Abstract
The intracellular and constitutive arylamidase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa was purified 528-fold by salt fractionation, ion-exchange chromatography, gel filtration, and adsorption chromatography. This enzyme hydrolyzed basic and neutral N-terminal amino acid residues from amino-β-naphthylamides, dipeptide-β-naphthylamides, and a variety of polypeptides. Only those substrates having an l-amino acid with an unsubstituted α-amino group as the N-terminal residue were susceptible to enzymatic hydrolysis. The molecular weight was estimated to be 71,000 daltons. The lowest Km values were associated with substrates having neutral or basic amino acid residues with large side chains with no substitution or branching on the β carbon atom.
Full text
PDF



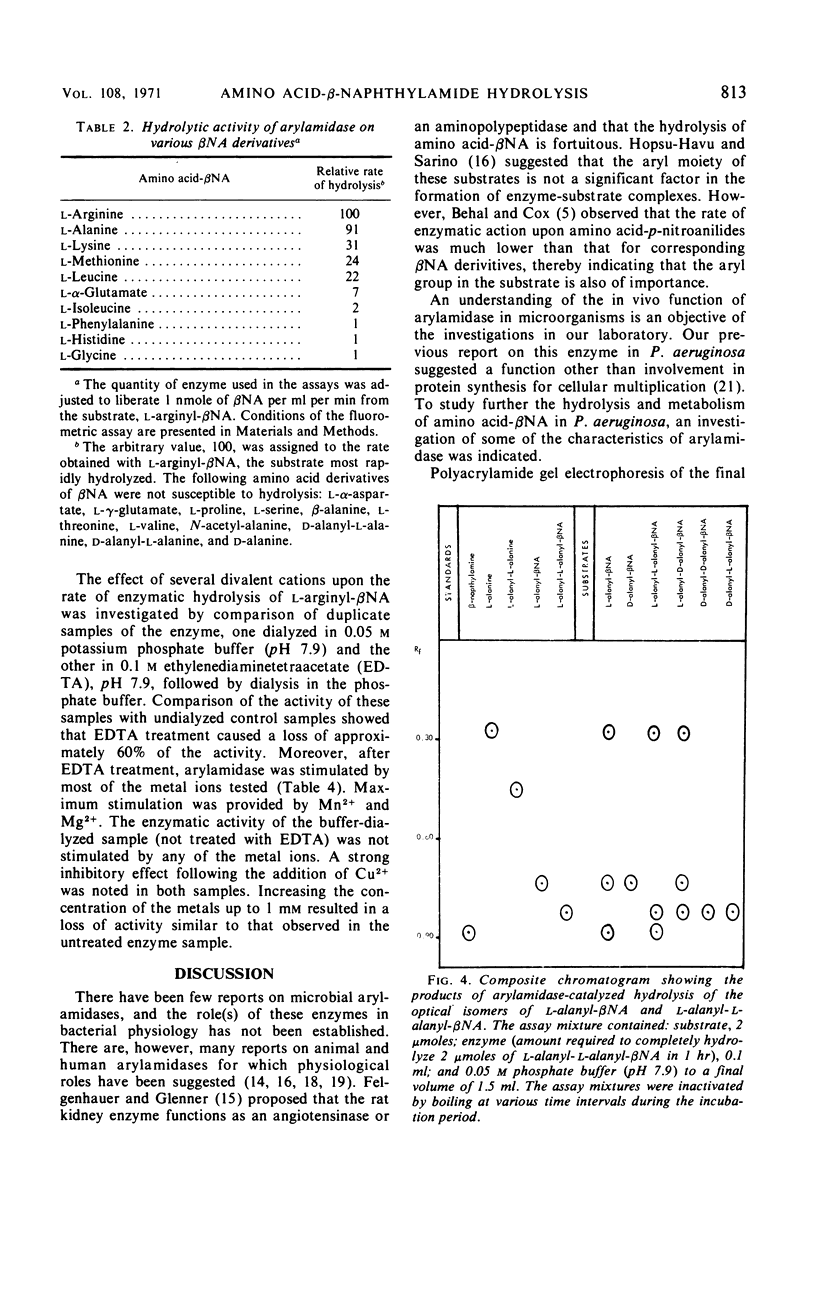
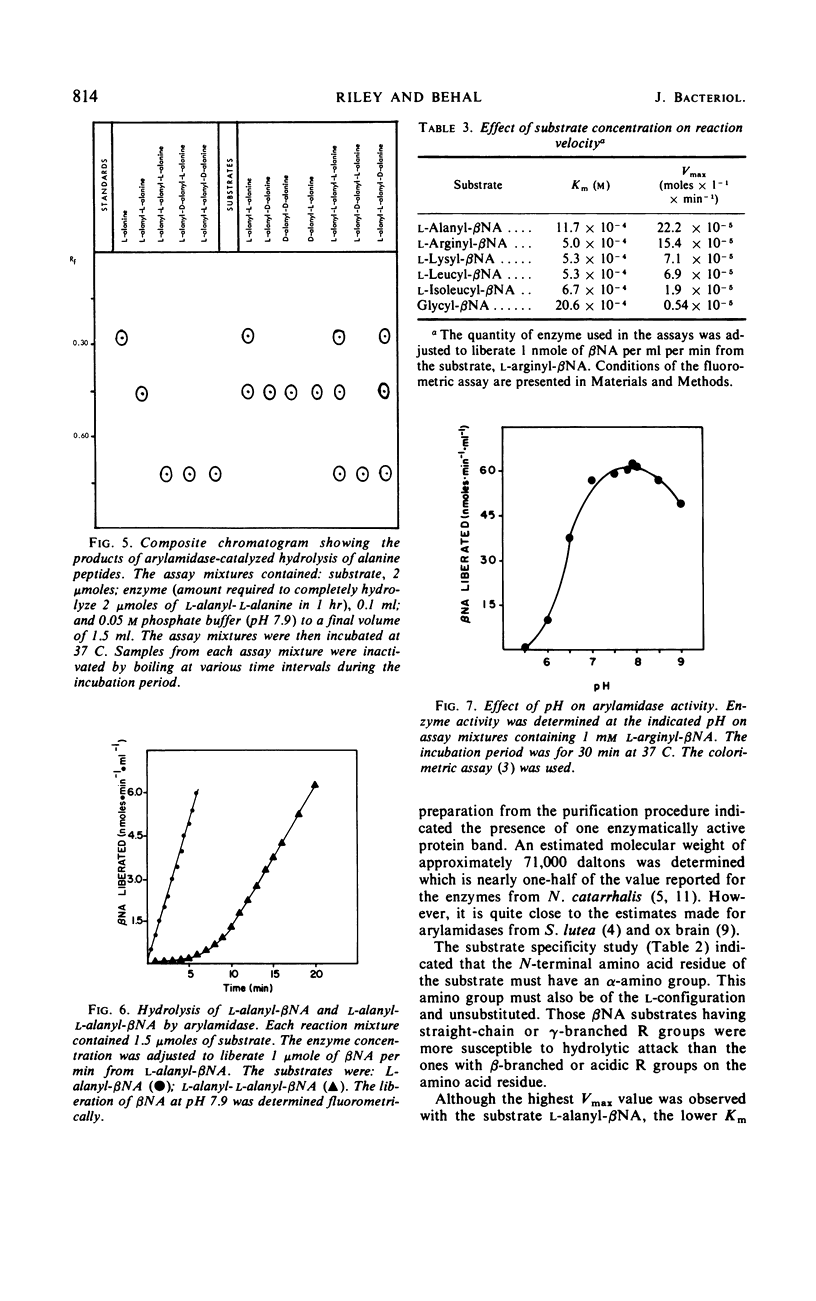


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews P. Estimation of the molecular weights of proteins by Sephadex gel-filtration. Biochem J. 1964 May;91(2):222–233. doi: 10.1042/bj0910222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aubert J. P., Millet J. Etude d'une L-leucyl-beta-naphtylamide hydrolase en relation avec la sporulation chez Bacillus megaterium. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1965 Nov 15;261(20):4274–4277. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behal F. J., Asserson B., Dawson F., Hardman J. A study of human tissue aminopeptidase components. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1965 Aug;111(2):335–344. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(65)90194-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behal F. J., Carter R. T. Naphthylamidases of Sarcina lutea. Can J Microbiol. 1971 Jan;17(1):39–45. doi: 10.1139/m71-007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behal F. J., Cox S. T. Arylamidase of Neisseria catarrhalis. J Bacteriol. 1968 Oct;96(4):1240–1248. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.4.1240-1248.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behal F. J., Folds J. D. A comparative study of bacterial alanine aminohydrolases. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 May 5;27(3):344–349. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(67)80104-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behal F. J., Little G. H. Arylamidase of human duodenum. Clin Chim Acta. 1968 Sep;21(3):347–355. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(68)90065-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behal F. J., Little G. H., Klein R. A. Arylamidase of human liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Mar 18;178(1):118–127. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(69)90138-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brecher A. S., Suszkiw J. B. Brain arylamidase. Purfication and characterization of the soluble bovine enzyme. Biochem J. 1969 Apr;112(3):335–342. doi: 10.1042/bj1120335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burton G., Blenden D. C., Goldberg H. S. Naphthylamidase activity of Leptospira. Appl Microbiol. 1970 Apr;19(4):586–588. doi: 10.1128/am.19.4.586-588.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox S. T., Behal F. J. Alpha-glutamic acid-beta-naphthylamidase from Neisseria catarrhalis. Can J Microbiol. 1969 Nov;15(11):1293–1300. doi: 10.1139/m69-234. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox S. T., Behal F. J. Specificity of Neisseria catarrhalis arylamidase. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1970 Apr;133(4):1247–1249. doi: 10.3181/00379727-133-34662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis S., Nuenke J. M. Dipeptidyl arylamidase III of the pituitary. Purification and characterization. J Biol Chem. 1967 Oct 25;242(20):4623–4629. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felgenhauer K., Glenner G. G. The enzymatic hydrolysis of amino acid beta-naphthylamides. II. Partial purification and properties of a particle-bound cobalt-activated rat kidney aminopeptidase. J Histochem Cytochem. 1966 May;14(5):401–413. doi: 10.1177/14.5.401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopsu-Havu V. K., Sarimo S. R. Purification and characterization of an aminopeptidase hydrolyzing glycyl-proline-naphthylamide. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1967 Nov;348(11):1540–1550. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1967.348.1.1540. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marks N., Datta R. K., Lajtha A. Partial resolution of brain arylamidases and aminopeptidases. J Biol Chem. 1968 Jun 10;243(11):2882–2889. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muftić M. Application of chromogenic substrates to the determination of peptidases in mycobacteria. Folia Microbiol (Praha) 1967;12(6):500–507. doi: 10.1007/BF02875711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riley P. S., Behal F. J. Amino acid-beta-naphthylamide uptake by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1971 Mar;105(3):747–752. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.3.747-752.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH E. L., SPACKMAN D. H. Leucine aminopeptidase. V. Activation, specificity, and mechanism of action. J Biol Chem. 1955 Jan;212(1):271–299. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. S., Matheson A. T. Purification and properties of a ribosomal peptidase from Escherichia coli B. Can J Biochem. 1965 Oct;43(10):1643–1652. doi: 10.1139/o65-181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westley J. W., Anderson P. J., Close V. A., Halpern B., Lederberg E. M. Aminopeptidase profiles of various bacteria. Appl Microbiol. 1967 Jul;15(4):822–825. doi: 10.1128/am.15.4.822-825.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




