycetes, order Physarales. Mycologia. 1972 Jul-Aug;64(4):830–840. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREUELL E. H., SIERRA G. Studies on bacterial esterases. II. Paper-electrophoresis of the esterases of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1957;23(3-4):273–277. doi: 10.1007/BF02545879. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARTLEY B. S., KILBY B. A. The reaction of p-nitrophenyl esters with chymotrypsin and insulin. Biochem J. 1954 Feb;56(2):288–297. doi: 10.1042/bj0560288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardman M. J., Valenzuela P., Bender M. L. Acylation of - and -chymotrypsins by p-nitrophenyl acetate. Enzyme-substrate complex formation and pH dependence. J Biol Chem. 1971 Oct 10;246(19):5907–5913. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedrick J. L., Smith A. J. Size and charge isomer separation and estimation of molecular weights of proteins by disc gel electrophoresis. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1968 Jul;126(1):155–164. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(68)90569-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higerd T. B., Spizizen J. Isolation of two acetyl esterases from extracts of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1973 Jun;114(3):1184–1192. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.3.1184-1192.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOVIN T., CHRAMBACH A., NAUGHTON M. A. AN APPARATUS FOR PREPARATIVE TEMPERATURE-REGULATED POLYACRYLAMIDE GEL ELECTROPHORESIS. Anal Biochem. 1964 Nov;9:351–369. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(64)90192-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaneko A., Dempo K., Onoé T. Heterogeneity of esterases and cell types in rat liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Sep 19;284(1):128–135. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(72)90052-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingsbury N., Masters C. J. Heterogeneity, molecular weight interrelationships and developmental genetics of the esterase isoenzymes of the rainbow trout. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Feb 28;258(2):455–465. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(72)90237-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanz W. W., Williams P. P. Characterization of esterases produced by a ruminal bacterium identified as Butyrivibrio fibrisolvens. J Bacteriol. 1973 Mar;113(3):1170–1176. doi: 10.1128/jb.113.3.1170-1176.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li C. Y., Lam K. W., Yam L. T. Esterases in human leukocytes. J Histochem Cytochem. 1973 Jan;21(1):1–12. doi: 10.1177/21.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund B. M. A comparison by the use of gel electrophoresis of soluble protein components and esterase enzymes of some group D Streptococci. J Gen Microbiol. 1965 Sep;40(3):413–419. doi: 10.1099/00221287-40-3-413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer J. A., Renard J. L. Protein and esterase patterns of two formae speciales of Fusarium oxysporum. Phytopathology. 1969 Oct;59(10):1409–1411. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norgaard M. J., Montgomery M. W. Some esterases of the pea (Pisum sativum L.). Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Mar 25;151(3):587–596. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(68)90005-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHACHMAN H. K. THE ULTRACENTRIFUGE: PROBLEMS AND PROSPECTS. Biochemistry. 1963 Sep-Oct;2:887–905. doi: 10.1021/bi00905a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
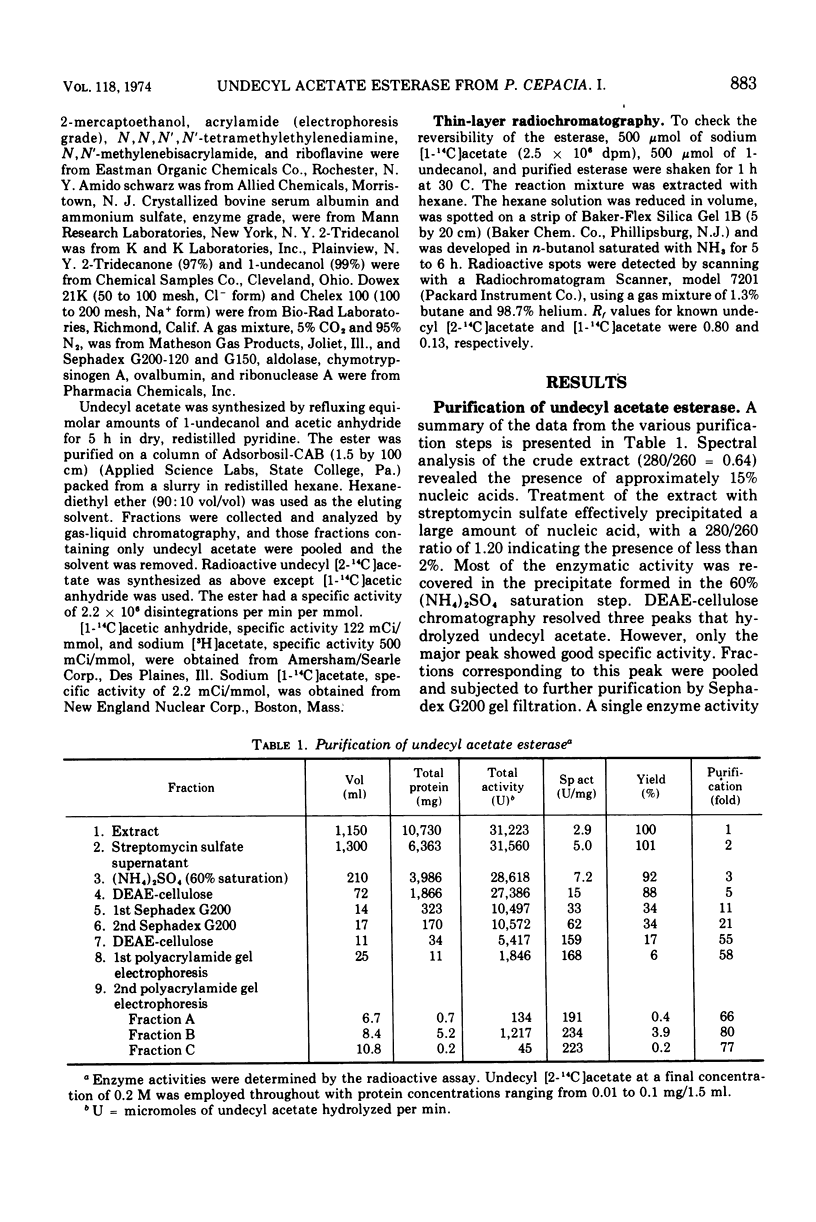
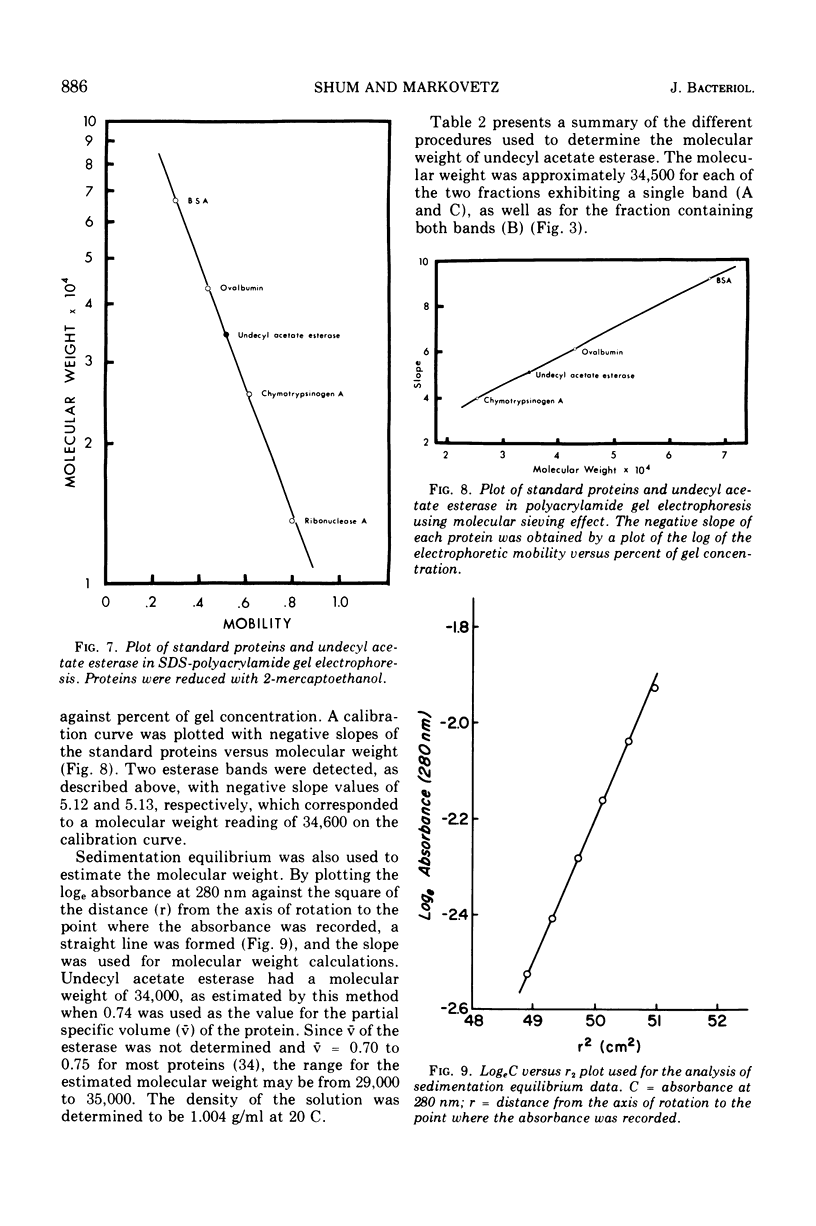
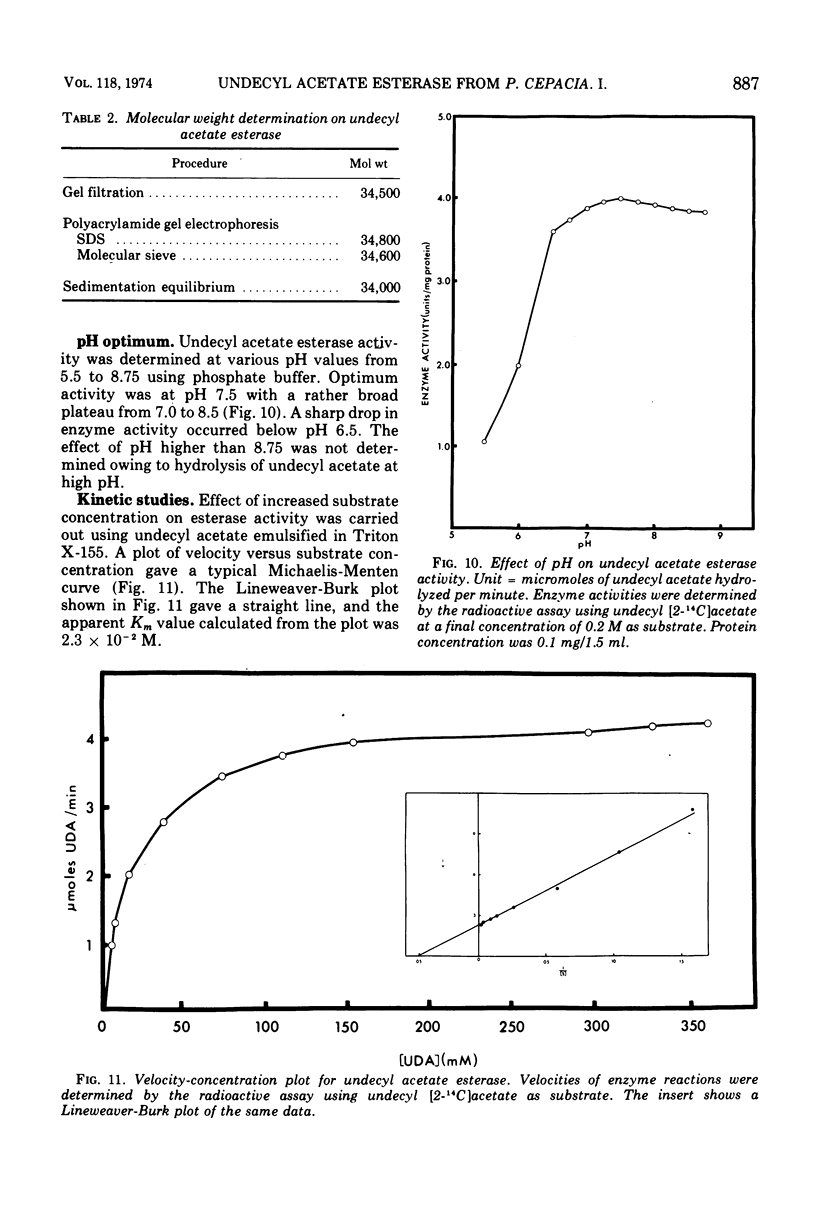
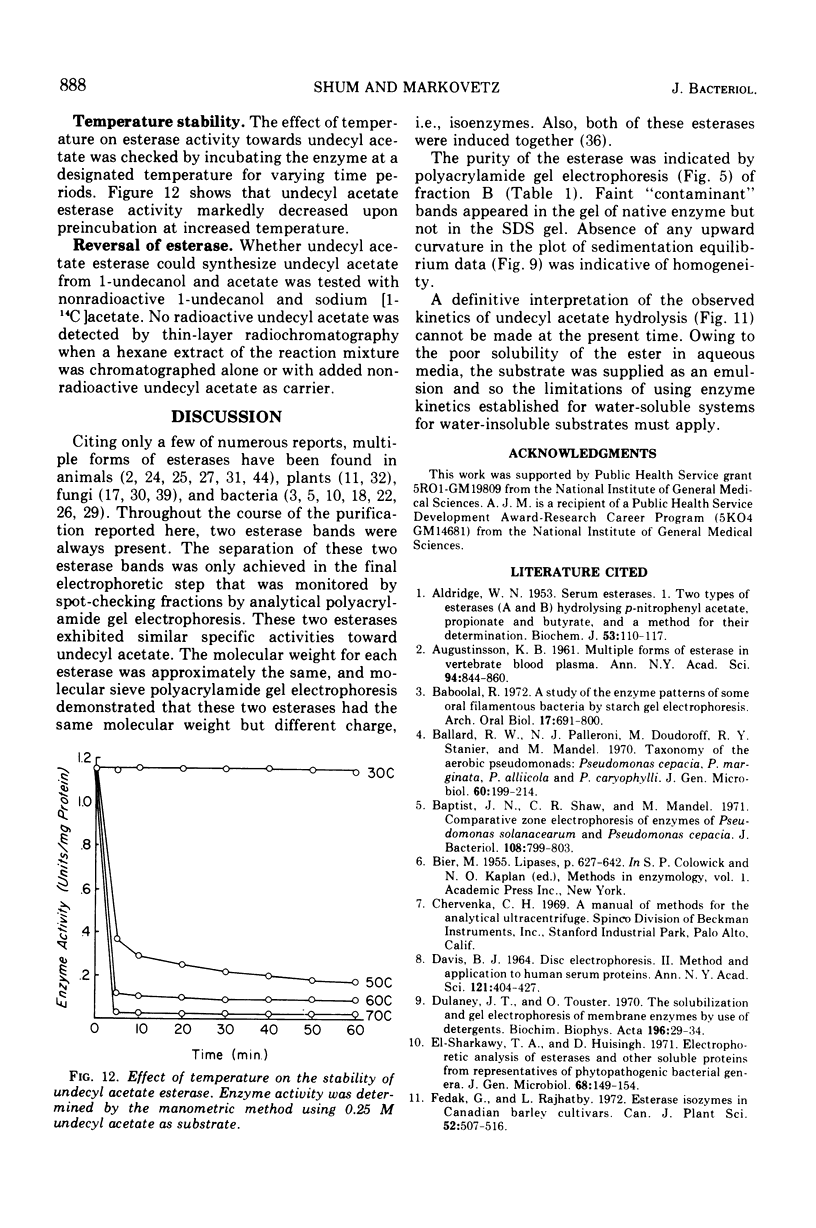
- Shum A. C., Markovetz A. J. Specificity and induction of undecyl acetate esterase from Pseudomonas cepacia grown on 2-tridecanone. J Bacteriol. 1974 Jun;118(3):890–897. doi: 10.1128/jb.118.3.890-897.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanier R. Y., Palleroni N. J., Doudoroff M. The aerobic pseudomonads: a taxonomic study. J Gen Microbiol. 1966 May;43(2):159–271. doi: 10.1099/00221287-43-2-159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner H., Lindskog S. Effects of high concentrations of salt on the esterase activity of human carbonic anhydrase. FEBS Lett. 1972 Jul 15;24(1):85–88. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80832-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
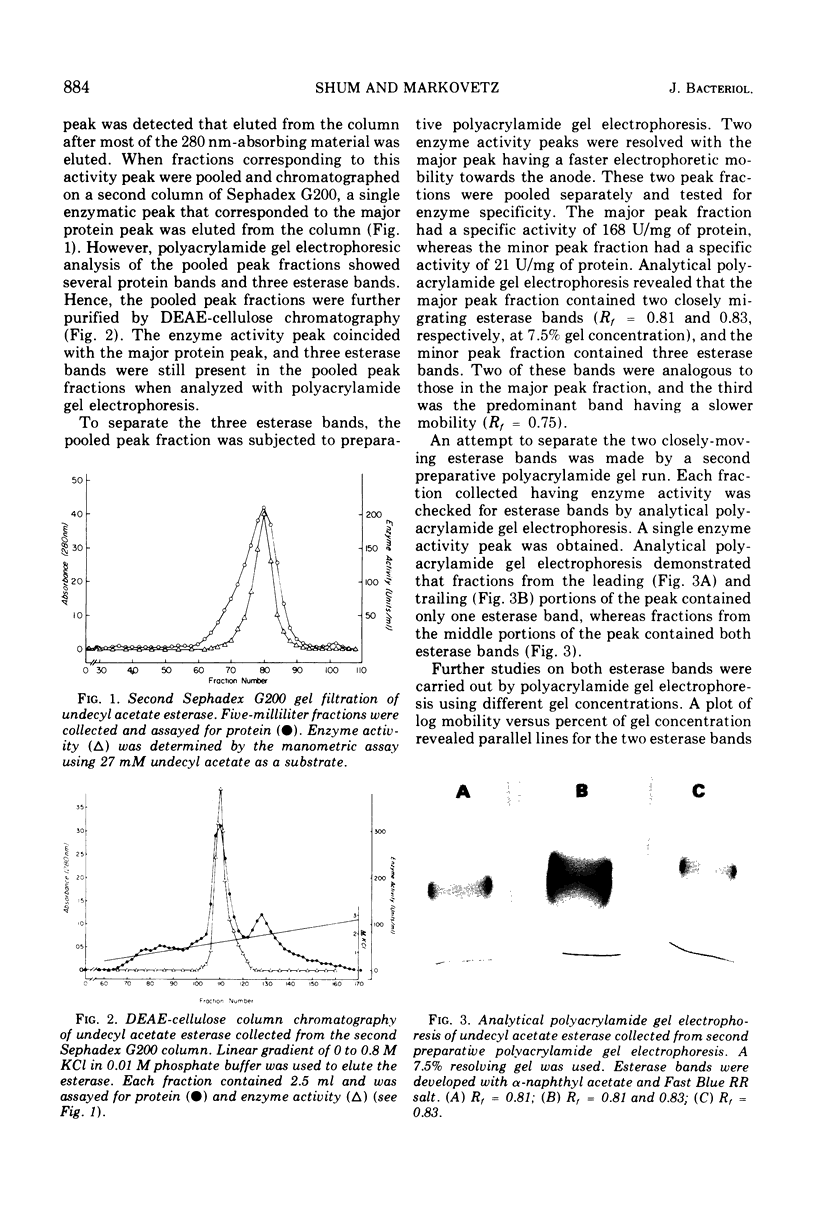
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]