Abstract
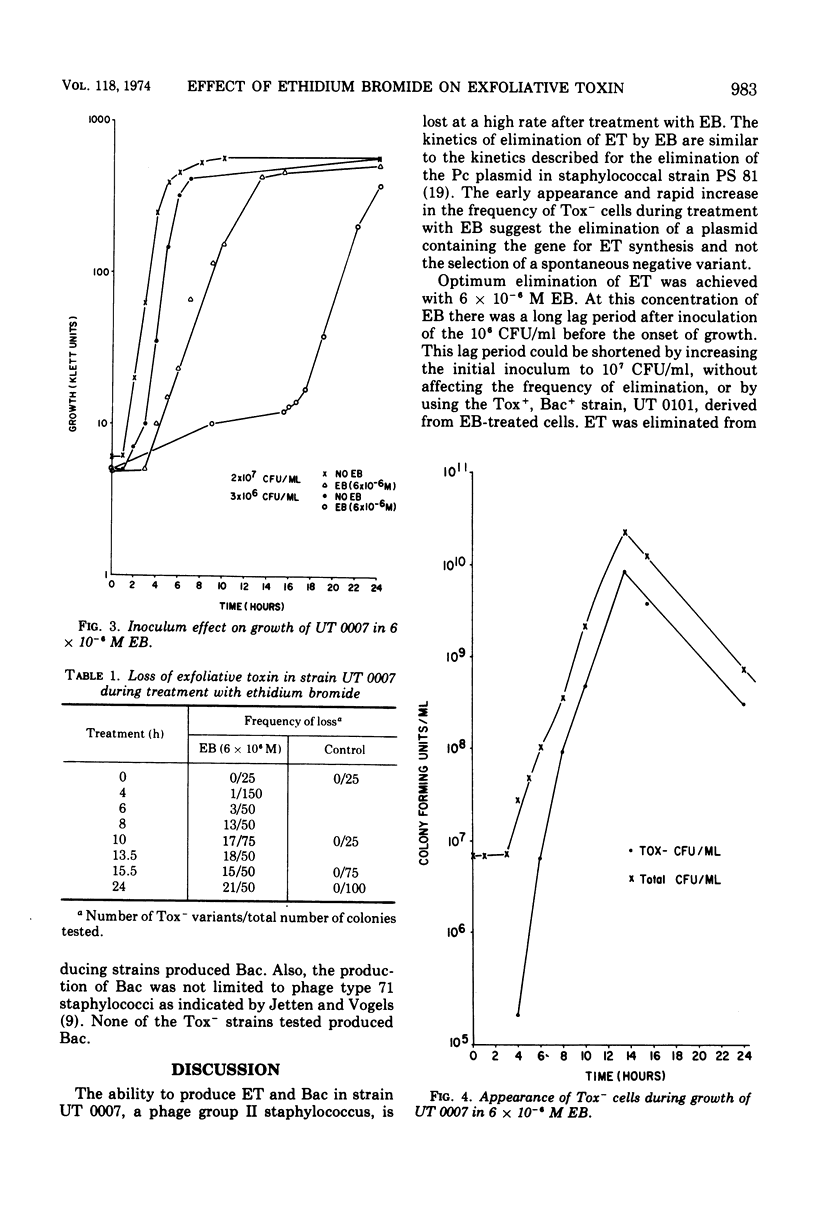
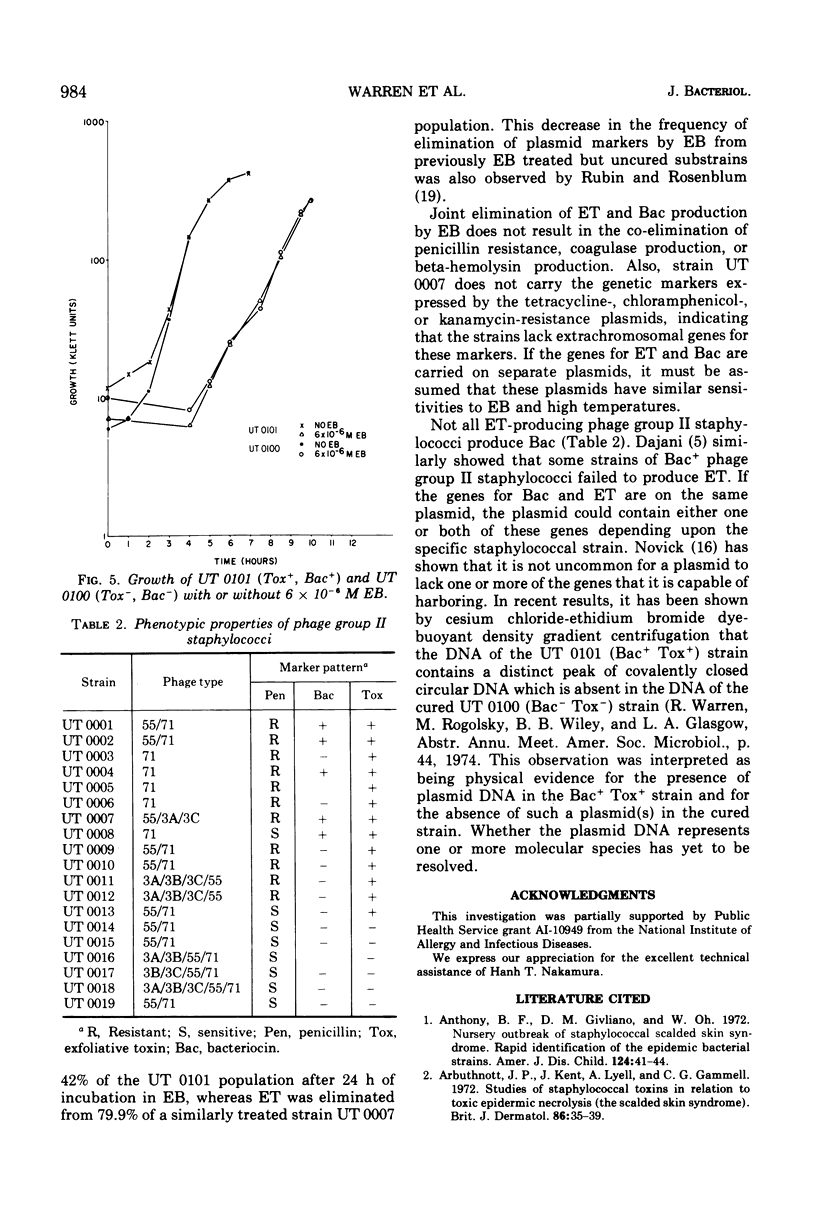
The scalded skin syndrome has been associated with phage group II staphylococci. The clinical manifestations of scalded skin syndrome, Ritter's disease, scarlatiniform erythema, and localized bullous impetigo, are due to the production of an extracellular protein, designated exfoliative toxin. Phage group II staphylococci can also produce an extracellular protein, bacteriocin, which is bacteriocidal for specific gram-positive microorganisms. Strain UT 0007 produces both bacteriocin and exfoliative toxin which appear to be products of extrachromosomal genes. These genes are jointly eliminated from strain UT 0007 after growth in either ethidium bromide or at high temperatures.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anthony B. F., Giuliano D. M., Oh W. Nursery outbreak of staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome. Rapid identification of the epidemic bacterial strain. Am J Dis Child. 1972 Jul;124(1):41–44. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1972.02110130043006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BAUER A. W., PERRY D. M., KIRBY W. M. Single-disk antibiotic-sensitivity testing of staphylococci; an analysis of technique and results. AMA Arch Intern Med. 1959 Aug;104(2):208–216. doi: 10.1001/archinte.1959.00270080034004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouanchaud D. H., Scavizzi M. R., Chabbert Y. A. Elimination by ethidium bromide of antibiotic resistance in enterobacteria and staphylococci. J Gen Microbiol. 1968 Dec;54(3):417–425. doi: 10.1099/00221287-54-3-417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dajani A. S., Gray E. D., Wannamaker L. W. Bactericidal substance from Staphylococcus aureus. Biological properties. J Exp Med. 1970 May 1;131(5):1004–1015. doi: 10.1084/jem.131.5.1004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dajani A. S., Gray E. D., Wannamaker L. W. Effect of Bactericidal Substance from Staphylococcus aureus on Group A Streptococci I. Biochemical Alterations. Infect Immun. 1970 May;1(5):485–490. doi: 10.1128/iai.1.5.485-490.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dajani A. S. The scalded-skin syndrome: relation to phage-group II staphylococci. J Infect Dis. 1972 May;125(5):548–551. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.5.548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friend P. L., Slade M. D. Characteristics of group A streptococcal bacteriophages. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jul;92(1):148–154. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.1.148-154.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jetten A. M., Vogels G. D. Characterization and extrachromosomal control of bacteriocin production in Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Jul;4(1):49–57. doi: 10.1128/aac.4.1.49. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapral F. A., Miller M. M. Product of Staphylococcus aureus responsible for the scalded-skin syndrome. Infect Immun. 1971 Nov;4(5):541–545. doi: 10.1128/iai.4.5.541-545.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondo I., Sakurai S., Sarai Y. Purification of exfoliatin produced by Staphylococcus aureus of bacteriophage group 2 and its physicochemical properties. Infect Immun. 1973 Aug;8(2):156–164. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.2.156-164.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melish M. E., Glasgow L. A. Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome: the expanded clinical syndrome. J Pediatr. 1971 Jun;78(6):958–967. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(71)80425-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melish M. E., Glasgow L. A. The staphylococcal scalded-skin syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1970 May 14;282(20):1114–1119. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197005142822002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melish M. E., Glasgow L. A., Turner M. D. The staphylococcal scalded-skin syndrome: isolation and partial characterization of the exfoliative toxin. J Infect Dis. 1972 Feb;125(2):129–140. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.2.129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick R. P. Extrachromosomal inheritance in bacteria. Bacteriol Rev. 1969 Jun;33(2):210–263. doi: 10.1128/br.33.2.210-263.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick R. P., Roth C. Plasmid-linked resistance to inorganic salts in Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1968 Apr;95(4):1335–1342. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.4.1335-1342.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogolsky M., Warren R., Wiley B. B., Nakamura H. T., Glasgow L. A. Nature of the genetic determinant controlling exfoliative toxin production in Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1974 Jan;117(1):157–165. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.1.157-165.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin S. J., Rosenblum E. D. Effects of ethidium bromide on growth and on loss of the penicillinase plasmid of Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1971 Dec;108(3):1200–1204. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.3.1200-1204.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


