Abstract
Background
Quantitative Trait Loci (QTL) affecting meat tenderness have been reported on Bovine chromosome 10. Here we examine variation at the Calpain 3 (CAPN3) gene in cattle, a gene located within the confidence interval of the QTL, and which is a positional candidate gene based on the biochemical activity of the protein.
Results
We identified single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP) in the genomic sequence of the CAPN3 gene and tested three of these in a sample of 2189 cattle. Of the three SNP genotyped, the CAPN3:c.1538+225G>T had the largest significant additive effect, with an allele substitution effect in the Brahman of α = -0.144 kg, SE = 0.060, P = 0.016, and the polymorphism explained 1.7% of the residual phenotypic variance in that sample of the breed. Significant haplotype substitution effects were found for all three breeds, the Brahman, the Belmont Red, and the Santa Gertrudis. For the common haplotype, the haplotype substitution effect in the Brahman was α = 0.169 kg, SE = 0.056, P = 0.003. The effect of this gene was compared to Calpastatin in the same sample. The SNP show negligible frequencies in taurine breeds and low to moderate minor allele frequencies in zebu or composite animals.
Conclusion
These associations confirm the location of a QTL for meat tenderness in this region of bovine chromosome 10. SNP in or near this gene may be responsible for part of the overall difference between taurine and zebu breeds in meat tenderness, and the greater variability in meat tenderness found in zebu and composite breeds. The evidence provided so far suggests that none of these tested SNP are causative mutations.
Background
The status of DNA tests for meat tenderness has been recently discussed [1] and so far there are only two genes identified that have consistent effects on meat tenderness reported in the literature, that for Calpastatin and Calpain 1 [2-5]. There are two polymorphisms in Calpain 1 (CAPN1), one appearing to be more useful in taurine breeds and one more useful in zebu breeds. On the other hand, although several possible causative mutations have been identified in Calpastatin (CAST), variation at this gene appears to affect all breed types.
Quantitative trait loci (QTL) for meat tenderness were located to bovine chromosome 10 in a Charolais × Brahman experimental population [1]. The authors suggested that the Calpain 3 (CAPN3) gene could be implicated because it occurred within the confidence interval of the location of the QTL and that calpain 3 protein activity had been implicated in meat tenderness in sheep [6,7], although DNA variants for CAPN3 have not been tested to determine whether they are associated with meat tenderness in any species.
Here we report the identification of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP) in CAPN3 and the testing of these SNP for associations to meat tenderness in a large sample of cattle of several breeds. We found that polymorphisms in the gene were not common in taurine cattle, so associations were only tested in zebu and composite animals, the term crossbred being reserved for animals with parents from different breeds. Zebu breeds and their tropically adapted composites are reported to have a 2 to 3 times greater heritability for meat tenderness than taurine breeds as well as a slightly higher mean value for shear force, a measure of meat tenderness [8]. These SNP appear to contribute primarily to the variation in tenderness in zebu or tropically adapted composite cattle.
Methods
Cattle Samples
The Beef CRC cattle, the methods of measurement of phenotypes, and the methods of DNA extraction have been reported previously [3,9,10]. After initial testing (cf. Results) the study was performed on the Brahman (BRM), Belmont Red (BEL) and Santa Gertrudis (SGT) animals in the sample. For the sample that was used, the number of sires and average number of offspring per sire for Brahman was 59 sires and a mean of 10.7 offspring per sire, for Belmont Red was 69 sires and a mean of 12.8 offspring per sire, and for Santa Gertrudis was 72 sires and a mean of 9.2 offspring per sire.
Meat tenderness was measured in kilograms using peak force measurements for the Musculus longissimus lumborum (LLPF) as described previously [9]. The least square means, standard deviations and heritabilities of this trait have been previously published for these animals [11]. The LLPF measurements of all of these animals were analysed by a general linear mixed model using restricted maximum likelihood in ASReml [12] where LLPF ~N(μ + kill group + herd of origin + age of slaughter + carcass weight + sire, σ2e) and where sire was fitted as a random effect as previously described [3,13], and variance components were estimated. The model accounted for the fixed effects of herd of origin and kill group, for the covariates of age at slaughter and carcass weight and the random effect of sire. There are several herds of origin associated with each breed so the average genetic effects due to breed and sire were included in the model as well as fixed environmental treatment effects; this avoids false associations due to inappropriate lumping of groups. To prevent the model being affected by the particular choice of animals or the estimates of the allelic effects being influenced by missing genotypic data, phenotypes for all animals were included in the model rather than only those that were genotyped.
SNP discovery
Genomic DNA for SNP discovery was obtained by direct sequencing of PCR products. Primers were obtained from the cDNA sequence for CAPN3 deposited by Ilian and coworkers (Genbank AF115744.1). The location of the exons was placed onto the sequence using a comparative analysis of sequences from other species. Then primers to amplify three segments of the gene were synthesized, one set flanking exon 6, one incorporating introns 10 and 11 and one that incorporated from intron 24 towards the 3' UTR (untranslated region) of the gene. DNA sequences were obtained using the Big-Dye 3.1 terminator kit from Applied Biosystems Inc. (ABI, Foster City, CA), using the manufacturer's instructions. Each fragment was sequenced in both directions in 10 animals including the Angus, Shorthorn and Brahman breeds. The DNA sequences were compared to sequences in Genbank using BLAST [14] to confirm the identity of the exons. These sequences were assessed, then they were assembled into contigs using phred and Phrap [15] and viewed using Consed [16]. PolyPhred [17] was used to identify variable bases with a threshold phred quality score (PQS) of 20. SNP were described using standard nomenclature [18].
SNP genotyping
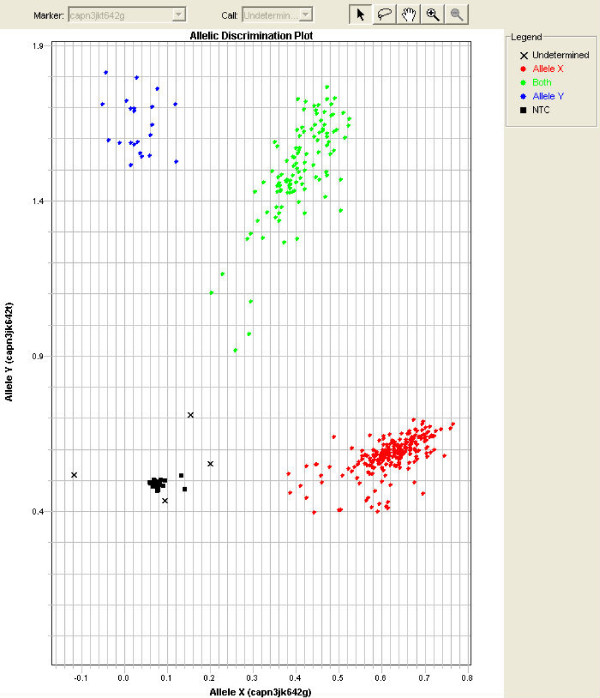
SNP were genotyped using the Taqman™ MGB allele discrimination method (ABI, Foster City, CA) as before [3] by two individuals. An example of one of the SNP is shown in Figure 1 following the recommendation of the NCI-NHGRI working group on initial reports of associations of genotypes and phenotypes [19]. Scoring was always performed without knowing the phenotypes. For ease of analysis and compact reporting of the data in the tables, genotypes were coded as 0, 1, 2 and 5 where 5 is unknown, 1 is always the heterozygote, 0 is the homozygote higher up the alphabet and 2 is the homozygote lower down the alphabet – so CC is 2 when AA is the alternative homozygote but 0 when GG is the alternative homozygote.
Figure 1.
The Taqman™ assay for CAPN3:c.1538+225G>T on cattle DNA.
Genotypes were tested for Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium (HWE), inferred haplotypes were used to calculate linkage disequilibrium (LD) as measured by r2 and differences in frequency between breeds were tested as previously described [3,20,21]. The significance of an r2 value was determined as χ21 = Nr2 where N is the sample size [20]. The genotypes and residual meat tenderness values were used to estimate the additive and allele substitution effects and their standard errors by regressing the number of copies of an allele against the trait value using the equation α = a + d(q-p) where α is the allele substitution effect, a is the additive effect, d is the dominance effect, and p + q = 1 and are the allele frequencies [3,22-25]. Equivalent results for this regression can be obtained from a linear model in a statistical program, treating the genotypes as a variate of 0, 1 and 2 copies of a particular allele. To obtain breed specific estimates the genotypes are nested within breed. The probability of the association was obtained directly from the t-test of the effect divided by its standard error. The proportion of the residual variance explained by a SNP or combination of SNP was calculated as the square of the correlation between the genotypes and the residual trait values. Epistasis between CAPN3 and CAST SNP was tested using the software EPEE [3], which uses the G2A model [22] to assess epistasis between two loci.
To estimate the effect of CAPN3 haplotypes on meat tenderness, the number of copies of the common haplotype was regressed against the residual meat tenderness values in the same way as the allele substitution effect. Two-locus haplotypes were used in the analysis for the following reasons. Firstly, two-locus SNP haplotypes can be obtained unambiguously from genotypes, except for the double heterozygote and it was ignored in this analysis. Secondly, the analysis was to regress the trait against the number of copies of the common haplotype. Using two-locus haplotypes reduces the genotypic heterogeneity of the one-copy and the no-copy groups, compared to analyses that use haplotypes based on more SNP. The expected number of genotypes equals 3n for n loci. Thirdly, the larger the number of loci making up the haplotype the smaller the number of individuals in the two-copies group, which will affect the accuracy of the estimates. The additive effect and the haplotype substitution effect of the common haplotype were calculated in the same way as the additive and allele substitution effects (cf. above). The use of two-locus haplotypes has the advantage that the analysis is essentially of the interval between the two SNP. With a large number of SNP one might restrict the analysis to adjacent intervals, but as there are only three SNP and therefore only three possible comparisons, all three intervals were analysed.
Results
We examined the DNA sequence traces to find polymorphisms that were present in all breeds. All of the SNP that were discovered were either polymorphic in the Brahman animals in the panel or were differences between Brahman on the one hand and the Angus and Shorthorn on the other hand. We chose three SNP that were polymorphic in the Brahman breed for further study, one for each of the fragments that we had sequenced (Table 1). These were 1) the amino acid replacing CAPN3:c.53T>G (Met18Arg), dbSNP id ss102661473, 2) the intronic CAPN3:c.1538+225G>T, ss102661474, and 3) the intronic CAPN3:c.2443-103G>C, ss102661475.
Table 1.
Primer sequences for the CAPN3 single nucleotide polymorphisms
| SNP | Name | 5'-3' sequence |
| CAPN3:c.53T>G | ||
| MGB-probes | CAPN3E6100T | 6FAM-TGAGCCCATGTCC |
| CAPN3E6100G | VIC-TGAGCCCAGGTCC | |
| Primers | CAPN3E6G100TU1 | ATGCCGACCGTCATTAGC |
| CAPN3E6G100TD1 | GAGTAGATGCCACTTGGGTTTC | |
| CAPN3:c.1538+225G>T | ||
| MGB-probes | CAPN3JK-V2-642G | VIC-TACACGCTCACATGC |
| CAPN3JK-V2-642T | 6FAM-ACACTCTCACATGCT | |
| Primers | CAPN3JKG642TU2 | ATTGCATGGCCTCCTGAC |
| CAPN3JKG642TD2 | CTCCAGAACACCTCTGGACTG | |
| CAPN3:c.2443-103G>C | ||
| MGB-probes | CAPN3X3-266G | 6FAM-CTTCCGTGTCTGGC |
| CAPN3X3-266C | VIC-TCTTCCCTGTCTGGC | |
| Primers | CAPN3X3G266CU2 | AGCCTCAGTTATGGCTTTATGC |
| CAPN3X3G266CD1 | AGATCAGAATGCACAATGAGACA |
To determine whether it was worth genotyping animals of all breeds, because these SNP were discovered in Brahman animals, we tested a group of taurine animals of three breeds. Testing the first SNP, c.2443-103G>C, there was 1 heterozygote in 124 taurine animals from the Angus, Hereford and Shorthorn breeds, so we did not use taurine samples for further genotyping because the chance of finding sufficient homozygotes of each genotype in those breeds would be low.
We examined the genotypes for deviations from HWE and for differences between breeds because significant differences in these measures could affect the subsequent analysis of association between DNA markers and the trait. The genotypes for all three SNP were in HWE and there were highly significant differences in genotype frequencies between breeds. The allele frequencies of the minor allele in the composite breeds were approximately half that found in the Brahman breed (Table 2), and given the very large sample sizes, these differences were extremely significant.
Table 2.
The means and standard errors for CAPN3 and CAST SNP and peak force in the longissimus muscle
| Locus | Breed | Homozygote 0 | Heterozygote 1 | Homozygote 2 | ||||||
| N1 | x2 | SE3 | N | x | SE | N | x | SE | ||
| CAPN3 | ||||||||||
| GG | GT | TT | ||||||||
| c.53T>G | BRM4 | 62 | -0.02 | 0.10 | 238 | -0.11 | 0.05 | 314 | 0.08 | 0.05 |
| c.53T>G | BEL5 | 26 | 0.06 | 0.12 | 203 | 0.10 | 0.05 | 609 | -0.02 | 0.03 |
| c.53T>G | SGT6 | 22 | 0.05 | 0.14 | 203 | -0.06 | 0.05 | 405 | 0.04 | 0.04 |
| GG | GT | TT | ||||||||
| c.1538+225G>T | BRM | 153 | -0.10 | 0.06 | 279 | -0.02 | 0.05 | 134 | 0.19 | 0.08 |
| c.1538+225G>T | BEL | 673 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 113 | -0.05 | 0.07 | 3 | 0.79 | 0.82 |
| c.1538+225G>T | SGT | 371 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 213 | -0.00 | 0.05 | 32 | -0.18 | 0.08 |
| CC | CG | GG | ||||||||
| c.2443-103G>C | BRM | 58 | -0.06 | 0.10 | 209 | -0.10 | 0.05 | 295 | 0.08 | 0.05 |
| c.2443-103G>C | BEL | 19 | 0.15 | 0.15 | 154 | 0.11 | 0.06 | 487 | -0.02 | 0.03 |
| c.2443-103G>C | SGT | 19 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 134 | -0.05 | 0.06 | 393 | 0.04 | 0.04 |
| CAST | ||||||||||
| AA | AG | GG | ||||||||
| c.2832A>G | BRM | 172 | -0.12 | 0.06 | 279 | -0.00 | 0.05 | 105 | 0.11 | 0.08 |
| c.2832A>G | BEL | 379 | -0.06 | 0.04 | 239 | 0.16 | 0.05 | 28 | 0.18 | 0.16 |
| c.2832A>G | SGT | 256 | -0.07 | 0.05 | 208 | 0.10 | 0.06 | 47 | 0.17 | 0.11 |
1Joint genotypes and phenotypes for genotype 0, 2 mean residual phenotype for genotype 0, 3 Standard error for the mean phenotype of genotype 0, 4 BRM Brahman, 5 BEL Belmont Red, 6 SGT Santa Gertrudis
To determine whether there may be high levels of LD between alleles, which may affect the interpretation of the allelic association to the trait, r2 was calculated from haplotypes inferred using the EM algorithm. The alleles were in significant LD in all breeds (Table 3). Some of the r2 values were small (r2~0.01) and were significant only because the sample size was large. CAPN3:c.1538+225G>T showed moderate LD to c.53T>G and c.2443-103G>C in Brahman but very low LD in Belmont Red and Santa Gertrudis. CAPN3:c.53T>C and c.2443-103G>C showed very high LD in all breeds. All the CAPN3 SNP showed very low LD to CAST:c.2832G>A in all breeds with an average r2 = 0.003, SE = 0.001, N = 9, as expected for unlinked loci. None of the CAPN3-CAST r2 values were significant.
Table 3.
Estimated LD between CAPN3 alleles in different breeds
| SNP pair | Breed | r2 | P |
| c.53T>G c.1538+225G>T | BRM | 0.366 | <<0.00001 |
| c.53T>G c.1538+225G>T | BEL | 0.008 | 0.01513 |
| c.53T>G c.1538+225G>T | SGT | 0.062 | <<0.00001 |
| c.53T>G c.2443-103G>C | BRM | 0.915 | <<0.00001 |
| c.53T>G c.2443-103G>C | BEL | 0.853 | <<0.00001 |
| c.53T>G c.2443-103G>C | SGT | 0.801 | <<0.00001 |
| c.1538+225G>T c.2443-103G>C | BRM | 0.374 | <<0.00001 |
| c.1538+225G>T c.2443-103G>C | BEL | 0.014 | 0.00317 |
| c.1538+225G>T c.2443-103G>C | SGT | 0.040 | <<0.00001 |
BRM, Brahman, BEL, Belmont Red, SGT, Santa Gertrudis
Significant associations were found between a CAPN3 SNP and LLPF in the Brahman and Belmont Red breeds but not in the Santa Gertrudis (Table 4). The strongest effect, in terms of residual variance explained, was found in the Brahman breed for the c.1538+225G>T SNP, where the GG genotype had increased meat tenderness. Both additive and allele substitution effects (α = 0.19 σp), were significant and the dominance effect was not significant. Although the Belmont Red breed also showed a large significant additive effect, this is based on a few animals and so should be treated with caution. In particular, the allele substitution effect was not significant and was essentially zero. The Belmont Red breed showed significant allele substitution effects for both c.53T>G and c.2443-103G>C. The Brahman breed showed large but non-significant effects for these latter two SNP, but the favourable genotype was reversed and so the allele substitution effect was of opposite polarity.
Table 4.
Association between the CAPN3 and CAST SNP and peak force in the longissimus muscle
| Locus | Breed | p01 | Vr2 | a3kg | SEa4 | Pa5 | α6kg | SEα | Pα |
| CAPN3 | |||||||||
| c.53T>G | BRM7 | 0.29 | 0.0111 | -0.046 | 0.082 | 0.578 | -0.103 | 0.060 | 0.088 |
| c.53T>G | BEL8 | 0.15 | 0.0043 | 0.037 | 0.057 | 0.520 | 0.089 | 0.044 | 0.046 |
| c.53T>G | SGT9 | 0.20 | 0.0038 | 0.005 | 0.074 | 0.942 | -0.058 | 0.058 | 0.315 |
| c.1538+225G>T | BRM | 0.52 | 0.0172 | -0.147 | 0.066 | 0.026 | -0.144 | 0.060 | 0.016 |
| c.1538+225G>T | BEL | 0.92 | 0.0052 | -0.380 | 0.046 | 0.000† | 0.003 | 0.037 | 0.944 |
| c.1538+225G>T | SGT | 0.78 | 0.0040 | 0.108 | 0.066 | 0.102 | 0.068 | 0.060 | 0.260 |
| c.2443-103G>C | BRM | 0.29 | 0.0108 | -0.067 | 0.080 | 0.402 | -0.115 | 0.063 | 0.068 |
| c.2443-103G>C | BEL | 0.15 | 0.0061 | 0.083 | 0.065 | 0.203 | 0.114 | 0.053 | 0.031 |
| c.2443-103G>C | SGT | 0.16 | 0.0021 | -0.005 | 0.087 | 0.959 | -0.058 | 0.065 | 0.371 |
| CAST | |||||||||
| c.2832A>G | BRM | 0.56 | 0.0088 | -0.113 | 0.065 | 0.082 | -0.113 | 0.061 | 0.064 |
| c.2832A>G | BEL | 0.77 | 0.0195 | -0.120 | 0.047 | 0.011 | -0.171 | 0.040 | 0.000† |
| c.2832A>G | SGT | 0.70 | 0.0142 | -0.120 | 0.061 | 0.051 | -0.140 | 0.055 | 0.011 |
1Allele frequency for allele 0, 2 proportion of the residual variance explained by the SNP, 3 additive effect, 4 standard error of the additive effect, 5 P value of the additive effect, 6 allele substitution effect, 7 BRM Brahman, 8 BEL Belmont Red, 9 SGT Santa Gertrudis, † P < 0.0001
Significant associations were found for haplotypes of CAPN3 and LLPF (Tables 5 and 6). Interval 2 (Int2), between c.1538+225G>T and c.2443-103G>C, showed significant additive or allele substitution effects in all breeds, where the haplotype substitution effect in Brahman equalled 0.22 σp. The effect of Int1, between c.53T>G and c.1538+225G>T, was not significant in all breeds, and the effect of Int3, between c.53T>G and c.2443-103G>C, was not significant in any breed. Notably, the effects of Int1 and Int2 were significant in the Santa Gertrudis even though the individual locus effects were not significant in that breed. The haplotype substitution effects had more similar sizes than the individual SNP allele substitution effects in the different breeds. The haplotype substitution effect had the opposite polarity in the Santa Gertrudis to the other breeds.
Table 5.
Means and standard errors of CAPN3 two-locus haplotypes and meat tenderness in different breeds
| Locus | Breed | No copies1 | One copy2 | Two copies3 | ||||||
| N4 | x5kg | SE6 | N | × kg | SE | N | × kg | SE | ||
| No GT haplotypes | One GT haplotype | Two GT haplotypes | ||||||||
| Int17 | BRM10 | 185 | 0.13 | 0.06 | 192 | -0.04 | 0.06 | 28 | -0.10 | 0.15 |
| Int1 | BEL11 | 28 | 0.14 | 0.14 | 261 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 458 | -0.02 | 0.03 |
| Int1 | SGT12 | 51 | -0.06 | 0.08 | 282 | -0.07 | 0.04 | 206 | 0.12 | 0.06 |
| No TG haplotypes | One TG haplotype | Two TG haplotypes | ||||||||
| Int28 | BRM | 176 | 0.13 | 0.07 | 184 | -0.01 | 0.06 | 27 | -0.23 | 0.15 |
| Int2 | BEL | 22 | 0.23 | 0.17 | 212 | 0.03 | 0.05 | 379 | -0.01 | 0.04 |
| Int2 | SGT | 49 | -0.10 | 0.07 | 227 | -0.07 | 0.05 | 211 | 0.10 | 0.05 |
| No GG haplotypes | One GG haplotype | Two GG haplotypes | ||||||||
| Int39 | BRM | 61 | -0.02 | 0.10 | 13 | -0.29 | 0.24 | 276 | 0.09 | 0.05 |
| Int3 | BEL | 24 | 0.10 | 0.13 | 16 | 0.09 | 0.15 | 467 | -0.03 | 0.04 |
| Int3 | SGT | 22 | 0.05 | 0.14 | 26 | -0.08 | 0.12 | 354 | 0.05 | 0.04 |
1No copies of the haplotype for the common allele, 2 one copy of the haplotype for the common allele, 3 two copies of the haplotype of the common allele, 4 N sample size, 5 × average meat tenderness, 6 SE standard error, 7 Int1 haplotype between CAPN3:c.53T>G and CAPN3:c.1538+225G>T, 8 Int2 haplotype between CAPN3:c.1538+225G>T and CAPN3:c.2443-103G>C, 9 Int3 haplotype between CAPN3:c.53T>G and CAPN3:c.2443-103G>C, 10 BRM Brahman, 11 BEL Belmont Red, 12 SGT Santa Gertrudis
Table 6.
Association between CAPN3 two-locus haplotypes and meat tenderness
| Locus | Breed | p21 | Vr2 | a3 kg | SE4 | Pa5 | α6gg | SE | Pα |
| Int17 | BRM | 0.31 | 0.0118 | 0.117 | 0.060 | 0.054 | 0.137 | 0.058 | 0.018 |
| Int1 | BEL | 0.79 | 0.0031 | 0.077 | 0.046 | 0.094 | 0.073 | 0.042 | 0.082 |
| Int1 | SGT | 0.64 | 0.0150 | -0.090 | 0.055 | 0.104 | -0.119 | 0.053 | 0.026 |
| Int28 | BRM | 0.31 | 0.0149 | 0.183 | 0.060 | 0.003 | 0.169 | 0.056 | 0.003 |
| Int2 | BEL | 0.79 | 0.0040 | 0.122 | 0.044 | 0.005 | 0.076 | 0.042 | 0.069 |
| Int2 | SGT | 0.67 | 0.0136 | -0.103 | 0.052 | 0.050 | -0.125 | 0.050 | 0.012 |
| Int39 | BRM | 0.81 | 0.0092 | -0.057 | 0.092 | 0.540 | -0.260 | 0.168 | 0.122 |
| Int3 | BEL | 0.94 | 0.0020 | 0.064 | 0.060 | 0.288 | 0.110 | 0.125 | 0.381 |
| Int3 | SGT | 0.91 | 0.0016 | -0.001 | 0.081 | 0.992 | -0.107 | 0.175 | 0.542 |
1Frequency of common haplotype, 2 proportion of the residual variance explained by the common haplotype, 3 additive effect, 4 standard error of the additive effect, 5 P value of the additive effect, 6 haplotype substitution effect, 7 Int1 haplotype between CAPN3:c.53T>G and CAPN3:c.1538+225G>T, 8 Int2 haplotype between CAPN3:c.1538+225G>T and CAPN3:c.2443-103G>C, 9 Int3 haplotype between CAPN3:c.53T>G and CAPN3:c.2443-103G>C, 10 BRM Brahman, 11 BEL Belmont Red, 12 SGT Santa Gertrudis
The significant associations for CAST:c2832G>A were included because breed specific values have not previously been reported for this data set, only values for combined data (Table 4). The allele substitution effects had the same polarity in all breeds. This CAST SNP had similar sized effects in all three breeds. That differs from the CAPN3 SNP in this study, which showed different sizes in different breeds. In the Brahman, the CAPN3:c.1538+225G>T SNP showed a similar size to the CAST:c.2832G>A SNP.
We found no strong evidence of epistatic interactions between CAPN3 SNP and CAST. One comparison out of 12 had a P value < 0.05, for the additive × additive component in the Santa Gertrudis breed for the comparison between CAPN3:c.1538+225G>T and CAST:c.2832A>G, with aa = 0.19 kg, SE = 0.100, P value = 0.038, which was close to expected for the number of tests performed.
Discussion
SNP at the CAPN3 gene confirm that there is a QTL affecting meat tenderness on bovine chromosome 10. The associations are consistent with CAPN3 being a positional candidate gene for the effect, with the strongest evidence found in Brahman animals. Further genotyping should be performed on neighbouring genes and the surrounding genetic region to exclude other genes. The intronic CAPN3:c.1538+225G>T SNP shows the largest effect, while the other SNP have weaker and inconsistent effects in different breeds. As c.1538+225G>T is located between the other two SNP, this might suggest that the causal mutations lie near to it. However, given the pattern of LD between the three SNP, that the two flanking SNP are in high LD in all breeds but in low LD to the central SNP in the composite breeds, it is possible that the causative mutations do not lie centrally in the gene; only the Brahman breed had some LD between c.1538+225G>T and the other SNP, and only in the Brahman breed was there similarity in the association to meat tenderness for all SNP. This suggests that haplotypes in the Brahman are more closely aligned to the causative mutation than in the composite breeds. Nevertheless, the differences in association between these SNP in different breeds could point to there being more than one causative mutation. These results suggest that it may be useful to discover other SNP in and around the CAPN3 gene and to examine these for functional, mechanistic explanations for the differences in meat tenderness as well as other traits.
The haplotype substitution effect is significant in all breeds for a haplotype that spans the 3' half of the gene. The common allele at each of the three SNP is not associated consistently with increased meat tenderness in any breed, so testing a haplotype of the common alleles is not biased towards a particular result. The analysis of the haplotypes shows stronger effects than the individual SNP associations. The significant haplotype effects suggest that a QTL exists for this trait in all breeds, despite the lack of association in the Santa Gertrudis in the single SNP analysis. The failure of the single SNP analysis in the Santa Gertrudis, as well as the haplotype substitution effect being of opposite polarity to the other breeds, suggests that the Santa Gertrudis breed has a more complex LD structure of SNP around the causative mutation. This may be a consequence of its composite origins. The failure to find evidence in any particular single SNP association test is likely to be due to differences in the amount and polarity of allelic association between the SNP and the causative mutation in that particular breed, as well as the power of the experiment to detect the association at a particular significance threshold. This echos the critique of using TAG SNP [26] as a tool for association mapping because the LD relationships between genotyped SNP cannot be used to predict the LD relationships for unknown SNP and hence for SNP-trait associations [27]. Nevertheless, the high LD between c.53T>G and c.2443-103G>C in all breeds but the failure to detect a haplotype substitution effect for these two SNP may suggest that the QTL is not in strong LD with these two SNP.
These SNP appear to be detecting a nearby QTL but they are not merely markers of difference between taurine and zebu cattle. Due to the many differences between zebu and taurine cattle, the analysis of fixed zebu-taurine differences in composite cattle is a way of tracking the influence of particular DNA segments, but such differences only explain increased genetic variability of recently crossbred cattle. However, in this case, because these DNA variants are SNP discovered in the Brahman, and are studied within that breed, the association indicated that the QTL contributes to the greater genetic variance for meat tenderness in the Brahman and other tropically adapted cattle. Identifying more SNP within the Brahman in this genetic region, particularly those in high LD to c.1538+225G>T, would be the start of a better understanding of how this gene or the surrounding genetic region affects meat tenderness.
Conclusion
SNP in the positional candidate gene CAPN3 in a population association study confirm the location of a QTL for meat tenderness to bovine chromosome 10 originally identified in a QTL linkage experiment. The SNP variants were largely found in the zebu and composite breeds and this study implicates the QTL they detect in the greater heritability and mean trait values for meat tenderness found in zebu cattle compared to taurine cattle.
Authors' contributions
WB planned the experiment, designed primers, analysed data and drafted the manuscript. BH and RB generated and scored genotypes for CAPN3. MT sequenced the CAPN3 gene. All authors read the manuscript.
Acknowledgments
Acknowledgements
We thank D.J. Johnston for making available the LLPF measurements of tropical cattle in the Beef CRC database, M.E. Goddard for discussion of the estimation of standard errors of allele substitution effects, and A. Reverter, K.C. Prayaga and two anonymous referees for comments that improved the manuscript. This work was funded as part of a co-operative research agreement between Meat and Livestock Australia, the core parties of the CRC for Cattle and Beef Quality – CSIRO, New South Wales DPI, Queensland DPI&F, and the University of New England -, and Catapult Genetics P/L.
Contributor Information
William Barendse, Email: Bill.Barendse@csiro.au.
Blair E Harrison, Email: Blair.Harrison@csiro.au.
Rowan J Bunch, Email: Rowan.Bunch@csiro.au.
Merle B Thomas, Email: merle.thomas@cpsu.org.au.
References
- Davis GP, Moore SS, Drinkwater RD, Shorthose WR, Loxton ID, Barendse W, Hetzel DJS. QTL for meat tenderness in the M. longissimus lumborum of cattle. Anim Genet. 2008;39:40–45. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2052.2007.01677.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barendse W. DNA markers for meat tenderness. WO02064820. 2002. pp. 1–88.
- Barendse W, Harrison BE, Hawken RJ, Ferguson DM, Thompson JM, Thomas MB, Bunch RJ. Epistasis between calpain 1 and its inhibitor calpastatin within breeds of cattle. Genetics. 2007;176:2601–2610. doi: 10.1534/genetics.107.074328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Page BT, Casas E, Heaton MP, Cullen NG, Hyndman DL, Morris CA, Crawford AM, Wheeler TL, Koohmaraie M, Keele JW, Smith TPL. Evaluation of single-nucleotide polymorphisms in CAPN1 for association with meat tenderness in cattle. J Anim Sci. 2002;80:3077–3085. doi: 10.2527/2002.80123077x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White SN, Casas E, Wheeler TL, Shackelford SD, Koohmaraie M, Riley DG, Chase Jr CC, Johnson DD, Keele JW, Smith TPL. A new single nucleotide polymorphism in CAPN1 extends the current tenderness marker test to include cattle of Bos indicus, Bos taurus, and crossbred descent. J Anim Sci. 2005;83:2001–2008. doi: 10.2527/2005.8392001x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ilian MA, Bekhit AE, Bickerstaffe R. The relationship between meat tenderization, myofibril fragmentation and autolysis of calpain 3 during post-mortem aging. Meat Sci. 2004;66:387–397. doi: 10.1016/S0309-1740(03)00125-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ilian MA, Morton JD, Bekhit AED, Roberts N, Palmer B, Sorimachi H, Bickerstaffe R. Effect of preslaughter feed withdrawal period on longissimus tenderness and the expression of calpains in the ovine. J Agric Food Chem. 2001;49:1990–1998. doi: 10.1021/jf0010026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reverter A, Johnston DJ, Ferguson DM, Perry D, Goddard ME, Burrow HM, Oddy VH, Thompson JM, Bindon BM. Genetic and phenotypic characterisation of animal, carcass, and meat quality traits from temperate and tropically adapted beef breeds. 4. Correlations among animal, carcass, and meat quality traits. Aust J Agric Res. 2003;54:149–158. doi: 10.1071/AR02088. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Perry D, Shorthose WR, Ferguson DM, Thompson JM. Methods used in the CRC program for the determination of carcass yield and beef quality. Aust J Exp Agr. 2001;41:953–957. doi: 10.1071/EA00092. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Upton W, Burrow HM, Dundon A, Robinson DL, Farrell EB. CRC breeding program design, measurements and database: methods that underpin CRC research results. Aust J Exp Agr. 2001;41:943–952. doi: 10.1071/EA00064. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston DJ, Reverter A, Ferguson DM, Thompson JM, Burrow HM. Genetic and phenotypic characterisation of animal, carcass, and meat quality traits from temperate and tropically adapted beef breeds. 3. Meat quality traits. Aust J Agric Res. 2003;54:135–147. doi: 10.1071/AR02087. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmour AR, Thompson R, Cullis BR. Average information REML: An efficient algorithm for variance parameter estimation in linear mixed models. Biometrics. 1995;51:1440–1450. doi: 10.2307/2533274. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Barendse W, Bunch RJ, Kijas JW, Thomas MB. The effect of genetic variation of the retinoic acid receptor-related orphan receptor C gene on fatness in cattle. Genetics. 2007;175:843–853. doi: 10.1534/genetics.106.064535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990;215:403–410. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewing B, Hillier L, Wendl MC, Green P. Base-calling of automated sequencer traces using phred. I. Accuracy assessment. Genome Res. 1998;8:175–185. doi: 10.1101/gr.8.3.175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon D, Abajian C, Green P. Consed: a graphical tool for sequence finishing. Genome Res. 1998;8:195–202. doi: 10.1101/gr.8.3.195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nickerson DA, Tobe VO, Taylor SL. PolyPhred: Automating the detection and genotyping of single nucleotide substitutions using fluorescence-based resequencing. Nucl Acids Res. 1997;25:2745–2751. doi: 10.1093/nar/25.14.2745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Den Dunnen JT, Antonarakis SE. Mutation nomenclature extensions and suggestions to describe complex mutations: a discussion. Hum Mut. 2000;15:7–12. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1098-1004(200001)15:1<7::AID-HUMU4>3.0.CO;2-N. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chanock SJ, Manolio T, Boehnke M, Boerwinkle E, Hunter DJ, Thomas G, Hirschhorn JN, Abecasis G, Altshuler D, Bailey-Wilson JE, Brooks LD, Cardon LR, Daly M, Donnelly P, Fraumeni JF, Freimer NB, Gerhard DS, Gunter C, Guttmacher AE, Guyer MS, Harris EL, Hoh J, Hoover R, Kong CA, Merikangas KR, Morton CC, Palmer LJ, Phimister EG, Rice JP, Roberts J, Rotimi C, Tucker MA, Vogan KJ, Wacholder S, Wijsman EM, Winn DM, Collins FS. Replicating genotype-phenotype associations. Nature. 2007;447:655–660. doi: 10.1038/447655a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill WG, Robertson A. Linkage disequilibrium in finite populations. Theor Appl Genet. 1968;38:226–231. doi: 10.1007/BF01245622. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weir BS. Genetic Data Analysis II. Second. Sunderland, MA , Sinauer Associates, Inc; 1996. pp. 1–445. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng ZB, Wang T, Zou W. Modeling quantitative trait loci and interpretation of models. Genetics. 2005;169:1711–1725. doi: 10.1534/genetics.104.035857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher RA. The correlation between relatives on the supposition of Mendelian inheritance. Trans Roy Soc Edin. 1918;52:399–433. [Google Scholar]
- Fisher RA. Average excess and average effect of a gene substitution. Ann Eugen. 1941;11:53–63. [Google Scholar]
- Lande R, Thompson R. Efficiency of marker-assisted selection in the improvement of quantitative traits. Genetics. 1990;124:743–756. doi: 10.1093/genetics/124.3.743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman JM, Cooper JD, Todd JA, Clayton DG. Detecting disease associations due to linkage disequilibrium using haplotype tags: a class of tests and the determinants of statistical power. Hum Hered. 2003;56:18–31. doi: 10.1159/000073729. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terwilliger JD, Hiekkalinna T. An utter refutation of the 'Fundamental Theorem of the HapMap'. Eur J Hum Genet. 2006;14:426–437. doi: 10.1038/sj.ejhg.5201583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]