Abstract
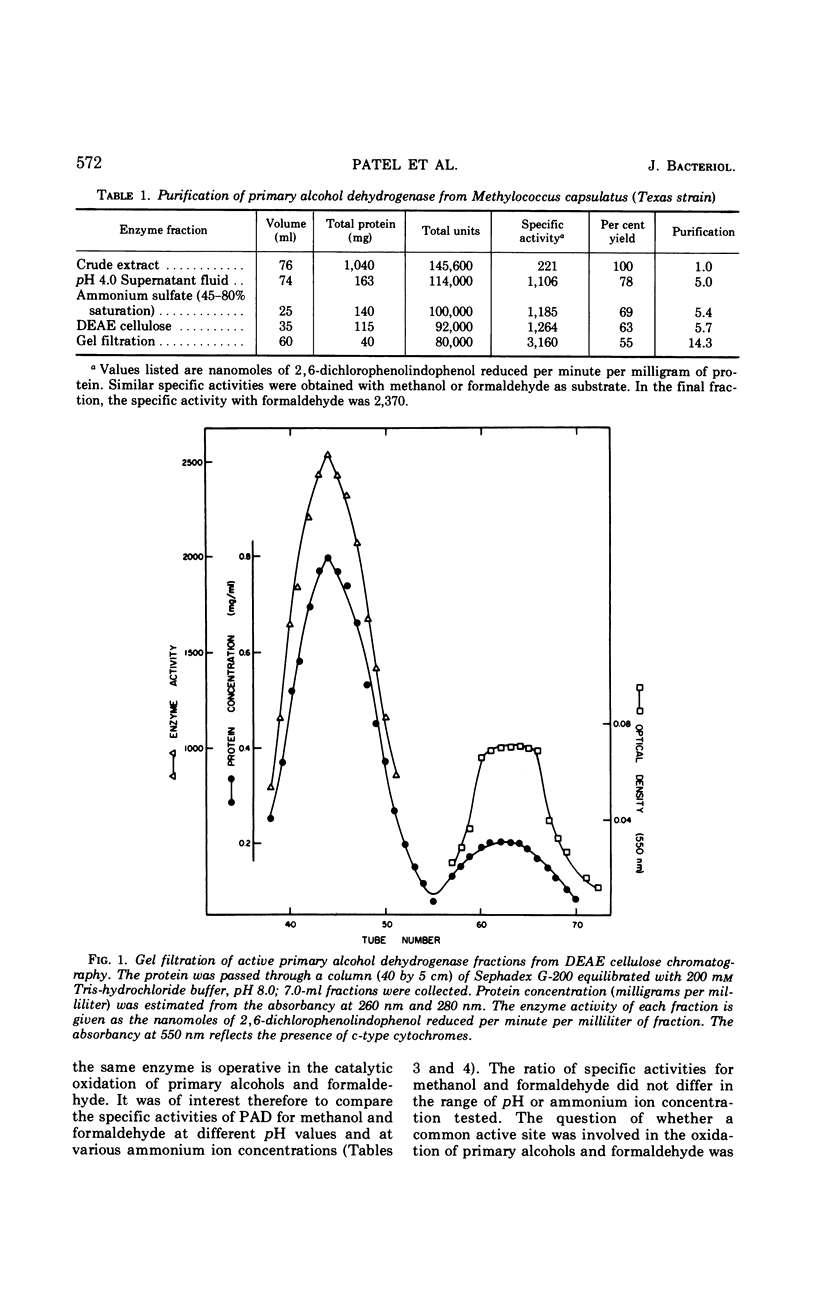
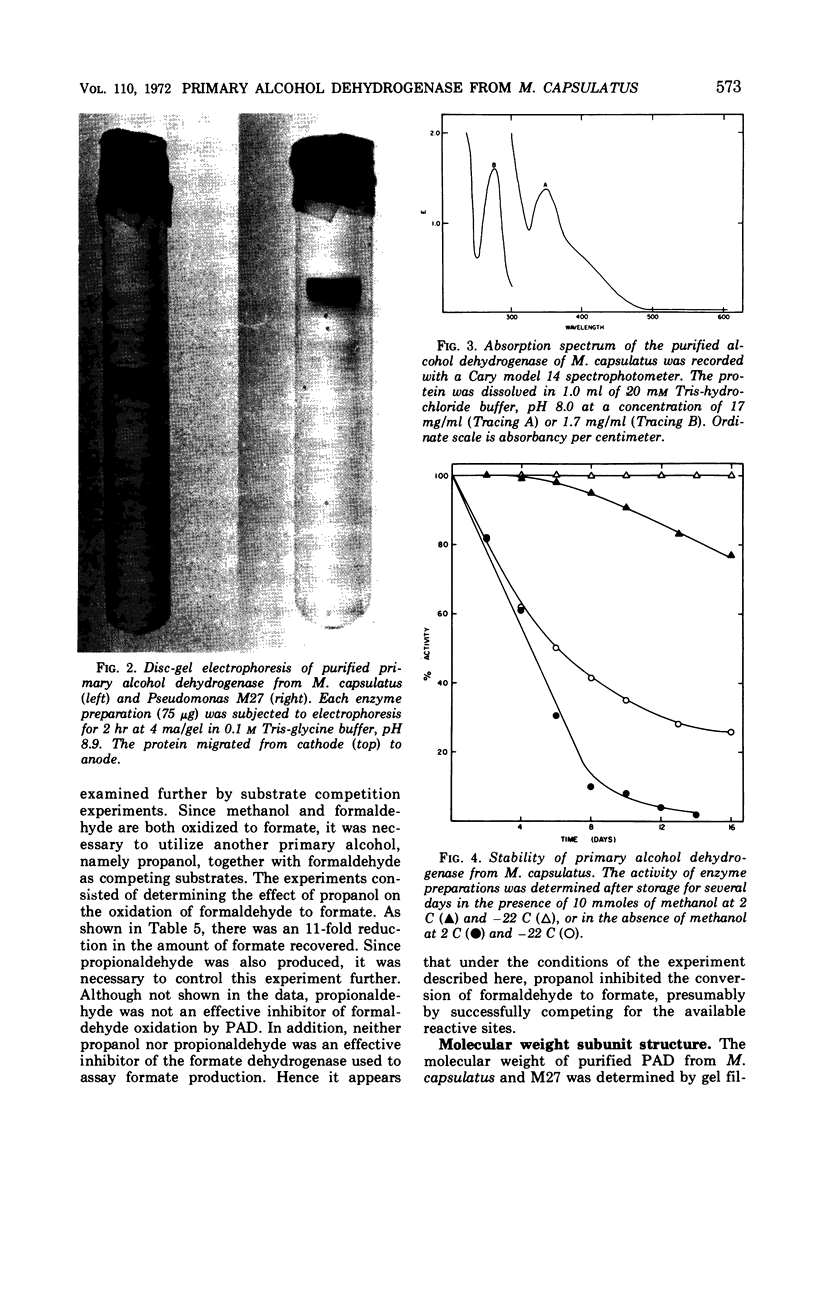
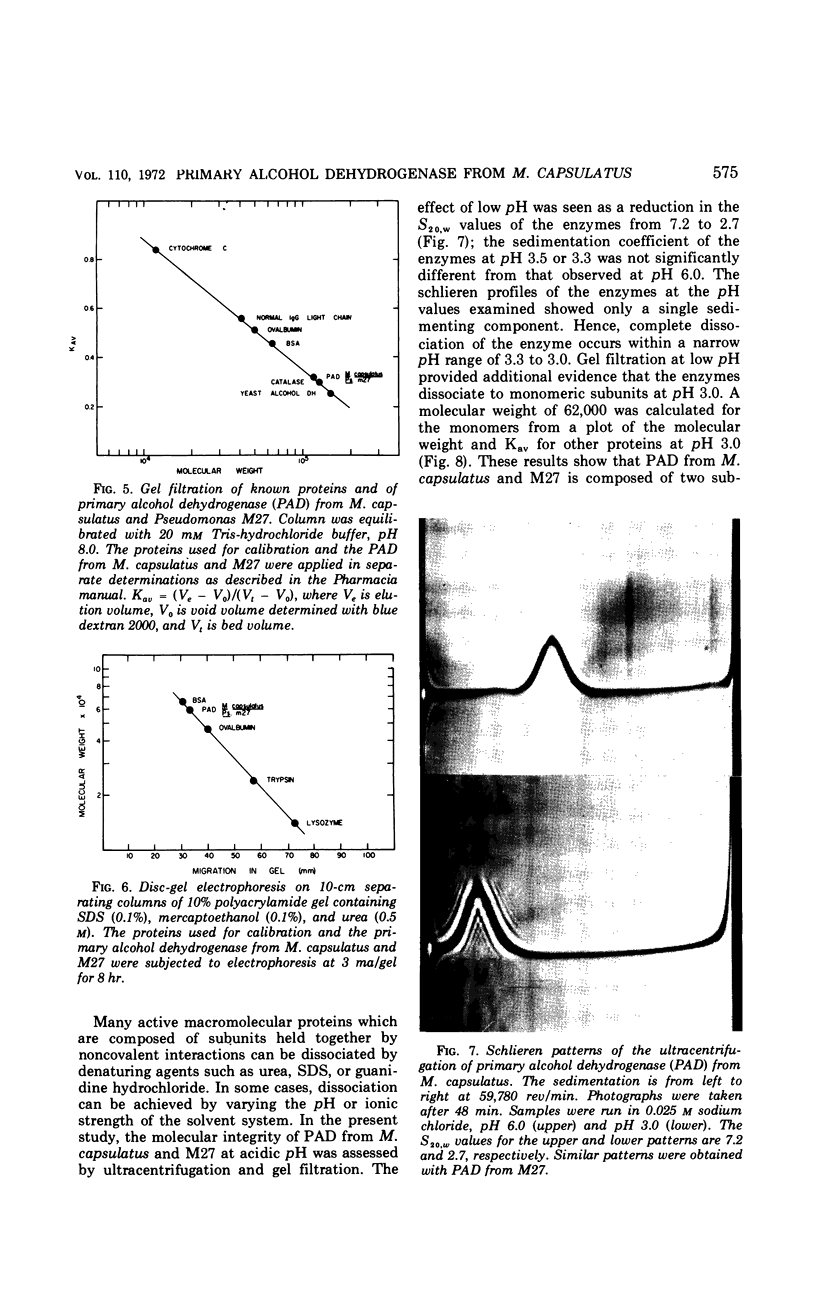
A primary alcohol dehydrogenase has been purified from Methylococcus capsulatus (Texas strain). The purified enzyme catalyzes the oxidation of methanol and formaldehyde to formate; other primary alcohols are oxidized to their corresponding aldehydes. Ammonium ions are required for enzyme activity. The enzyme has a molecular weight of 120,000 daltons and consists of two 62,000 molecular-weight subunits which dissociate at acidic pH. The enzyme is similar to an alcohol dehydrogenase enzyme isolated from Pseudomonas sp. M27.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews P. Estimation of the molecular weights of proteins by Sephadex gel-filtration. Biochem J. 1964 May;91(2):222–233. doi: 10.1042/bj0910222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anthony C., Zatman L. J. The microbial oxidation of methanol. 1. Isolation and properties of Pseudomonas sp. M27. Biochem J. 1964 Sep;92(3):609–614. doi: 10.1042/bj0920609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anthony C., Zatman L. J. The microbial oxidation of methanol. Purification and properties of the alcohol dehydrogenase of Pseudomonas sp. M27. Biochem J. 1967 Sep;104(3):953–959. doi: 10.1042/bj1040953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anthony C., Zatman L. J. The microbial oxidation of methanol. The alcohol dehydrogenase of Pseudomonas sp. M27. Biochem J. 1965 Sep;96(3):808–812. doi: 10.1042/bj0960808. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anthony C., Zatman L. J. The microbial oxidation of methanol. The prosthetic group of the alcohol dehydrogenase of Pseudomonas sp. M27: a new oxidoreductase prosthetic group. Biochem J. 1967 Sep;104(3):960–969. doi: 10.1042/bj1040960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay A. J., Skehel J. J., Burke D. C. Proteins synthesized in chick cells following infection with Semliki Forest virus. J Gen Virol. 1968 Sep;3(2):175–184. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-3-2-175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heptinstall J., Quayle J. R. Pathways leading to and from serine during growth of Pseudomonas AM1 on C1 compounds or succinate. Biochem J. 1970 Apr;117(3):563–572. doi: 10.1042/bj1170563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel R. N., Hoare D. S. Physiological studies of methane and methanol-oxidizing bacteria: oxidation of C-1 compounds by Methylococcus capsulatus. J Bacteriol. 1971 Jul;107(1):187–192. doi: 10.1128/jb.107.1.187-192.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribbons D. W., Harrison J. E., Wadzinski A. M. Metabolism of single carbon compounds. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1970;24:135–158. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.24.100170.001031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHEIDEGGER J. J. Une micro-méthode de l'immuno-electrophorèse. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1955;7(2):103–110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers D. F., Maizel J. V., Jr, Darnell J. E., Jr Evidence for virus-specific noncapsid proteins in poliovirus-infected HeLa cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Aug;54(2):505–513. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.2.505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





