Abstract
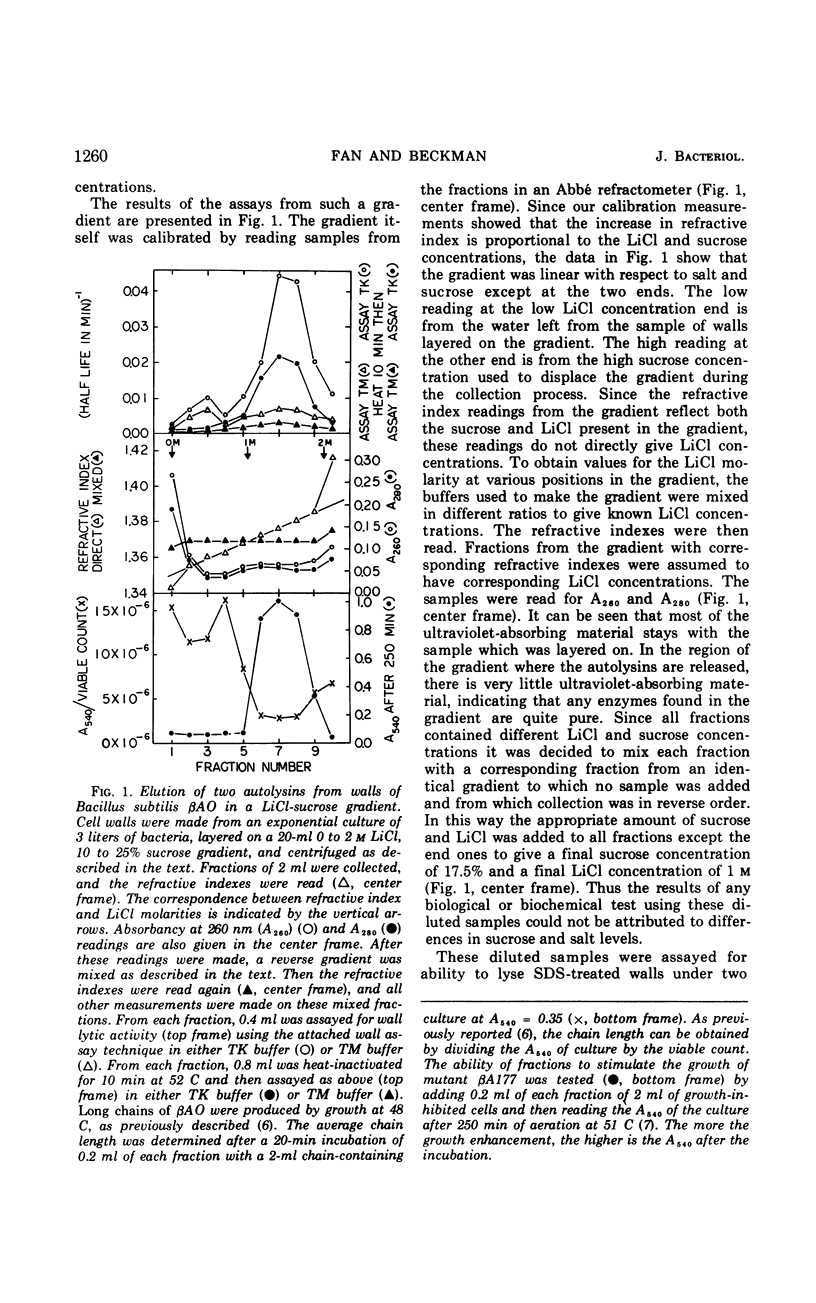
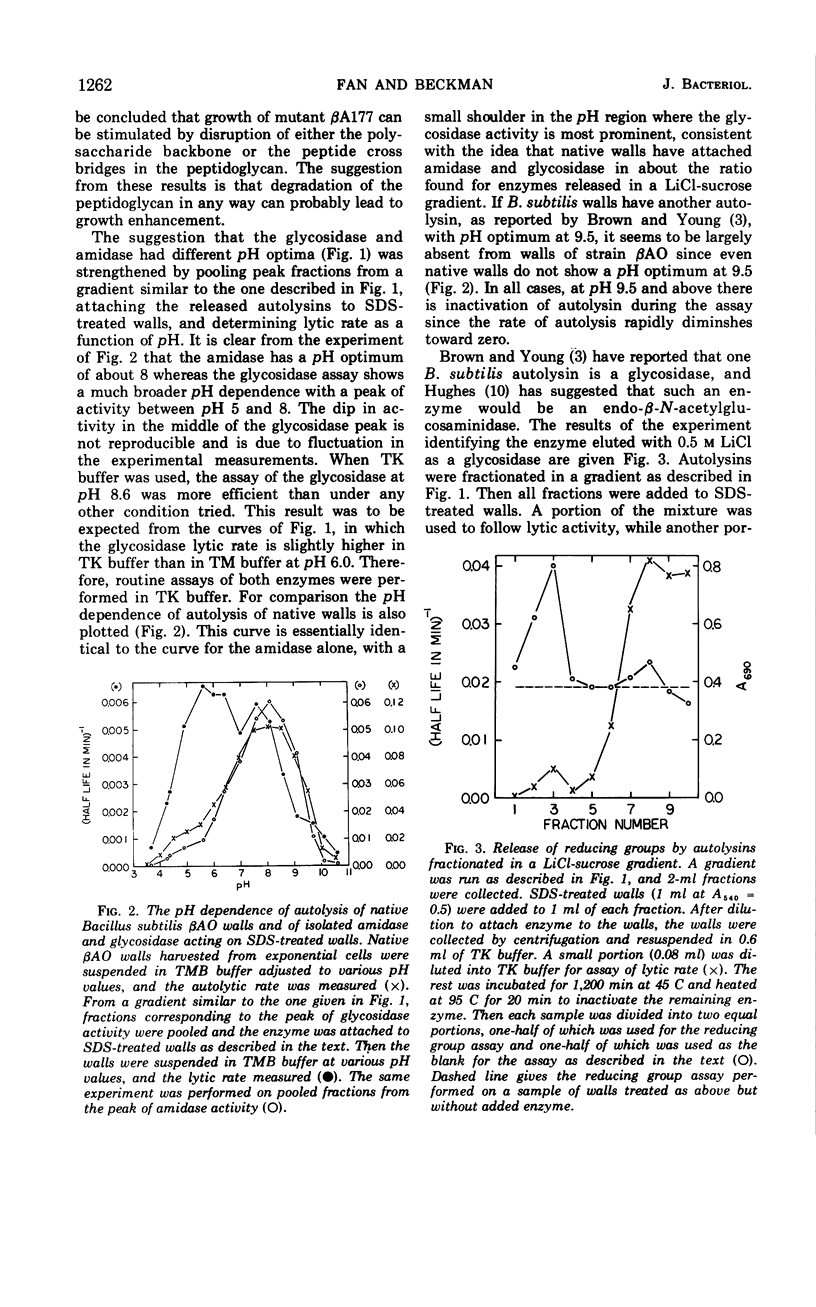
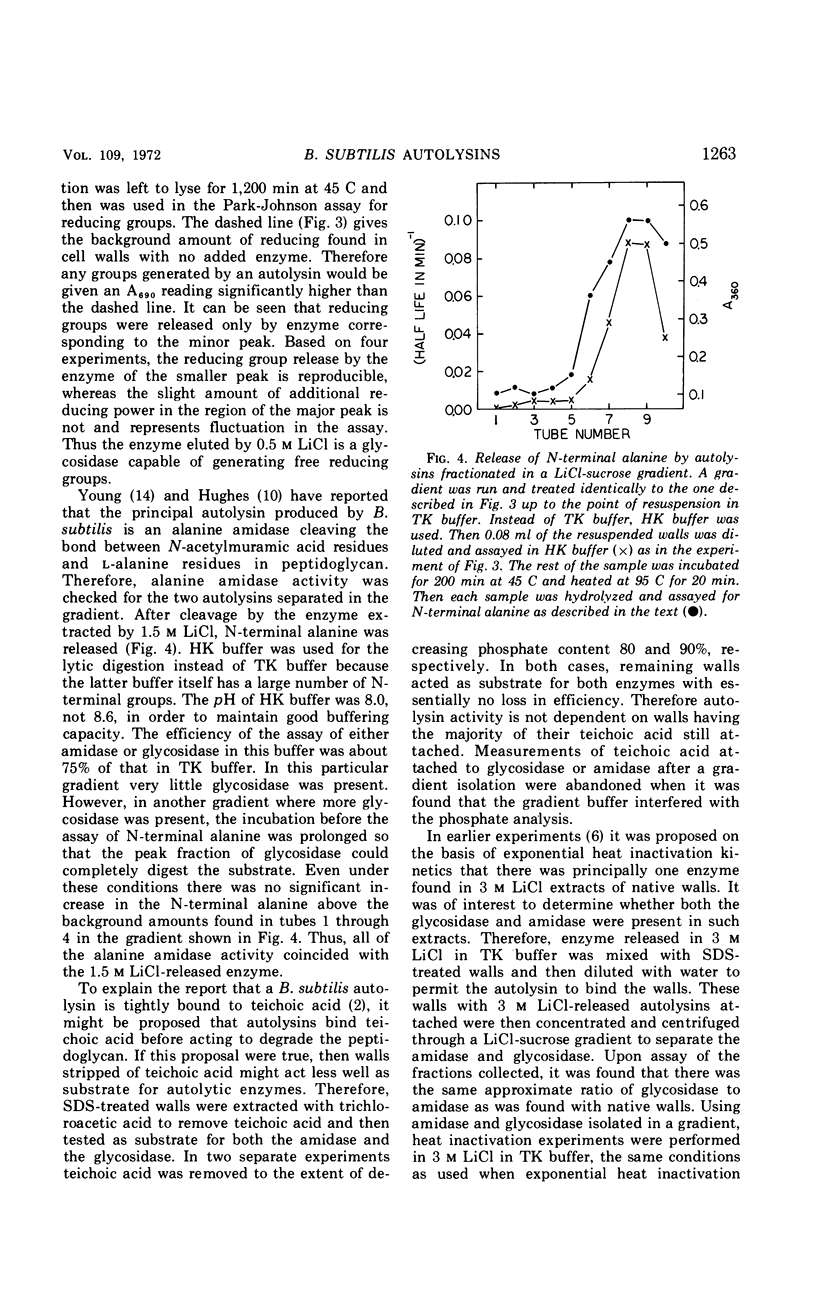
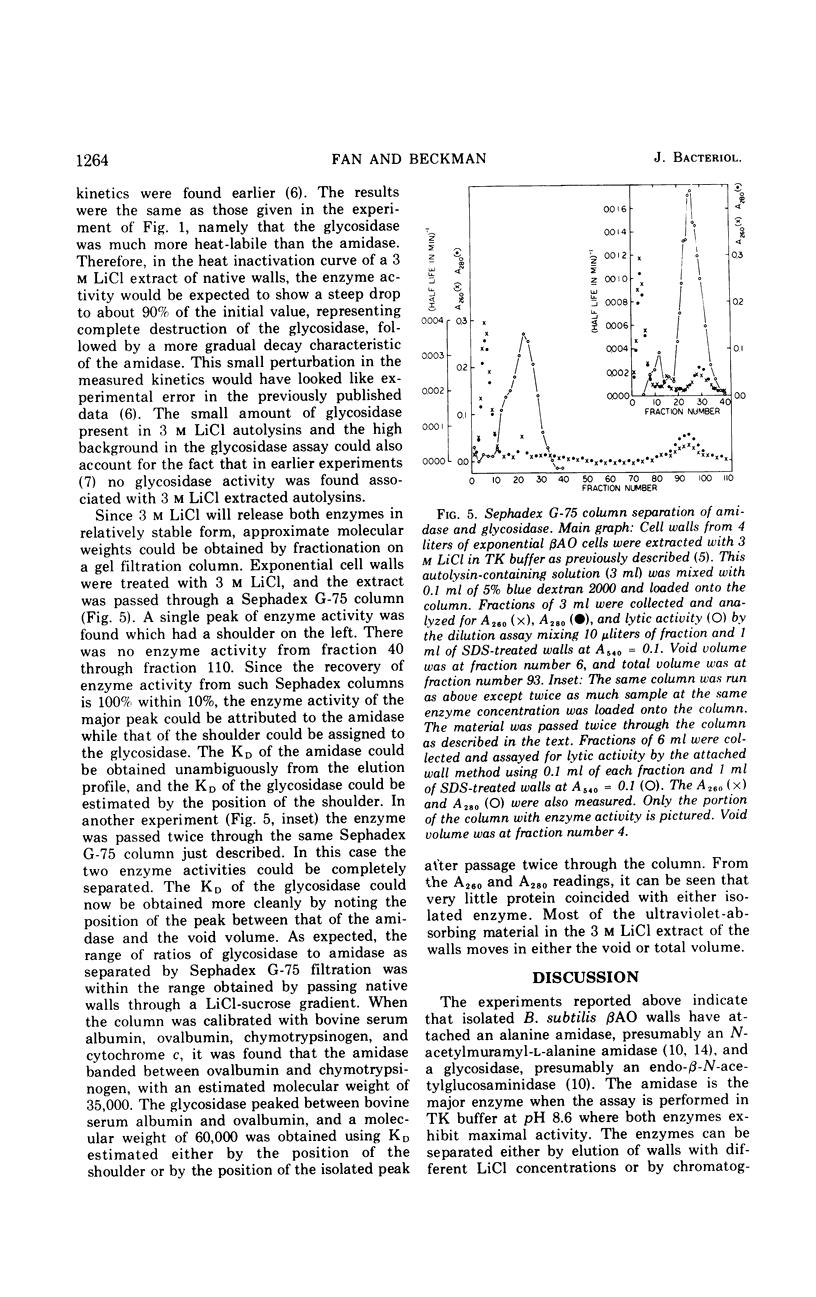
Bacillus subtilis cell walls can be centrifuged through a linear gradient of 0 to 2 m LiCl and 10 to 25% sucrose so that different autolysins are removed by different salt concentrations and banded in separate positions as the walls pass through the gradient. Using this technique we have found that B. subtilis cell walls are isolated with two autolytic enzymes attached. One autolysin, a glycosidase, can be eluted from walls with 0.5 m LiCl, has a pH optimum between 5 and 8, is relatively heat-sensitive, and has a molecular weight of 60,000. The other autolysin, an alanine amidase, can be eluted from walls with 1.5 m LiCl, has a pH optimum around 8, is relatively heat-stable, has a molecular weight of 35,000, and is present in quantities ten times greater than the glycosidase.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akrigg A., Ayad S. R. Studies on the competence-inducing factor of Bacillus subtilis. Biochem J. 1970 Apr;117(2):397–403. doi: 10.1042/bj1170397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown W. C., Fraser D. K., Young F. E. Problems in purification of a Bacillus subtilis autolytic enzyme caused by association with teichoic acid. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Feb 11;198(2):308–315. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(70)90063-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown W. C., Young F. E. Dynamic interactions between cell wall polymers, extracellular proteases and autolytic enzymes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Feb 20;38(4):564–568. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90618-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan D. P. Autolysin(s) of Bacillus subtilis as dechaining enzyme. J Bacteriol. 1970 Aug;103(2):494–499. doi: 10.1128/jb.103.2.494-499.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan D. P., Beckman M. M. Mutant of Bacillus subtilis demonstrating the requirement of lysis for growth. J Bacteriol. 1971 Feb;105(2):629–636. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.2.629-636.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan D. P. Cell wall binding properties of the Bacillus subtilis autolysin(s). J Bacteriol. 1970 Aug;103(2):488–493. doi: 10.1128/jb.103.2.488-493.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsberg C., Rogers H. J. Autolytic enzymes in growth of bacteria. Nature. 1971 Jan 22;229(5282):272–273. doi: 10.1038/229272a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes R. C. Autolysis of isolated cell walls of Bacillus licheniformis N.C.T.C. 6346 and Bacillus subtilis Marburg Strain 168. Separation of the products and characterization of the mucopeptide fragments. Biochem J. 1970 Oct;119(5):849–860. doi: 10.1042/bj1190849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart C. R., Marmur J. Increase in lytic activity in competent cells of Bacillus subtilis after uptake of deoxyribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol. 1970 Feb;101(2):449–455. doi: 10.1128/jb.101.2.449-455.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streips U. N., Young F. E. Mode of action of the competence-inducing factor of Bacillus stearothermophilus. J Bacteriol. 1971 Jun;106(3):868–875. doi: 10.1128/jb.106.3.868-875.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young F. E. Autolytic enzyme associated with cell walls of Bacillus subtilis. J Biol Chem. 1966 Aug 10;241(15):3462–3467. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



