Abstract
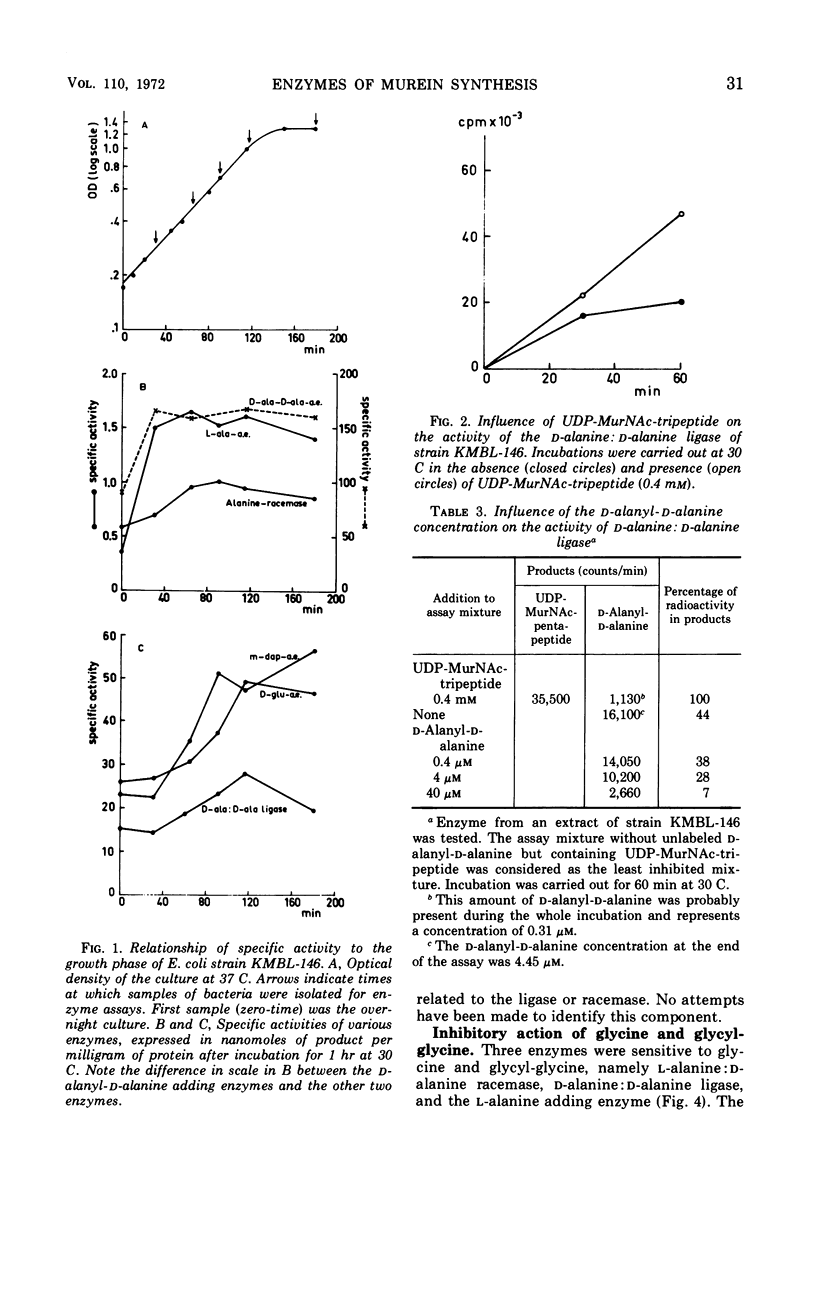
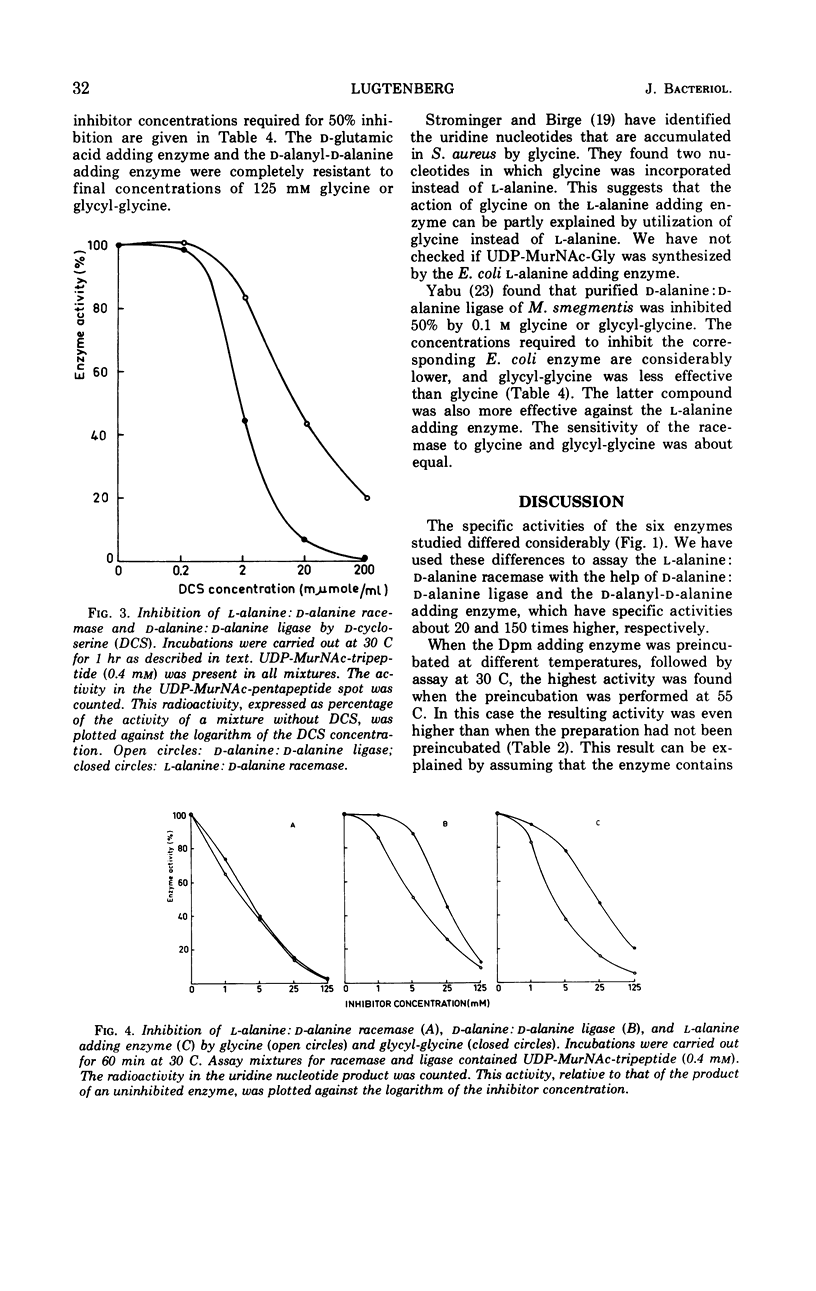
The specific activities of l-alanine:d-alanine racemase, d-alanine:d-alanine ligase, and the l-alanine, d-glutamic acid, meso-diaminopimelic acid, and d-alanyl-d-alanine adding enzymes were followed during growth of Escherichia coli. The specific activities were nearly independent of the growth phase. d-Alanine:d-alanine ligase was inhibited by d-alanyl-d-alanine, d-cycloserine, glycine, and glycyl-glycine. l-Alanine:d-alanine racemase was found to be sensitive to d-cycloserine, glycine, and glycyl-glycine. The l-alanine adding enzyme was inhibited by glycine and glycyl-glycine.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berberich R., Kaback M., Freese E. D-amino acids as inducers of L-alanine dehydrogenase in Bacillus subtilis. J Biol Chem. 1968 Mar 10;243(5):1006–1011. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COMB D. G. The enzymatic addition of D-alanyl-D-alanine to a uridine nucleotide-peptide. J Biol Chem. 1962 May;237:1601–1604. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fung P. H., Winter A. J. Effects of penicillin and glycine on cell wall glycopeptides of the two varieties of Vibrio fetus. J Bacteriol. 1968 Dec;96(6):1889–1894. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.6.1889-1894.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izaki K., Matsuhashi M., Strominger J. L. Biosynthesis of the peptidoglycan of bacterial cell walls. 8. Peptidoglycan transpeptidase and D-alanine carboxypeptidase: penicillin-sensitive enzymatic reaction in strains of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1968 Jun 10;243(11):3180–3192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lugtenberg E. J., De Haas-Menger L., Ruyters W. H. Murein synthesis and identification of cell wall precursors of temperature-sensitive lysis mutants of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1972 Jan;109(1):326–335. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.1.326-335.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lugtenberg E. J., de Haan P. G. A simple method for following the fate of alanine-containing components in murein synthesis in Escherichia coli. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1971;37(4):537–552. doi: 10.1007/BF02218524. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lugtenberg E. J., v Schijndel-van Dam A., van Bellegem T. H. In vivo and in vitro action of new antibiotics interfering with the utilization of N-acetyl-glucosamine-N-acetyl-muramyl-pentapeptide. J Bacteriol. 1971 Oct;108(1):20–29. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.1.20-29.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEUHAUS F. C., LYNCH J. L. THE ENZYMATIC SYNTHESIS OF D-ALANYL-D-ALANINE. 3. ON THE INHIBITION OF D-ALANYL-D-ALANINE SYNTHETASE BY THE ANTIBIOTIC D-CYCLOSERINE. Biochemistry. 1964 Apr;3:471–480. doi: 10.1021/bi00892a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEUHAUS F. C. The enzymatic synthesis of D-alanyl-D-alanine. I. Purification and properties of D-alanyl-D-alanine synthetase. J Biol Chem. 1962 Mar;237:778–786. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuhaus F. C. Selective inhibition of enzymes utilizing alanine in the biosynthesis of peptidoglycan. Antimicrob Agents Chemother (Bethesda) 1967;7:304–313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosso G., Takashima K., Adams E. Coenzyme content of purified alanine racemase from Pseudomonas. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Jan 6;34(1):134–140. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90539-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STROMINGER J. L., BIRGE C. H. NUCLEOTIDE ACCUMULATION INDUCED IN STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS BY GLYCINE. J Bacteriol. 1965 Apr;89:1124–1127. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.4.1124-1127.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strominger J. L., Izaki K., Matsuhashi M., Tipper D. J. Peptidoglycan transpeptidase and D-alanine carboxypeptidase: penicillin-sensitive enzymatic reactions. Fed Proc. 1967 Jan-Feb;26(1):9–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WISHNOW R. M., STROMINGER J. L., BIRGE C. H., THRENN R. H. BIOCHEMICAL EFFECTS OF NOVOBIOCIN ON STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS. J Bacteriol. 1965 Apr;89:1117–1123. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.4.1117-1123.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yabu K. Reversal of the growth inhibitory action of glycine and glycylglycine by alanylalanine in Mycobacterium smegmatis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Jul 30;184(2):460–463. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(69)90051-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



