Abstract
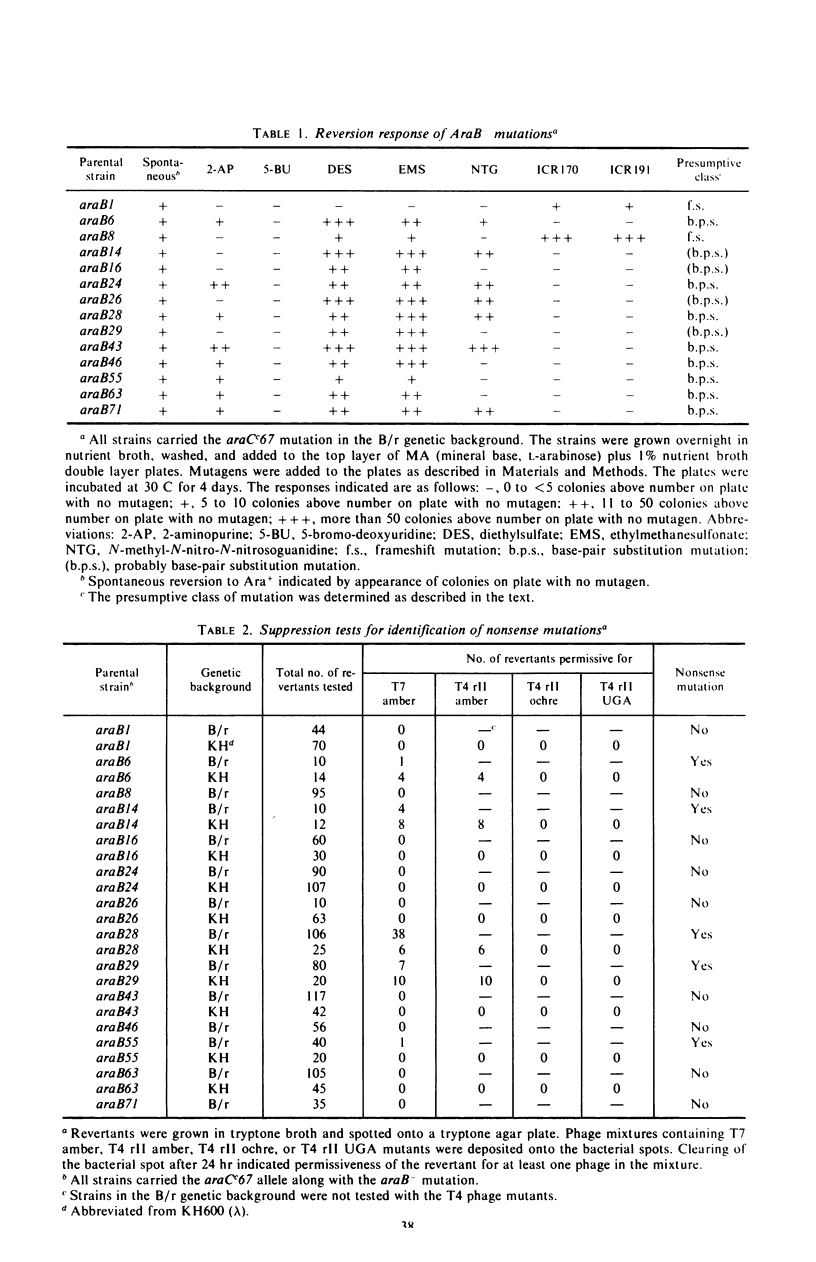
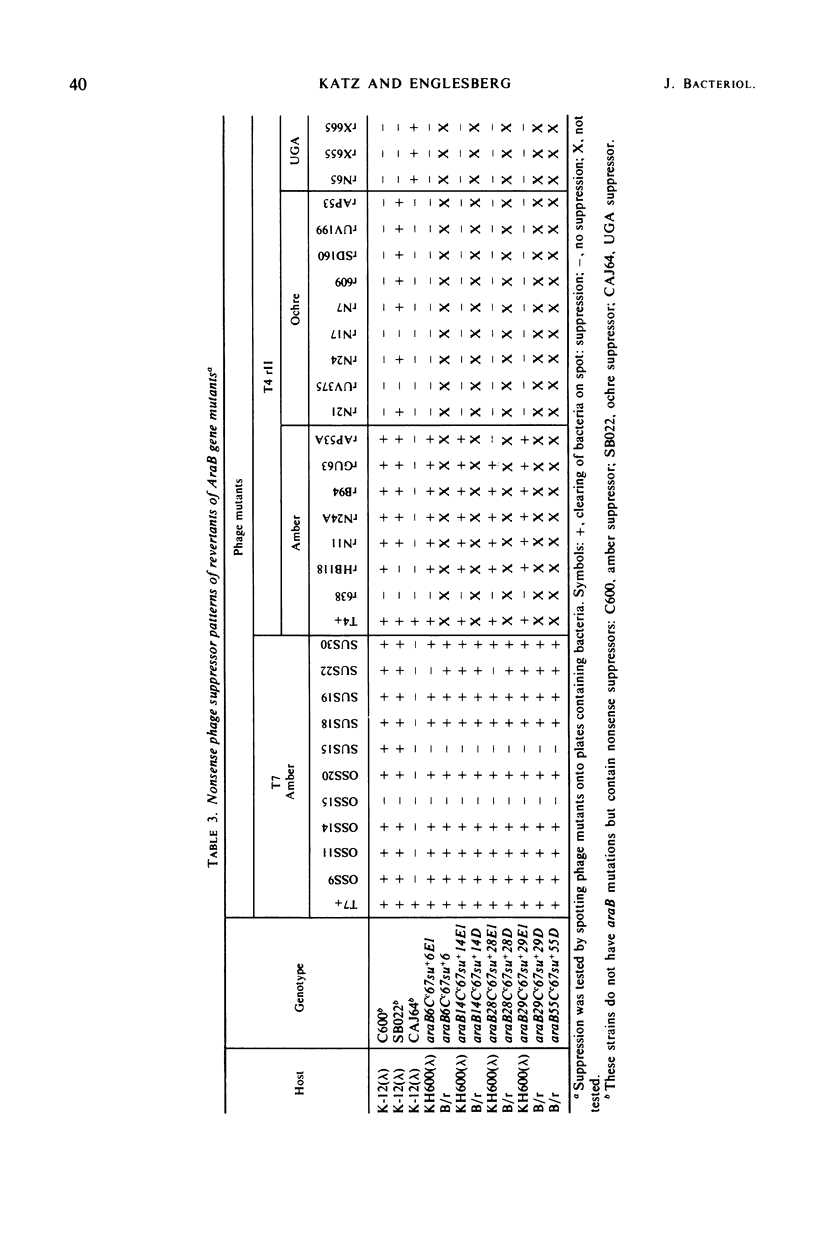
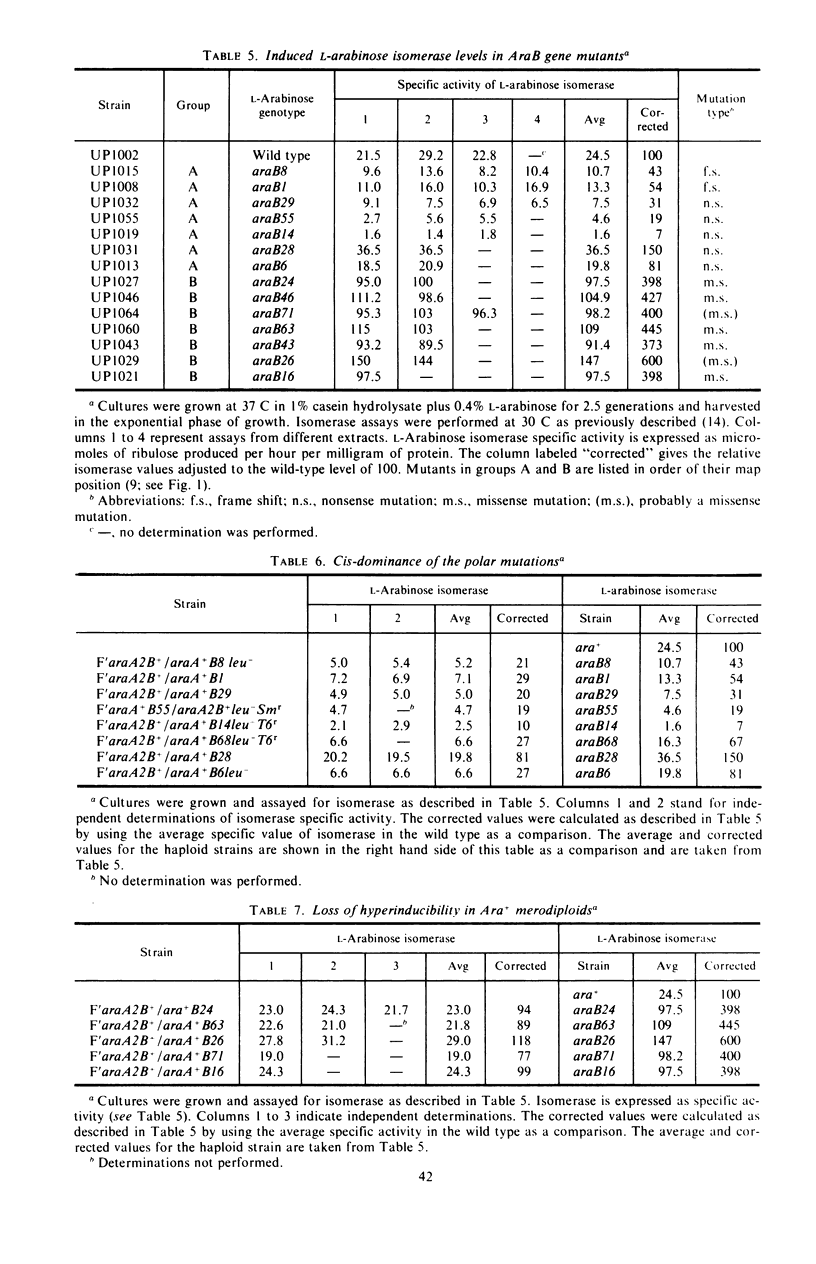
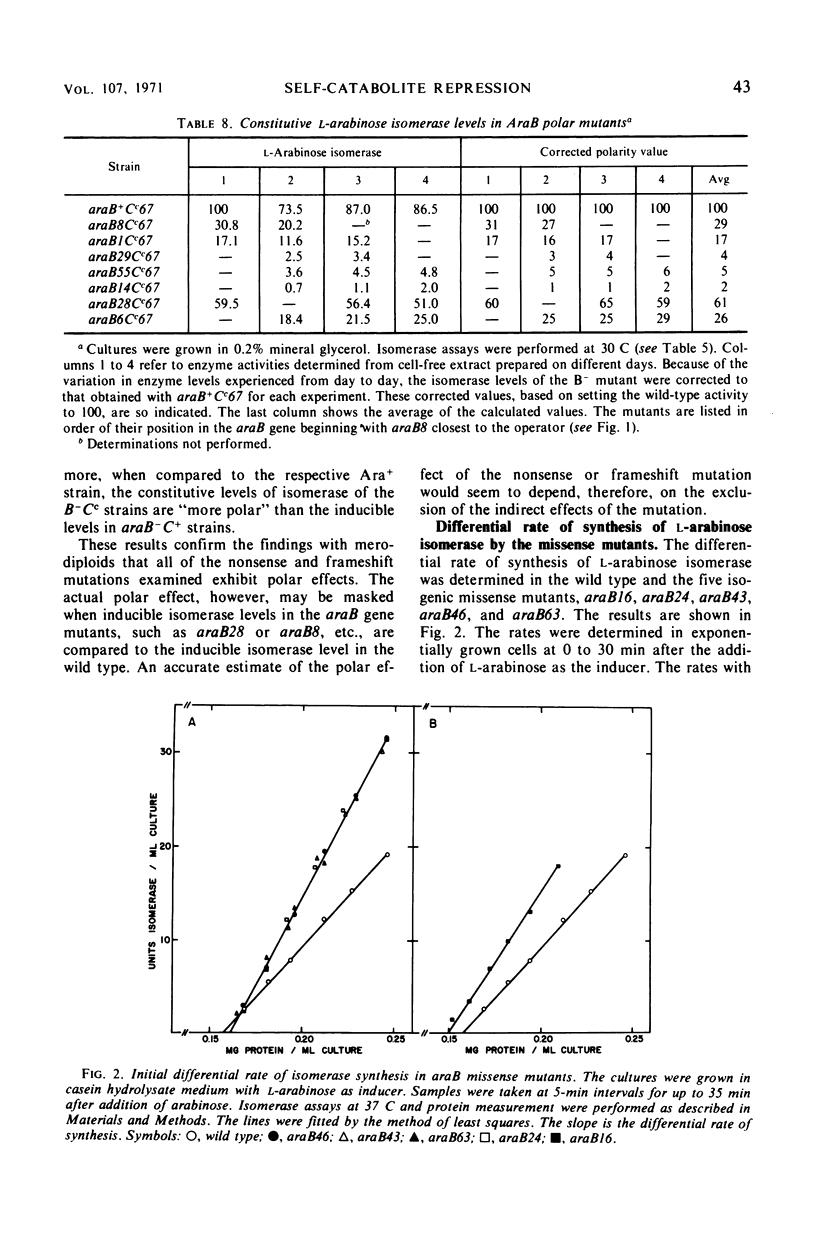
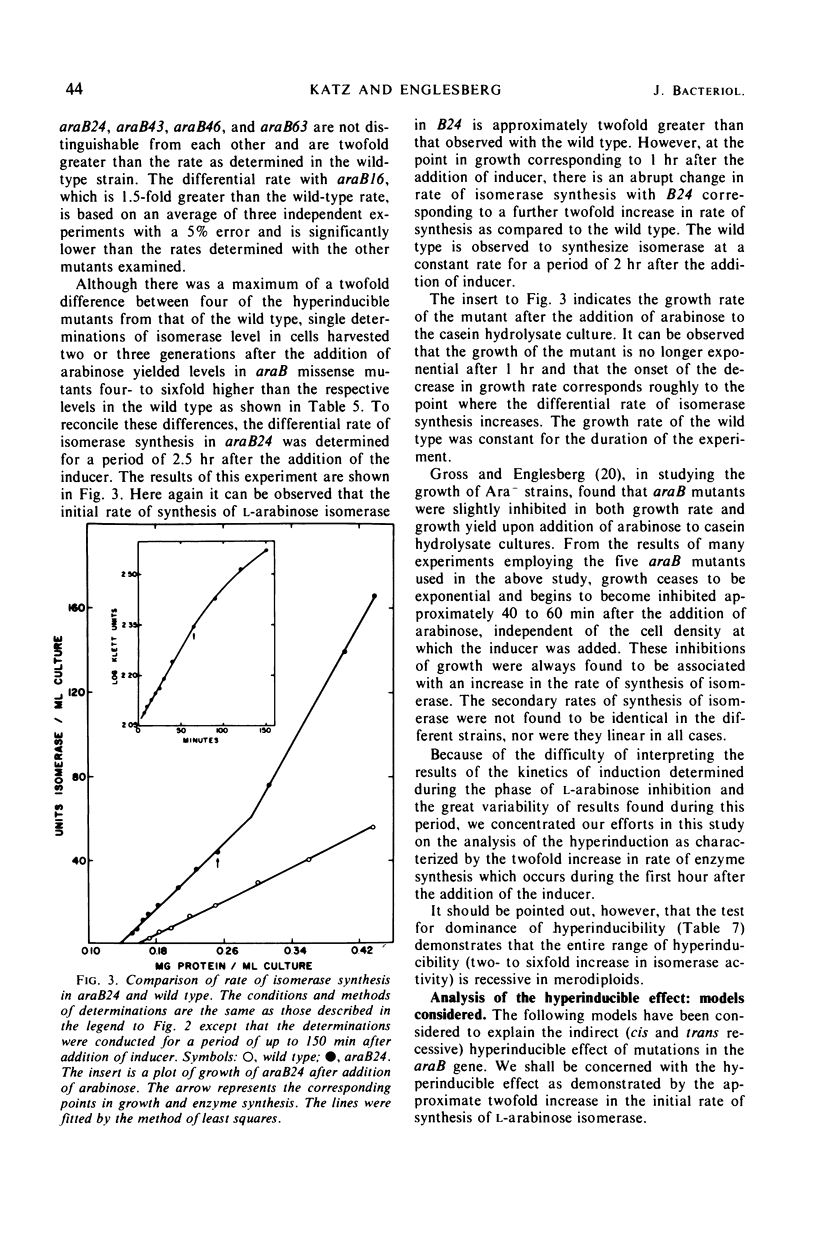
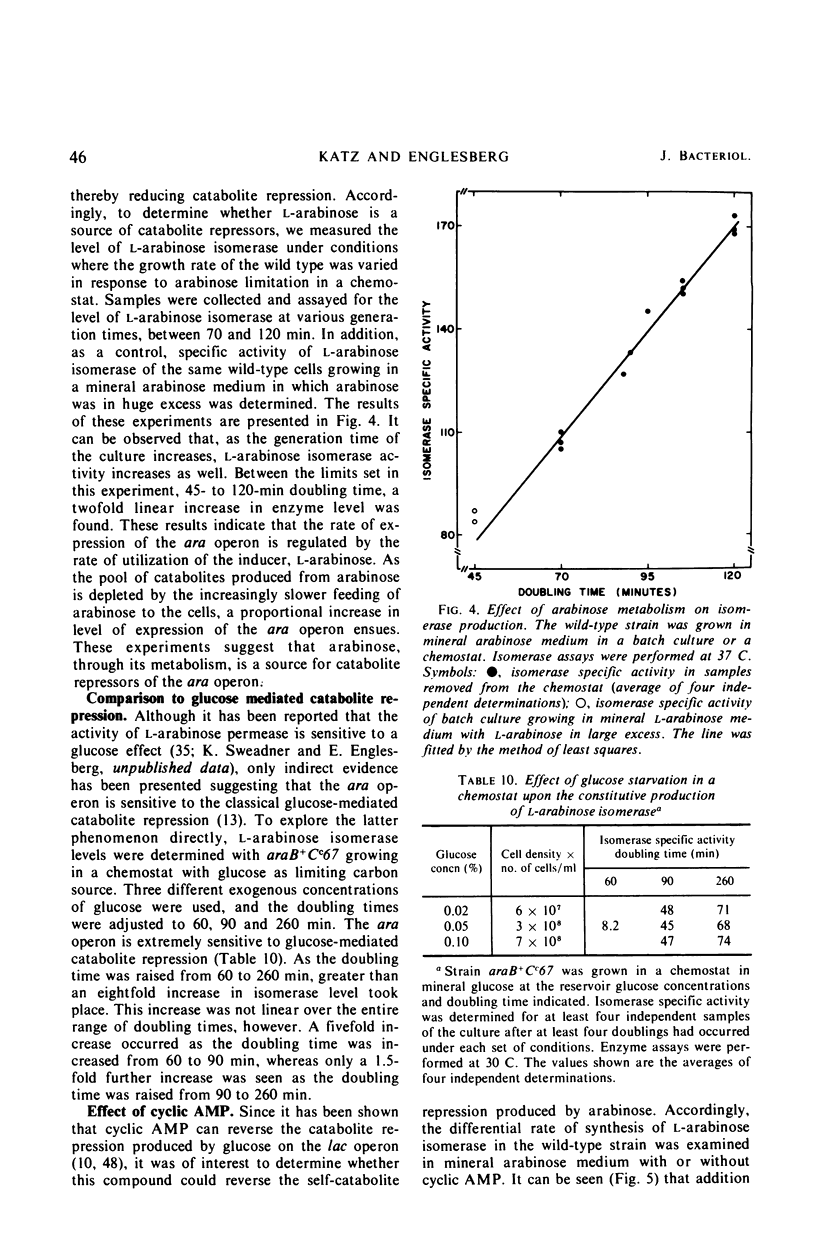
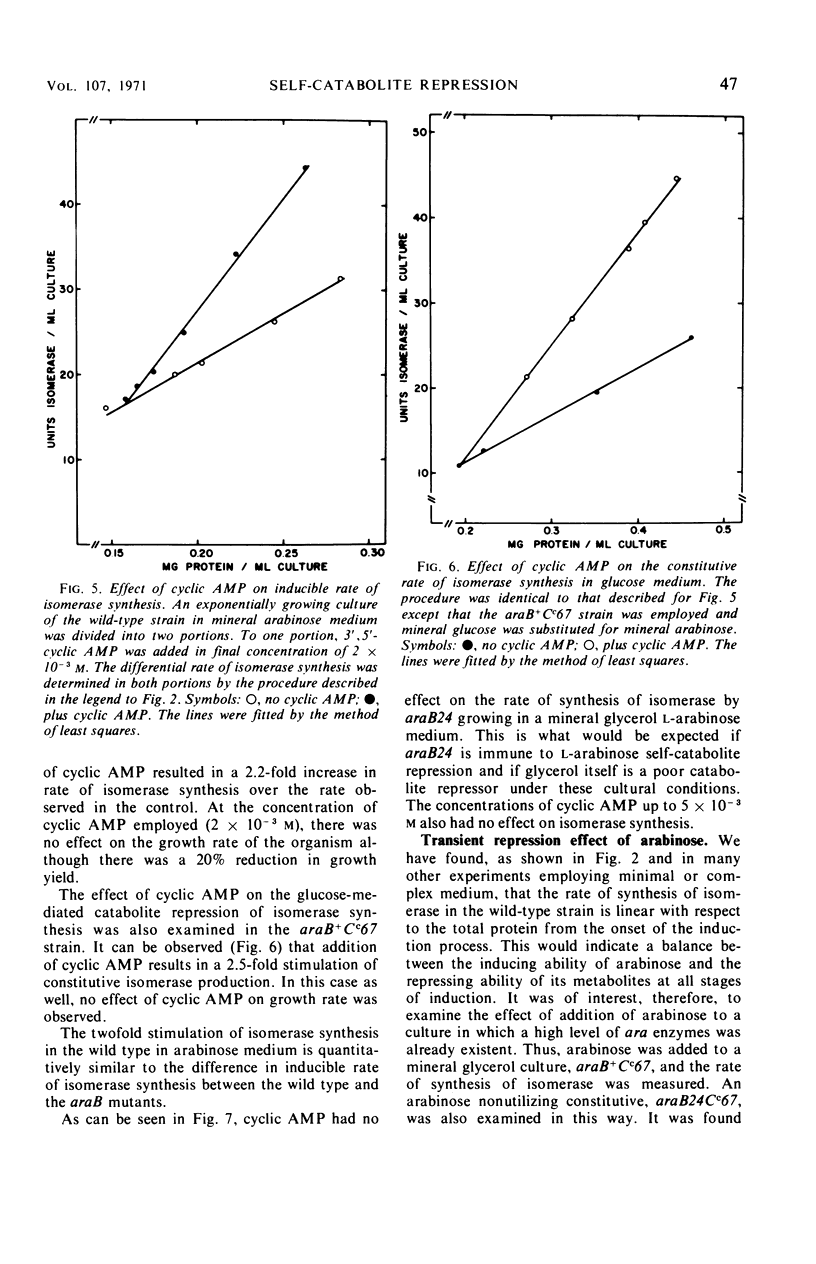
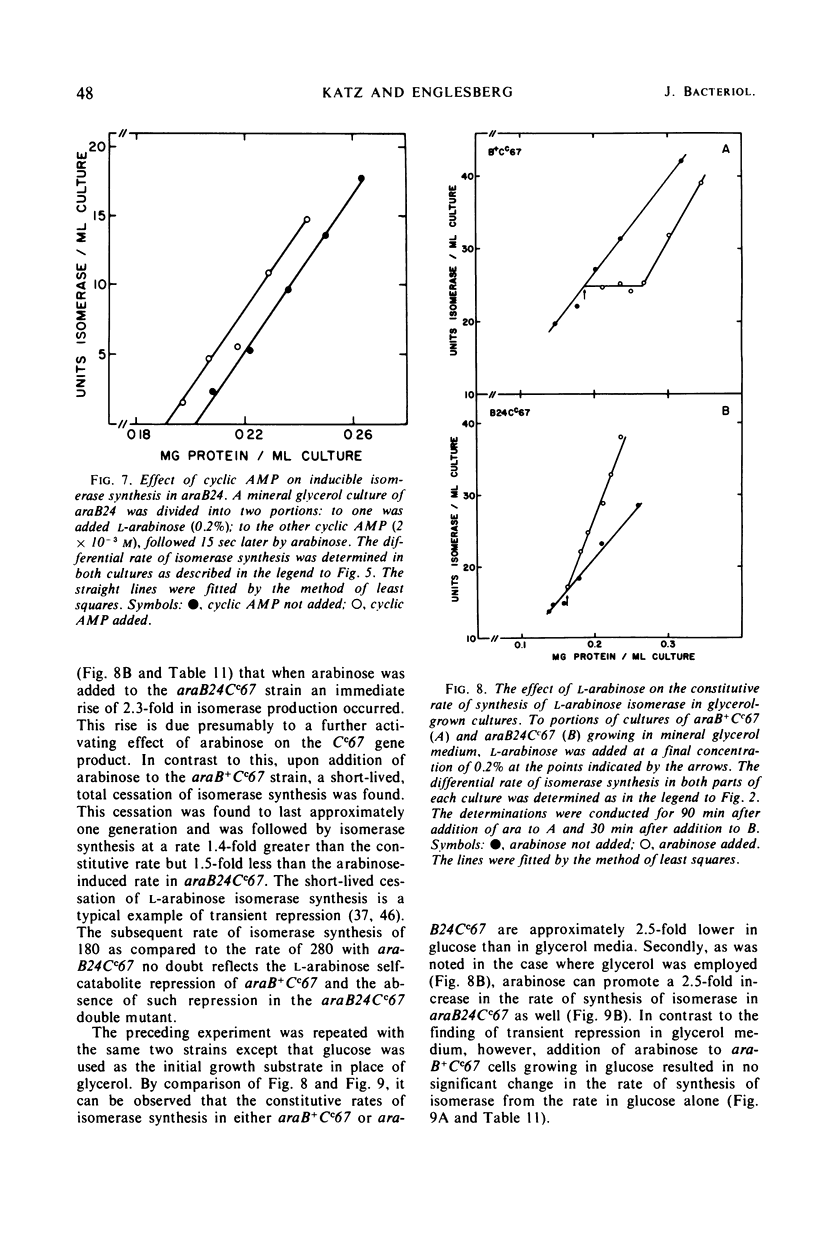
Mutations in gene araB producing an l-arabinose-negative phenotype cause either an increase (hyperinducible), decrease (polar), or have no effect at all on the inducible rate of expression of the l-arabinose operon. Fourteen araB gene mutants exhibiting such effects were shown to be the result of: nonsense, frameshift, or missense mutations. All missense mutants were hyperinducible, exhibiting approximately a twofold increase in rate of l-arabinose isomerase production. All frameshift and most nonsense mutants exhibited polar effect. One nonsense mutant was hyperinducible. The cis-dominant polar effect of nonsense and frameshift mutants (as compared to induced wild type) were more pronounced in arabinose-utilizing merodiploids and in araBaraCc double mutants where inducible and constitutive enzyme levels are respectively determined. On the other hand, in arabinose-utilizing merodiploids, missense mutations no longer exhibited hyperinducibility but displayed a wild-type level of operon expression. Increases in the wild type-inducible rate of expression of the operon were found when growth rate was dependent on the concentration of l-arabinose. Cyclic 3′,5′-adenosine monophosphate also stimulated expression of the operon with the wild type in a mineral l-arabinose medium. These observations are explained on the basis that the steady-state expression of the l-arabinose operon OIBAD is dependent on the concentration of (i) l-arabinose, the effector of this system, which stimulates the expression of the operon, and (ii) catabolite repressors, produced from l-arabinose, which dampen the expression of the operon. We have termed the latter phenomenon “self-catabolite” repression.
Full text
PDF









Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ames B. N., Whitfield H. J., Jr Frameshift mutagenesis in Salmonella. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1966;31:221–225. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1966.031.01.030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOYER H., ENGLESBERG E., WEINBERG R. Direct selection of L-arabinose negative mutants of Escherichia coli strain B@rl. Genetics. 1962 Apr;47:417–425. doi: 10.1093/genetics/47.4.417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger H., Brammar W. J., Yanofsky C. Spontaneous and ICR191-A-induced frameshift mutations in the A gene of Escherichia coli tryptophan synthetase. J Bacteriol. 1968 Nov;96(5):1672–1679. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.5.1672-1679.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beverin S., Sheppard D. E., Park S. S. D-Fucose as a gratuitous inducer of the L-arabinose operon in strains of Escherichia coli B-r mutant in gene araC. J Bacteriol. 1971 Jul;107(1):79–86. doi: 10.1128/jb.107.1.79-86.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner S., Stretton A. O., Kaplan S. Genetic code: the 'nonsense' triplets for chain termination and their suppression. Nature. 1965 Jun 5;206(988):994–998. doi: 10.1038/206994a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRIBBS R., ENGLESBERG E. L-ARABINOSE NEGATIVE MUTANTS OF THE L-RIBULOKINASE STRUCTURAL GENE AFFECTING THE LEVELS OF L-ARABINOSE ISOMERASE IN ESCHERICHIA COLI. Genetics. 1964 Jan;49:95–108. doi: 10.1093/genetics/49.1.95. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cozzarelli N. R., Freedberg W. B., Lin E. C. Genetic control of L-alpha-glycerophosphate system in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1968 Feb 14;31(3):371–387. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90415-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cribbs R. M. Reversions of the L-ribulokinase structural gene of Escherichia coli. Genetics. 1965 Jul;52(1):99–106. doi: 10.1093/genetics/52.1.99. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Crombrugghe B., Perlman R. L., Varmus H. E., Pastan I. Regulation of inducible enzyme synthesis in Escherichia coli by cyclic adenosine 3', 5'-monophosphate. J Biol Chem. 1969 Nov 10;244(21):5828–5835. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ENGLESBERG E., ANDERSON R. L., WEINBERG R., LEE N., HOFFEE P., HUTTENHAUER G., BOYER H. L-Arabinose-sensitive, L-ribulose 5-phosphate 4-epimerase-deficient mutants of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1962 Jul;84:137–146. doi: 10.1128/jb.84.1.137-146.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ENGLESBERG E. Enzymatic characterization of 17 L-arabinose negative mutants of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1961 Jun;81:996–1006. doi: 10.1128/jb.81.6.996-1006.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eichhorn M. M., Nolte A. A study of catabolite repression with L-arabinose negative mutants of Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Oct 25;110(1):198–201. doi: 10.1016/s0926-6593(65)80110-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Englesberg E., Sheppard D., Squires C., Meronk F., Jr An analysis of "revertants" of a deletion mutant in the C gene of the L-arabinose gene complex in Escherichia coli B-r: isolation of initiator constitutive mutants (Ic). J Mol Biol. 1969 Jul 28;43(2):281–298. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90268-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Englesberg E., Squires C., Meronk F., Jr The L-arabinose operon in Escherichia coli B-r: a genetic demonstration of two functional states of the product of a regulator gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Apr;62(4):1100–1107. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.4.1100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GROSS J., ENGLESBERG E. Determination of the order of mutational sites governing L-arabinose utilization in Escherichia coli B/r bv transduction with phage Plbt. Virology. 1959 Nov;9:314–331. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(59)90125-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garen A. Sense and nonsense in the genetic code. Three exceptional triplets can serve as both chain-terminating signals and amino acid codons. Science. 1968 Apr 12;160(3824):149–159. doi: 10.1126/science.160.3824.149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gartner T. K., Orias E. Effects of mutations to streptomycin resistance on the rate of translation of mutant genetic information. J Bacteriol. 1966 Mar;91(3):1021–1028. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.3.1021-1028.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grodzicker T., Zipser D. A mutation which creates a new site for the re-initiation of polypeptide synthesis in the z gene of the lac operon of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1968 Dec;38(3):305–314. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90388-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HELLING R. B., WEINBERG R. COMPLEMENTATION STUDIES OF ARABINOSE GENES IN ESCHERICHIA COLI. Genetics. 1963 Oct;48:1397–1410. doi: 10.1093/genetics/48.10.1397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler D. P., Englesberg E. Arabinose-leucine deletion mutants of Escherichia coli B-r. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jun;98(3):1159–1169. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.3.1159-1169.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEE N., ENGLESBERG E. COORDINATE VARIATIONS IN INDUCED SYNTHESES OF ENZYMES ASSOCIATED WITH MUTATIONS IN A STRUCTURAL GENE. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Oct;50:696–702. doi: 10.1073/pnas.50.4.696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEE N., ENGLESBERG E. Dual effects of structural genes in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Mar 15;48:335–348. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.3.335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAGASANIK B. Catabolite repression. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1961;26:249–256. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1961.026.01.031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAKMAN R. S., SUTHERLAND E. W. ADENOSINE 3',5'-PHOSPHATE IN ESCHERICHIA COLI. J Biol Chem. 1965 Mar;240:1309–1314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCFALL E., MANDELSTAM J. SPECIFIC METABOLIC REPRESSION OF THREE INDUCED ENZYMES IN ESCHERICHIA COLI. Biochem J. 1963 Nov;89:391–398. doi: 10.1042/bj0890391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malamy M. H. Frameshift mutations in the lactose operon of E. coli. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1966;31:189–201. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1966.031.01.027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin R. G. Frameshift mutants in the histidine operon of Salmonella typhimurium. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):311–328. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90300-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin R. G., Silbert D. F., Smith W. E., Whitfield H. J., Jr Polarity in the histidine operon. J Mol Biol. 1966 Nov 14;21(2):357–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(66)90104-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse D. E., Yanofsky C. Polarity and the degradation of mRNA. Nature. 1969 Oct 25;224(5217):329–331. doi: 10.1038/224329a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newton W. A., Beckwith J. R., Zipser D., Brenner S. Nonsense mutants and polarity in the lac operon of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1965 Nov;14(1):290–296. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80250-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novotny C. P., Englesberg E. The L-arabinose permease system in Escherichia coli B/r. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Mar 28;117(1):217–230. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(66)90169-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oeschger N. S., Hartman P. E. ICR-induced frameshift mutations in the histidine operon of Salmonella. J Bacteriol. 1970 Feb;101(2):490–504. doi: 10.1128/jb.101.2.490-504.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paigen K. Phenomenon of transient repression in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1966 Mar;91(3):1201–1209. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.3.1201-1209.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pastan I., Perlman R. Cyclic adenosine monophosphate in bacteria. Science. 1970 Jul 24;169(3943):339–344. doi: 10.1126/science.169.3943.339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Power J. The L-rhamnose genetic system in Escherichia coli K-12. Genetics. 1967 Mar;55(3):557–568. doi: 10.1093/genetics/55.3.557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SOFFER R. L. Enzymatic expression of genetic units of function concerned with galactose metabolism in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1961 Oct;82:471–478. doi: 10.1128/jb.82.4.471-478.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz M. Expression phénotypique et localisation génétique de mutations affectant le métabolisme du maltose chez Escherichia coli K 12. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1967 Jun;112(6):673–698. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sesnowitz-Horn S., Adelberg E. A. Proflavin treatment of Escherichia coli: generation of frameshift mutations. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1968;33:393–402. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1968.033.01.045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheppard D. E., Englesberg E. Further evidence for positive control of the L-arabinose system by gene araC. J Mol Biol. 1967 May 14;25(3):443–454. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90197-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheppard D. E., Walker D. A. Polarity in gene araB of the l-Arabinose operon in Escherichia coli B/r. J Bacteriol. 1969 Nov;100(2):715–723. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.2.715-723.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyler B., Loomis W. F., Jr, Magasanik B. Transient repression of the lac operon. J Bacteriol. 1967 Dec;94(6):2001–2011. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.6.2001-2011.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyler B., Magasanik B. Physiological basis of transient repression of catabolic enzymes in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1970 May;102(2):411–422. doi: 10.1128/jb.102.2.411-422.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullmann A., Monod J. Cyclic AMP as an antagonist of catabolite repression in Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett. 1968 Nov;2(1):57–60. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(68)80100-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanofsky C., Ito J. Nonsense codons and polarity in the tryptophan operon. J Mol Biol. 1966 Nov 14;21(2):313–334. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(66)90102-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zubay G., Schwartz D., Beckwith J. Mechanism of activation of catabolite-sensitive genes: a positive control system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 May;66(1):104–110. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.1.104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



