Abstract
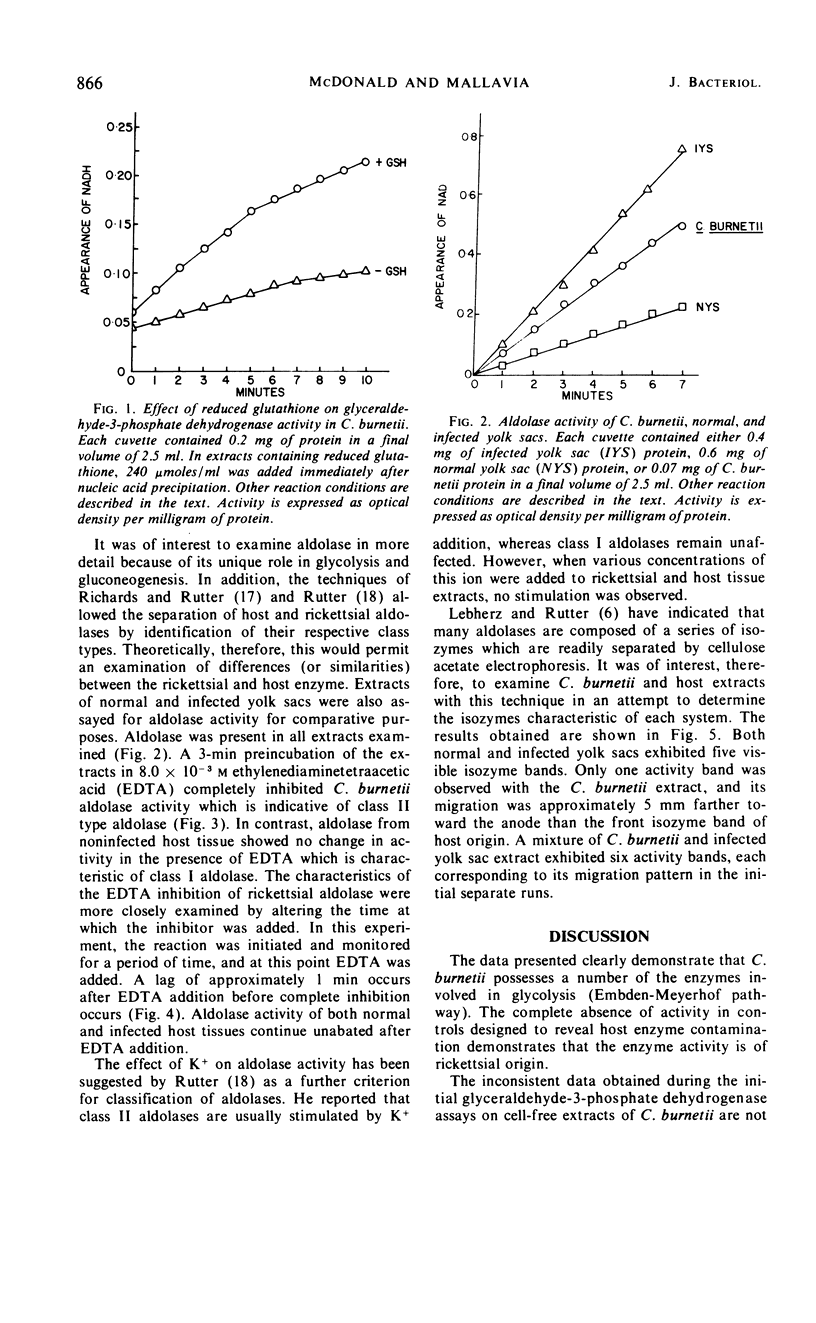
Purified preparations of Coxiella burnetii were examined for enzymes of the glycolytic pathway. Glucose-phosphate isomerase, fructose-1,6-diphosphatase, aldolase, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase, and pyruvate kinase were shown to be present in C. burnetii extracts. Heat-killed C. burnetii purified with normal yolk sacs demonstrated no activity after disruption. Aldolase was shown to be of the class II type by complete inhibition of activity in the presence of 8 × 10−3m ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid. The host enzyme activity (normal and infected yolk sacs) was not affected by the same treatment. When cellulose acetate electrophoresis was performed on the extracts, aldolase from both normal and infected yolk sacs exhibited five isozyme bands, whereas aldolase from the C. burnetii extract appeared as a single band.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atkinson D. E. Regulation of enzyme function. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1969;23:47–68. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.23.100169.000403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CONSIGLI R. A., PARETSKY D. Oxidation of glucose 6-phosphate and isocitrate by Coxiella burnetii. J Bacteriol. 1962 Jan;83:206–207. doi: 10.1128/jb.83.1.206-207.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebherz H. G., Rutter W. J. Distribution of fructose diphosphate aldolase variants in biological systems. Biochemistry. 1969 Jan;8(1):109–121. doi: 10.1021/bi00829a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MERRICK J. M., DOUDOROFF M. DEPOLYMERIZATION OF POLY-BETA-HYDROXYBUTYRATE BY INTRACELLULAR ENZYME SYSTEM. J Bacteriol. 1964 Jul;88:60–71. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.1.60-71.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald T. L., Mallavia L. Biochemistry of Coxiella burnetii: 6-phosphogluconic acid dehydrogenase. J Bacteriol. 1970 Apr;102(1):1–5. doi: 10.1128/jb.102.1.1-5.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ORMSBEE R. A., PEACOCK M. G. METABOLIC ACTIVITY IN COXIELLA BURNETII. J Bacteriol. 1964 Nov;88:1205–1210. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.5.1205-1210.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ormsbee R. A. Rickettsiae (as organisms). Annu Rev Microbiol. 1969;23:275–292. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.23.100169.001423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARETSKY D., DOWNS C. M., CONSIGLI R. A., JOYCE B. K. Studies on the physiology of rickettsiae. I. Some enzyme systems of Coxiella burnetii. J Infect Dis. 1958 Jul-Aug;103(1):6–11. doi: 10.1093/infdis/103.1.6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paretsky D. Biochemistry of rickettsiae and their infected hosts, with special reference to Coxiella burneti. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig. 1968 Apr;206(3):283–291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penhoet E., Rajkumar T., Rutter W. J. Multiple forms of fructose diphosphate aldolase in mammalian tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Oct;56(4):1275–1282. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.4.1275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RICHARDS O. C., RUTTER W. J. Comparative properties of yeast and muscle aldolase. J Biol Chem. 1961 Dec;236:3185–3192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUTTER W. J. EVOLUTION OF ALDOLASE. Fed Proc. 1964 Nov-Dec;23:1248–1257. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rees H. B., Jr, Weiss E. Glutamate catabolism of Rickettsia rickettsi and factors affecting retention of metabolic activity. J Bacteriol. 1968 Feb;95(2):389–396. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.2.389-396.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



