Abstract
N-type Ca2+ channels mediate Ca2+ influx, which initiates fast exocytosis of neurotransmitters at synapses, and they interact directly with the SNARE proteins syntaxin and SNAP-25 (synaptosome-associated protein of 25 kDa) through a synaptic protein interaction (synprint) site in the intracellular loop connecting domains II and III of their α1B subunits. Introduction of peptides containing the synprint site into presynaptic neurons reversibly inhibits synaptic transmission, confirming the importance of interactions with this site in synaptic transmission. Here we report a direct interaction of the synprint peptide from N-type Ca2+ channels with synaptotagmin I, an important Ca2+ sensor for exocytosis, as measured by an affinity-chromatography binding assay and a solid-phase immunoassay. This interaction is mediated by the second C2 domain (C2B) of synaptotagmin I, but is not regulated by Ca2+. Using both immobilized recombinant proteins and native presynaptic membrane proteins, we found that the synprint peptide and synaptotagmin competitively interact with syntaxin. This interaction is Ca2+-dependent because of the Ca2+ dependence of the interactions between syntaxin and these two proteins. These results provide a molecular basis for a physical link between Ca2+ channels and synaptotagmin, and suggest that N-type Ca2+ channels may undergo a complex series of Ca2+-dependent interactions with multiple presynaptic proteins during neurotransmission.
During synaptic transmission, exocytosis of synaptic vesicles in neurons is initiated by the rapid influx of Ca2+ through voltage-gated Ca2+ channels within 200 μsec. Major progress has been made toward the understanding of the molecular mechanisms that underlie Ca2+-dependent exocytosis by identifying proteins that are involved in this process and analyzing their interactions (1, 2). Vesicle docking and fusion are mediated by a core complex of proteins including the synaptic vesicle protein VAMP/synaptobrevin (3) and the plasmalemmal proteins syntaxin and synaptosome-associated protein of 25 kDa (SNAP-25) (4–11). The synaptic vesicle protein p65 or synaptotagmin (12) binds Ca2+ (13, 14) and interacts with syntaxin in a Ca2+-dependent manner (15, 16). It is thought to serve as a Ca2+ sensor for fast, Ca2+-dependent neurotransmitter release (17–22).
N-type Ca2+ channels are localized in nerve terminals (23–25) and participate in neurotransmitter release in central and peripheral synapses (26–28). They are coimmunoprecipitated and copurified with proteins of the synaptic core complex in immunochemical studies (4, 5, 29), and they are closely associated with sites of transmitter release in physiological experiments (30). The α1B subunits of N-type Ca2+ channels (31, 32) interact with the synaptic core complex through a synaptic protein interaction (synprint) site in the intracellular loop connecting domains II and III (33, 34) in a Ca2+ -dependent manner with maximum binding in the range of 10–30 μM (35). Peptides containing the synprint site of N-type Ca2+ channels reversibly inhibit synaptic transmission in cultured sympathetic neurons, suggesting that synprint peptides compete with N-type Ca2+ channels for binding to syntaxin and/or SNAP-25 in vivo (36). These results implicate direct interactions of N-type Ca2+ channels with syntaxin and SNAP-25 in the docking and exocytosis of synaptic vesicles.
In addition to their interactions with syntaxin and SNAP-25, N-type Ca2+ channels are coimmunoprecipitated with synaptotagmin (5, 9, 29, 37, 38), suggesting a possible interaction between them. Here we report that the synprint site of N-type Ca2+ channels interacts with the second C2 domain (C2B) of synaptotagmin I (syt I) and competes with synaptotagmin for interaction with syntaxin in a Ca2+-dependent manner. Our results provide a molecular basis for the close association of N-type Ca2+ channels with the Ca2+ sensor and suggest the possibility that N-type Ca2+ channels may undergo Ca2+-dependent, sequential interactions with several presynaptic proteins during the synaptic vesicle docking/fusion processes.
EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURES
Construction and Expression of Fusion Proteins.
Recombinant glutathione S-transferase (GST)-synaptotagmin fusion proteins were synthesized from the expression plasmids in the vector pGEX-2T (Pharmacia) (13, 39): GST-syt I and II, full-length cytoplasmic domains containing residues 80–421 and 88–422 of syt I and syt II, respectively; GST-syt I–C2A, residues 128–269; GST-syt I–C2B, residues 262–385. GST-syntaxin fusion protein encoding full-length syntaxin 1A, His-fusion proteins containing the syntaxin- and SNAP 25-binding region of the intracellular loop between domains II and III of the Ca2+ channel α1B subunit [LII–III(718–963)], and as a control, the corresponding region of the L-type Ca2+ channel α1S subunit, LII–III(670–800), were expressed and purified as described (36). All recombinant proteins were expressed in Escherichia coli BL26 cells, a protease-deficient strain (Novagen). The fusion proteins were extracted by mild sonication in PBS (50 mM sodium phosphate, pH 8.0/300 mM NaCl plus protease inhibitors), and His-fusion proteins were purified by binding to Ni2+-charged nitrilotriacetic acid agarose columns (Qiagen, Chatsworth, CA), and eluted with 500 mM imidazole in PBS. The eluates were concentrated with Centriprep-10 filtration units (Amicon) and dialyzed in a 10,000 mw cutoff dialysis cassette (Pierce) against PBS with 0.1% Triton X-100 and 0.1% glycerol. Amounts of proteins used were standardized based on Coomassie blue stained SDS gels or estimated with a standard curve relating the intensity of the immunoblotting signal to the amount of a standard fusion protein applied.
Immunoprecipitation.
Immunoprecipitation was performed in TBS buffer with a Ca2+-buffering system (50 mM Tris⋅HCl/140 mM NaCl/50 mM Hepes, pH 7.2/5 mM N-hydroxyethylethylenediaminetriacetic acid/0.3% Triton X-100/CaCl2), which produced indicated free [Ca2+] as calculated using the max chelator software (version 6.63). After a 15 hr incubation at 4°C, the precipitates immobilized to protein A-Sepharose beads were washed three times with the TBS–Ca2+ buffer. Proteins bound to the beads were solubilized with SDS sample buffer at 95°C for 5 min, separated by 10% SDS/PAGE or 10–20% SDS/tricine gradient gel electrophoresis (Novex), and blotted with monoclonal antibodies 10H5, against syntaxin 1, and 1D12 (5) against synaptotagmin.
Measurement of Synprint Binding by Affinity Chromatography.
GST-fusion proteins were bound to glutathione-Sepharose beads (Pharmacia) in TBS–Ca2+ buffer, incubated at 4°C for 1 hr with constant agitation, and washed with incubation buffer to remove unbound proteins. Glutathione-Sepharose beads coupled with similar amounts of GST-fusion protein were added to the lysates containing His-tagged LII–III(718–963) fusion protein and incubated with gentle mixing for 3 hr at 4°C. The binding reactions were carried out in a Ca2+ buffering system, TBS–Ca2+ with 0.1% Triton X-100. The beads were washed three times with incubation buffer and bound proteins were eluted in 15 mM reduced glutathione and 50 mM Tris⋅HCl (pH 8). Eluates were separated from the beads by centrifugation at 10,000 × g for 1 min and processed for 10–20% SDS/tricine gradient gel electrophoresis and immunoblotted with the T7.Tag antibody (Novagen), a monoclonal antibody (mAb) against the leader peptide sequence of His-tagged fusion proteins. For competition studies with recombinant and native proteins, the cytoplasmic domain (80–421) of syt I was expressed as a GST-fusion protein, purified by affinity chromatography on glutathione-Sepharose, and cleaved from the GST tag with thrombin (Novagen). Synaptosomes from rat brain were solubilized in buffer containing 10 mM Hepes (pH 7.4), 150 mM NaCl, 2 mM MgCl2, and 1.2% Triton X-100, and insoluble proteins were removed by centrifugation.
Measurement of Synprint Binding by Solid-Phase Immunoassay.
Purified fusion proteins were quantitated by the bicinchoninic (BCA) method (Pierce). Binding calibration curves were generated by coating 96-well MaxiSorp microtiter plates (Nunc) with 5 μg/ml LII–III(718–963) in buffer B (10 mM Tris⋅HCl, pH 8.0/150 mM NaCl) followed by blocking in the same solution supplemented with 1% gelatin and 0.1% Tween-20. Plates were washed three times with buffer B, incubated for 2 hr at 37°C with 2-fold serial dilutions of the GST-fusion proteins in buffer A, and washed three times in the same buffer. Protein complexes were then incubated with a mouse IgG-2b anti-GST mAb (Zymed) at 2.25 μg/ml in buffer B supplemented with 0.1% Tween-20, followed by three washes, incubation for 2 hr at 37°C with an anti-mouse IgG-2b-specific alkaline phosphatase-conjugated mAb (Zymed) at 2.25 μg/ml in buffer B with 0.1% Tween-20, and six washes. Colorimetric reactions were initiated with p-nitrophenyl phosphate (Sigma), terminated at 10 min with 2 N NaOH, and absorbance was measured at 410 nm (A410) on an MR 650 plate reader using immunosoft 2.2 for Macintosh (Dynatech). Duplicate measurements for each sample were averaged, and nonspecific binding of the GST-control protein was subtracted. A reference curve relating A410 to picomoles of the anti-mouse IgG-2b-specific alkaline phosphatase-conjugated mAb was generated in solution and read on the same microtiter plate with the same developing time and reagents as for the adsorbed test samples. The reference plot was linear for A410 from 0 to 1.5, corresponding to 0 to 8 pmol of anti-mouse IgG-2b-specific alkaline phosphatase-conjugated antibody bound. It was used to calibrate the amount of bound 1:1:1 ternary complex of GST-fusion protein:anti-GST antibody:anti-mouse IgG-2b alkaline phosphatase-conjugated antibody. A 90% adsorption efficiency for LII–III(718–963) on the MaxiSorp microtiter plate was estimated by Western blot analysis of a postadsorbed sample compared with a series of preadsorbed standards, and stoichiometry estimates were corrected for this adsorption efficiency.
RESULTS
Binding of the N-Type Ca2+ Channel Synprint Protein to the C2B Domain of Synaptotagmin.
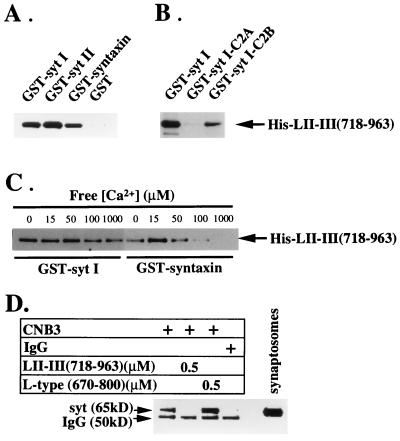
To determine whether the synprint site of N-type Ca2+ channels can bind to synaptotagmin, we performed in vitro binding studies using recombinant fusion proteins. Full-length syt I, syt II, and syntaxin 1A were expressed as GST-fusion proteins, immobilized by binding to glutathione-Sepharose, and incubated with a constant concentration of the His-tagged synprint peptide, LII–III(718–963). After extensive washing, binding of LII–III(718–963) was determined by immunoblot analysis using an antibody against the leader peptide sequence of His-tagged fusion protein. As shown in Fig. 1A, LII–III(718–963) specifically bound to immobilized full-length syt I, syt II, and syntaxin 1A, but did not bind to GST alone.
Figure 1.
Binding of the N-type Ca2+ channel synprint peptide to the C2B domain of synaptotagmin. (A) Binding of the synprint peptide [LII–III(718–963)] to GST-fusion proteins containing the full-length cytoplasmic domains of syt I and syt II, full-length syntaxin 1A, and GST alone. (B) Synprint peptide binding to the C2B domain but not the C2A domain of syt I. (C) Ca2+ independence of the interaction between the synprint peptide and syt I. GST-fusion proteins (2 μg) were immobilized on glutathione-Sepharose and incubated with His-LII–III(718–963) (31 nM). The binding reactions were performed in a Ca2+ buffering system (5 mM N-hydroxyethylethylenediaminetriacetic acid-Ca2+/50 mM Hepes, pH 7.2/150 mM NaCl) containing free Ca2+ concentrations estimated using the max chelator software (version 6.63) as described. The concentrations of free Ca2+ in the binding buffers were 15 μM in A and B, and 0, 10, 20, 50, 100 μM, and 1 mM, as indicated, in C. After extensive washing with the incubation buffers, the proteins bound to the beads were eluted with 15 mM reduced glutathione in 50 mM Tris⋅HCl (pH 8), and subjected to electrophoresis and immunoblotting. The bound His-LII-III(718–963) was detected using the T7.Tag antibody. (D) N-type Ca2+ channels were solubilized from synaptosomal membranes and immunoprecipitated with the anti-CNB3 antibody (24) as described in Experimental Procedures with the additions indicated. The immunoprecipitates were resolved by SDS/PAGE and immunoblotted with antibody 1D12 against synaptotagmin. The label IgG indicates the position of the heavy chain of IgG that is labeled by the secondary antibody reagent used in the immunoblot.
The cytoplasmic portion of synaptotagmin contains the two highly conserved Ca2+-binding domains, C2A and C2B, which are related in amino acid sequence to the C2 regulatory motif of protein kinase C. LII–III(718–963) bound specifically to immobilized GST-syt I-C2B, but little or no binding was observed to GST-syt I-C2A (Fig. 1B). Because these two domains are similar in structure and function, these results provide further evidence that the synprint site of N-type Ca2+ channels specifically associates with synaptotagmin and implicate the C2B motif in that interaction.
The C2B domain of synaptotagmin mediates its interaction with the clathrin adaptor protein AP-2 (38) and inositol polyphosphates (40, 41) in a Ca2+-independent manner, but is responsible for Ca2+-dependent binding of synaptotagmin to the synaptic vesicle protein SV2 (42). To determine the effect of Ca2+ on the interaction between LII–III (718–963) and syt I, we measured binding using fusion proteins in the absence or presence of various buffered free Ca2+ concentrations. As shown in Fig. 1C, Ca2+ has a biphasic effect on the binding of LII–III(718–963) to immobilized GST-syntaxin, with maximal binding at 15 μM of free Ca2+ (34). In contrast, we did not observe a significant effect of Ca2+ on the binding of LII–III(718–963) to GST-syt I up to 1 mM Ca2+.
To test whether native N-type Ca2+ channels interact with synaptotagmin through the synprint site, coimmunoprecipitation experiments were carried out in the presence and absence of synprint peptide (Fig. 1D). Anti-CNB-3, directed against the COOH-terminal of α1B (24), coimmunoprecipitated synaptotagmin, while control IgG did not. Coimmunoprecipitation was inhibited by the synprint peptide LII–III(718–963) from the N-type Ca2+ channel but not by the corresponding peptide segment from an L-type Ca2+ channel, consistent with specific interaction of synaptotagmin at the synprint site on α1B.
Binding of Synaptotagmin, Syntaxin, and SNAP-25 to Immobilized Synprint Peptide in a Solid-Phase Immunoassay.
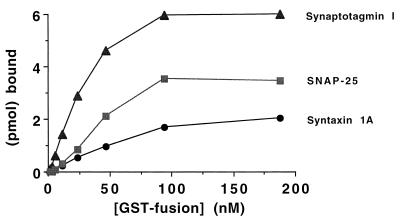
To confirm the specific interaction of the synprint peptide with synaptotagmin, syntaxin, and SNAP-25 in a different experimental system, we developed a solid-phase immunoassay in which synprint peptide is immobilized on the surface of an assay dish and bound ligands are detected by labeling with an alkaline phosphatase-conjugated antibody. Binding of GST was considered background and subtracted from the results for test proteins. Under these conditions, syntaxin, SNAP-25, and synaptotagmin bound specifically to immobilized synprint peptide (Fig. 2). At saturating concentrations of the probe ligand, the stoichiometry of binding was 0.31 mol syntaxin per mol of synprint, 0.55 mol SNAP-25 per mol of synprint, and 0.94 mol synaptotagmin per mol of synprint. The level of binding at saturating concentrations of probe ligand in a solid-phase assay is influenced by the fraction of the immobilized acceptor protein, which is available for binding, as well as by the stoichiometry of interaction between the two proteins, so these values represent a lower limit of the true binding stoichiometry. Apparent KD values were approximately 50 nM for syntaxin, 40 nM for SNAP-25, and 25 nM for synaptotagmin, respectively, in the solid-phase immunoassay. This apparent KD value for syntaxin is approximately 5-fold lower than estimated in previous experiments using the affinity-chromatography method for binding measurements (35), but this is likely due to differences in experimental conditions in the two assay systems. These solid-phase immunoassay results provide independent support for the specificity of interaction of these three SNARE proteins with the synprint site of N-type Ca2+ channels. The high affinity and stoichiometry of interaction in vitro are consistent with the hypothesis that all three proteins bind to the synprint site of N-type Ca2+ channels in vivo. Inhibition of synaptic transmission by microinjected synprint peptide in intact neurons supports an important role for these interactions in exocytosis (36).
Figure 2.
Measurement of synprint interactions in a solid-phase immunoassay. Stoichiometric interaction of the synprint peptide with syntaxin 1A, SNAP-25, and syt I. Picomoles of specific, bound GST-syntaxin 1A (•), GST-syt I (80–421) (▴), or GST-SNAP-25 (▪) are plotted as a function of the concentration of GST-fusion protein added. Microtiter plates were coated with 6.4 pmol of purified LII–III(718–963) (corrected for adsorption efficiency) followed by incubation with 2-fold serial dilutions of purified GST-syntaxin 1A, GST-syt I (80–421), GST-SNAP-25, or a GST control protein, and detection with a mouse IgG-2b anti-GST mAb and an anti-mouse IgG-2b-specific mAb conjugated to alkaline phosphatase. Absorbance readings were converted to molar concentrations of bound GST-fusion protein via a reference curve relating A410 to pmol of the anti-mouse IgG-2b-specific alkaline phosphatase conjugated mAb. Stoichiometries are calculated as the molar ratio of bound GST-fusion protein to adsorbed LII–III(718–963).
Displacement of Synaptotagmin Binding to Syntaxin by Synprint Peptide.
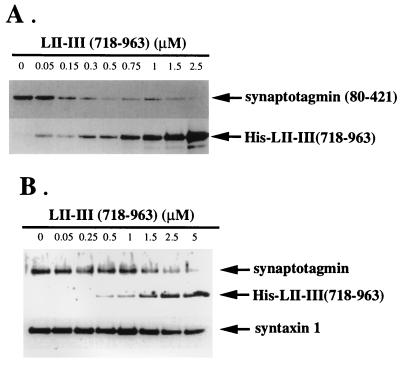
We have previously shown that synprint peptides from both N-type and P/Q-type Ca2+ channels bind to a GST-syntaxin deletion construct containing only the C-terminal one-third (amino acids 181–288) of syntaxin 1A (33, 34). Interestingly, the same region of syntaxin 1A also mediates its interaction with synaptotagmin (16, 43). We investigated whether the synprint peptide and synaptotagmin occupy the same or overlapping binding sites in competition binding assays. GST-syntaxin 1A was bound to glutathione-Sepharose beads and incubated with a constant amount of the purified recombinant cytoplasmic domain (residues 80–421) of syt I, along with increasing amounts of LII–III(718–963). As shown in Fig. 3A, the signal intensity of syt I(80–421) (upper band) diminishes progressively, whereas the signal intensity of LII–III(718–963) of the N-type channel (lower band) increases. These results indicate that the synprint peptide and synaptotagmin compete for binding to syntaxin.
Figure 3.
Displacement of synaptotagmin binding to syntaxin by the synprint peptide. (A) Synprint peptide competes with the binding of recombinant syt I to syntaxin 1A. GST-syntaxin 1A bound to glutathione-Sepharose beads was incubated with a constant amount of the purified recombinant cytoplasmic domain (residues 80–421) of syt I and increasing amounts of His-LII–III(718–963) as indicated, in a binding buffer containing 20 μM of free Ca2+. Beads were washed, and bound proteins were eluted with 15 mM reduced glutathione in 50 mM of Tris⋅HCl (pH 8), and analyzed by immunoblotting with 1D12, a mAb against the carboxyl terminals of both syt I and syt II, and T7.Tag antibody as described. (B) The synprint peptide competes for the interaction of native synaptotagmin with syntaxin. GST-VAMP/synaptobrevin 2 bound to glutathione-Sepharose beads was incubated with a constant amount of solubilized synaptosomes and an increasing amount of His-LII–III(718–963) as indicated, in a binding buffer with 20 μM free Ca2+. Syntaxin and SNAP-25 from solubilized synaptosomes were associated with GST-VAMP/synaptobrevin 2 bound to glutathione-Sepharose as described (35) to form an SDS-resistant complex, which serves as an acceptor for binding either recombinant LII–III(718–963) or native synaptotagmin from solubilized synaptosomes. After extensive washing with incubation buffer, GST-VAMP/synaptobrevin 2-bound protein complexes were eluted with reduced glutathione and analyzed by immunoblotting with T7.Tag, 1D12, and 10H5, a syntaxin 1 antibody. Each lane contains an equivalent amount of GST-syntaxin 1A (A) and GST-VAMP/synaptobrevin 2 (B), bound to beads, as confirmed by anti-GST immunoblotting (data not shown).
To exclude possible experimental artifacts from use of recombinant fusion proteins in our competition binding assays, we measured competitive binding using native synaptic proteins from solubilized synaptosome preparations. Immobilized GST-VAMP/synaptobrevin 2 was incubated with a constant amount of solubilized synaptosomes and increasing amounts of LII–III(718–963) as indicated in Fig. 3B. Syntaxin and SNAP-25 in solubilized synaptosomes associate with GST-VAMP/synaptobrevin 2 on glutathione-Sepharose beads to form an SDS-resistant complex (9). This complex can serve as an acceptor for binding either recombinant LII-III(718–963) or native synaptotagmin from solubilized extracts of synaptosomes under these experimental conditions (35). In the absence of synprint peptide, synaptotagmin is bound to the core complex (Fig. 3B). However, increasing concentrations of the synprint peptide LII-III(718–963) displace native synaptotagmin from its binding site on native syntaxin (Fig. 3B). These results confirm that the synprint peptide from N-type Ca2+ channels and native synaptotagmin do indeed compete for the same binding region on native syntaxin.
The Synprint Peptide Blocks Coimmunoprecipitation of Native Synaptotagmin with Syntaxin.
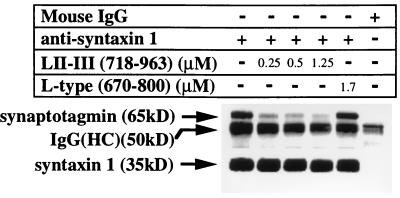
Binding of synaptotagmin to recombinant syntaxin or to native synaptic core complexes in vitro is prevented by a fusion protein containing the synprint site of the α1B subunit (Fig. 3 A and B). However, it is not known whether synprint peptides can cause dissociation of preformed complexes of syntaxin and synaptotagmin. We tested whether purified synprint fusion protein can disrupt the interaction between the native syntaxin and synaptotagmin bound to the synaptic complex solubilized from synaptosomes using a specific anti-syntaxin 1 antibody, 10H5 (5), to precipitate the complex. Antibody 10H5 specifically coimmunoprecipitated synaptotagmin with syntaxin under control conditions (Fig. 4). This coimmunoprecipitation was partially blocked by incubation with 0.25 μM synprint peptide, and this block appears to be concentration-dependent since increasing the synprint peptide to 1.25 μM almost completely inhibits the association of syntaxin with synaptotagmin. A control fusion protein, LII–III(670–800) from the α1S subunit of an L-type Ca2+ channel, did not block coimmunoprecipitation of synaptotagmin at even higher concentrations. These results provide further support for the conclusion that syntaxin associates with synaptotagmin and show that this interaction can be disrupted specifically by excess fusion protein containing the synprint site of N-type Ca2+ channels.
Figure 4.
Block of coimmunoprecipitation of native synaptotagmin with syntaxin by synprint peptide. Concentration-dependent inhibition of the association of native synaptotagmin with syntaxin by the synprint peptide His-LII–III(718–963). The complex of syntaxin with synaptotagmin was coimmunoprecipitated from solubilized rat brain synaptosomes with a monoclonal anti-syntaxin antibody (10H5) in the presence or absence of an increasing amount of His-LII–III(718–963), as indicated, or in the presence of 1.7 μM of a control fusion protein, LII–III(670–800), from the rat skeletal muscle L-type calcium channel α1S.
Since the same region of syntaxin mediates interactions with both synaptotagmin and N-type Ca2+ channels in a Ca2+ dependent manner (15, 16, 35, 43), it is interesting to determine the effect of Ca2+ on the inhibition of coimmunoprecipitation of syntaxin and synaptotagmin by the synprint peptide. As shown in Fig. 5, Ca2+ dramatically increased the level of synaptotagmin associated with syntaxin as shown previously (15, 16, 43). In contrast, the blocking efficiency of the synprint peptide was maximal at low Ca2+ (10–20 μM), which is in the same range of Ca2+ concentration for maximal binding of N-type Ca2+ channels to syntaxin (35), and was reduced at higher concentration. The synprint peptide (0.5 μM) reduced synaptotagmin binding to syntaxin by approximately 50% at low Ca2+ or at 1 mM Ca2+, but inhibited binding by approximately 90% at 10 μM and 80% at 20 μM, respectively. These results suggest that the increased affinity for binding of the synprint peptide for syntaxin in the presence of 10–20 μM Ca2+ (35) results in the most efficient dissociation of the complex of syntaxin and synaptotagmin.
Figure 5.
Ca2+-dependent inhibition of the binding of native synaptotagmin with syntaxin by the synprint peptide. Coimmunoprecipitation of syntaxin and synaptotagmin was measured as described for Fig. 4 in the presence of 0.5 μM of His-LII–III(718–963) from α1B or 0.5 μM of His-LII–III(670–800) from the L-type α1S under Ca2+-buffering conditions containing 0, 10, 20, and 1000 μM of free Ca2+ as indicated. The immunoprecipitates were analyzed by SDS/PAGE, immunoblotted with anti-synaptotagmin (1D12) and anti-syntaxin (10H5) antibodies, and visualized with rabbit anti-mouse IgG coupled to horseradish peroxidase and enhanced chemiluminescence detection. The amount of immunoprecipitated synaptotagmin was measured by densitometry and compared with control samples in the absence of competing peptides. The migration positions of synaptotagmin and mouse IgG in the immunoprecipitation are indicated.
DISCUSSION
Multiple Presynaptic Proteins Interact with the Synprint Site.
Our results show that at least three presynaptic proteins interact directly with N-type Ca2+ channels via the synprint site: syntaxin, SNAP-25, and synaptotagmin. However, it is unlikely that all of these interactions take place at the same time. Instead, these multiple interactions described for N-type Ca2+ channels may reflect functionally distinct stages in the complex processes of docking, priming, and fusion of synaptic vesicles. We previously demonstrated that the affinity of N-type Ca2+ channels for binding to syntaxin is modulated by the Ca2+ concentration, with maximal binding in the range of 10–30 μM near the threshold for neurotransmitter release (35). In contrast, maximum binding of syntaxin to syt I and syt II requires higher concentrations of Ca2+ in the range from 100 μM to 1 mM (15, 16, 43). As the Ca2+ concentration increases beyond 30 μM, interaction of syntaxin with the synprint site will be weakened and interaction with synaptotagmin will be stengthened. Thus, these studies provide potential biochemical correlates for the sequence of events during Ca2+-dependent synaptic vesicle exocytosis.
Functional Competition Between Synaptotagmin and the Synprint Site.
Previous studies have shown that a complex of N-type Ca2+ channels, syntaxin, and synaptotagmin can be isolated from brain membranes (5, 29, 38), suggesting that syntaxin can bind N-type Ca2+ channels and synaptotagmin at the same time. However, our results demonstrating competition between the Ca2+ channel synprint peptide and synaptotagmin for binding to syntaxin suggest that the ternary complex of Ca2+ channels, synaptotagmin, and syntaxin is not stable. Therefore, it is likely that these isolated preparations contained a mixture of binary complexes of N-type Ca2+ channels with either synaptotagmin or syntaxin bound to them, but not both. Alternatively, a quaternary complex containing SNAP-25 may have been isolated in which the N-type Ca2+ channel was bound to SNAP-25 through its synprint site, syntaxin was bound to SNAP-25, and synaptotagmin was bound to syntaxin. In either case, the previous biochemical experiments are not in conflict with our results.
On the basis of the available data, we speculate that sequential interactions between syntaxin, synaptotagmin, and N-type Ca2+ channels play a role in priming and fusion processes of docked vesicles. Free synprint peptides inhibit fast, synchronous synaptic transmission and enhance asynchronous transmission (36), consistent with the hypothesis that Ca2+ channels must bind to presynaptic proteins via the synprint site for efficient synaptic transmission. The Ca2+-dependent displacement of synaptotagmin by the synprint peptide observed in these experiments supports the conclusion that the binding of N-type Ca2+ channels to syntaxin is physiologically significant and implies that synaptotagmin competes with the Ca2+ channel for binding to a common site on syntaxin. Thus, one of the roles of the synprint site on the Ca2+ channel may be to bind syntaxin after vesicle docking to prevent the core complex from gaining access to synaptotagmin. Higher levels of Ca2+ (above 30 μM) may be needed to enable displacement of syntaxin from the Ca2+ channel and efficient binding of synaptotagmin in order for fusion to proceed. Thus, sequential Ca2+-dependent interactions of multiple proteins with syntaxin may serve to order the biochemical events leading to membrane fusion.
The efficiency of synaptic transmission could also be regulated by modulating the binding interactions of these proteins. Synaptic transmission is regulated by multiple receptor pathways that act through G proteins and protein phosphorylation. Further studies on the regulation of the interactions between Ca2+ channels and presynaptic proteins in in vitro and in vivo systems should help to elucidate the regulatory mechanisms of synaptic transmission at the molecular level.
Functions of the C2B Domain of Synaptotagmin.
The C2A domain of native synaptotagmin contributes to Ca2+-dependent phospholipid and syntaxin binding (13–16, 43). Surprisingly, the C2B domain is ineffective in binding to phospholipid and syntaxin despite a high degree of sequence similarity with C2A. Although recent results show that the C2B domain of syt I is capable of Ca2+-triggered self-association (44) and Ca2+-dependent binding to SV2 (42), it binds AP-2 (14, 45), inositol polyphosphates (40), and the synprint site of N-type Ca2+ channels in a Ca2+-independent manner, suggesting a functional specialization of C2A and C2B domains in synaptotagmins. Current evidence indicates that the C2A domain of synaptotagmin may be directly related to the fusion of synaptic vesicles that results in transmitter release (18, 19, 46), through a mechanism involving Ca2+-triggered binding of phospholipid and syntaxin. In contrast, the C2B domain seems to be required for the recycling of vesicles by interacting with the clathrin adaptor protein AP-2 (41, 45). Our results suggest that it may also direct synaptic vesicles to dock in the vicinity of Ca2+ entry sites through the interaction with the synprint site of N-type Ca2+ channels, which likely presents a strategic advantage for the triggering of rapid transmitter release.
Acknowledgments
We thank Carl Baker and Hélène Bochan for purification of His-fusion protein and synaptosome preparations, respectively, Dr. Masami Takahashi (Mitsubishi–Kasei Life Sciences Institute, Machida, Tokyo) for anti-syntaxin and anti-synaptotagmin antibodies, and Dr. Masami Takahashi and Dr. Sandra Bajjalieh for critical review of the manuscript. This study was supported by National Institutes of Health Research Fellowship 1F32 MH10775–01 (Z.-H.S.), National Institutes of Health Grant NS22625 and a grant from the University of Washington Royalty Research Fund (W.A.C.), and a National Research Service Award from National Institutes of Health Training Grant T32 GM07108-19 to C.T.Y.
ABBREVIATIONS
- GST
glutathione S-transferase
- LII–III
intracellular loop between domains II and III of the Ca2+ channel α1 subunit
- SNAP-25
synaptosome-associated protein of 25 kDa
- syt I and syt II
synaptotagmins I and II
- synprint
synaptic protein interaction site
References
- 1.Bajjalieh S M, Scheller R H. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:1971–1974. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.5.1971. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Südhof T C. Nature (London) 1995;375:645–653. doi: 10.1038/375645a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Trimble W S, Cowan D M, Scheller R H. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1988;85:4538–4542. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Bennett M K, Calakos N, Scheller R H. Science. 1992;257:255–259. doi: 10.1126/science.1321498. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Yoshida A, Oho C, Omori A, Kuwahara R, Ito T, Takahashi M. J Biol Chem. 1992;267:24925–24928. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Oyler G A, Higgins G A, Hart R A, Battenberg E, Billingsley M, Bloom F E, Wilson M C. J Cell Biol. 1989;109:3039–3052. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.6.3039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Söllner T, Whiteheart S W, Brumner M, Erdjument-Bromage H, Geromanos S, Tempst P, Rothman J E. Nature (London) 1993;362:318–324. doi: 10.1038/362318a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Calakos N, Bennett M K, Peterson K E, Scheller R H. Science. 1994;263:1146–1149. doi: 10.1126/science.8108733. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.O’Conner V M, Shamotienko O, Grishin E, Betz H. FEBS Lett. 1993;326:255–261. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)81802-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Hayashi T, McMahon H, Yamasaki S, Binz T, Hata Y, Südhof T C, Niemann H. EMBO J. 1994;13:5051–5061. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06834.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Chapman E R, An S, Barton N, Jahn R. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:27427–27432. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Matthew W D, Tsavaler L, Reichardt L F. J Cell Biol. 1981;91:257–269. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.1.257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Perin M S, Fried V A, Mignery G A, Jahn R, Südhof T C. Nature (London) 1990;345:260–263. doi: 10.1038/345260a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Li C, Davletov B A, Südhof T C. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:24898–24902. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.42.24898. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Li C, Ullrich B, Zhang J Z, Anderson R G W, Brose N, Südhof T C. Nature (London) 1995;357:594–599. doi: 10.1038/375594a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Chapman E R, Hanson P I, An S, Jahn R. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:23667–23671. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.40.23667. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Elferink L A, Peterson M R, Scheller R H. Cell. 1993;72:153–159. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90059-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Bommert K, Charlton M P, DeBello W M, Chin G J, Betz H, Augustine G J. Nature (London) 1993;363:163–165. doi: 10.1038/363163a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Geppert M, Goda Y, Hammer R E, Li C, Rosahl T W, Stevens C F, Südhof T C. Cell. 1994;79:717–727. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90556-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Broadie K, Bellen H J, DiAntonio A, Littleton J T, Schwarz T L. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1994;91:10727–10731. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.22.10727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Littleton J T, Stern M, Schulze K, Perin M, Bellen H J. Cell. 1993;74:1125–1134. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90733-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Nonet M L, Grundahl K, Meyer B J, Rand J B. Cell. 1993;73:1291–1305. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90357-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Robitaille R, Adler E M, Charlton M P. Neuron. 1990;5:773–779. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90336-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Westenbroek R E, Hell J W, Warner C, Dubel S J, Snutch T P, Catterall W A. Neuron. 1992;9:1099–1115. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90069-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Westenbroek R E, Sakurai T, Elliott E M, Hell J M, Starr T V, Snutch T P, Catterall W A. J Neurosci. 1995;15:6403–6418. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.15-10-06403.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Tsien R W, Lipscombe D, Madison D V, Bley K R, Fox A P. Trends Neurosci. 1988;11:431–438. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(88)90194-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Wu L-G, Saggau P. J Neurosci. 1994;14:5613–5622. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.14-09-05613.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Mintz I M, Sabatini B L, Regehr W G. Neuron. 1995;15:675–688. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(95)90155-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Lévêque C, El Far O, Martin-Moutot N, Sato K, Kato R, Takahashi M, Seagar M J. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:6306–6312. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Stanley E F. Neuron. 1993;11:1007–1011. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90214-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Dubel S J, Starr T V P, Hell J, Ahlijanian M K, Enyeart J J, Catterall W A, Snutch T P. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1992;89:5058–5062. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.11.5058. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Williams M E, Brust P F, Feldman D H, Patthi S, Simerson S, Maroufi A, Velicelebi G, Ellis S B, Harpold M M. Science. 1992;257:389–395. doi: 10.1126/science.1321501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Sheng Z-H, Rettig J, Takahashi M, Catterall W A. Neuron. 1994;13:1303–1313. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90417-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Rettig J, Sheng Z-H, Kim D K, Hodson C D, Snutch T P, Catterall W A. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1996;93:7363–7368. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.14.7363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Sheng Z-H, Rettig J, Cook T, Catterall W A. Nature (London) 1996;379:451–454. doi: 10.1038/379451a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Mochida S, Sheng Z-H, Baker C, Kobayashi H, Catterall W A. Neuron. 1996;17:781–788. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(00)80209-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.David P, El Far O, Martin-Moutot N, Poupon M F, Takahashi M, Seagar M J. FEBS Lett. 1993;326:135–139. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)81777-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Lévêque C, Hosho T, David P, Shoji-Kasai Y, Leys K, Omori A, Lang B, El Far O, Sato K, Martin-Moutot N, Seagar M J, Takahashi M. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1992;89:3625–3629. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.8.3625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Geppert M, Archer B T, III, Südhof T. J Biol Chem. 1991;266:13548–13552. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Fukuda M, Aruga J, Ninobe M, Aimoto S, Mikoshiba K. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:29206–29211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Fukuda M, Moreira J E, Lewis F M T, Sugimori M, Ninobe M, Mikoshiba K, Llinás R. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1995;92:10708–10712. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.23.10708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Schivell A, Bachelor R, Bajjalieh S. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:27770–27775. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.44.27770. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Kee Y, Scheller R H. J Neurosci. 1996;16:1975–1981. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.16-06-01975.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Sugita S, Hata Y, Südhof T C. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:1262–1265. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.3.1262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Zhang J Z, Davletov B A, Südhof T C, Anderson R G W. Cell. 1994;78:751–760. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(94)90442-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Mikoshiba K, Fukuda M, Moreira J E, Lewis F M T, Sugimori M, Ninobe M, Llinás R. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1995;92:10703–10707. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.23.10703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]