Abstract
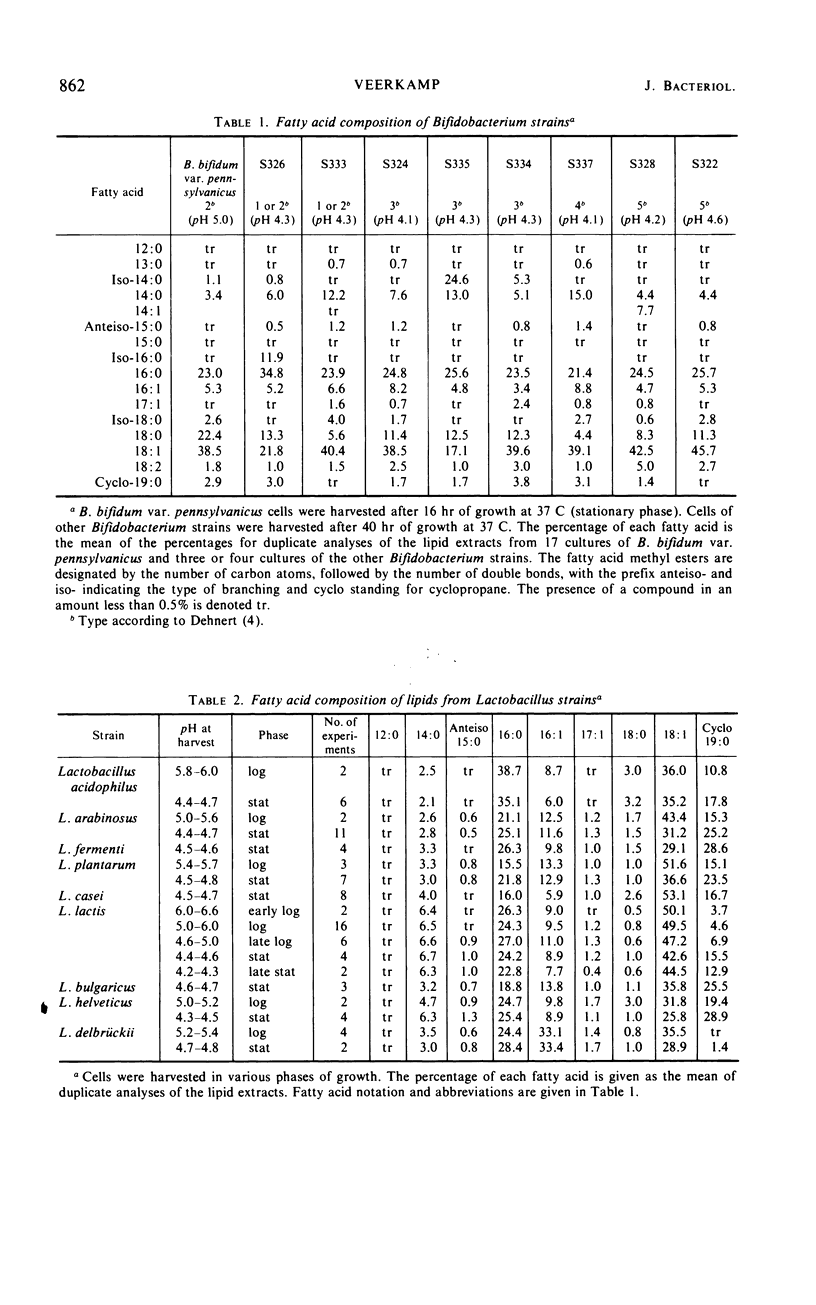
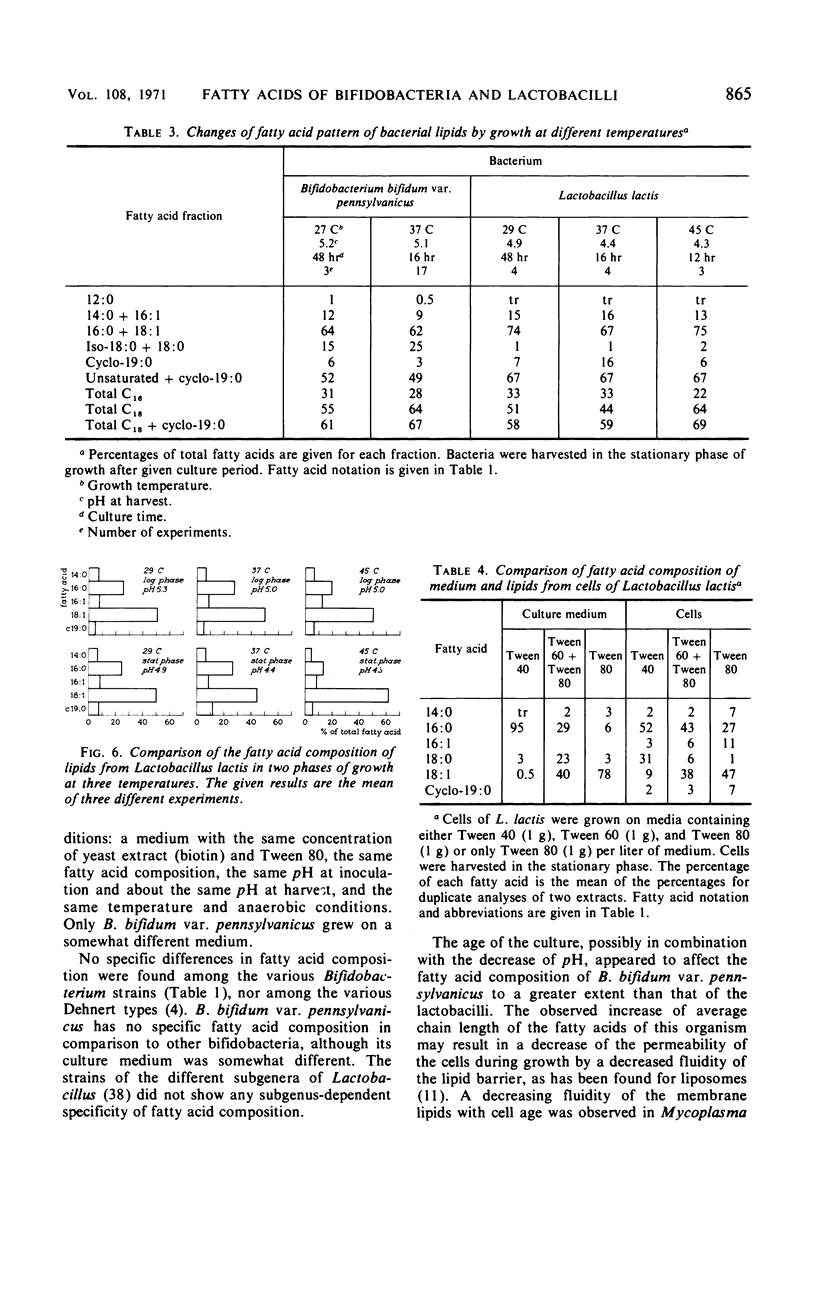
Normal C14, C16, and C18 saturated acids and C16 and C18 monoenoic acids are the main fatty acids of nine strains of Bifidobacterium. Their lactobacillic acid content was less than 5%. Lactobacillus strains contained the same fatty acids as main compounds except for octadecanoic acid, which was present only in very low amounts. Eight of nine Lactobacillus strains contained in the stationary phase more than 15% lactobacillic acid. No correlation was observed between the fatty acid composition and other physiological characteristics used in the literature for classification of strains of one genus. Aging of the culture, which involved a decrease of the pH, caused a lengthening of the chain length of the fatty acids of B. bifidum var. pennsylvanicus but only a conversion of octadecenoic to lactobacillic acid in the lactobacilli. Lowering of the temperature of cultivation decreased the chain length of the fatty acids of B. bifidum var. pennsylvanicus. L. lactis did not show any influence of the temperature on the chain length of the fatty acids. The percentage of unsaturated acids was temperature independent in both organisms.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BISHOP D. G., STILL J. L. FATTY ACID METABOLISM IN SERRATIA MARCESCENS. IV. THE EFFECT OF TEMPERATURE ON FATTY ACID COMPOSITION. J Lipid Res. 1963 Jan;4:87–90. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLIGH E. G., DYER W. J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Aug;37(8):911–917. doi: 10.1139/o59-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown C. M., Rose A. H. Fatty-acid composition of Candida utilis as affected by growth temperature and dissolved-oxygen tension. J Bacteriol. 1969 Aug;99(2):371–378. doi: 10.1128/jb.99.2.371-378.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEHNERT J. Untersuchung über die gram-positive Stuhlflora des Brustmilchkindes. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig. 1957 Jul;169(1-2):66–83. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esfahani M., Barnes E. M., Jr, Wakil S. J. Control of fatty acid composition in phospholipids of Escherichia coli: response to fatty acid supplements in a fatty acid auxotroph. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Nov;64(3):1057–1064. doi: 10.1073/pnas.64.3.1057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Exterkate F. A., Otten B. J., Wassenberg H. W., Veerkamp J. H. Comparison of the phospholipid composition of Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus strains. J Bacteriol. 1971 Jun;106(3):824–829. doi: 10.1128/jb.106.3.824-829.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Exterkate F. A., Veerkamp J. H. Biochemical changes in Bifidobacterium bifidum var. Pennsylvanicus after cell wall inhibition. I. Composition of lipids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Jan 21;176(1):65–77. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(69)90075-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrell J., Rose A. Temperature effects on microorganisms. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1967;21:101–120. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.21.100167.000533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farshtchi D., McClung N. M. Effect of substrate on fatty acid production in Nocardia asteroides. Can J Microbiol. 1970 Apr;16(4):213–217. doi: 10.1139/m70-039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haest C. W., de Gier J., van Deenen L. L. Changes in the chemical and the barrier properties of the membrane lipids of E. coli by variation of the temperature of growth. Chem Phys Lipids. 1969 Dec;3(4):413–417. doi: 10.1016/0009-3084(69)90048-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock I. C., Meadow P. M. The extractable lipids of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Oct 28;187(3):366–379. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(69)90010-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joyce G. H., Hammond R. K., White D. C. Changes in membrane lipid composition in exponentially growing Staphylococcus aureus during the shift from 37 to 25 C. J Bacteriol. 1970 Oct;104(1):323–330. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.1.323-330.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATES M., ADAMS G. A., MARTIN S. M. LIPIDS OF SERRATIA MARCESCENS. Can J Biochem. 1964 Apr;42:461–479. doi: 10.1139/o64-054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATES M., BAXTER R. M. Lipid composition of mesophilic and psychrophilic yeasts (Candida species) as influenced by environmental temperature. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1962 Sep;40:1213–1227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATES M., HAGEN P. O. INFLUENCE OF TEMPERATURE ON FATTY ACID COMPOSITION OF PSYCHROPHILIC AND MESOPHILIC SERRATIA SPECIES. Can J Biochem. 1964 Apr;42:481–488. doi: 10.1139/o64-055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaneda T. Fatty acids in the genus Bacillus. II. Similarity in the fatty acid compositions of Bacillus thuringiensis, Bacillus anthracis, and Bacillus cereus. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jun;95(6):2210–2216. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.6.2210-2216.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kates M. Bacterial lipids. Adv Lipid Res. 1964;2:17–90. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kates M. Biosynthesis of lipids in microorganisms. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1966;20:13–44. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.20.100166.000305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kates M., Wassef M. K. Lipid chemistry. Annu Rev Biochem. 1970;39:323–358. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.39.070170.001543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knivett V. A., Cullen J. Fatty acid synthesis in Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1967 May;103(2):299–306. doi: 10.1042/bj1030299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knivett V. A., Cullen J. Some factors affecting cyclopropane acid formation in Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1965 Sep;96(3):771–776. doi: 10.1042/bj0960771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LENNARZ W. J., SCHEUERBRANDT G., BLOCH K. The biosynthesis of oleic and 10-methylstearic acids in Mycobacterium phlei. J Biol Chem. 1962 Mar;237:664–671. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marr A. G., Ingraham J. L. EFFECT OF TEMPERATURE ON THE COMPOSITION OF FATTY ACIDS IN ESCHERICHIA COLI. J Bacteriol. 1962 Dec;84(6):1260–1267. doi: 10.1128/jb.84.6.1260-1267.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss C. W., Dowell V. R., Jr, Farshtchi D., Raines L. J., Cherry W. B. Cultural characteristics and fatty acid composition of propionibacteria. J Bacteriol. 1969 Feb;97(2):561–570. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.2.561-570.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Leary W. M. Decenoic, dodecenoic, and tetradecenoic acids in the Lactobacteriaceae. Biochemistry. 1965 Aug;4(8):1621–1627. doi: 10.1021/bi00884a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okuyama H. Phospholipid metabolism in Escherichia coli after a shift in temperature. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Jan 21;176(1):125–134. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panos C., Rottem S. Incorporation and elongation of fatty acid isomers by Mycoplasma laidlawii A. Biochemistry. 1970 Jan 20;9(2):407–412. doi: 10.1021/bi00804a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson G. W. Effect of culture temperature on fatty acid composition of Chlorella sorokiniana. Lipids. 1970 Jul;5(7):597–600. doi: 10.1007/BF02531336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin S. Structure and function in mycoplasma. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1969;23:317–356. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.23.100169.001533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin S., Tourtellotte M. E., McElhaney R. N., Pollack J. D. Influence of lipid components of Mycoplasma laidlawii membranes on osmotic fragility of cells. J Bacteriol. 1966 Feb;91(2):609–616. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.2.609-616.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rottem S., Hubbell W. L., Hayflick L., McConnell H. M. Motion of fatty acid spin labels in the plasma membrane of mycoplasma. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970;219(1):104–113. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(70)90065-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell N. J. Alteration in fatty acid chain length in Micrococcus cryophilus grown at different temperatures. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Feb 2;231(1):254–256. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(71)90277-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scandella C. J., Kornberg A. Biochemical studies of bacterial sporulation and germination. XV. Fatty acids in growth, sporulation, and germination of Bacillus megaterium. J Bacteriol. 1969 Apr;98(1):82–86. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.1.82-86.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THORNE K. J., KODICEK E. The metabolism of acetate and mevalonic acid by lactobacilli. IV. Analysis of the fatty acids by gas-liquid chromatography. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 May 21;59:306–312. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90178-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urakami C., Umetani K. Compositions of phosphatides from Bacillus natto at various growth phases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Sep 2;164(1):64–71. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veerkamp J. H. Biochemical changes in Bifidobacterium bifidum var. Pennsylvanicus after cell wall inhibition. II. Fatty acid composition. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Jul 14;210(2):267–275. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(70)90171-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Váczi L., Rédai I., Réthy A. Changes in the fatty acid composition of Staphylococcus aureus under various cultural conditions. Acta Microbiol Acad Sci Hung. 1967;14(3):293–298. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeks G., Wakil S. J. Studies on the control of fatty acid metabolism. II. The inhibition of fatty acid synthesis in Lactobacillus plantarum by exogenous fatty acid. J Biol Chem. 1970 Apr 25;245(8):1913–1921. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Gier J., Mandersloot J. G., van Deenen L. L. Lipid composition and permeability of liposomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Jun 11;150(4):666–675. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(68)90056-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



