Abstract
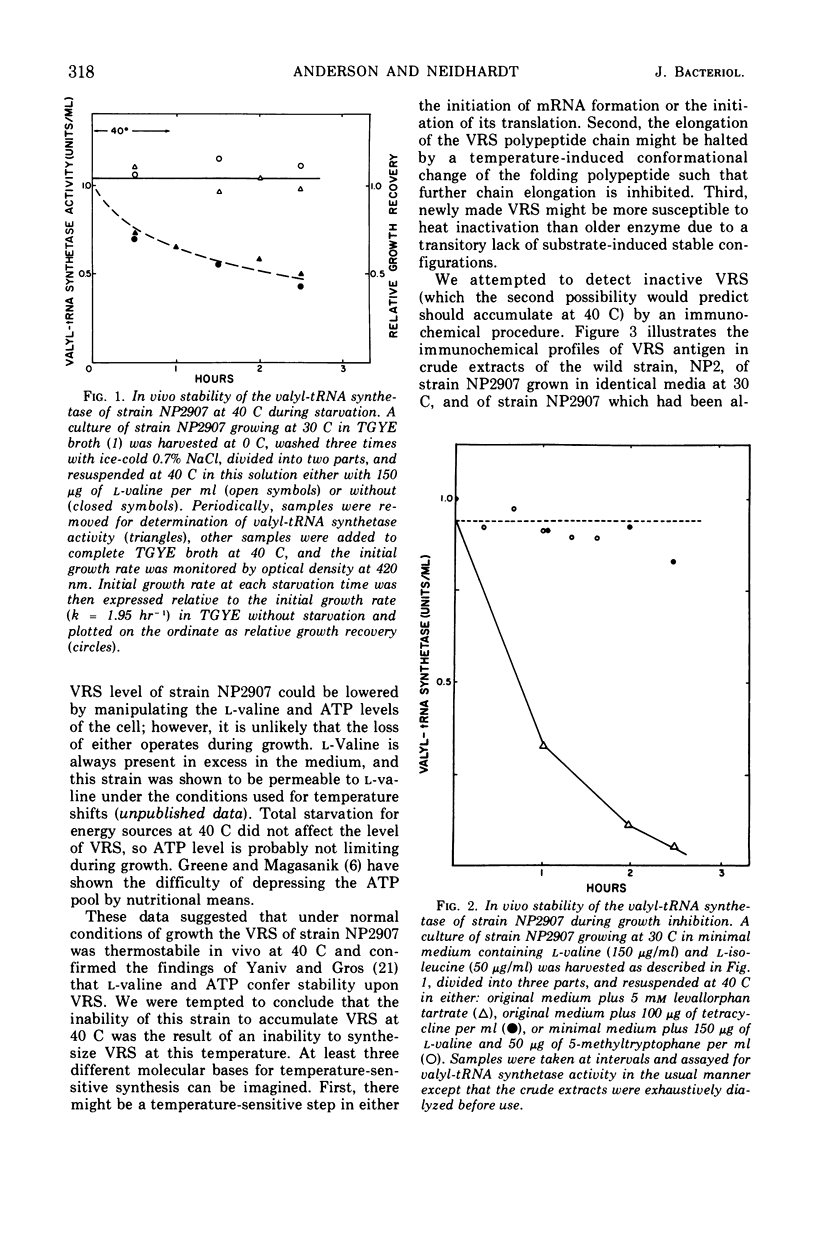
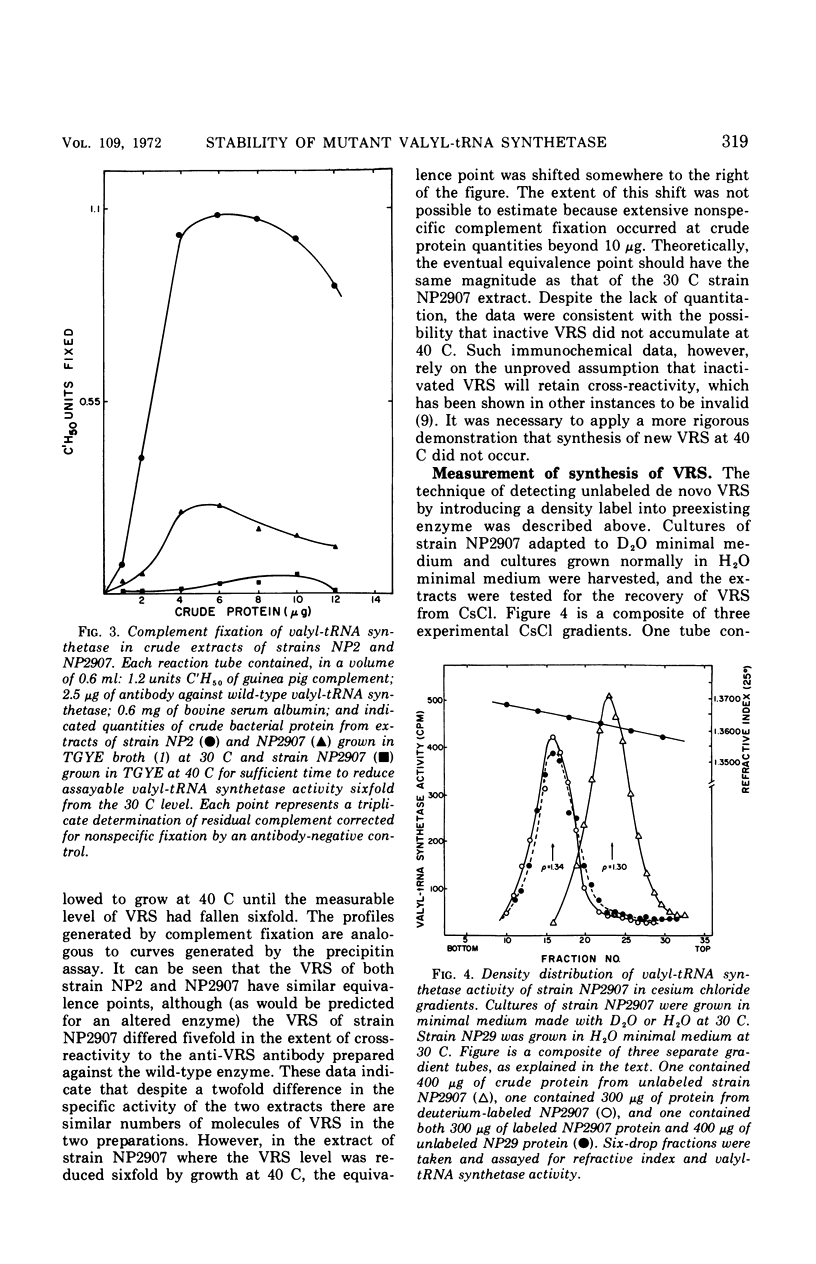
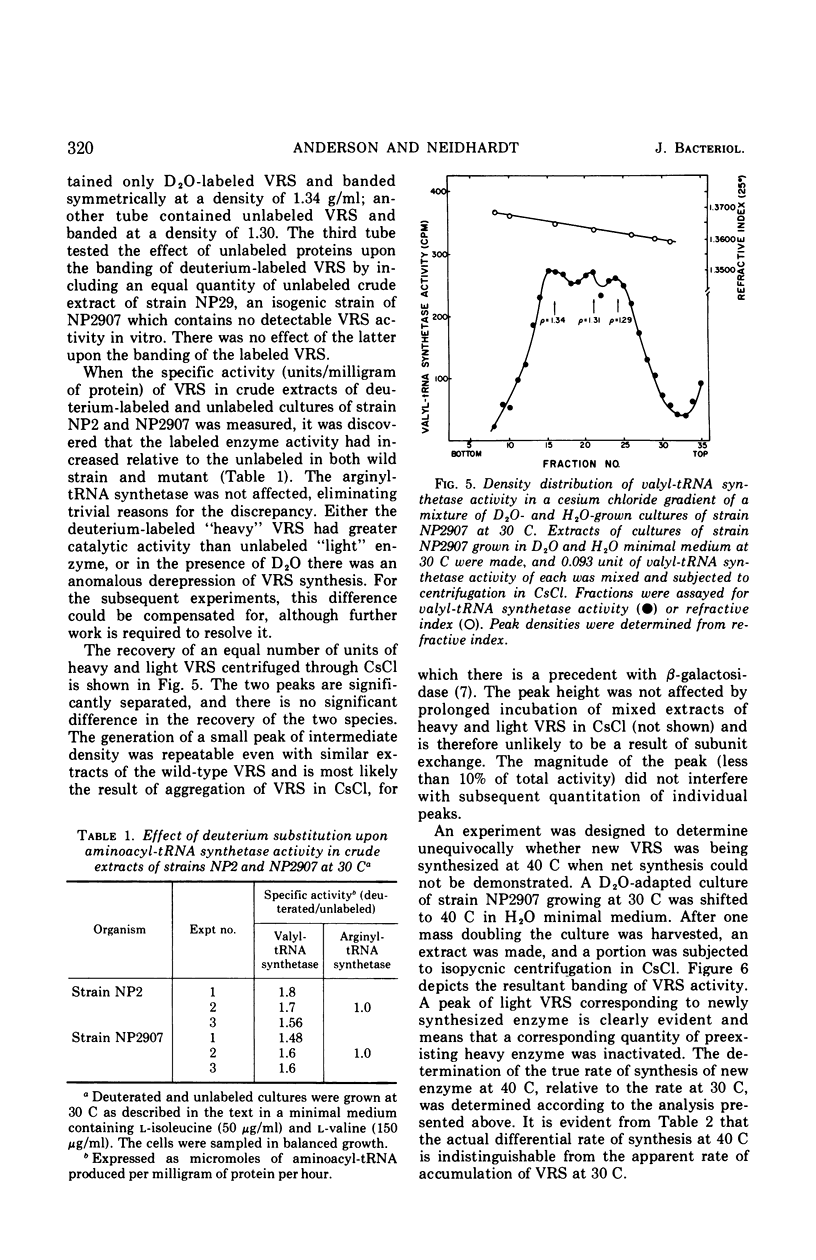
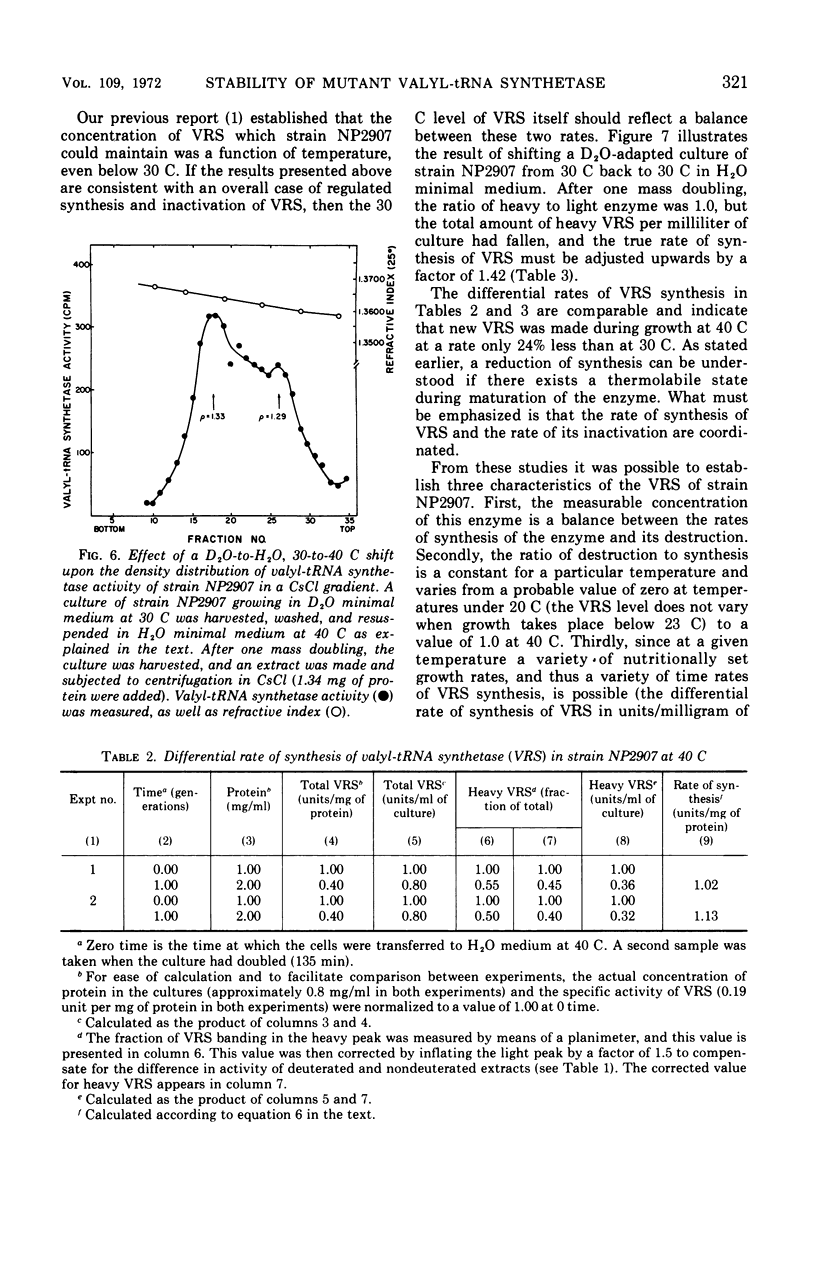
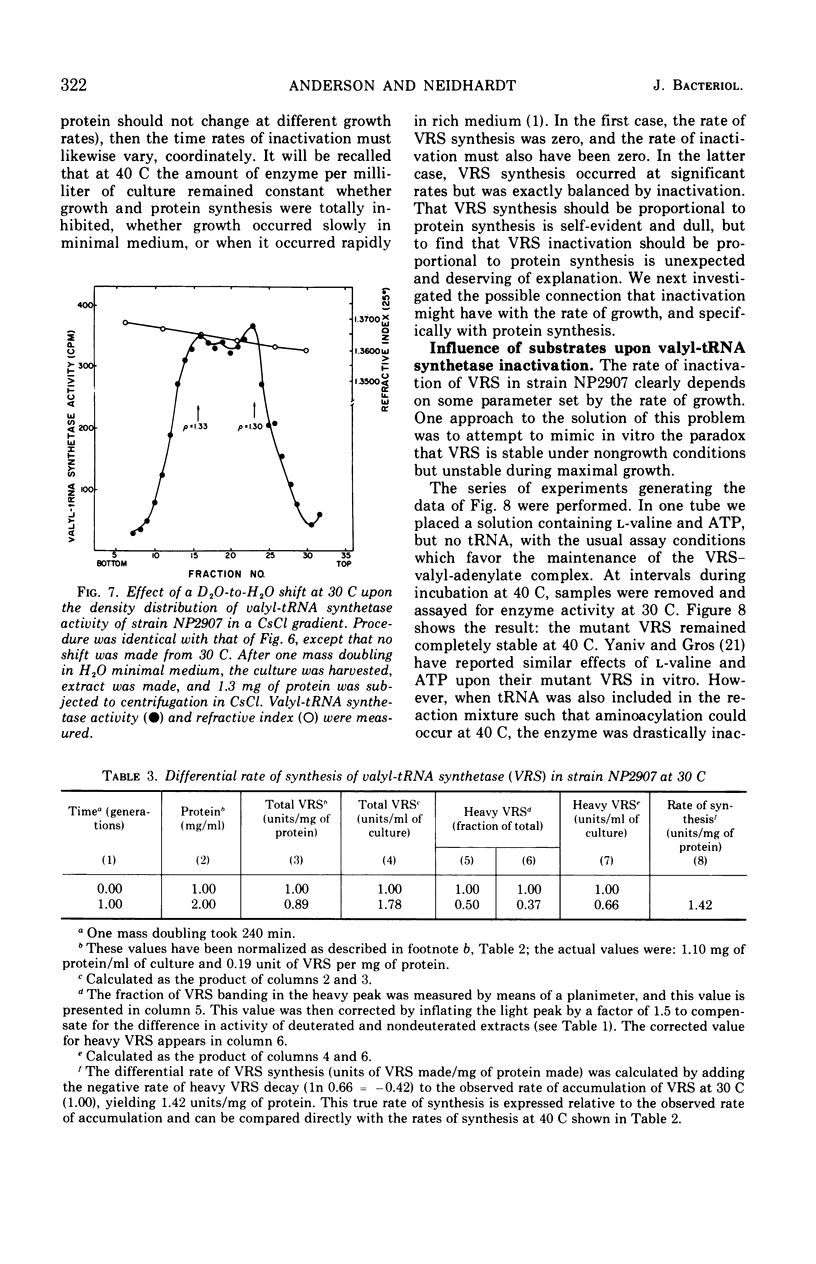
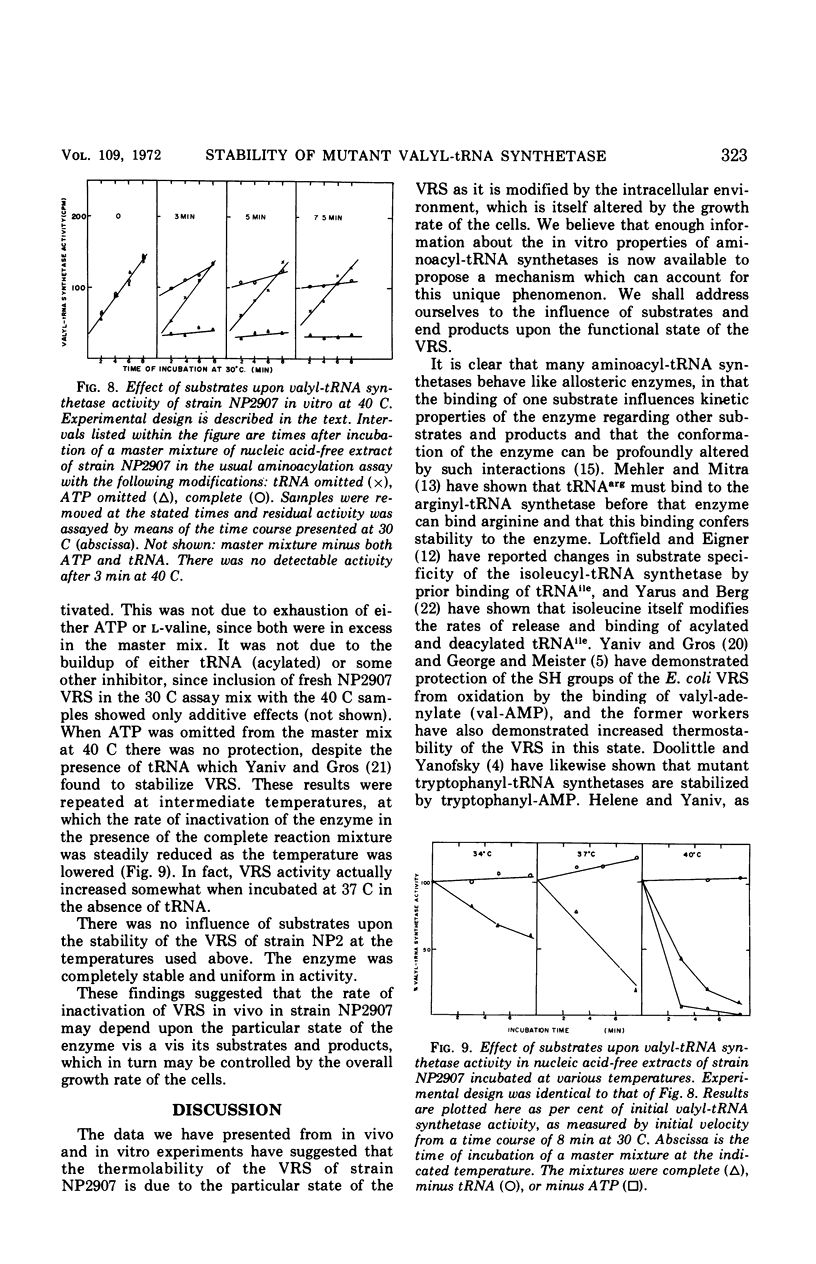
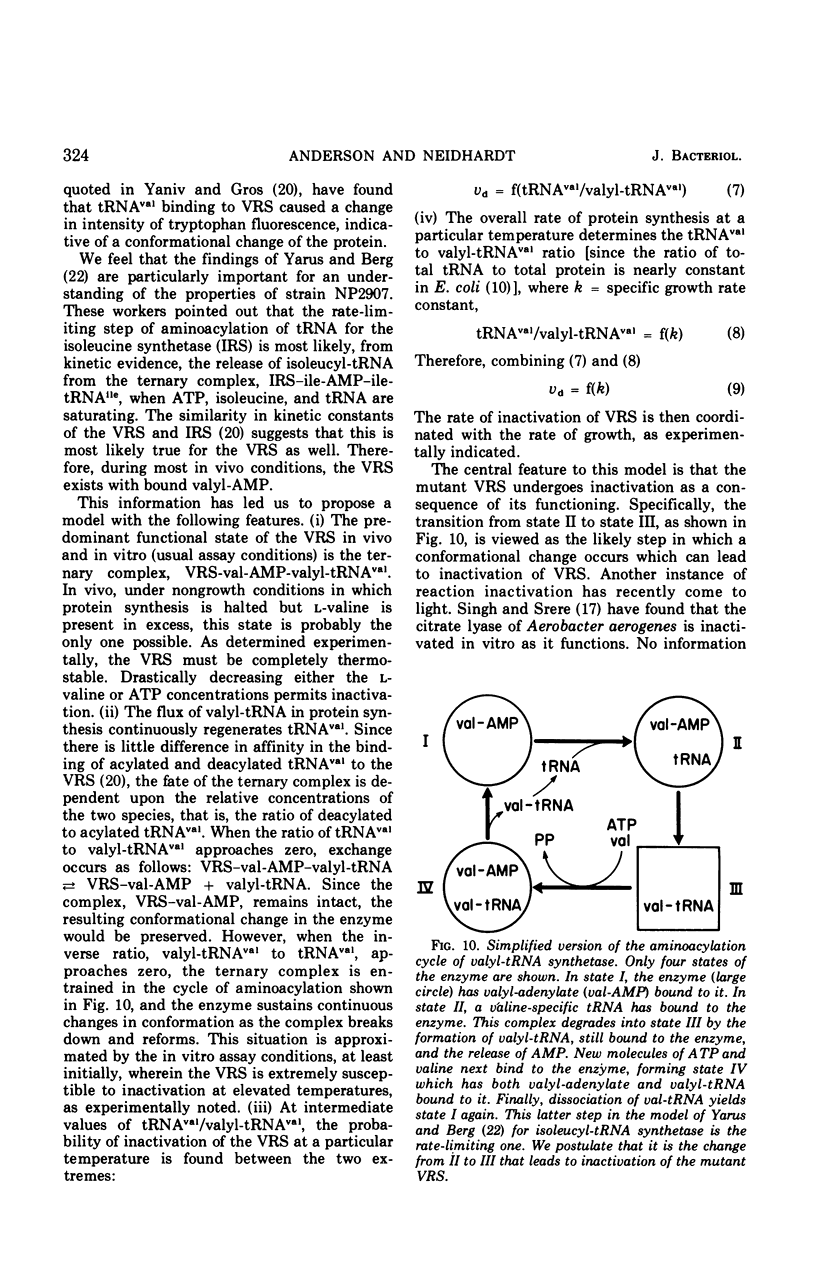
The valyl-transfer ribonucleic acid (tRNA) synthetase of Escherichia coli strain NP2907, previously described as having an elevated Km for adenosine triphosphate and reduced stability in vitro compared to the wild type, was found to be conditionally thermolabile in vivo. The rate of inactivation of this enzyme at a particular temperature appears to be coordinated with the rate of growth; at 40 C this coordination results in equal rates of synthesis and destruction over a wide range of growth rates. In vitro studies showed that conditions favoring maintenance of the valyl-tRNA synthetase-valyl adenylate complex conferred complete protection against inactivation at 40 C, whereas the further addition of uncharged tRNA caused rapid, irreversible decay. We propose that the rate of inactivation of this mutant valyl-tRNA synthetase in vivo is a function of the ratio of deacylated to acylated tRNAval and that this ratio is a function of growth rate. The event which renders the valyl-tRNA synthetase susceptible to inactivation is likely to be the normal breakdown of the valyl-tRNA synthetase–valyl-adenylate complex during a cycle of aminoacylation of tRNAval.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson J. J., Neidhardt F. C. Unusual valyl-transfer ribonucleic acid synthetase mutant of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1972 Jan;109(1):307–314. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.1.307-314.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chrispeels M. J., Boyd R. F., Williams L. S., Neidhardt F. C. Modification of valyl tRNA synthetase by bacteriophage in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1968 Feb 14;31(3):463–475. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90421-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Condon S., Ingraham J. L. Cold-sensitive mutation of Pseudomonas putida affecting enzyme synthesis at low temperature. J Bacteriol. 1967 Dec;94(6):1970–1981. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.6.1970-1981.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doolittle W. F., Yanofsky C. Mutants of Escherichia coli with an altered tryptophanyl-transfer ribonucleic acid synthetase. J Bacteriol. 1968 Apr;95(4):1283–1294. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.4.1283-1294.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George H., Meister A. Purification and properties of l-valyl-sRNA synthetase from Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Jan 11;132(1):165–174. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(67)90202-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene R., Magasanik B. The mode of action of levallorphan as an inhibitor of cell growth. Mol Pharmacol. 1967 Sep;3(5):453–472. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HU A. S., BOCK R. M., HALVORSON H. O. Separation of labeled from unlabeled proteins by equilibrium density gradient sedimentation. Anal Biochem. 1962 Dec;4:489–504. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(62)90129-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler D., Levine L., Fasman G. Some conformational and immunological properties of a bovine brain acidic protein (S-100). Biochemistry. 1968 Feb;7(2):758–764. doi: 10.1021/bi00842a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornberg H. L., Smith J. Temperature-sensitive synthesis of isocitrate lyase in Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Sep;123(3):654–657. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(66)90243-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehler A. H., Mitra S. K. The activation of arginyl transfer ribonucleic acid synthetase by transfer ribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1967 Dec 10;242(23):5495–5499. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SADLER J. R., NOVICK A. THE PROPERTIES OF REPRESSOR AND THE KINETICS OF ITS ACTION. J Mol Biol. 1965 Jun;12:305–327. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80255-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh M., Srere P. A. The reaction inactivation of citrate lyase from Aerobacter aerogenes. J Biol Chem. 1971 Jun 25;246(12):3847–3850. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WASSERMAN E., LEVINE L. Quantitative micro-complement fixation and its use in the study of antigenic structure by specific antigen-antibody inhibition. J Immunol. 1961 Sep;87:290–295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams L. S., Neidhardt F. C. Synthesis and inactivation of aminoacyl-transfer RNA synthetases during growth of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1969 Aug 14;43(3):529–550. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90357-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaniv M., Gros F. Studies on valyl-tRNA synthetase and tRNA from Escherichia coli. 3. Valyl-tRNA synthetases from thermosensitive mutants of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1969 Aug 28;44(1):31–45. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90403-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaniv M., Gros F. Studies on valyl-tRNA synthetase and tRNA from Escherichia coli. II. Interaction between valyl-tRNA synthetase and valine acceptor tRNA. J Mol Biol. 1969 Aug 28;44(1):17–30. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90402-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarus M., Berg P. Recognition of tRNA by isoleucyl-tRNA synthetase. Effect of substrates on the dynamics of tRNA-enzyme interaction. J Mol Biol. 1969 Jun 14;42(2):171–189. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90037-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



