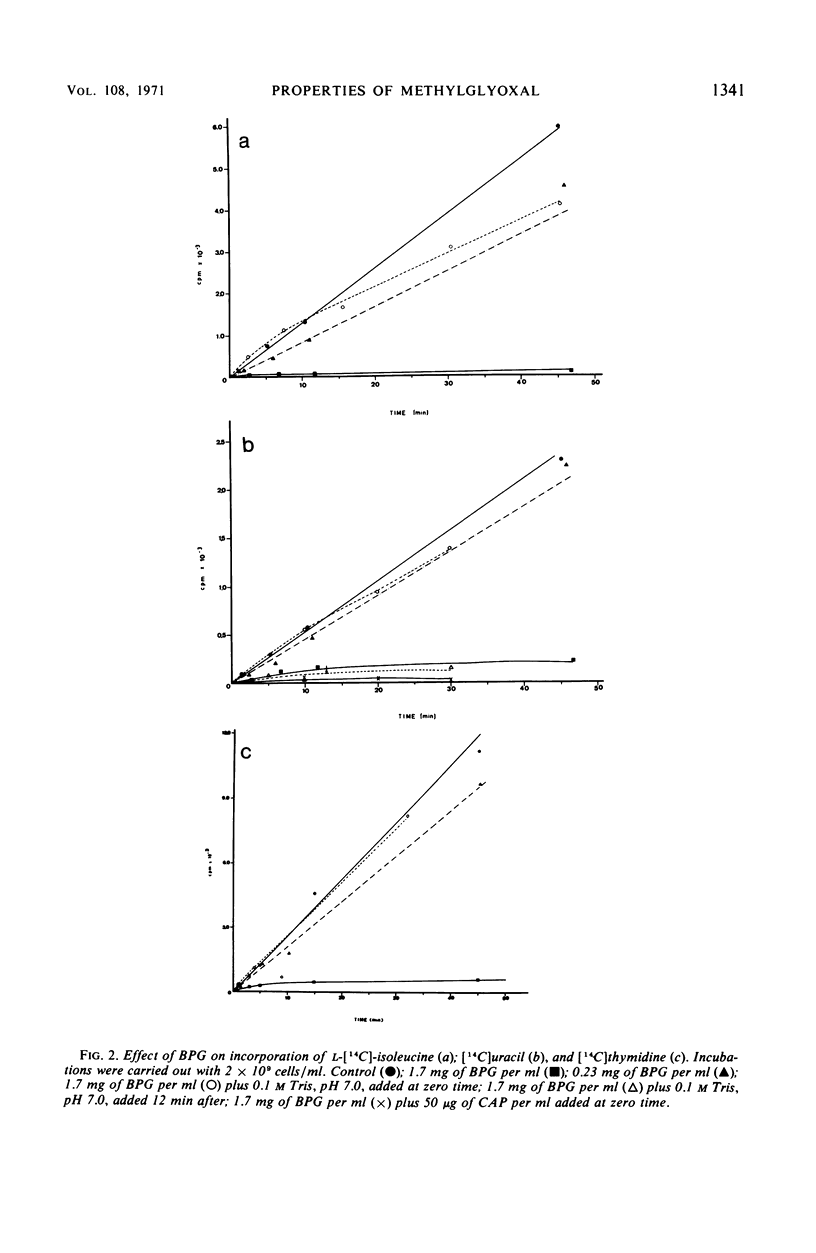
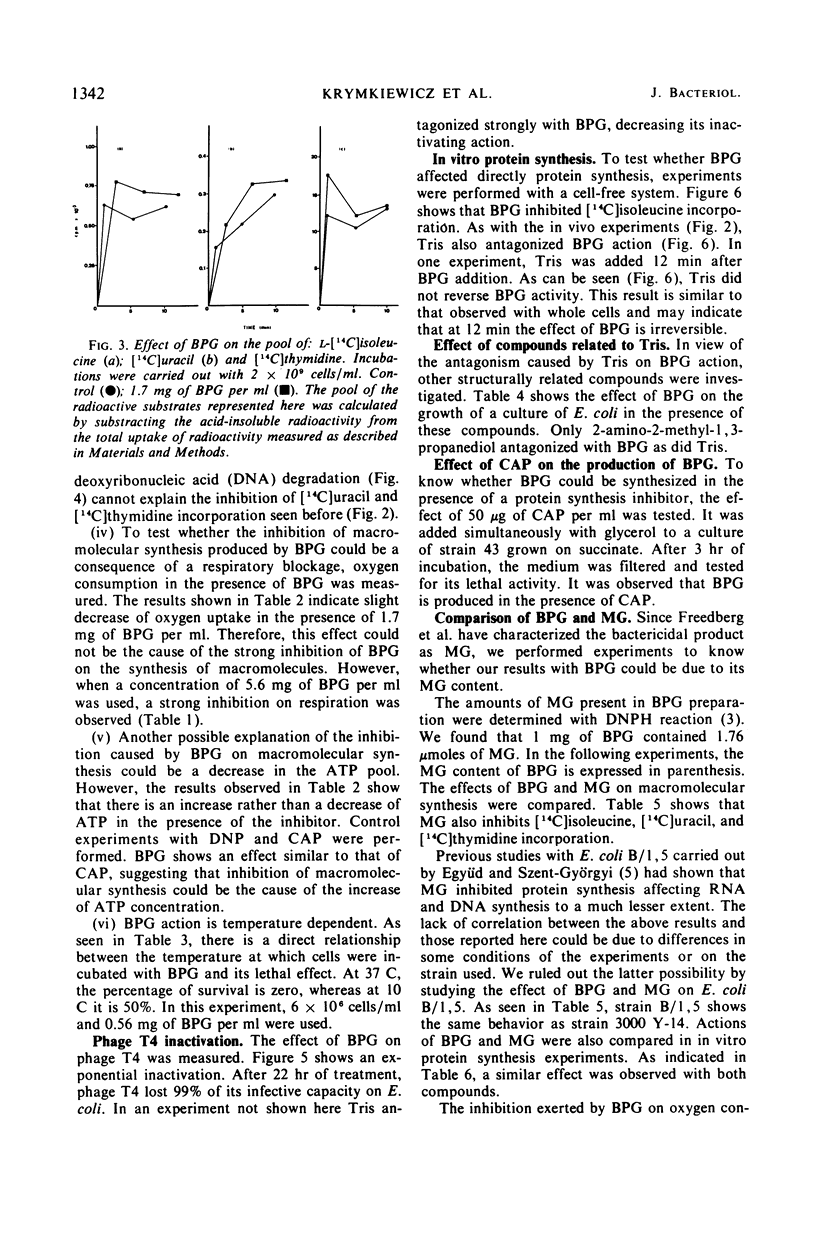
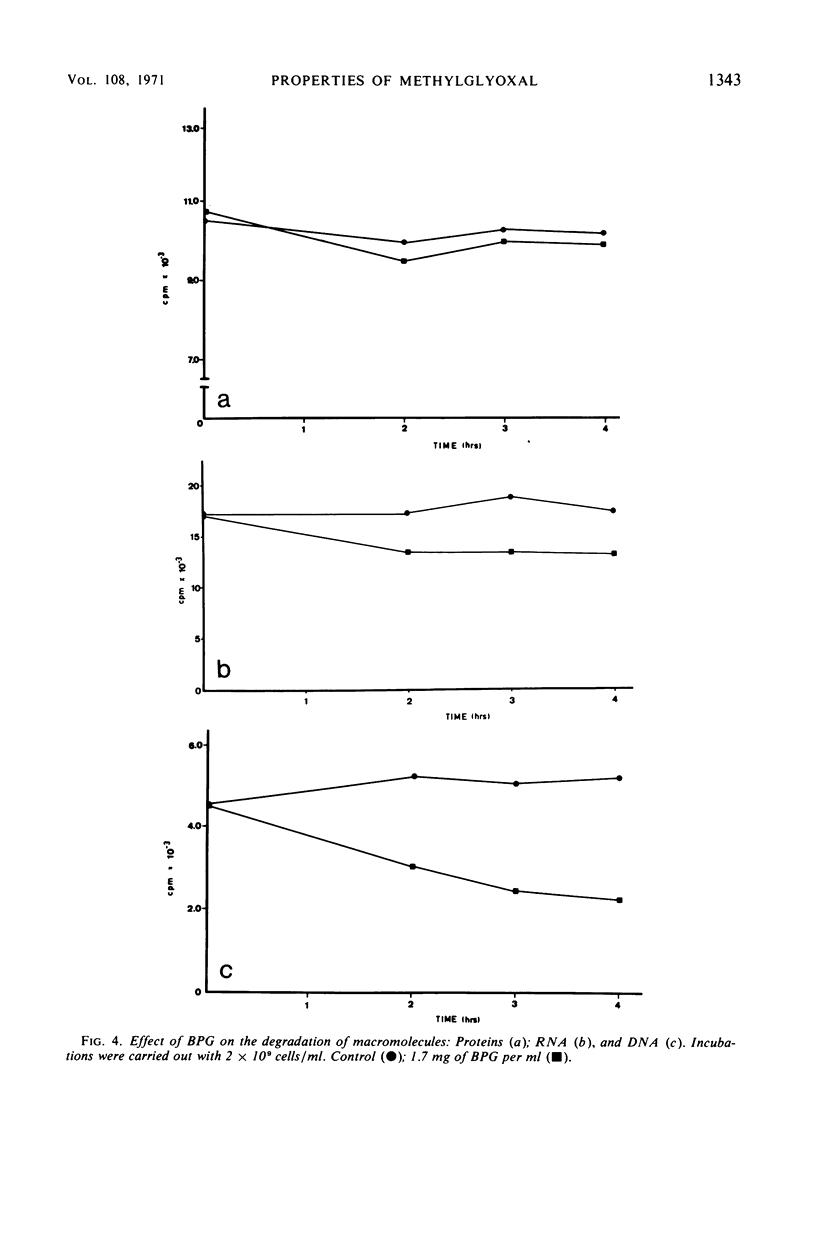
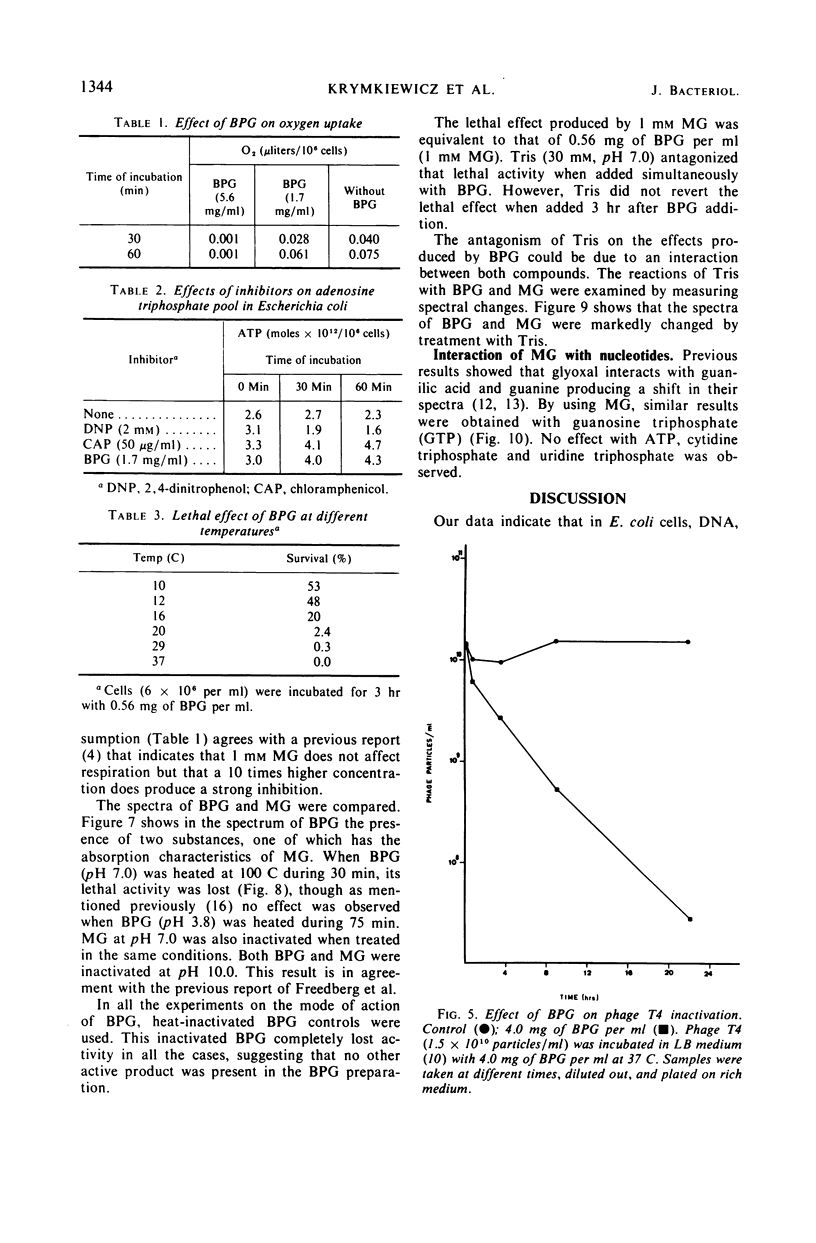
Abstract
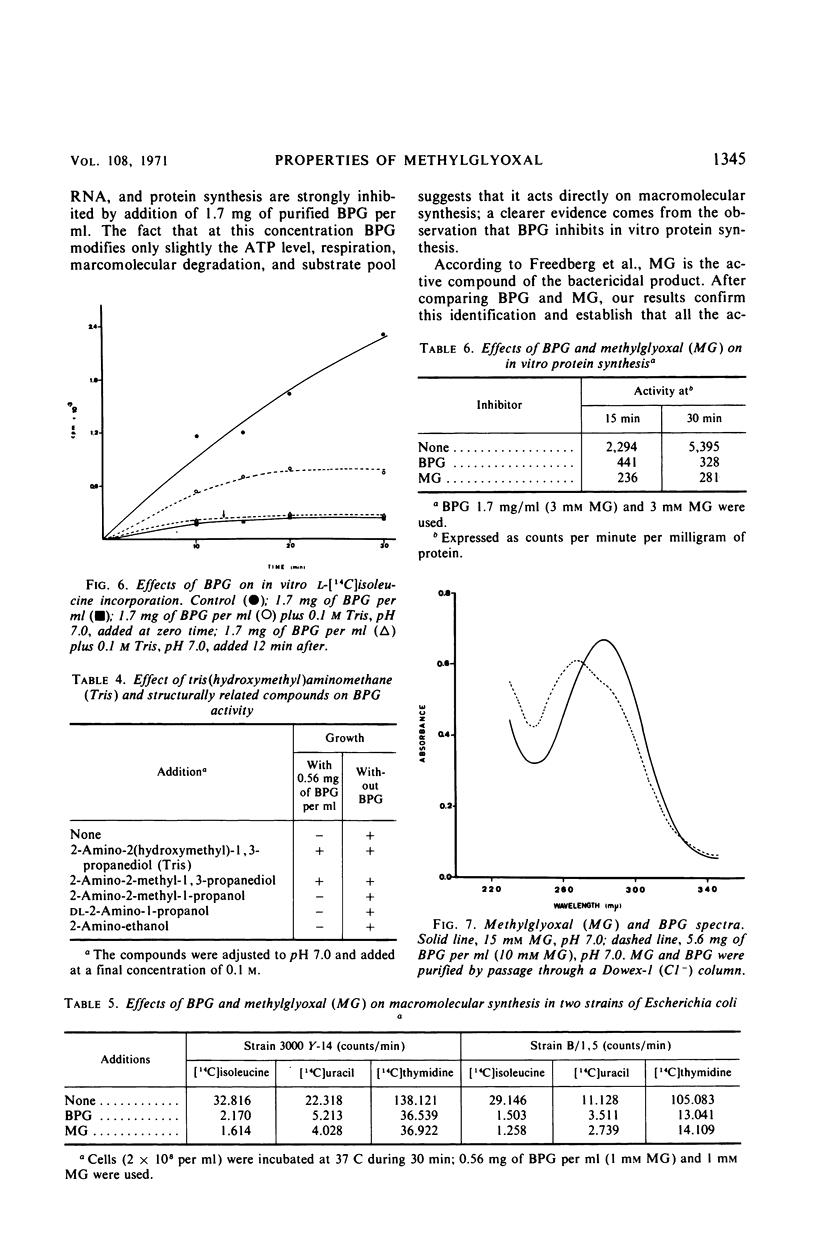
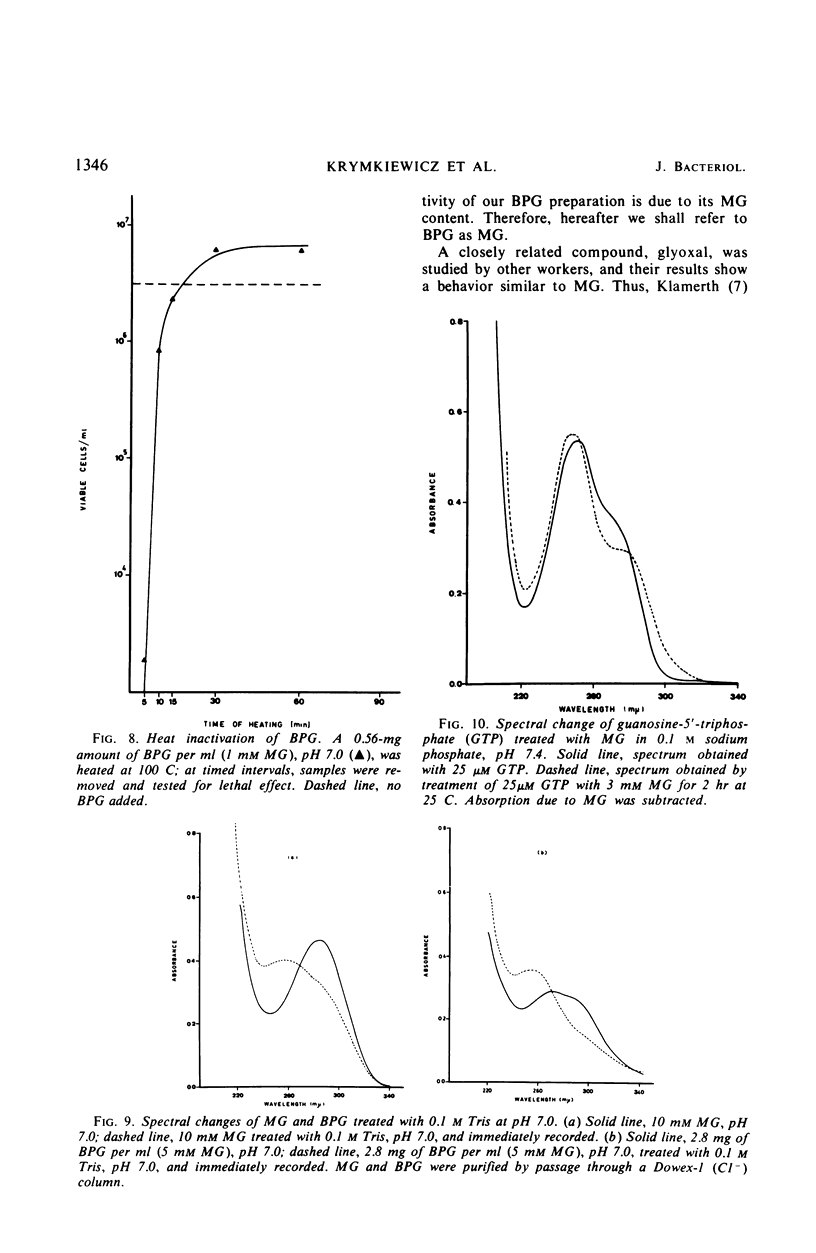
A lethal product (BPG) produced by a glycerol kinase mutant of Escherichia coli was purified, and its mode of action on E. coli was studied. At concentrations where BPG strongly inhibits in vivo deoxyribonucleic acid, ribonucleic acid, and protein synthesis, it produces small effects on other functions: slight inhibition of respiration and small changes in intracellular pools of substrates, nucleic acids degradation, and adenosine triphosphate levels. BPG also inhibits in vitro protein synthesis and produces inactivation of bacteriophage T4. The bactericidal product has been identified in another laboratory as methylglyoxal (MG). By comparing BPG and MG, we confirmed this observation and concluded that the activity found in our BPG preparation is due to its MG content. We also observed that MG is able to react with guanosine triphosphate. According to these results, it is interpreted that MG could act directly on macromolecular synthesis by reacting with the guanine residues of nucleic acids and its precursors.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brooks B. R., Klamerth O. L. Interaction of DNA with bifunctional aldehydes. Eur J Biochem. 1968 Jul;5(2):178–182. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1968.tb00355.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole H. A., Wimpenny J. W., Hughes D. E. The ATP pool in Escherichia coli. I. Measurement of the pool using modified luciferase assay. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967;143(3):445–453. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(67)90050-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper R. A., Anderson A. The formation and catabolism of methylglyoxal during glycolysis in Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett. 1970 Dec 11;11(4):273–276. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(70)80546-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Együd L. G., Szent-Györgyi A. Cell division, SH, ketoaldehydes, and cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Feb;55(2):388–393. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.2.388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Együd L. G., Szent-Györgyi A. On the regulation of cell division. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Jul;56(1):203–207. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.1.203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopper D. J., Cooper R. A. The regulation of Escherichia coli methylglyoxal synthase; a new control site in glycolysis? FEBS Lett. 1971 Mar 16;13(4):213–216. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80538-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klamerth O. L. Influence of glyoxal on cell function. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Jan 29;155(1):271–279. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(68)90356-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krymkiewicz N., González-Cadavid N. The significance of the incorporation of [14C] leucine into different protein fractions by isolated ox heart mitochondria. Biochem J. 1970 Jan;116(2):269–276. doi: 10.1042/bj1160269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LURIA S. E., ADAMS J. N., TING R. C. Transduction of lactose-utilizing ability among strains of E. coli and S. dysenteriae and the properties of the transducing phage particles. Virology. 1960 Nov;12:348–390. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(60)90161-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MATTHAEI J. H., NIRENBERG M. W. Characteristics and stabilization of DNAase-sensitive protein synthesis in E. coli extracts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1961 Oct 15;47:1580–1588. doi: 10.1073/pnas.47.10.1580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakaya K., Takenaka O., Horinishi H., Shibata K. Reactions of glyoxal with nucleic acids. Nucleotides and their component bases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Jun 18;161(1):23–31. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(68)90290-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STAEHELIN M. Inactivation of virus nucleic acid with glyoxal derivatives. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1959 Feb;31(2):448–454. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(59)90019-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka S., Lerner S. A., Lin E. C. Replacement of a phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent phosphotransferase by a nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide-linked dehydrogenase for the utilization of mannitol. J Bacteriol. 1967 Feb;93(2):642–648. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.2.642-648.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zwaig N., Diéguez E. A bactericidal product obtained from a mutant of Escherichia coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Sep 30;40(6):1415–1422. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90025-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zwaig N., Kistler W. S., Lin E. C. Glycerol kinase, the pacemaker for the dissimilation of glycerol in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1970 Jun;102(3):753–759. doi: 10.1128/jb.102.3.753-759.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zwaig N., Lin E. C. Feedback inhibition of glycerol kinase, a catabolic enzyme in Escherichia coli. Science. 1966 Aug 12;153(3737):755–757. doi: 10.1126/science.153.3737.755. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


