Abstract
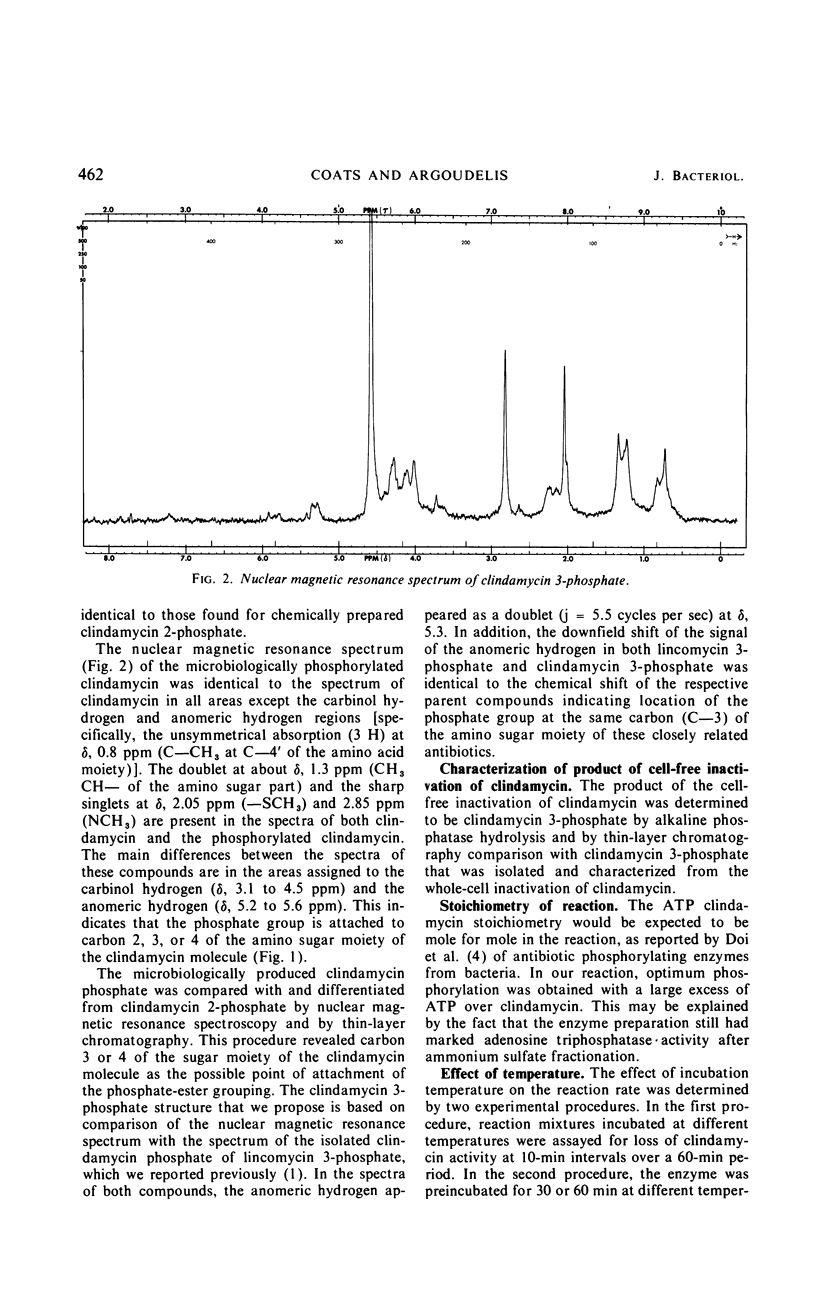
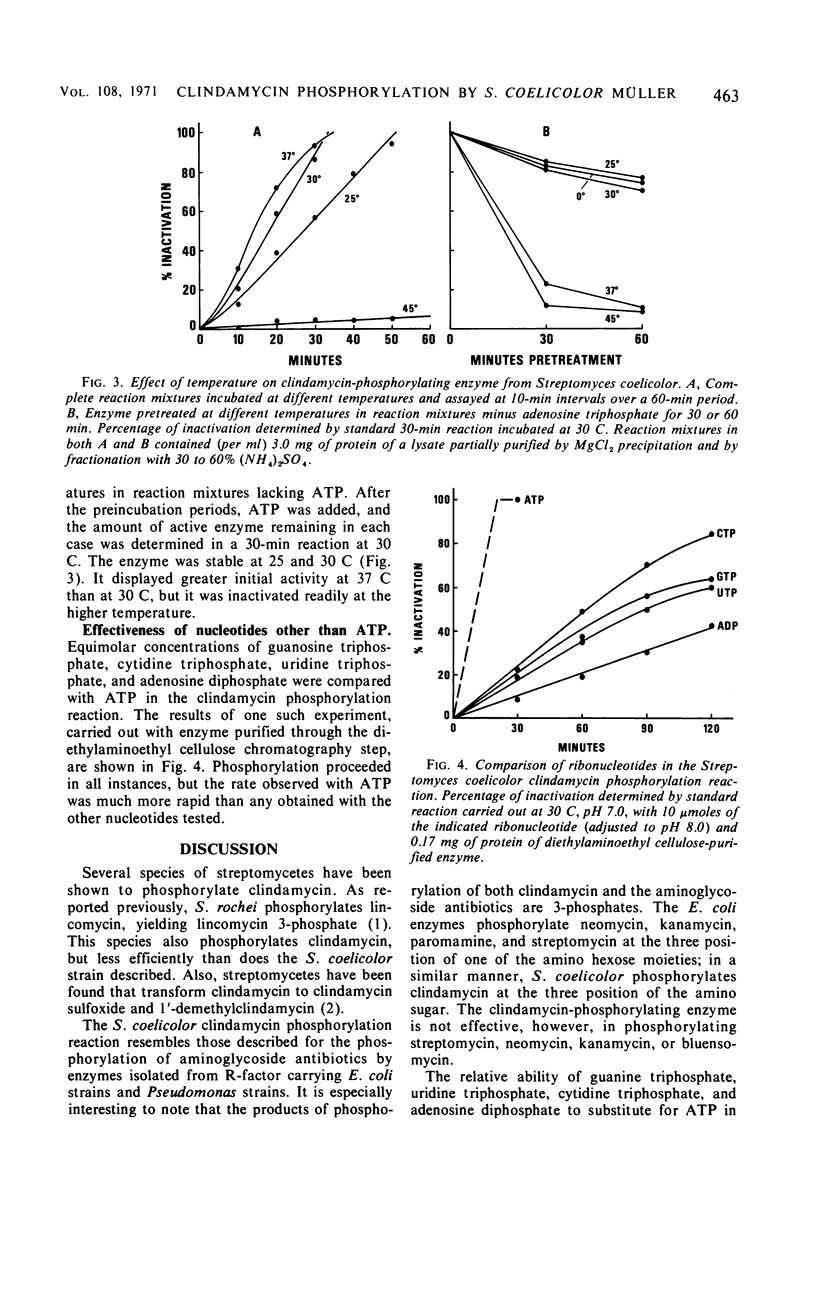
Addition of clindamycin to whole-cell cultures of Streptomyces coelicolor Müller resulted in the loss of in vitro activity against organisms sensitive to clindamycin. Incubation of such culture filtrates with alkaline phosphatase generated a biologically active material identified as clindamycin. Fermentation broths containing inactivated clindamycin yielded clindamycin 3-phosphate, the structure of which was established by physical-chemical and enzymatic studies. Clindamycin was phosphorylated by lysates and partially purified enzyme preparations from S. coelicolor Müller. These reactions require a ribonucleoside triphosphate and Mg2+. The product of the cell-free reactions was identified as clindamycin 3-phosphate.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Argoudelis A. D., Coats J. H., Mason D. J., Sebek O. K. Microbial transformation of antibiotics. 3. Conversion of clindamycin to 1'-demethylclindamycin and clindamycin sulfoxide by Streptomyces species. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1969 Jul;22(7):309–314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Argoudelis A. D., Coats J. H. Microbial transformation of antibiotics. II. Phosphorylation of lincomycin by Streptomyces species. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1969 Jul;22(7):341–343. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.22.341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doi O., Kondo S., Tanaka N., Umezawa H. Purification and properties of kanamycin-phosphorylating enzyme from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1969 Jun;22(6):273–282. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.22.273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doi O., Miyamoto M., Tanaka N., Umezawa H. Inactivation and phosphorylation of kanamycin by drug-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Appl Microbiol. 1968 Sep;16(9):1282–1284. doi: 10.1128/am.16.9.1282-1284.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doi O., Ogura M., Tanaka N., Umezawa H. Inactivation of kanamycin, neomycin, and streptomycin by enzymes obtained in cells of Pseudomonas aeruginoa. Appl Microbiol. 1968 Sep;16(9):1276–1281. doi: 10.1128/am.16.9.1276-1281.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hey A. E., Elbein A. D. Partial prufication and properties of a trehalase from Streptomyces hygroscopicus. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jul;96(1):105–110. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.1.105-110.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondo S., Okanishi M., Utahara R., Maeda K., Umezawa H. Isolation of kanamycin and paromamine inactivated by E. coli carrying R factor. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1968 Jan;21(1):22–29. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.21.22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magerlein B. J., Birkenmeyer R. D., Kagan F. Chemical modification of lincomycin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother (Bethesda) 1966;6:727–736. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morozowich W., Lamb D. J., Karnes H. A., Mackellar F. A., Lewis C., Stern K. F., Rowe E. L. Synthesis and bioactivity of lincomycin-2-phosphate. J Pharm Sci. 1969 Dec;58(12):1485–1489. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600581213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okanishi K., Kondo S., Utahara R., Umezawa H. Phosphorylation and inactivation of aminoglycosidic antibiotics by E. coli carrying R factor. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1968 Jan;21(1):13–21. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.21.13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozanne B., Benveniste R., Tipper D., Davies J. Aminoglycoside antibiotics: inactivation by phosphorylation in Escherichia coli carrying R factors. J Bacteriol. 1969 Nov;100(2):1144–1146. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.2.1144-1146.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spizizen J. TRANSFORMATION OF BIOCHEMICALLY DEFICIENT STRAINS OF BACILLUS SUBTILIS BY DEOXYRIBONUCLEATE. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1958 Oct 15;44(10):1072–1078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.44.10.1072. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umezawa H., Okanishi M., Kondo S., Hamana K., Utahara R., Maeda K., Mitsuhashi S. Phosphorylative inactivation of aminoglycosidic antibiotics by Escherichia coli carrying R factor. Science. 1967 Sep 29;157(3796):1559–1561. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada T., Tipper D., Davies J. Enzymatic inactivation of streptomycin by R factor-resistant Escherichia coli. Nature. 1968 Jul 20;219(5151):288–291. doi: 10.1038/219288a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



