Abstract
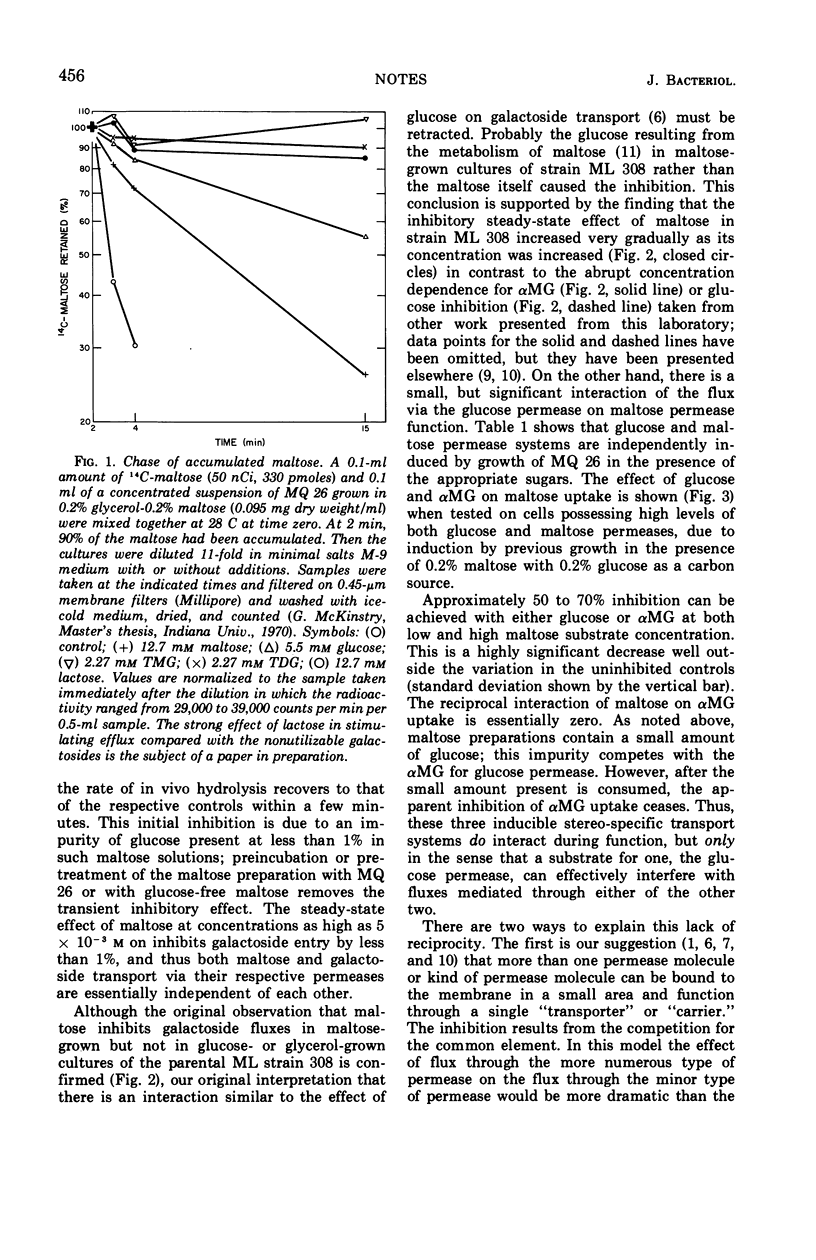
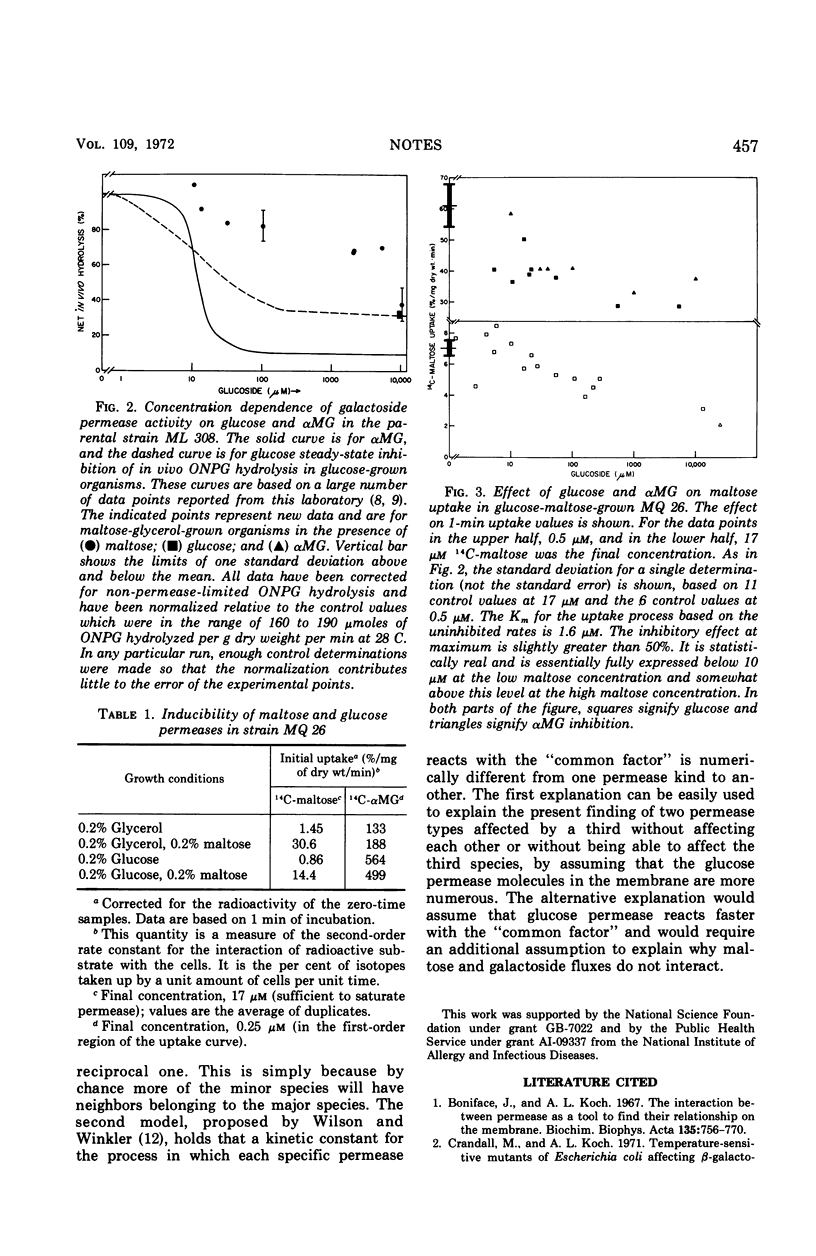
In cells of Escherichia coli possessing both maltose and galactoside permease, fluxes via one permease are independent of the substrate for the other permease. However, both fluxes are partially inhibited by glucose or α-methyl glucoside at low concentrations in cells grown on glucose. Neither maltose nor galactosides have an inhibitory effect on glucose permease function. These observations are consistent with the hypothesis that the number of glucose permease systems on the cell surface of such cells is much larger than the number for maltose or galactosides.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boniface J., Koch A. L. The interaction between permeases as a tool to find their relationship on the membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Sep 9;135(4):756–770. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(67)90107-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crandall M., Koch A. L. Temperature-sensitive mutants of Escherichia coli affecting beta-galactoside transport. J Bacteriol. 1971 Feb;105(2):609–619. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.2.609-619.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEPES A. [Kinetic studies on galactoside permease of Escherichia coli]. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 May 6;40:70–84. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)91316-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KESSLER D. P., RICKENBERG H. V. The competitive inhibition of alpha-methylglucoside uptake in Escherichia coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1963 Mar 25;10:482–487. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(63)90383-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOCH A. L. THE ROLE OF PERMEASE IN TRANSPORT. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Jan 27;79:177–200. doi: 10.1016/0926-6577(64)90050-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOCH A. L. The inactivation of the transport mechanism for beta-galactosides of Escherichia coli under various physiological conditions. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1963 Jan 21;102:602–620. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1963.tb13663.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch A. L., Boniface J. Intercalation of permeases during membrane growth. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Feb 2;225(2):239–247. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(71)90217-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch A. L. Energy expenditure is obligatory for the downhill transport of galactosides. J Mol Biol. 1971 Aug 14;59(3):447–459. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90309-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch A. L. Kinetics of permease catalyzed transport. J Theor Biol. 1967 Feb;14(2):103–130. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(67)90109-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch A. L. Local and non-local interactions of fluxes mediated by the glucose and galactoside permeases of Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Oct 12;249(1):197–215. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(71)90097-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz M., Hofnung M. La maltodextrine phosphorylase d'Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1967 Sep;2(2):132–145. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1967.tb00117.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler H. H., Wilson T. H. Inhibition of beta-galactoside transport by substrates of the glucose transport system in Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967;135(5):1030–1051. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(67)90073-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



