Abstract
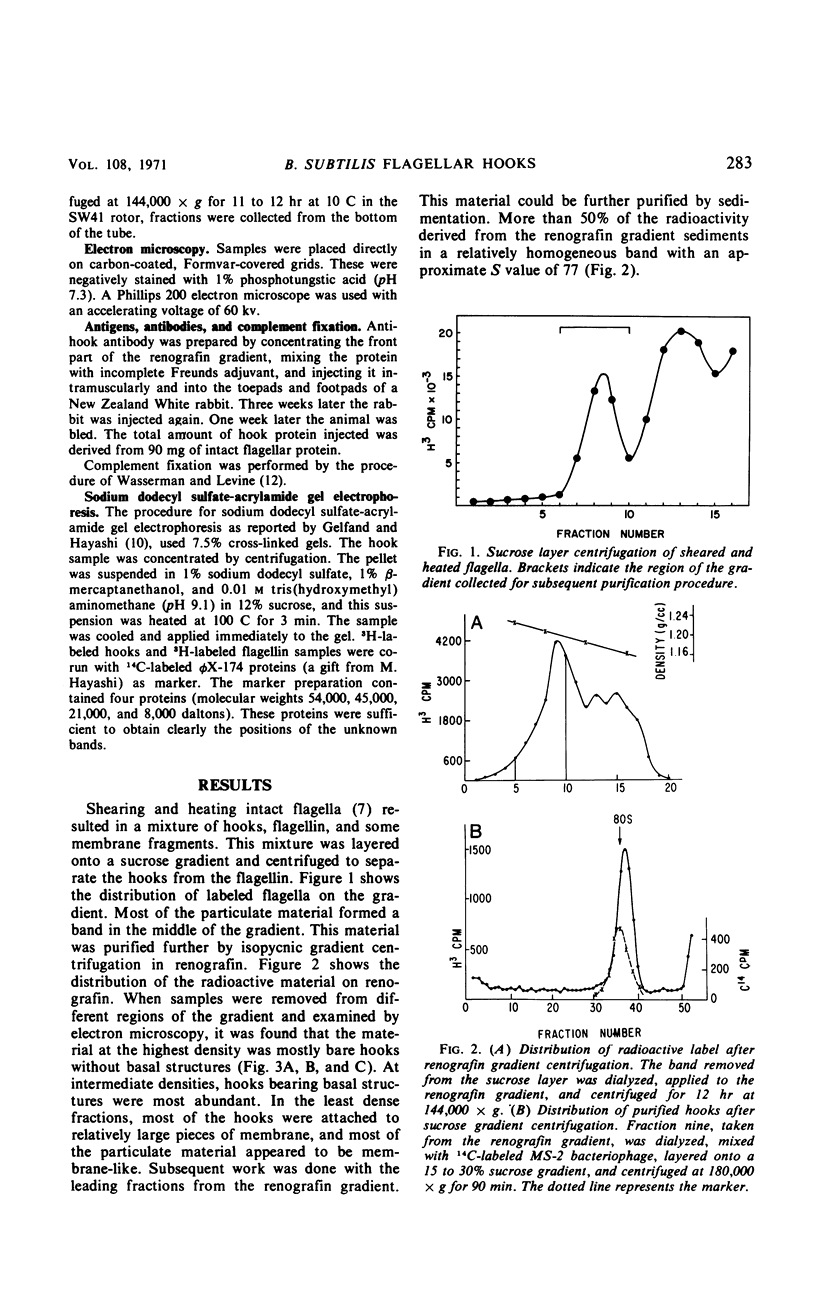
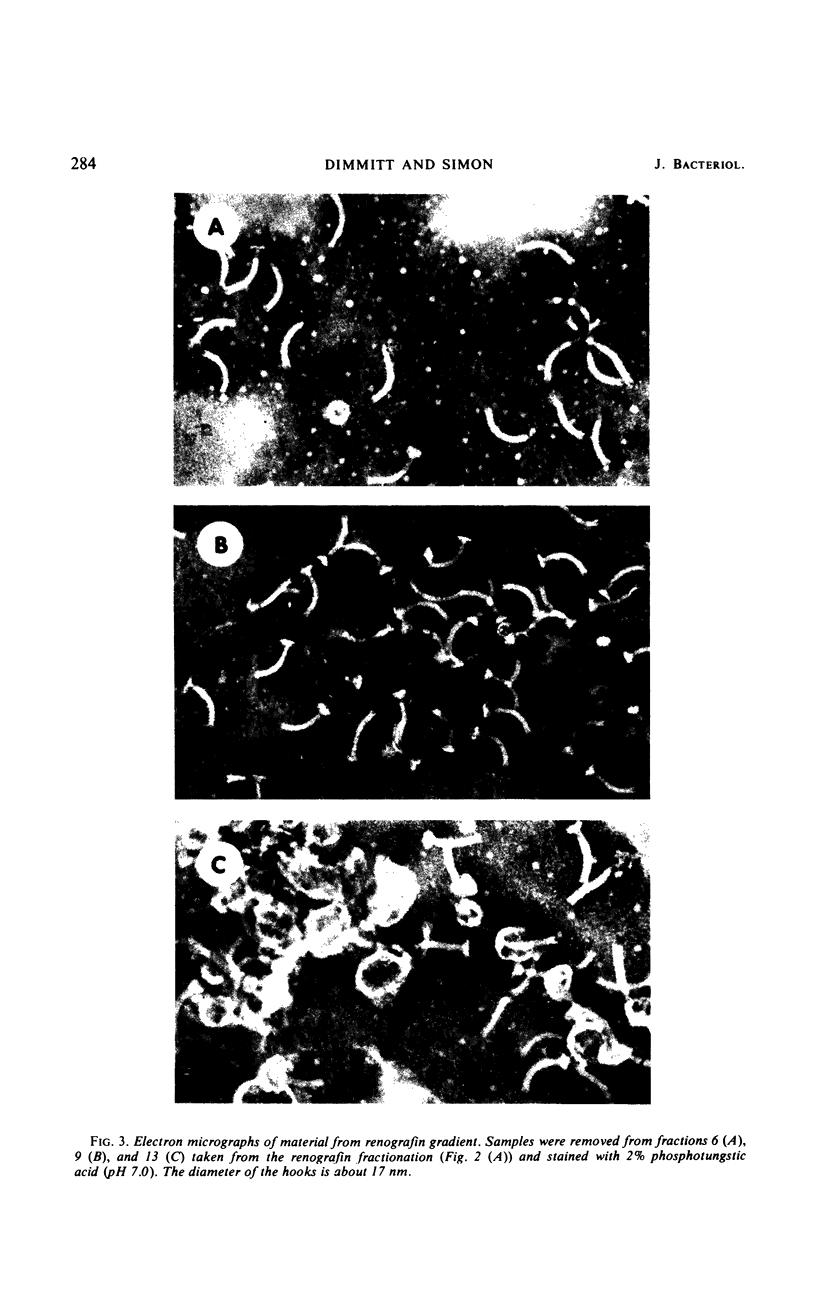
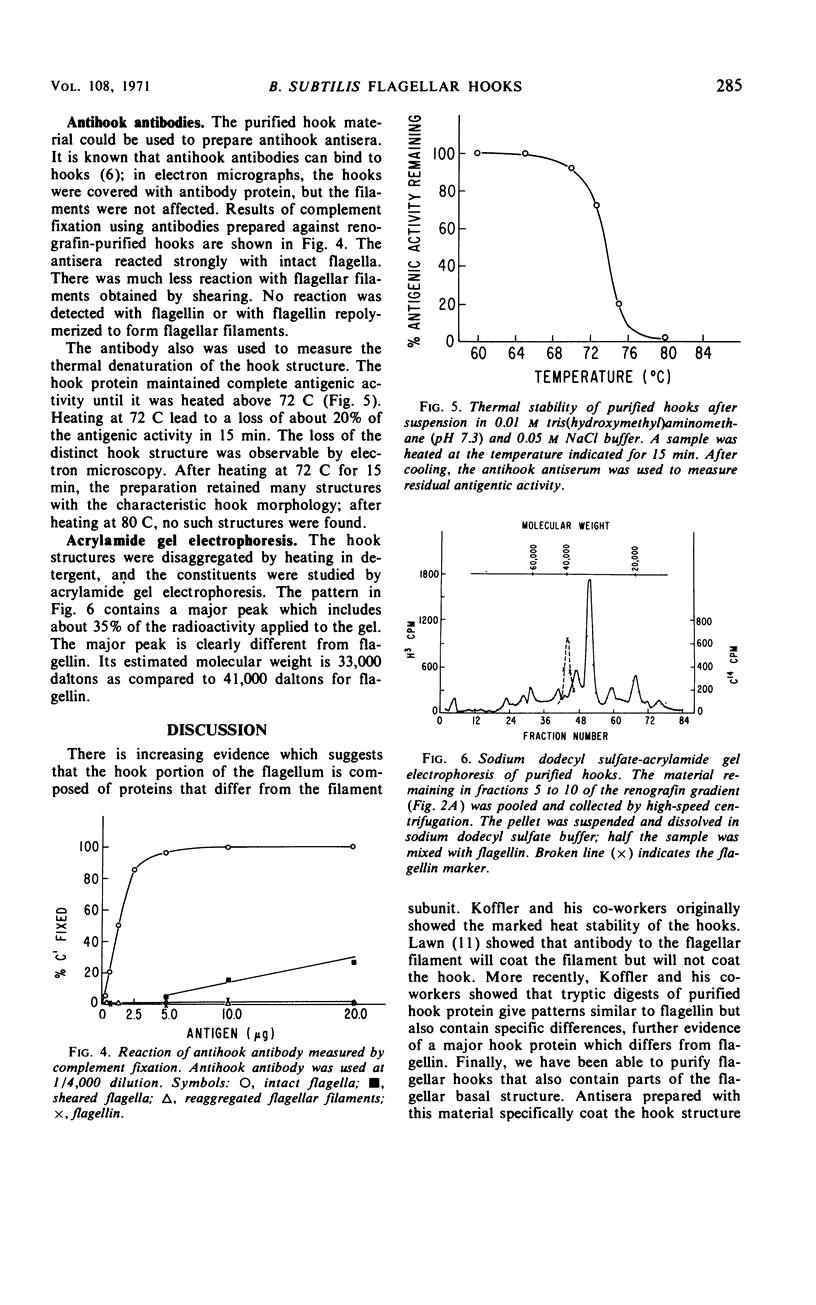
A method for preparing bacterial flagellar hook structures is described. The method involves isolating intact flagella from a mutant which makes thermally labile flagellar filaments and heat-treating them to disaggregate the filament preferentially. The resulting hook preparation can be separated and purified by velocity and isopycnic centrifugation. The purified hooks sediment at a relative S value of 77. On acrylamide gel electrophoresis in sodium dodecyl sulfate, they show one major and a number of minor protein bands. The purified hooks can be used to immunize rabbits, and the resulting antiserum is hook-specific. These results support the notion that hooks are composed of a protein that differs from flagellin.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abram D., Koffler H., Vatter A. E. Basal structure and attachment of flagella in cells of Proteus vulgaris. J Bacteriol. 1965 Nov;90(5):1337–1354. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.5.1337-1354.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
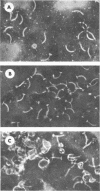
- Abram D., Mitchen J. R., Koffler H., Vatter A. E. Differentiation within the bacterial flagellum and isolation of the proximal hook. J Bacteriol. 1970 Jan;101(1):250–261. doi: 10.1128/jb.101.1.250-261.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abram D., Vatter A. E., Koffler H. Attachment and structural features of flagella of certain bacilli. J Bacteriol. 1966 May;91(5):2045–2068. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.5.2045-2068.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen-Bazire G., London J. Basal organelles of bacterial flagella. J Bacteriol. 1967 Aug;94(2):458–465. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.2.458-465.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DePamphilis M. L., Adler J. Fine structure and isolation of the hook-basal body complex of flagella from Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1971 Jan;105(1):384–395. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.1.384-395.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dimmitt K., Simon M. Antigenic nature of bacterial flagellar hook structures. Infect Immun. 1970 Feb;1(2):212–213. doi: 10.1128/iai.1.2.212-213.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dimmitt K., Simon M. Purification and thermal stability of intact Bacillus subtilis flagella. J Bacteriol. 1971 Jan;105(1):369–375. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.1.369-375.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doetsch R. N., Hageage G. J. Motility in procaryotic organisms: problems, points of view, and perspectives. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 1968 Aug;43(3):317–362. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-185x.1968.tb00963.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerson S. U., Tokuyasu K., Simon M. I. Bacterial flagella: polarity of elongation. Science. 1970 Jul 10;169(3941):190–192. doi: 10.1126/science.169.3941.190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelfand D. H., Hayashi M. Electrophoretic characterization of phiX174-specific proteins. J Mol Biol. 1969 Sep 28;44(3):501–516. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90376-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawn A. M. Simple immunological labelling method for electron microscopy and its application to the study of filamentous appendages of bacteria. Nature. 1967 Jun 10;214(5093):1151–1152. doi: 10.1038/2141151a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WASSERMAN E., LEVINE L. Quantitative micro-complement fixation and its use in the study of antigenic structure by specific antigen-antibody inhibition. J Immunol. 1961 Sep;87:290–295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]