Abstract
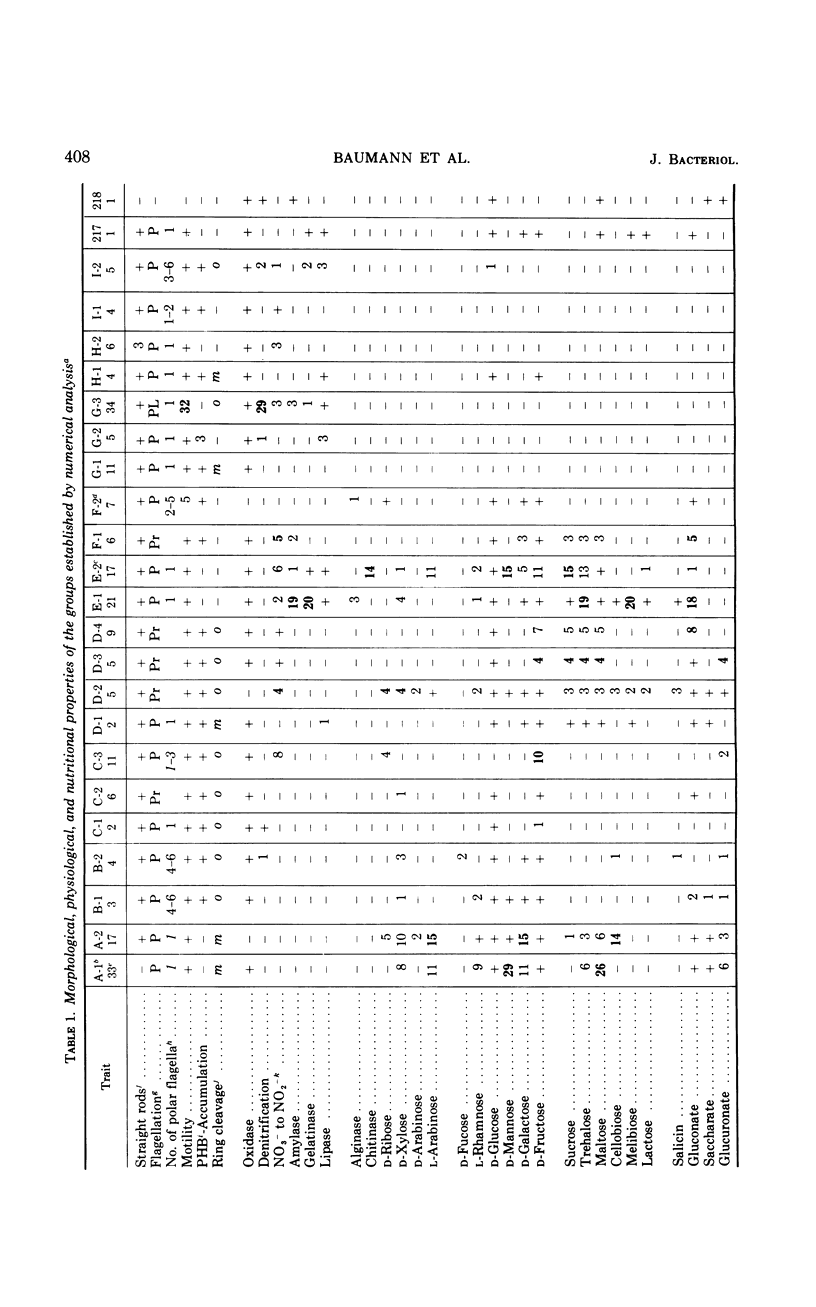
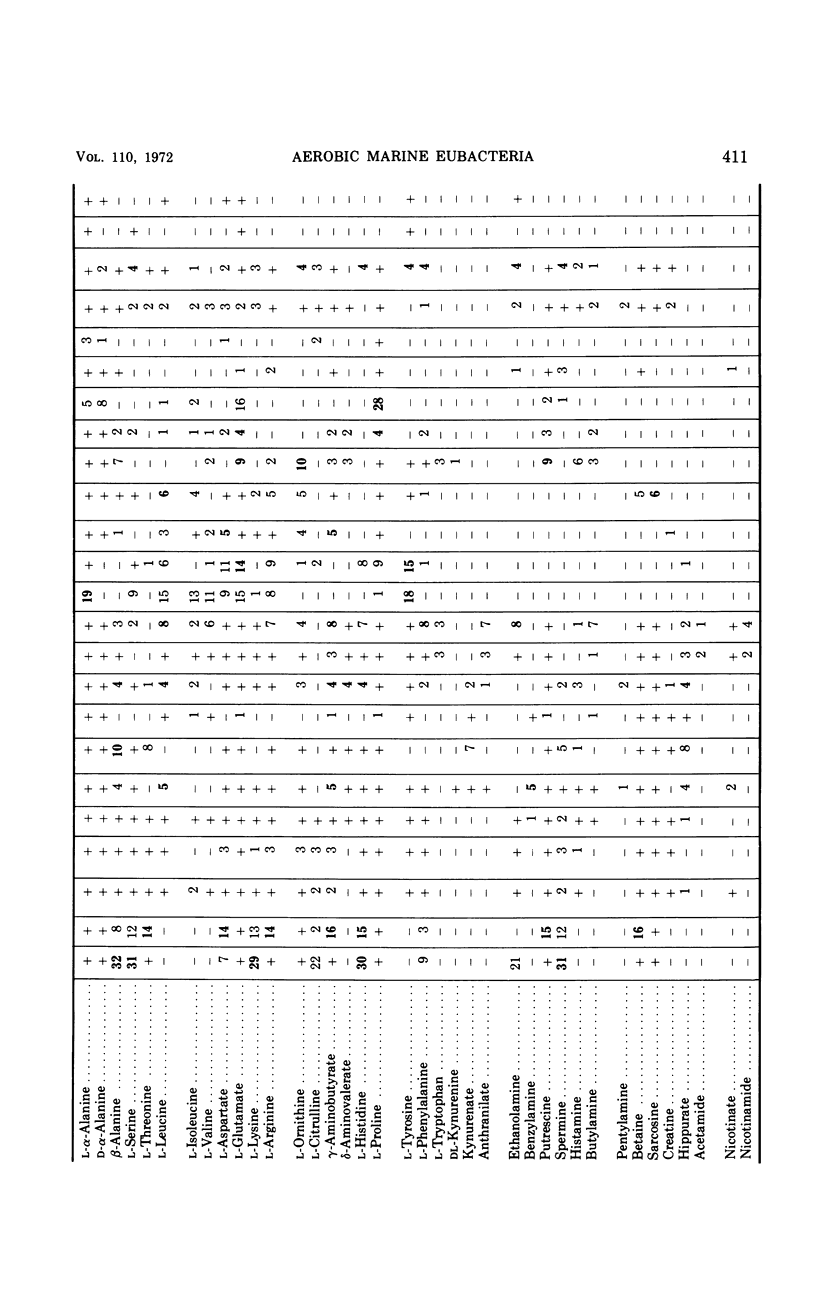
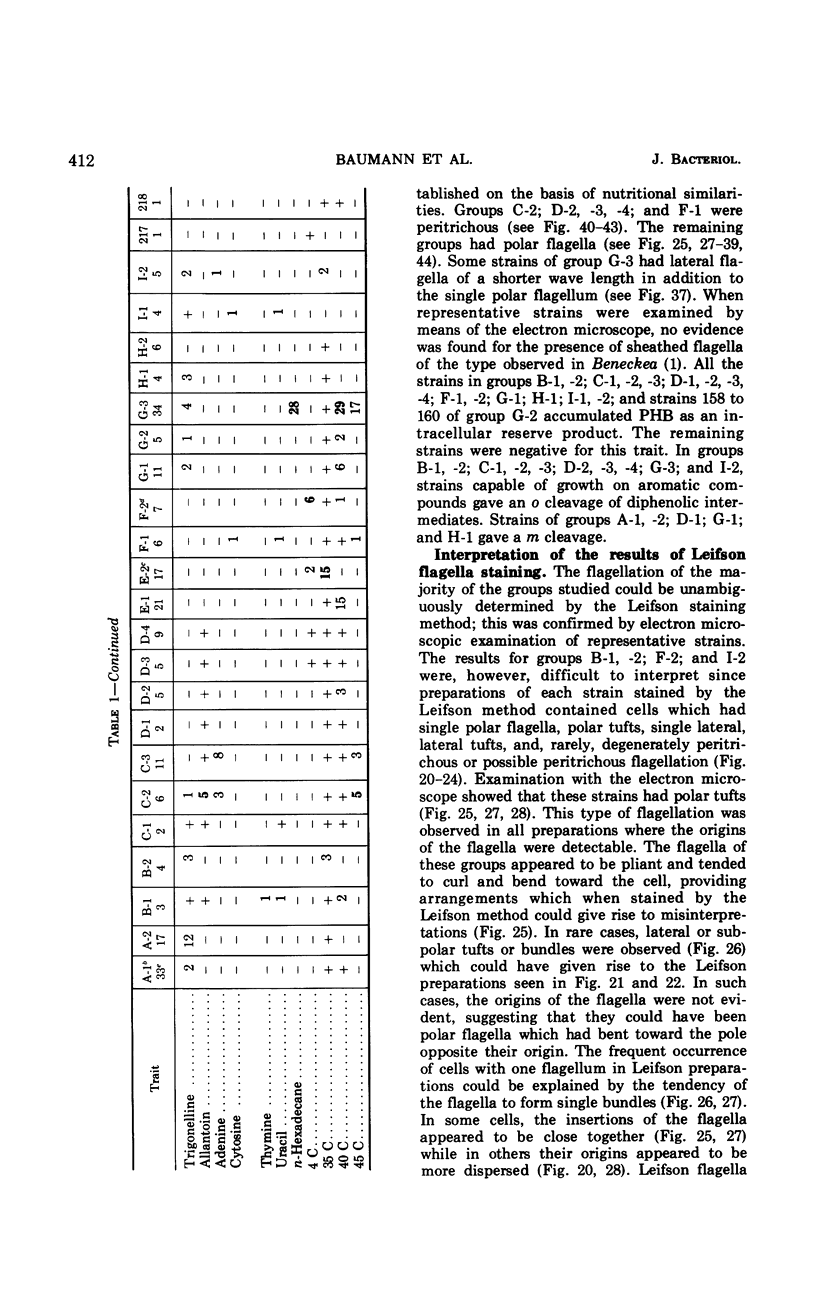
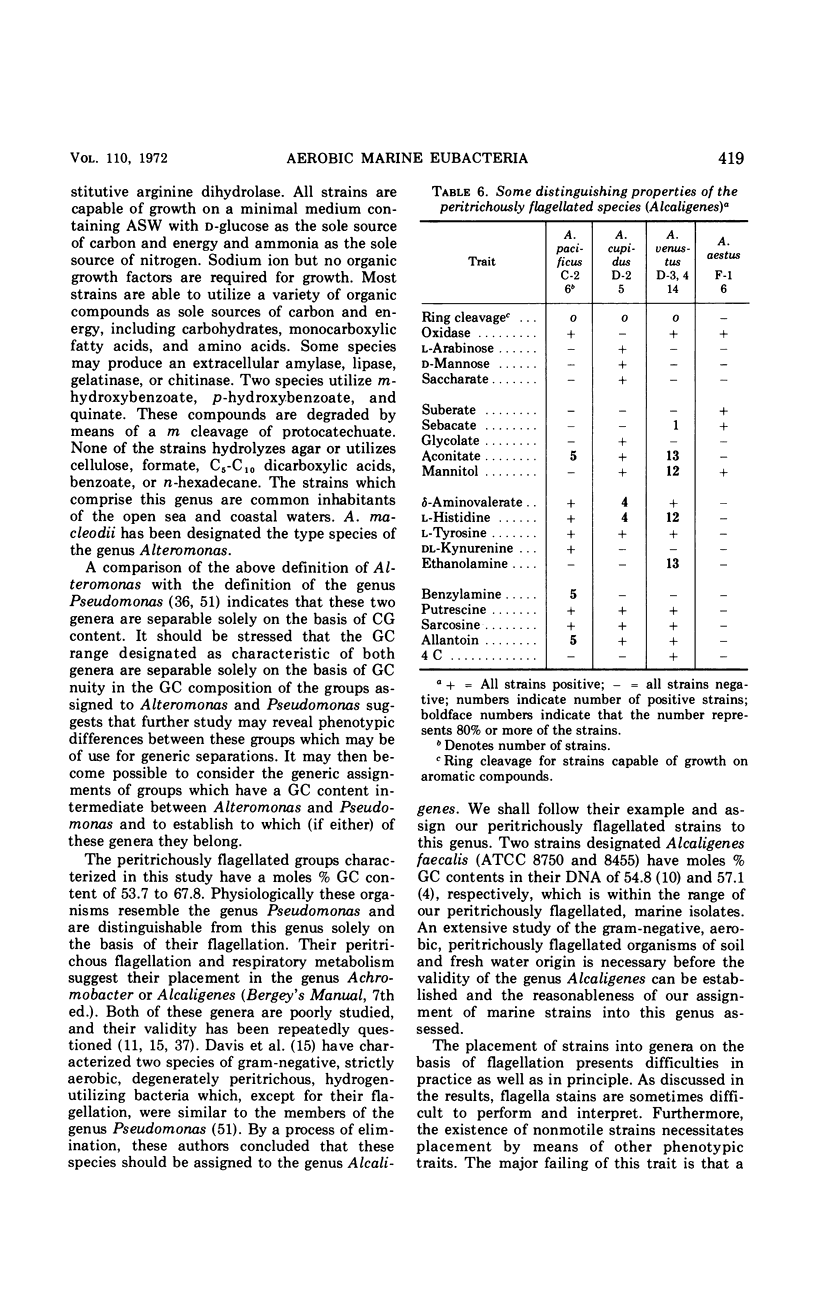
Two hundred and eighteen strains of nonfermentative marine bacteria were submitted to an extensive morphological, physiological, and nutritional characterization. All the strains were gram-negative, straight or curved rods which were motile by means of polar or peritrichous flagella. A wide variety of organic substrates served as sole sources of carbon and energy. The strains differed extensively in their nutritional versatility, being able to utilize from 11 to 85 carbon compounds. Some strains had an extracellular amylase, gelatinase, lipase, or chitinase and were able to utilize n-hexadecane and to denitrify. None of the strains had a yellow, cell-associated pigment or a constitutive arginine dihydrolase system, nor were they able to hydrolyze cellulose or agar. The results of the physiological and nutritional characterization were submitted to a numerical analysis which clustered the strains into 22 groups on the basis of phenotypic similarities. The majority of these groups were separable by a large number of unrelated phenotypic traits. Analysis of the moles per cent guanine plus cytosine (GC) content in the deoxyribonucleic acid of representative strains indicated that the peritrichously flagellated groups had a GC content of 53.7 to 67.8 moles%; polarly flagellated strains had a GC content of 30.5 to 64.7 moles%. The peritrichously flagellated groups were assigned to the genus Alcaligenes. The polarly flagellated groups, which had a GC content of 43.2 to 48.0 moles%, were placed into a newly created genus, Alteromonas; groups which had a GC content of 57.8 to 64.7 moles% were placed into the genus Pseudomonas; and the remaining groups were left unassigned. Twelve groups were given the following designations: Alteromonas communis, A. vaga, A. macleodii, A. marinopraesens, Pseudomonas doudoroffi, P. marina, P. nautica, Alcaligenes pacificus, A. cupidus, A. venustus, and A. aestus. The problems of assigning species of aerobic marine bacteria to genera are discussed.
Full text
PDF














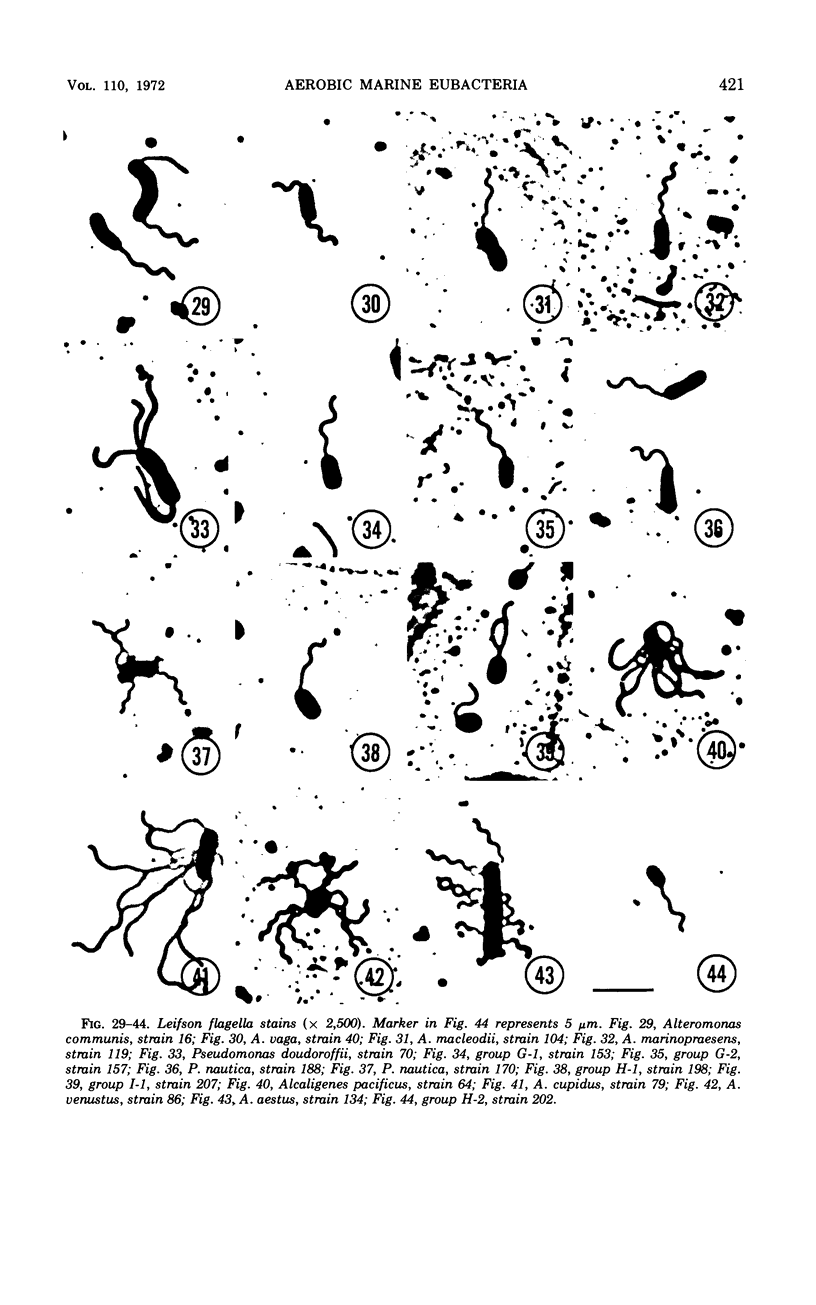








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen R. D., Baumann P. Structure and arrangement of flagella in species of the genus Beneckea and Photobacterium fischeri. J Bacteriol. 1971 Jul;107(1):295–302. doi: 10.1128/jb.107.1.295-302.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballard R. W., Doudoroff M., Stanier R. Y., Mandel M. Taxonomy of the aerobic psuedomonads: Pseudomonas diminuta and P. vesiculare. J Gen Microbiol. 1968 Oct;53(3):349–361. doi: 10.1099/00221287-53-3-349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballard R. W., Palleroni N. J., Doudoroff M., Stanier R. Y., Mandel M. Taxonomy of the aerobic pseudomonads: Pseudomonas cepacia, P. marginata, P. alliicola and P. caryophylli. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Feb;60(2):199–214. doi: 10.1099/00221287-60-2-199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baptist J. N., Shaw C. R., Mandel M. Zone electrophoresis of enzymes in bacterial taxonomy. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jul;99(1):180–188. doi: 10.1128/jb.99.1.180-188.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann P., Baumann L., Mandel M. Taxonomy of marine bacteria: the genus Beneckea. J Bacteriol. 1971 Jul;107(1):268–294. doi: 10.1128/jb.107.1.268-294.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COLWELL R. R., MANDEL M. ADANSONIAN ANALYSIS AND DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID BASE COMPOSITION OF SOME GRAM-NEGATIVE BACTERIA. J Bacteriol. 1964 Jun;87:1412–1422. doi: 10.1128/jb.87.6.1412-1422.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cobet A. B., Wirsen C., Jr, Jones G. E. The effect of nickel on a marine bacterium, Arthrobacter marinus sp.nov. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Aug;62(2):159–169. doi: 10.1099/00221287-62-2-159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen G. N., Stanier R. Y., Le Bras G. Regulation of the biosynthesis of amino acids of the aspartate family in Coliform bacteria and Pseudomonads. J Bacteriol. 1969 Sep;99(3):791–801. doi: 10.1128/jb.99.3.791-801.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colwell R. R. Polyphasic taxonomy of the genus vibrio: numerical taxonomy of Vibrio cholerae, Vibrio parahaemolyticus, and related Vibrio species. J Bacteriol. 1970 Oct;104(1):410–433. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.1.410-433.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conn H. J. Validity of the Genus Alcaligenes. J Bacteriol. 1942 Sep;44(3):353–360. doi: 10.1128/jb.44.3.353-360.1942. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costerton J. W., Forsberg C., Matula T. I., Buckmire F. L., MacLeod R. A. Nutrition and metabolism of marine bacteria. XVI. Formation of protoplasts, spheroplasts, and related forms from a gram-negative marine bacterium. J Bacteriol. 1967 Nov;94(5):1764–1777. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.5.1764-1777.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford I. P., Sikes S., Melhorn D. K. The natural relationships of Aeromonas formicans. Arch Mikrobiol. 1967;59(1):72–81. doi: 10.1007/BF00406318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAGLEY S., EVANS W. C., RIBBONS D. W. New pathways in the oxidative metabolism of aromatic compounds by microorganisms. Nature. 1960 Nov 12;188:560–566. doi: 10.1038/188560a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis D. H., Stanier R. Y., Doudoroff M., Mandel M. Taxonomic studies on some gram negative polarly flagellated "hydrogen bacteria" and related species. Arch Mikrobiol. 1970;70(1):1–13. doi: 10.1007/BF00691056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Voe I. W., Oginsky E. L. Antagonistic effect of monovalent cations in maintenance of cellular integrity of a marine bacterium. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jun;98(3):1355–1367. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.3.1355-1367.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Voe I. W., Oginsky E. L. Cation interactions and biochemical composition of the cell envelope of a marine bacterium. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jun;98(3):1368–1377. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.3.1368-1377.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drapeau G. R., Matula T. I., MacLeod R. A. Nutrition and metabolism of marine bacteria. XV. Relation of Na+-activated transport to the Na+ requirement of a marine pseudomonad for growth. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jul;92(1):63–71. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.1.63-71.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsberg C. W., Costerton J. W., Macleod R. A. Quantitation, chemical characteristics, and ultrastructure of the three outer cell wall layers of a gram-negative bacterium. J Bacteriol. 1970 Dec;104(3):1354–1368. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.3.1354-1368.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsberg C. W., Costerton J. W., Macleod R. A. Separation and localization of cell wall layers of a gram-negative bacterium. J Bacteriol. 1970 Dec;104(3):1338–1353. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.3.1338-1353.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAYES P. R. Studies on marine flavobacteria. J Gen Microbiol. 1963 Jan;30:1–19. doi: 10.1099/00221287-30-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hegeman G. D. Synthesis of the enzymes of the mandelate pathway by Pseudomonas putida. I. Synthesis of enzymes by the wild type. J Bacteriol. 1966 Mar;91(3):1140–1154. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.3.1140-1154.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jannasch H. W. Competitive elimination of Enterobacteriaceae from seawater. Appl Microbiol. 1968 Oct;16(10):1616–1618. doi: 10.1128/am.16.10.1616-1618.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen R. A., Stenmark S. L. Comparative allostery of 3-deoxy-D-arabino-heptulosonate-7-phosphate synthetase as a molecular basis for classification. J Bacteriol. 1970 Mar;101(3):763–769. doi: 10.1128/jb.101.3.763-769.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. M., Katarski M. E., Weisrock W. P. Correlation of taxonomic criteria for a collection of marine bacteria. Appl Microbiol. 1968 May;16(5):708–713. doi: 10.1128/am.16.5.708-713.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KING E. O., WARD M. K., RANEY D. E. Two simple media for the demonstration of pyocyanin and fluorescin. J Lab Clin Med. 1954 Aug;44(2):301–307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEIFSON E., COSENZA B. J., MURCHELANO R., CLEVERDON R. C. MOTILE MARINE BACTERIA. I. TECHNIQUES, ECOLOGY, AND GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS. J Bacteriol. 1964 Mar;87:652–666. doi: 10.1128/jb.87.3.652-666.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACLEOD R. A. THE QUESTION OF THE EXISTENCE OF SPECIFIC MARINE BACTERIA. Bacteriol Rev. 1965 Mar;29:9–24. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOORE H. B., PICKETT M. J. Organisms resembling Alcaligenes faecalis. Can J Microbiol. 1960 Feb;6:43–52. doi: 10.1139/m60-007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel M. Deoxyribonucleic acid base composition in the genus Pseudomonas. J Gen Microbiol. 1966 May;43(2):273–292. doi: 10.1099/00221287-43-2-273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norton C. F., Jones G. E. A marine isolate of Pseudomonas nigrifaciens. I. Classification and nutrition. Can J Microbiol. 1968 Dec;14(12):1333–1340. doi: 10.1139/m68-223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palleroni N. J., Doudoroff M. Phenotypic characterization and deoxyribonucleic acid homologies of Pseudomonas solanacearum. J Bacteriol. 1971 Sep;107(3):690–696. doi: 10.1128/jb.107.3.690-696.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palleroni N. J., Doudoroff M., Stanier R. Y., Solánes R. E., Mandel M. Taxonomy of the aerobic pseudomonads: the properties of the Pseudomonas stutzeri group. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Feb;60(2):215–231. doi: 10.1099/00221287-60-2-215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfister R. M., Burkholder P. R. Numerical taxonomy of some bacteria isolated from antarctic and tropical seawaters. J Bacteriol. 1965 Oct;90(4):863–872. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.4.863-872.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redfearn M. S., Palleroni N. J., Stanier R. Y. A comparative study of Pseudomonas pseudomallei and Bacillus mallei. J Gen Microbiol. 1966 May;43(2):293–313. doi: 10.1099/00221287-43-2-293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohlfing S. R., Crawford I. P. Purification and characterization of the beta-galactosidase of Aeromonas formicans. J Bacteriol. 1966 Mar;91(3):1085–1097. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.3.1085-1097.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SNEATH P. H. The change from polar to peritrichous flagellation in Chromobacterium spp. J Gen Microbiol. 1956 Aug;15(1):99–105. doi: 10.1099/00221287-15-1-99. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STANIER R. Y., INGRAHAM J. L. Protocatechuic acid oxidase. J Biol Chem. 1954 Oct;210(2):799–808. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sands D. C., Schroth M. N., Hildebrand D. C. Taxonomy of phytopathogenic pseudomonads. J Bacteriol. 1970 Jan;101(1):9–23. doi: 10.1128/jb.101.1.9-23.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanier R. Y., Palleroni N. J., Doudoroff M. The aerobic pseudomonads: a taxonomic study. J Gen Microbiol. 1966 May;43(2):159–271. doi: 10.1099/00221287-43-2-159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veldkamp H. Saprophytic coryneform bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1970;24:209–240. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.24.100170.001233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheelis M. L., Palleroni N. J., Stanier R. Y. The metabolism of aromatic acids by Pseudomonas testosteroni and P. acidovorans. Arch Mikrobiol. 1967;59(1):302–314. doi: 10.1007/BF00406344. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]






