Abstract
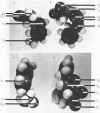
5-Methyl tryptophan was found to be an efficient inducer of penicillinase synthesis in Staphylococcus aureus. Addition of actinomycin D or tryptophan to the culture medium shuts off the 5-methyl tryptophan-induced synthesis of penicillinase with an apparent half-life of approximately 1 to 2 min, respectively. Hence, in the induction of penicillinase synthesis, 5-methyl tryptophan seems to function as a structural analogue of penicillin rather than by becoming incorporated in proteins and thereby creating faulty penicillinase repressor or antirepressor. This conclusion is supported by similarities in the structures of the two compounds as revealed by solid atomic models. The fact that S. aureus exposed to 14C-penicillin in the absence of protein synthesis failed to synthesize penicillinase at an increased level when cell growth was resumed strongly suggests that a protein involved in the regulation of penicillinase synthesis must be synthesized in the presence of the penicillinase inducer. In turn, this observation suggests that the penicillinase inducer promotes penicillinase synthesis by directing the penicillinase regulatory protein (i.e., the penicillinase antirepressor) to acquire a different conformation when it is synthesized in the presence of the penicillinase inducer. A working model for the regulation of penicillinase synthesis based on these and other data has been constructed and is presented.
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- COOPER P. D. Site of action of radiopenicillin. Bacteriol Rev. 1956 Mar;20(1):28–48. doi: 10.1128/br.20.1.28-48.1956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S., Sweeney H. M. Constitutive penicillinase formation in Staphylococcus aureus owing to a mutation unlinked to the penicillinase plasmid. J Bacteriol. 1968 Apr;95(4):1368–1374. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.4.1368-1374.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S., Vernon E. G., Sweeney H. M. Differential depression of staphylococcal plasmid and chromosomal penicillinase genes by a class of unlinked chromosomal mutations (R2-). J Bacteriol. 1970 Sep;103(3):616–621. doi: 10.1128/jb.103.3.616-621.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Csányi V., Jacobi G., Straub B. F. The regulation of penicillinase synthesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Sep 26;145(2):470–484. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(67)90065-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J. W., Collins J. F. The induction of Bacillus licheniformis penicillinase by vanadate, molybdate and tungstate anions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Oct 15;217(2):552–554. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(70)90557-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J. W. The stability and cell content of penicillinase messenger RNA in Bacillus licheniformis. J Gen Microbiol. 1969 Dec;59(2):171–184. doi: 10.1099/00221287-59-2-171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imsande J., Gerber M. J. Induction of penicillinase with inorganic phosphate. J Bacteriol. 1967 Nov;94(5):1672–1678. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.5.1672-1678.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imsande J. Regulation of penicillinase synthesis: evidence for a unified model. J Bacteriol. 1970 Jan;101(1):173–180. doi: 10.1128/jb.101.1.173-180.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leitner F. Kinetics of penicillinase induction and variation of penicillinase translation in Staphylococcus aureus. Biophys J. 2008 Dec 31;7(6):913–923. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(67)86629-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maass E. A., Johnson M. J. PENICILLIN UPTAKE BY BACTERIAL CELLS. J Bacteriol. 1949 Apr;57(4):415–422. doi: 10.1128/jb.57.4.415-422.1949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick R. P. Extrachromosomal inheritance in bacteria. Bacteriol Rev. 1969 Jun;33(2):210–263. doi: 10.1128/br.33.2.210-263.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POLLOCK M. R., PERRET C. J. The relation between fixation of penicillin sulphur and penicillinase adaptation in B cereus. Br J Exp Pathol. 1951 Oct;32(5):387–396. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POLLOCK M. R. Penicillinase adaptation in B. cereus; adaptive enzyme formation in the absence of free substrate. Br J Exp Pathol. 1950 Dec;31(6):739–753. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POLLOCK M. R. Penicillinase adaptation in Bacillus cereus; an analysis of three phases in the response of logarithmically growing cultures to induction of penicillinase formation by penicillin. Br J Exp Pathol. 1952 Dec;33(6):587–600. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RICHMOND M. H. DOMINANCE OF THE INDUCIBLE STATE IN STRAINS OF STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS CONTAINING TWO DISTINCT PENICILLINASE PLASMIDS. J Bacteriol. 1965 Aug;90:370–374. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.2.370-374.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers H. J. The inhibition of mucopeptide synthesis by benzylpenicillin in relation to irreversible fixation of the antibiotic by staphylococci. Biochem J. 1967 Apr;103(1):90–102. doi: 10.1042/bj1030090. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vernon E. G., Sweeney H. M., Cohen S. Evidence for genetic interaction between plasmid and chromosomal penicillinase linkage groups in Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1970 Sep;103(3):826–829. doi: 10.1128/jb.103.3.826-829.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zyskind J. W., Imsande J. Regulation of penicillinase synthesis: a mutation in Staphylococcus aureus unlinked to the penicillinase plasmid that reduced penicillinase inducibility. J Bacteriol. 1972 Jan;109(1):116–121. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.1.116-121.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]