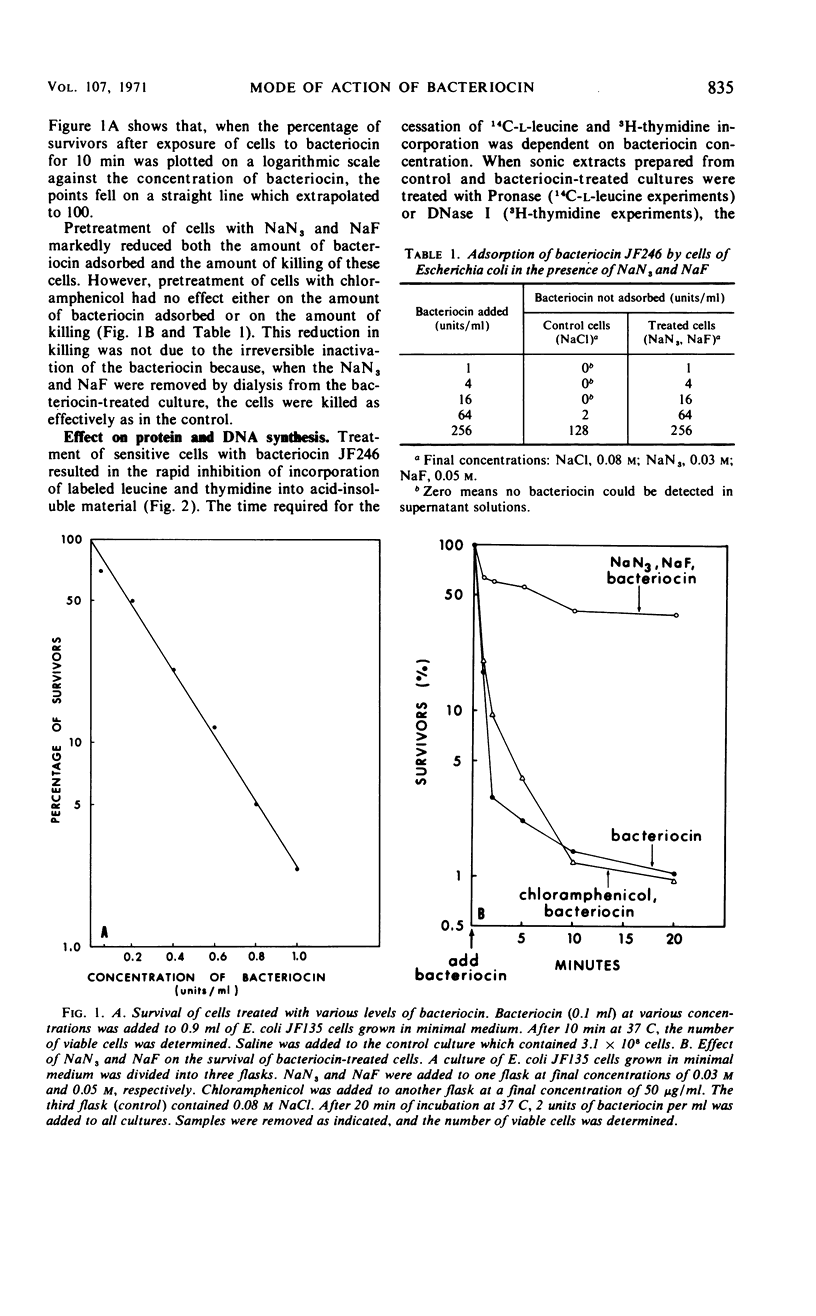
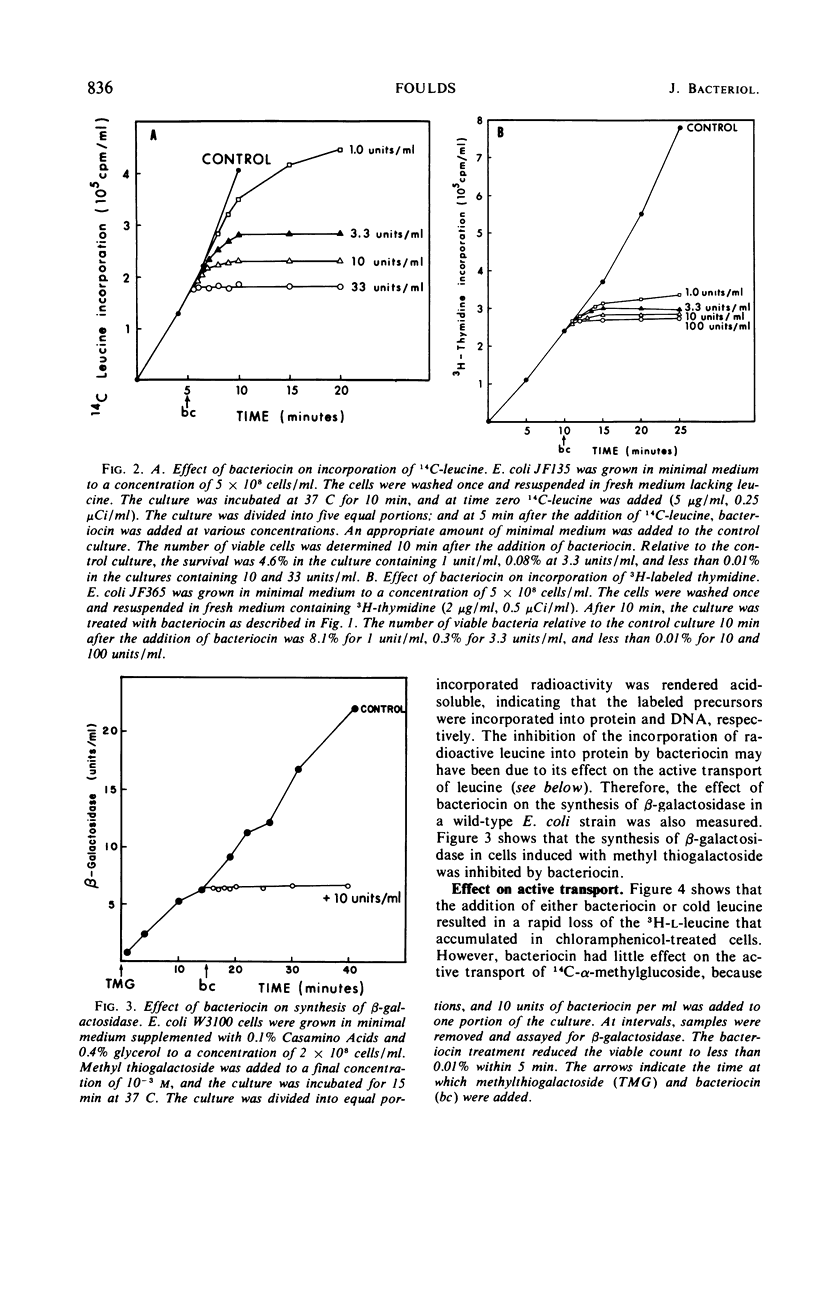
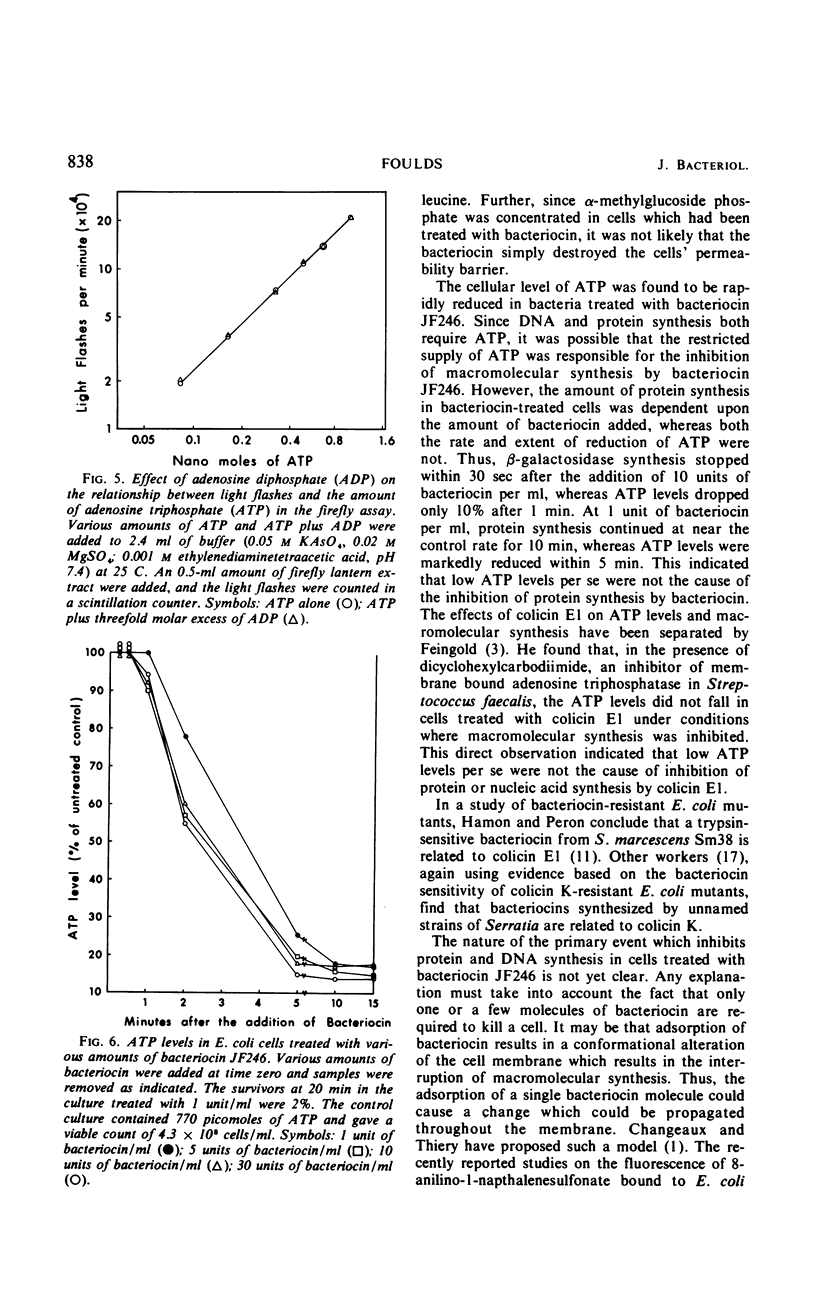
Abstract
The effects of bacteriocin JF246, produced by Serratia marcescens, on the incorporation of labeled leucine and thymidine, the synthesis of β-galactosidase, the active transport of labeled leucine and α-methyl-d-glucoside, and the cellular levels of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) in Escherichia coli were studied. This bacteriocin strongly inhibited the incorporation of leucine and thymidine into protein and deoxyribonucleic acid, respectively, as well as the active transport of leucine. The accumulation of α-methyl-d-glucoside, which is mediated by a phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent phosphotransferase system, was not markedly inhibited. The level of ATP in bacteriocin-treated cells rapidly fell to 10 to 15% of the control value. However, the kinetics of inhibition of macromolecular synthesis by various levels of bacteriocin was not related to the kinetics of ATP decline.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Changeux J. P., Thiéry J. On the mode of action of colicins: a model of regulation at the membrane level. J Theor Biol. 1967 Nov;17(2):315–318. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(67)90175-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cramer W. A., Phillips S. K. Response of an Escherichia coli-bound fluorescent probe to colicin E1. J Bacteriol. 1970 Nov;104(2):819–825. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.2.819-825.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FULLER A. T., HORTON J. M. Marcescin, an antibiotic substance from Serratia marcescens. J Gen Microbiol. 1950 Sep;4(3):417–433. doi: 10.1099/00221287-4-3-417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields K. L., Luria S. E. Effects of colicins E1 and K on cellular metabolism. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jan;97(1):64–77. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.1.64-77.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields K. L., Luria S. E. Effects of colicins E1 and K on transport systems. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jan;97(1):57–63. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.1.57-63.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foulds J. D., Shemin D. Concomitant synthesis of bacteriocin and bacteriocin inactivator from Serratia marcescens. J Bacteriol. 1969 Sep;99(3):661–666. doi: 10.1128/jb.99.3.661-666.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foulds J. D., Shemin D. Properties and characteristics of a bacteriocin from Serratia marcescens. J Bacteriol. 1969 Sep;99(3):655–660. doi: 10.1128/jb.99.3.655-660.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAMON Y., PERON Y. [Study of the bacteriocinogenic property in the genus Serratia]. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1961 Jun;100:818–821. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamon Y., Péron Y. Essai de classification de quelques marcescines. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1965 May 17;260(20):5401–5404. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamon Y., Péron Y. Relations de quelques marcescines actives sur E. coli avec certains types de colicines. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1966 Apr;110(4):556–561. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirata H., Fukui S., Ishikawa S. Initial events caused by colicin K infection--cation movement and depletion of ATP pool. J Biochem. 1969 May;65(5):843–847. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a129088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JACOB F., SIMINOVITCH L., WOLLMAN E. Sur la biosynthèse d'une colicine et sur son mode d'action. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1952 Sep;83(3):295–315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUNDIG W., GHOSH S., ROSEMAN S. PHOSPHATE BOUND TO HISTIDINE IN A PROTEIN AS AN INTERMEDIATE IN A NOVEL PHOSPHO-TRANSFERASE SYSTEM. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Oct;52:1067–1074. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.4.1067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaback H. R. The role of the phosphoenolpyruvate-phosphotransferase system in the transport of sugars by isolated membrane preparations of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1968 Jul 10;243(13):3711–3724. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagel de Zwaig R. Mode of action of colicin A. J Bacteriol. 1969 Sep;99(3):913–914. doi: 10.1128/jb.99.3.913-914.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomura M. Colicins and related bacteriocins. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1967;21:257–284. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.21.100167.001353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prinsloo H. E. Bacteriocins and phages produced by Serratia marcescens. J Gen Microbiol. 1966 Nov;45(2):205–212. doi: 10.1099/00221287-45-2-205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



