Abstract
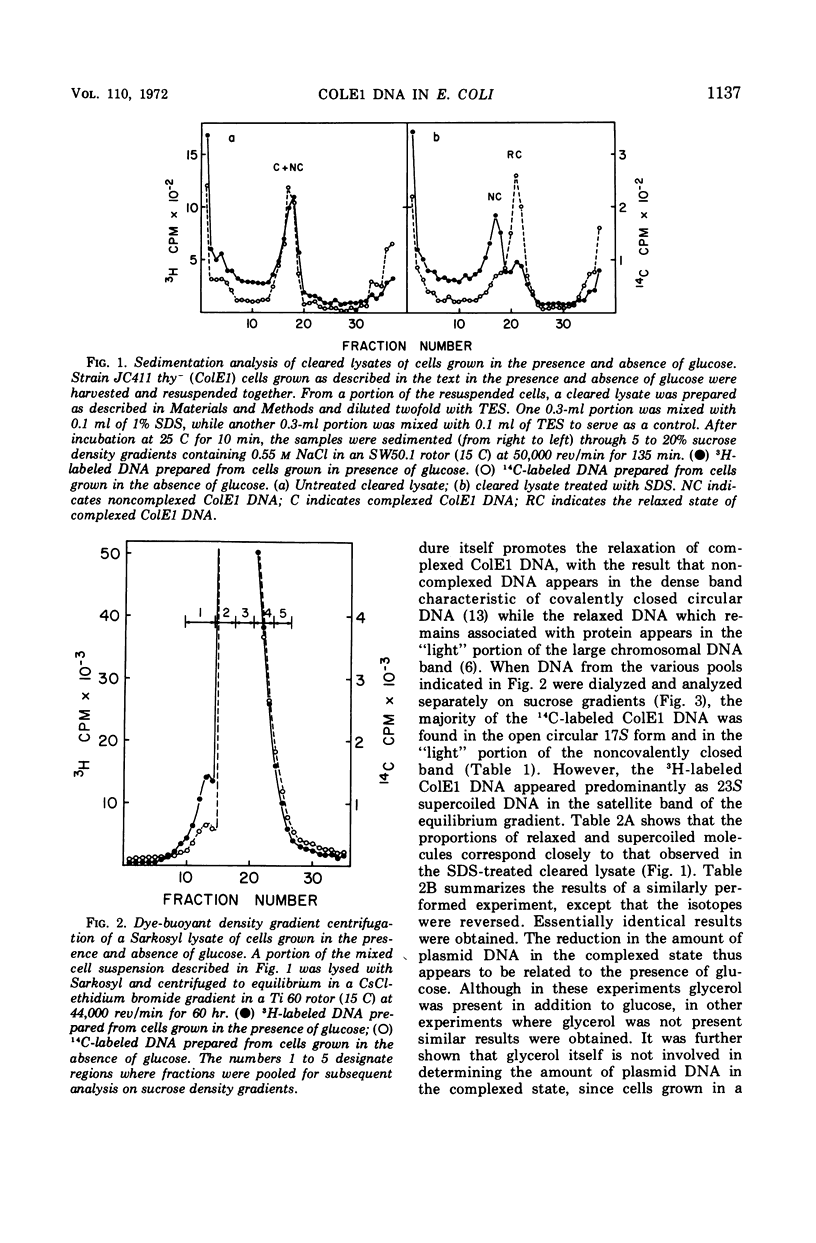
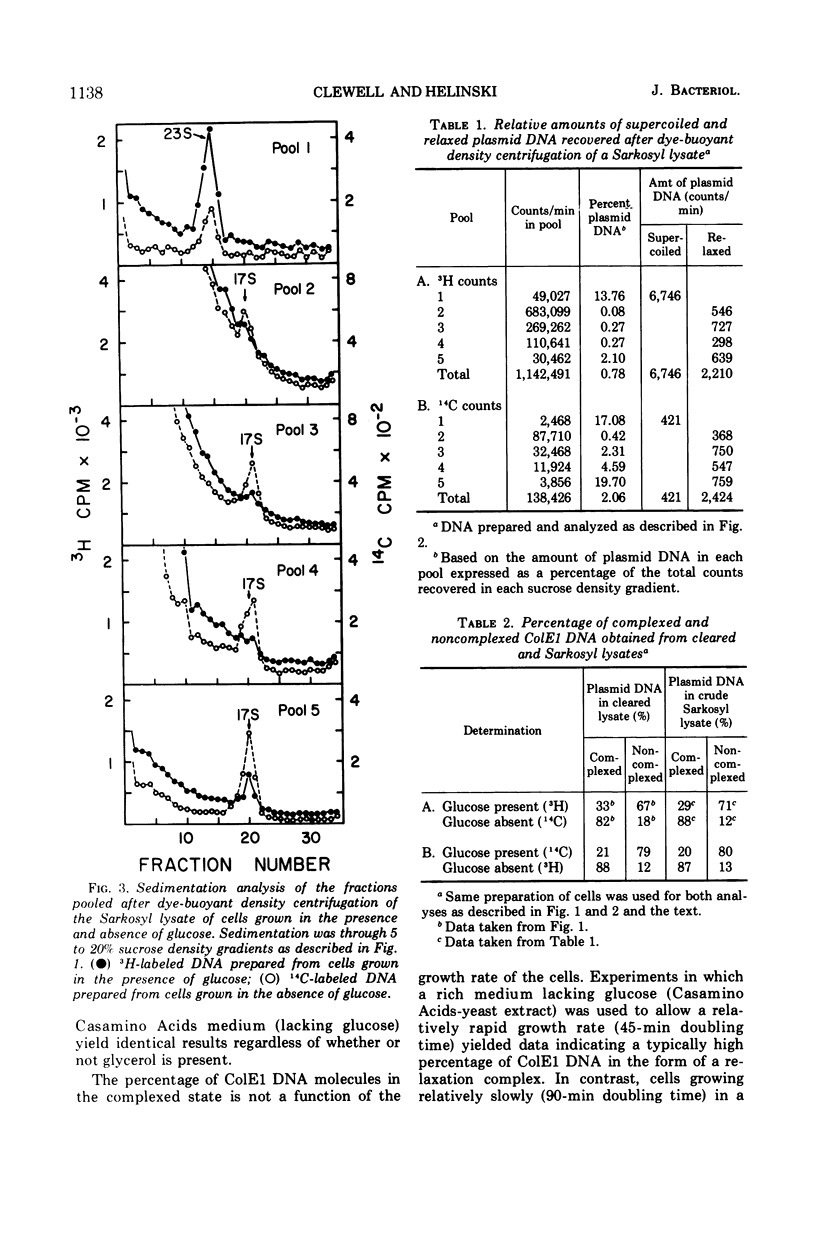
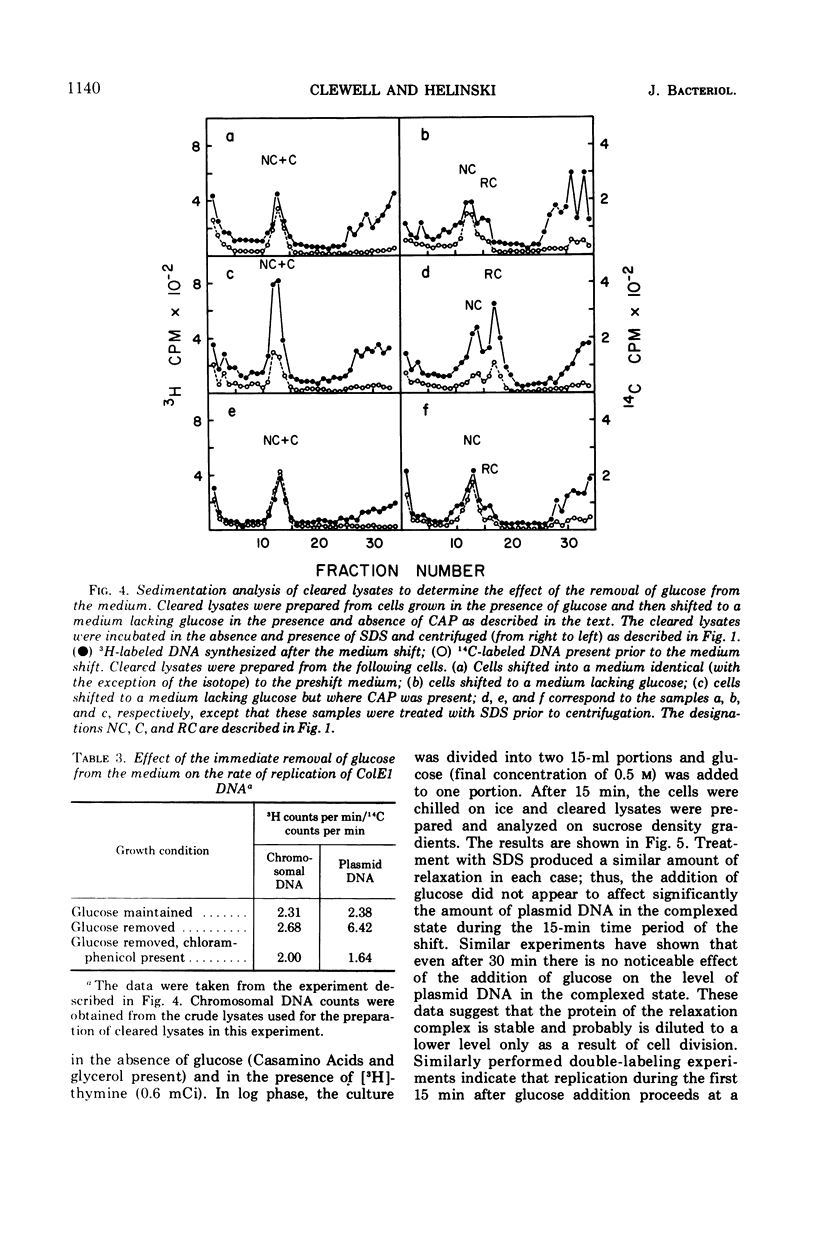
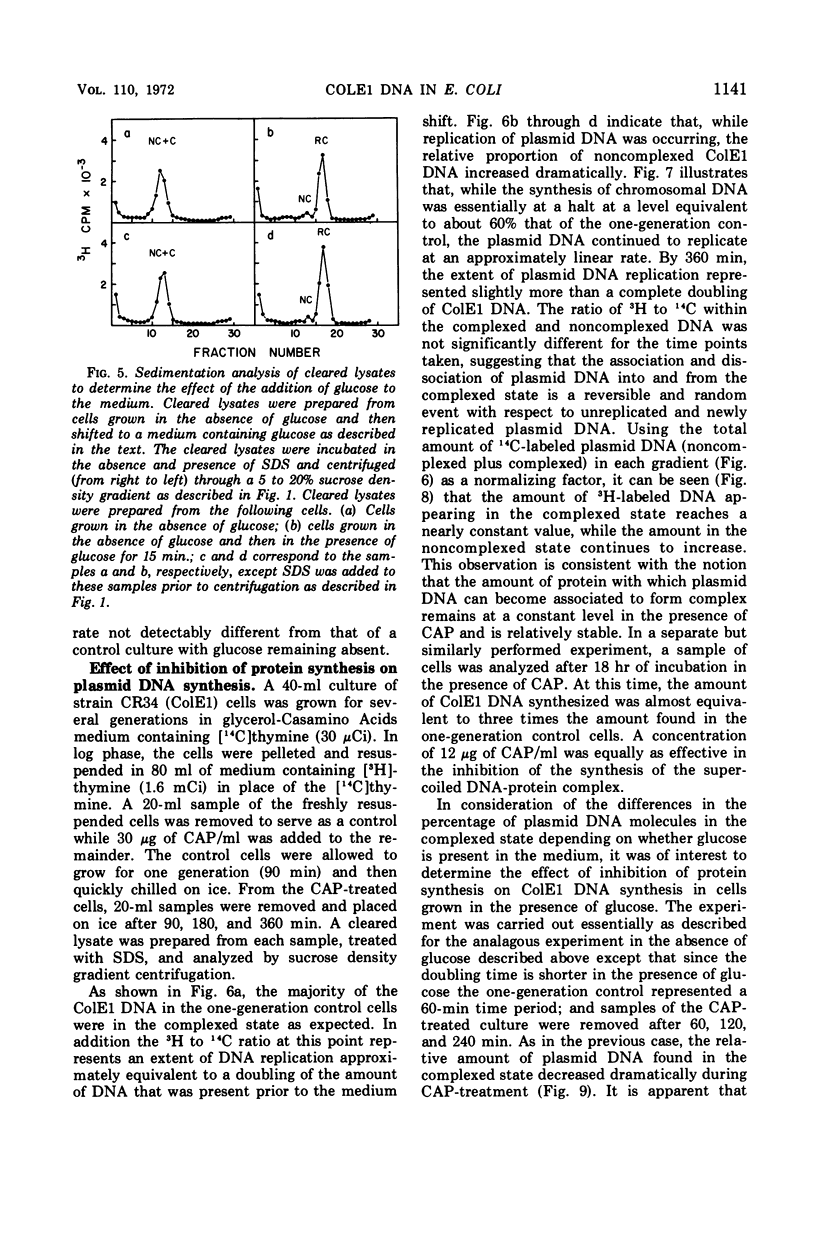
Colicinogenic factor E1 (ColE1) is present in Escherichia coli strain JC411 (ColE1) cells to the extent of about 24 copies per cell. This number does not appear to vary in situations which give rise to twofold differences in the amount of chromosomal deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) present per cell. If cells are grown in the absence of glucose, approximately 80% of the ColE1 molecules can be isolated as strand-specific DNA-protein relaxation complexes. When glucose is present in the medium, only about 30% of the plasmid molecules can be isolated as relaxation complexes. Medium shift experiments in which glucose was removed from the medium indicate that within 15 min after the shift the majority (>60%) of the plasmid can be isolated as relaxation complex. This rapid shift to the complexed state is accompanied by a two- to threefold increase in the rate of plasmid replication. The burst of replication and the shift to the complexed state are both inhibited by the presence of chloramphenicol. Inhibition of protein synthesis in log cultures by the addition of chloramphenicol or amino acid starvation allows ColE1 DNA to continue replicating long after chromosomal replication has ceased. Under these conditions, noncomplexed plasmid DNA accumulates while the amount of DNA that can be isolated in the complexed state remains constant at the level that existed prior to treatment. In the presence of chloramphenicol, there appears to be a random dissociation and association of ColE1 DNA and “relaxation protein” during or between rounds of replication.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BURTON K. A study of the conditions and mechanism of the diphenylamine reaction for the colorimetric estimation of deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochem J. 1956 Feb;62(2):315–323. doi: 10.1042/bj0620315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
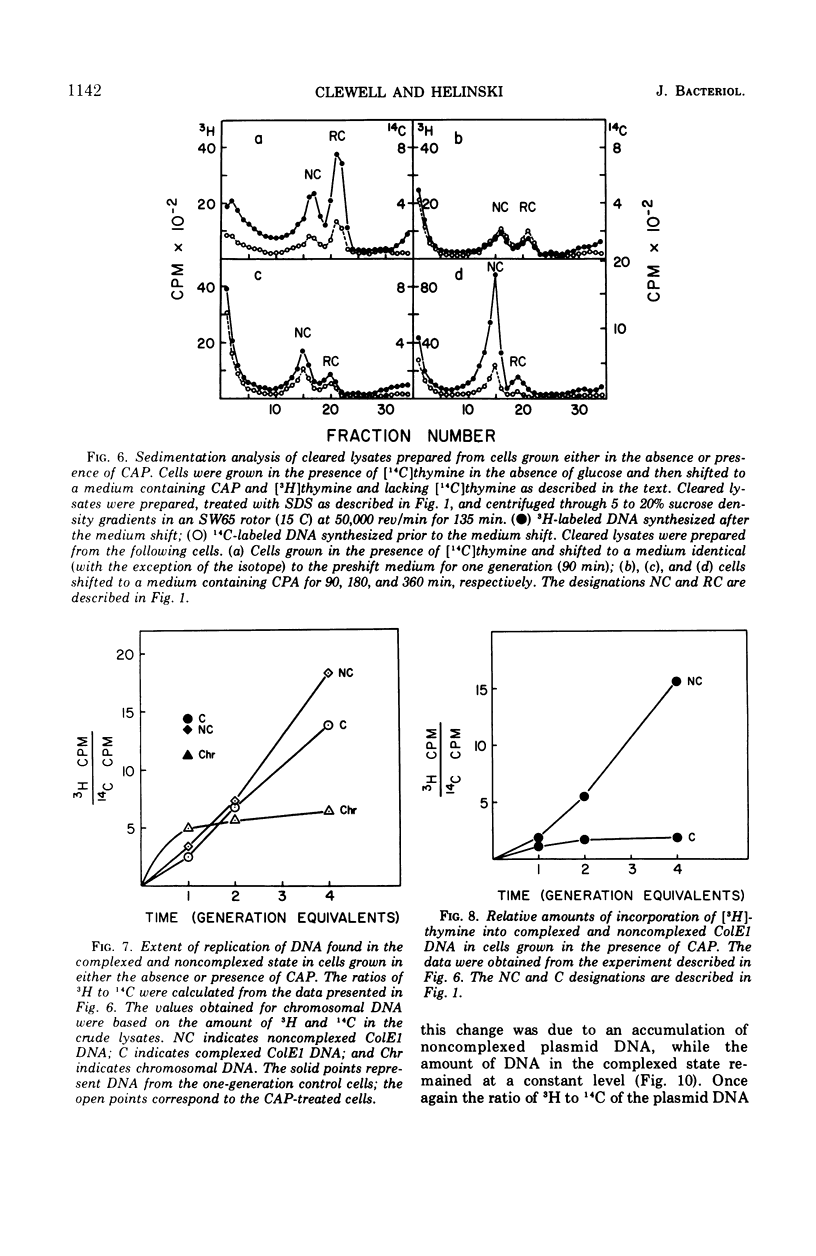
- Bazaral M., Helinski D. R. Replication of a bacterial plasmid and an episome in Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1970 Jan 20;9(2):399–406. doi: 10.1021/bi00804a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blair D. G., Clewell D. B., Sheratt D. J., Helinski D. R. Strand-specific supercoiled DNA-protein relaxation complexes: comparison of the complexes of bacterial plasmids ColE1 and ColE2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jan;68(1):210–214. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.1.210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
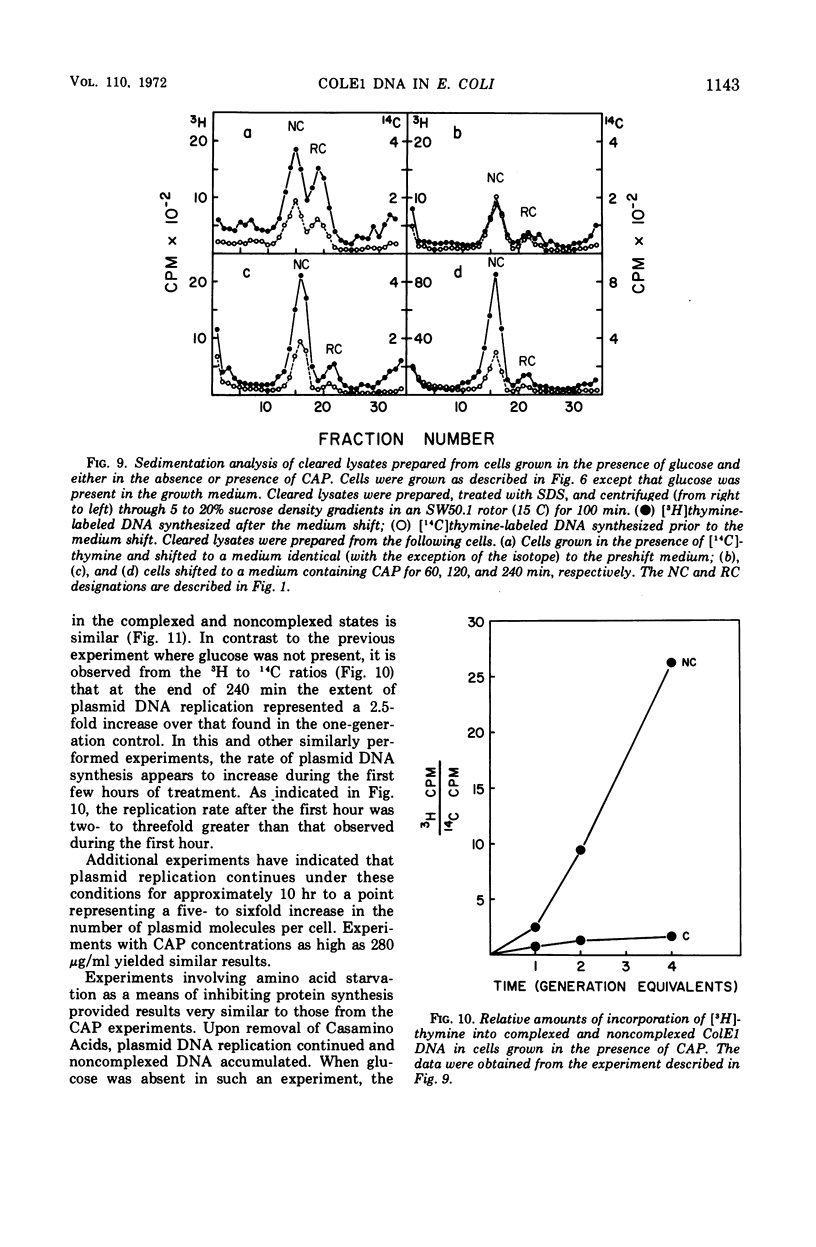
- CLARK A. J., MARGULIES A. D. ISOLATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF RECOMBINATION-DEFICIENT MUTANTS OF ESCHERICHIA COLI K12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Feb;53:451–459. doi: 10.1073/pnas.53.2.451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewell D. B., Helinski D. E. Existence of the colicinogenic factor-sex factor ColI-b-P9 as a supercoiled circular DNA-protein relaxation complex. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Oct 9;41(1):150–156. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90481-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
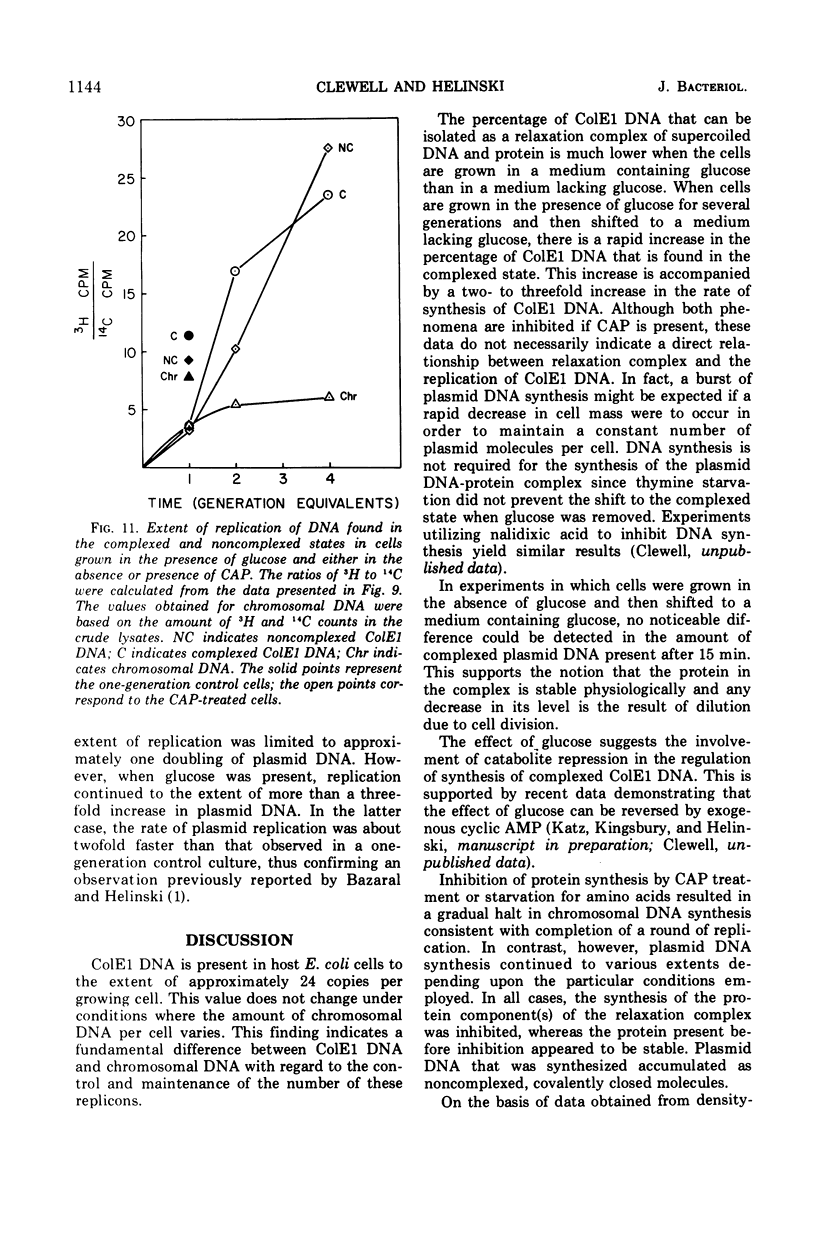
- Clewell D. B., Helinski D. R. Properties of a supercoiled deoxyribonucleic acid-protein relaxation complex and strand specificity of the relaxation event. Biochemistry. 1970 Oct 27;9(22):4428–4440. doi: 10.1021/bi00824a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewell D. B., Helinski D. R. Supercoiled circular DNA-protein complex in Escherichia coli: purification and induced conversion to an opern circular DNA form. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Apr;62(4):1159–1166. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.4.1159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper S., Helmstetter C. E. Chromosome replication and the division cycle of Escherichia coli B/r. J Mol Biol. 1968 Feb 14;31(3):519–540. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90425-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kline B. C., Helinski D. R. F 1 sex factor of Escherichia coli. Size and purification in the form of a strand-specific relaxation complex of supercoiled deoxyribonucleic acid and protein. Biochemistry. 1971 Dec 21;10(26):4975–4980. doi: 10.1021/bi00802a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OKADA T., YANAGISAWA K., RYAN F. J. Elective production of thymine-less mutants. Nature. 1960 Oct 22;188:340–341. doi: 10.1038/188340a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radloff R., Bauer W., Vinograd J. A dye-buoyant-density method for the detection and isolation of closed circular duplex DNA: the closed circular DNA in HeLa cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 May;57(5):1514–1521. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.5.1514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


