Abstract
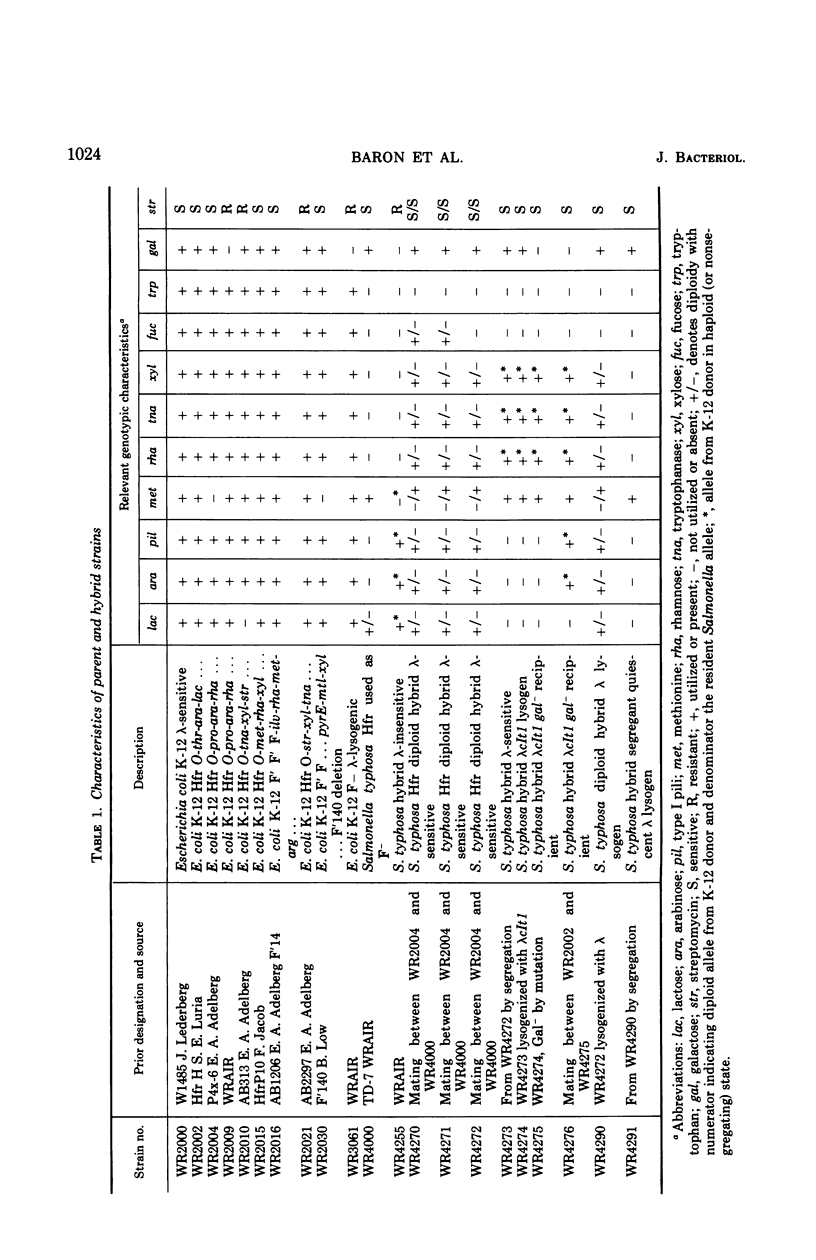
Hybrids between Escherichia coli K-12 and Salmonella typhosa which conserved a continuous K-12 chromosomal diploid segment extending from pro through ara to the strA locus were sensitive to plaque formation by wild-type λ. These partially diploid S. typhosa hybrids could be lysogenized with λ and subsequently induced to produce infectious phage particles. When the K-12 genes were segregated from a lysogenic S. typhosa hybrid, phage-productive ability was no longer detectable due to loss of a genetic region necessary for vegetative replication of λ. However, λ prophage was shown to persist in a quiescent state in the S. typhosa hybrid segregant with phage-productive ability being reactivated after replacement of the essential K-12 λ replication region. Low-frequency transduction and high-frequency transduction lysates containing the gal+ genes of S. typhosa were prepared by induction of λ-lysogenic S. typhosa hybrids indicating that the attλ site is chromosomally located in S. typhosa in close proximity to the gal locus as in E. coli K-12. After propagation in S. typhosa hybrids, λ was subject to restriction by E. coli K-12 recipients, thus establishing that S. typhosa does not perform the K-12 modification of λ deoxyribonucleic acid. Hybrids of S. typhosa, however, did not restrict λ grown previously on E. coli K-12. The K-12 genetic region required for λ phage production in S. typhosa was located within min 66 to min 72 on the genetic map of the E. coli chromosome. Transfer of an F-merogenote encompassing the 66 to 72 min E. coli chromosomal region to λ-insensitive S. typhosa hybrids enabled them to replicate wild-type λ. The λ-insensitive S. typhosa hybrid, WR4255, which blocks λ replication, can be mutagenized to yield mutant strains sensitive to λvir and λimm434. These WR4255 mutants remained insensitive to plaque formation by wild-type λ.
Full text
PDF


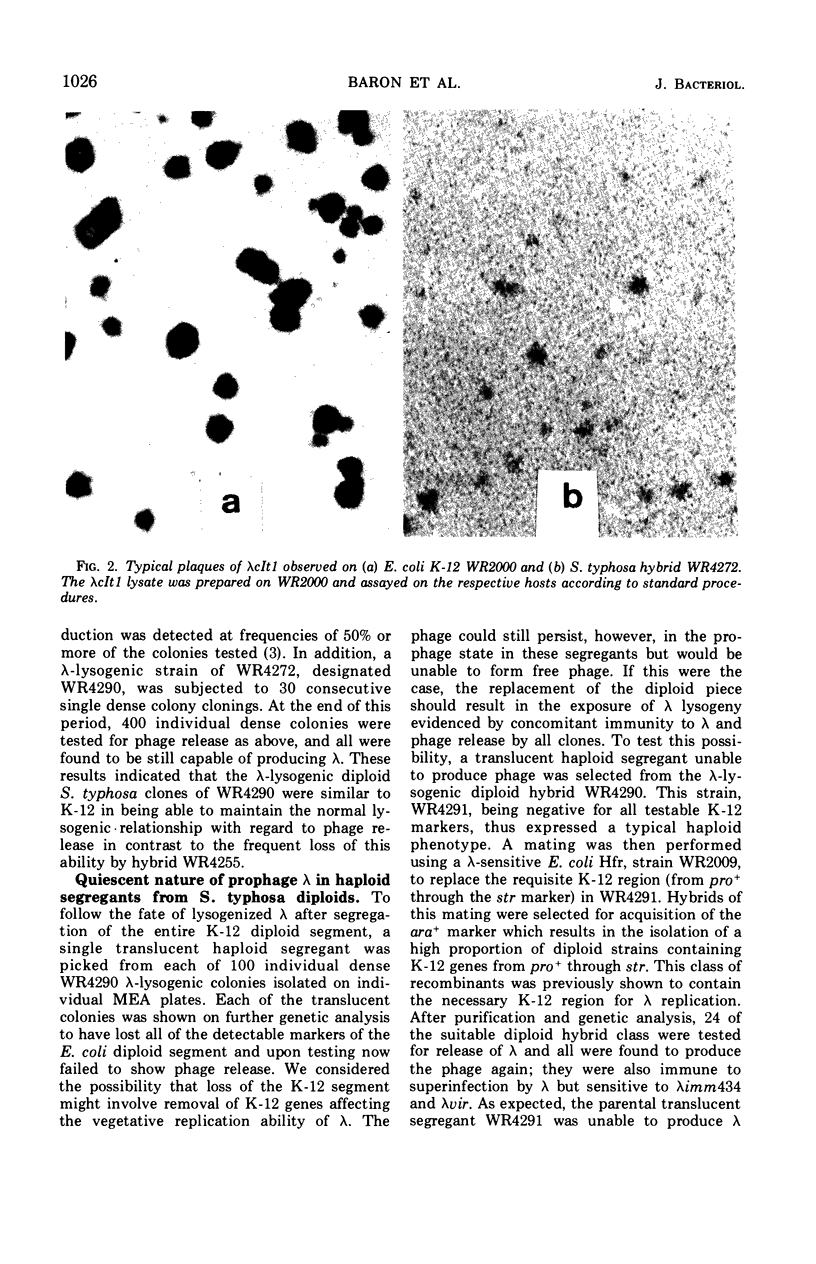





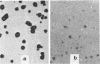
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARON L. S., SPILMAN W. M., CAREY W. F. Diploid heterozygous hybrids from matings between Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhosa. J Exp Med. 1960 Aug 1;112:361–372. doi: 10.1084/jem.112.2.361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARON L. S., SPILMAN W. M., CAREY W. F. Hybridization of Salmonella species by mating with Escherichia coli. Science. 1959 Sep 4;130(3375):566–567. doi: 10.1126/science.130.3375.566. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERTANI G., WEIGLE J. J. Host controlled variation in bacterial viruses. J Bacteriol. 1953 Feb;65(2):113–121. doi: 10.1128/jb.65.2.113-121.1953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron L. S., Carey W. F., Spilman W. M. GENETIC RECOMBINATION BETWEEN ESCHERICHIA COLI AND SALMONELLA TYPHIMURIUM. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1959 Jul;45(7):976–984. doi: 10.1073/pnas.45.7.976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron L. S., Penido E., Ryman I. R., Falkow S. Behavior of coliphage lambda in hybrids between Escherichia coli and Salmonella. J Bacteriol. 1970 Apr;102(1):221–233. doi: 10.1128/jb.102.1.221-233.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler B., Echols H. Regulation of bacteriophage lambda development by gene N: properties of a mutation that bypasses N control of late protein synthesis. Virology. 1970 Feb;40(2):212–222. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90396-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calendar R., Lindqvist B., Sironi G., Clark A. J. Characterization of REP- mutants and their interaction with P2 phage. Virology. 1970 Jan;40(1):72–83. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90380-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denhardt D. T., Dressler D. H., Hathaway A. THE ABORTIVE REPLICATION OF PhiX174 DNA IN A RECOMBINATION-DEFICIENT MUTANT OF Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Mar;57(3):813–820. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.3.813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falkow S., Baron L. S. Plasmid formation after lambda bacteriophage infection of Escherichia coli-Salmonella typhosa hybrids. J Bacteriol. 1970 Apr;102(1):288–290. doi: 10.1128/jb.102.1.288-290.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falkow S., Rownd R., Baron L. S. GENETIC HOMOLOGY BETWEEN ESCHERICHIA COLI K-12 AND SALMONELLA. J Bacteriol. 1962 Dec;84(6):1303–1312. doi: 10.1128/jb.84.6.1303-1312.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopkins N. Bypassing a positive regulator: isolation of a lambda mutant that does not require N product to grow. Virology. 1970 Feb;40(2):223–229. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90397-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOHNSON E. M., FALKOW S., BARON L. S. CHROMOSOME TRANSFER KINETICS OF SALMONELLA HFR STRAINS. J Bacteriol. 1964 Aug;88:395–400. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.2.395-400.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOHNSON E. M., FALKOW S., BARON L. S. RECIPIENT ABILITY OF SALMONELLA TYPHOSA IN GENETIC CROSSES WITH ESCHERICHIA COLI. J Bacteriol. 1964 Jan;87:54–60. doi: 10.1128/jb.87.1.54-60.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOHNSON E. M., KRAUSKOPF B., BARON L. S. GENETIC MAPPING OF VI AND SOMATIC ANTIGENIC DETERMINANTS IN SALMONELLA. J Bacteriol. 1965 Aug;90:302–308. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.2.302-308.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson E. M., Easterling S. B., Baron L. S. Conservation and transfer of Escherichia coli genetic segments by partial diploid Hfr strains of Salmonella typhosa. J Bacteriol. 1970 Nov;104(2):668–673. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.2.668-673.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson E. M., Krauskopf B., Baron L. S. Genetic analysis of the ViA-his chromosomal region in Salmonella. J Bacteriol. 1966 Nov;92(5):1457–1463. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.5.1457-1463.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kayajanian G. Plating of lambda derivatives on an Escherichia coli-Salmonella typhosa hybrid. Virology. 1970 Mar;40(3):763–767. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90225-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low B. Formation of merodiploids in matings with a class of Rec- recipient strains of Escherichia coli K12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 May;60(1):160–167. doi: 10.1073/pnas.60.1.160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naha P. M. Bacterial control of lambda replication. I. Initial characterization of a rep mutation of Escherichia coli K12. Virology. 1968 Nov;36(3):434–441. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(68)90168-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pironio M., Ghysen A. A bacterial mutation which affects recognition of the N gene product of bacteriophage lambda. Mol Gen Genet. 1970;108(4):374–375. doi: 10.1007/BF00267775. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. R. Specialized transduction of the Salmonella hut operons by coliphage lambda: deletion analysis of the hut operons employing lambda-phut. Virology. 1971 Jul;45(1):208–223. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90128-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor A. L. Current linkage map of Escherichia coli. Bacteriol Rev. 1970 Jun;34(2):155–175. doi: 10.1128/br.34.2.155-175.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]