Abstract
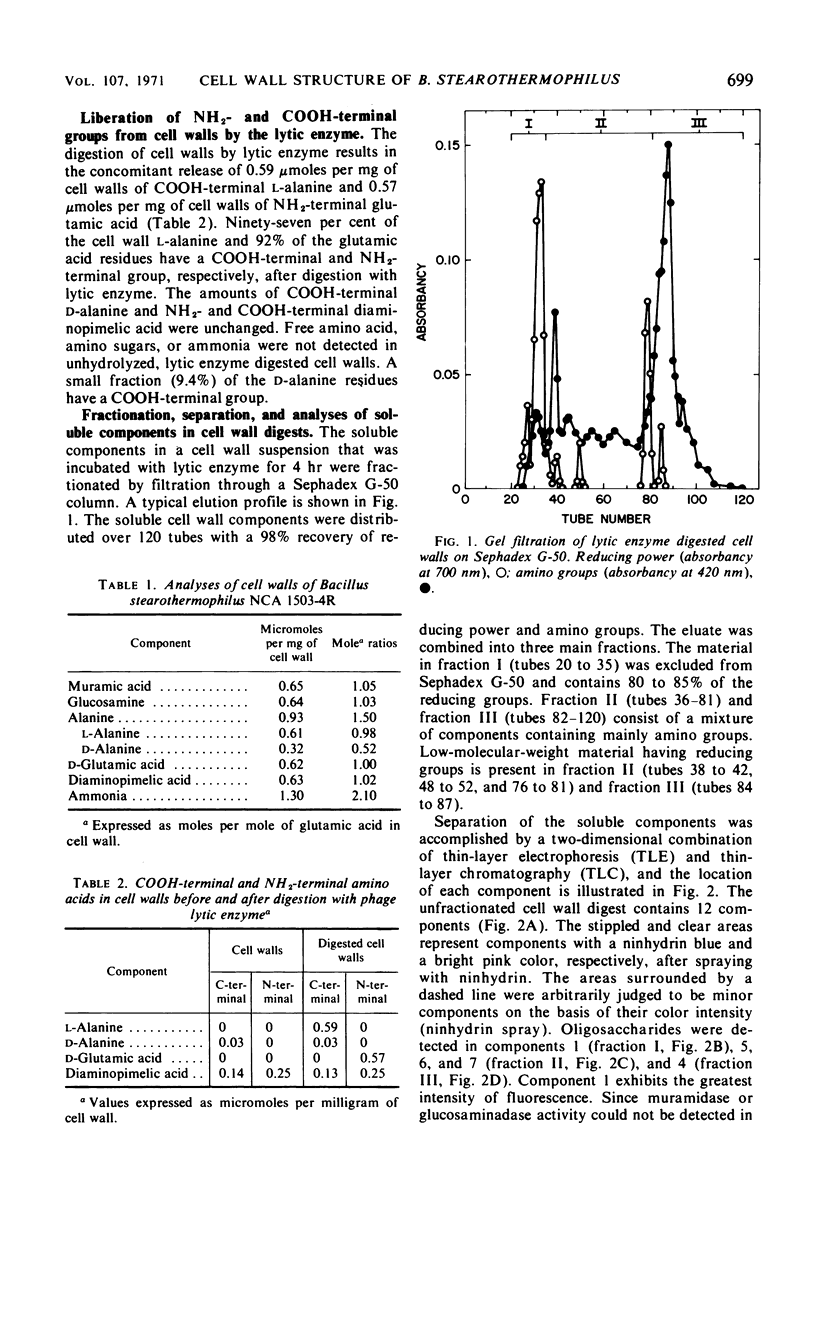
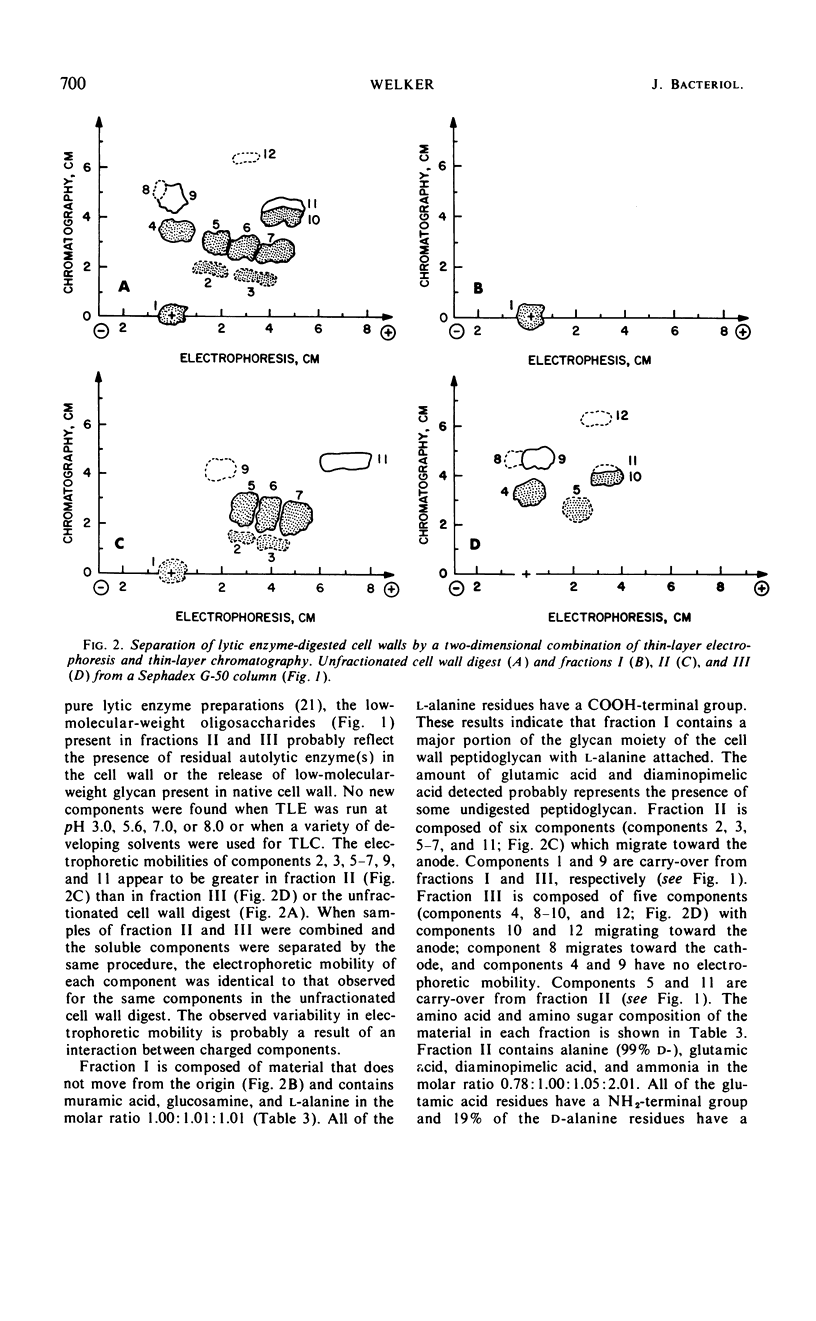
The mode of action of a bacteriophage lytic enzyme on cell walls of Bacillus stearothermophilus (NCA 1503-4R) has been investigated. The enzyme is an endopeptidase which catalyzes the hydrolysis of the l-alanyl-d-glutamyl linkage in peptide subunits of the cell wall peptidoglycan. Preliminary studies on the soluble components in lytic cell wall digests indicate that the glycan moiety is composed of alternating glucosamine and muramic acid; one half of the muramic acid residues contain the tripeptide, l-alanyl-d-glutamyldiaminopimelic acid, and the remaining residues contain the tetrapeptide, l-alanyl-d-glutamyldiaminopimeyl-d-alanine. Almost one half of the peptide subunits are involved in cross-linkages of chemotype I. A structure for the cell wall peptidoglycan is proposed in the light of these findings.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Forrester I. T., Wicken A. J. The chemical composition of the cell walls of some thermophilic bacilli. J Gen Microbiol. 1966 Jan;42(1):147–154. doi: 10.1099/00221287-42-1-147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghuysen J. M. Use of bacteriolytic enzymes in determination of wall structure and their role in cell metabolism. Bacteriol Rev. 1968 Dec;32(4 Pt 2):425–464. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grant W. D., Wicken A. J. Autolysis of cell walls of Bacillus stearothermophilus B65 and the chemical structure of the peptidoglycan. Biochem J. 1970 Aug;118(5):859–868. doi: 10.1042/bj1180859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes R. C., Pavlik J. G., Rogers H. J., Tanner P. J. Organization of polymers in the cell walls of some bacilli. Nature. 1968 Aug 10;219(5154):642–644. doi: 10.1038/219642a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes R. C. The cell wall of Bacillus licheniformis N.C.T.C. 6346. Composition of the mucopeptide component. Biochem J. 1968 Jan;106(1):41–48. doi: 10.1042/bj1060041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes R. C. The cell wall of Bacillus licheniformis N.C.T.C. 6346. Isolation of low-molecular-weight fragments from the soluble mucopeptide. Biochem J. 1968 Jan;106(1):49–59. doi: 10.1042/bj1060049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato K., Strominger J. L., Kotani S. Structure of the cell wall of Corynebacterium diphtheriae. I. Mechanism of hydrolysis by the L-3 enzyme and the structure of the peptide. Biochemistry. 1968 Aug;7(8):2762–2773. doi: 10.1021/bi00848a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingan S. L., Ensign J. C. Isolation and characterization of three autolytic enzymes associated with sporulation of Bacillus thuringiensis var. thuringiensis. J Bacteriol. 1968 Sep;96(3):629–638. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.3.629-638.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manning J. M., Moore S. Determination of D- and L-amino acids by ion exchange chromatography as L-D and L-L dipeptides. J Biol Chem. 1968 Nov 10;243(21):5591–5597. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda T., Kotani S., Kato K. Structure of the cell walls of Lactobacillus plantarum, ATCC 8014. 1. Isolation and identication of the peptides released from cell wall peptidoglycans by Streptomyces L-3 enzyme. Biken J. 1968 Jun;11(2):111–126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda T., Kotani S., Kato K. Structure of the cell walls of Lactobacillus plantarum, ATCC 8014. 2. Cross linkage between D-alanine and alpha,alpha'-diaminopimelic acid in the cell wall peptidoglycans studied with an L-11 enzyme from Flavobacterium sp. Biken J. 1968 Jun;11(2):127–138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARK J. T., JOHNSON M. J. A submicrodetermination of glucose. J Biol Chem. 1949 Nov;181(1):149–151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHARON N., SEIFTER S. A TRANSGLYCOSYLATION REACTION CATALYZED BY LYSOZYME. J Biol Chem. 1964 Jul;239:PC2398–PC2399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutow A. B., Welker N. E. Chemical composition of the cell walls of Bacillus stearothermophilus. J Bacteriol. 1967 Apr;93(4):1452–1457. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.4.1452-1457.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J. S., Shockman G. D. A modification of the Park and Johnson reducing sugar determination suitable for the assay of insoluble materials: its application to bacterial cell walls. Anal Biochem. 1968 Feb;22(2):260–268. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(68)90315-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Heijenoort J., Elbaz L., Dezélée P., Petit J. F., Bricas E., Ghuysen J. M. Structure of the meso-diaminopimelic acid containing peptidoglycans in Escherichia coli B and Bacillus megaterium KM. Biochemistry. 1969 Jan;8(1):207–213. doi: 10.1021/bi00829a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEIDEL W., PELZER H. BAGSHAPED MACROMOLECULES--A NEW OUTLOOK ON BACTERIAL CELL WALLS. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1964;26:193–232. doi: 10.1002/9780470122716.ch5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welker N. E. Purification and properties of a thermophilic bacteriophage lytic enzyme. J Virol. 1967 Jun;1(3):617–625. doi: 10.1128/jvi.1.3.617-625.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wicken A. J. The glycerol teichoic acid from the cell wall of Bacillus stearothermophilus B65. Biochem J. 1966 Apr;99(1):108–116. doi: 10.1042/bj0990108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YOUNG F. E., SPIZIZEN J., CRAWFORD I. P. BIOCHEMICAL ASPECTS OF COMPETENCE IN THE BACILLUS SUBTILIS TRANSFORMATION SYSTEM. I. CHEMICAL COMPOSITION OF CELL WALLS. J Biol Chem. 1963 Sep;238:3119–3125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



