Abstract
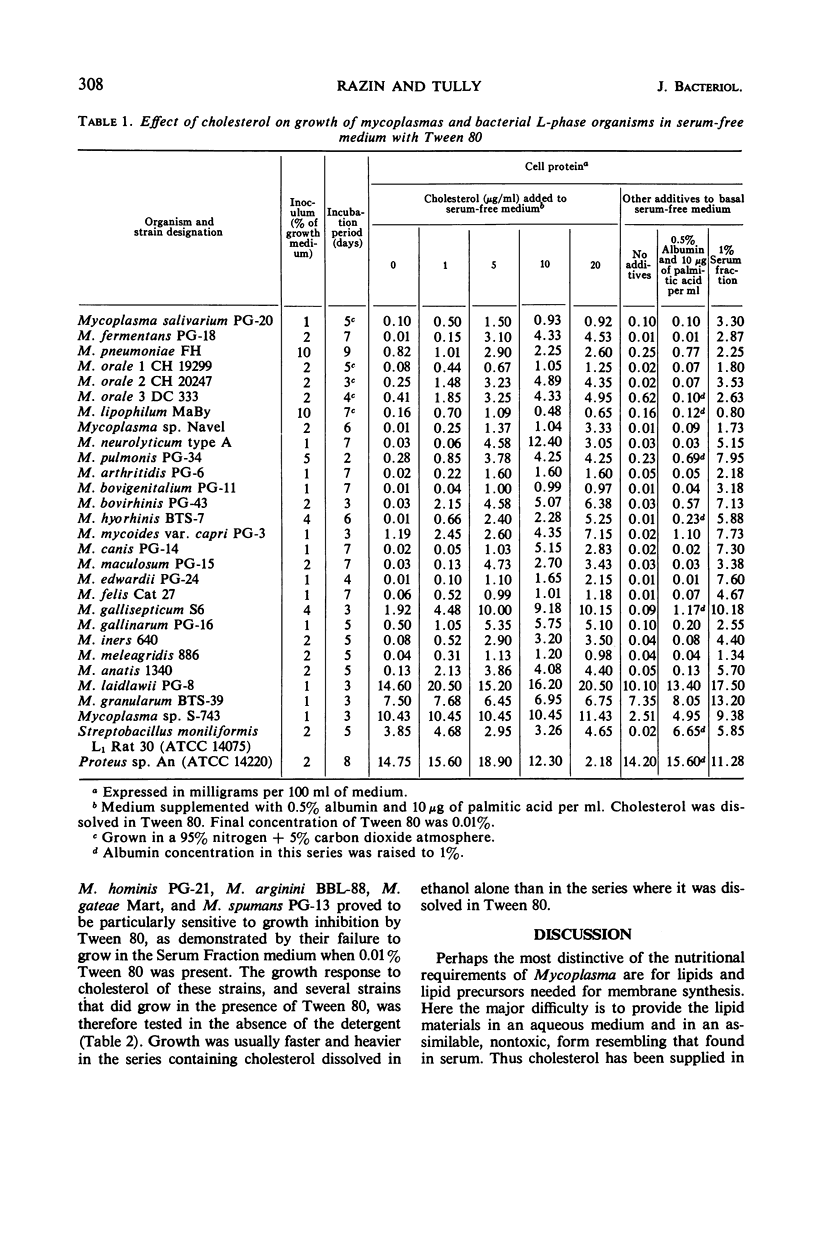
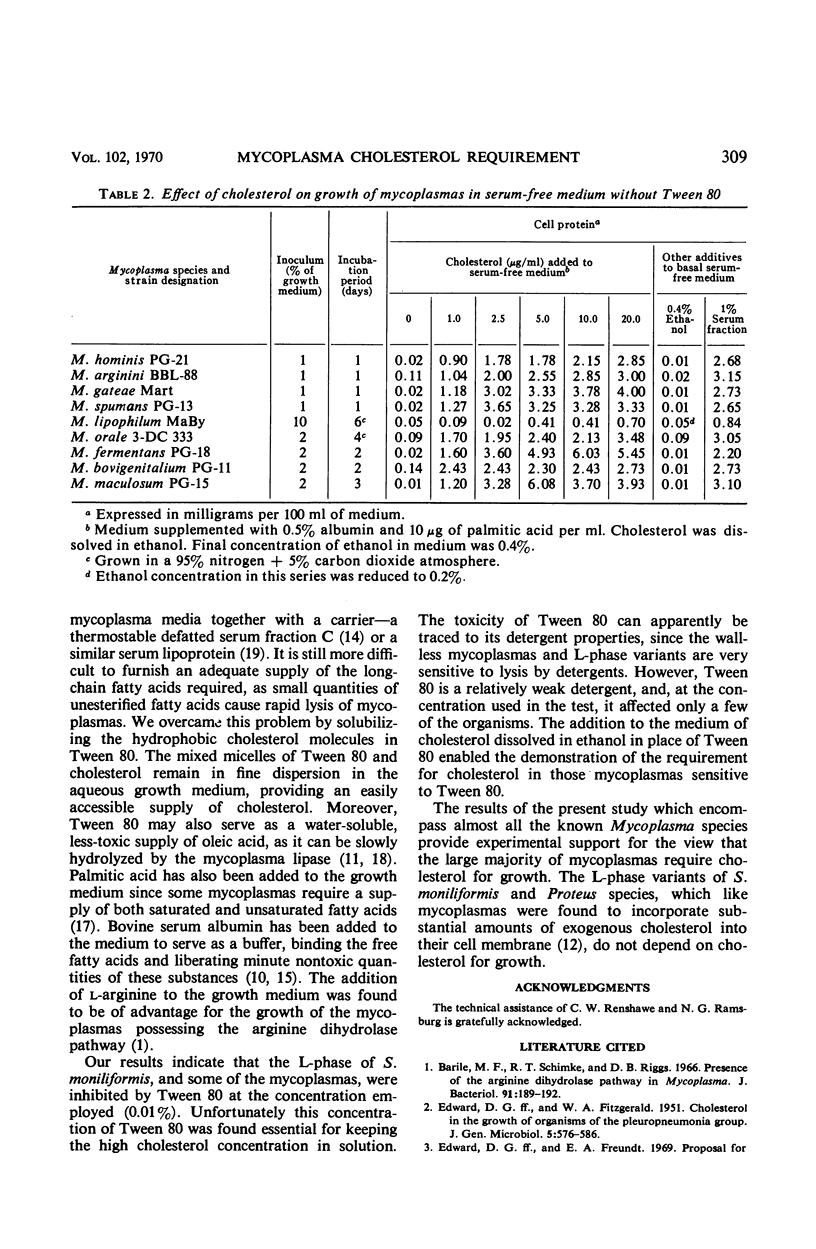
Cholesterol requirement for growth of mycoplasmas was tested in a serum-free medium supplemented with albumin, l-arginine, palmitic acid, and various concentrations of cholesterol dissolved in Tween 80. In cases in which Tween 80 was shown to inhibit growth, the test medium was supplemented with cholesterol dissolved in ethanol. Of the 31 species examined, all but Mycoplasma laidlawii, M. granularum, and Mycoplasma species strain S-743 exhibited a growth response to cholesterol. No requirement for cholesterol could be shown with the stable L-phase variants of Streptobacillus moniliformis and Proteus species. The results provide experimental support for the view that the large majority of the established Mycoplasma species require cholesterol for growth.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barile M. F., Schimke R. T., Riggs D. B. Presence of the arginine dihydrolase pathway in Mycoplasma. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jan;91(1):189–192. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.1.189-192.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EDWARD D. G., FITZGERALD W. A. Cholesterol in the growth of organisms of the pleuropneumonia group. J Gen Microbiol. 1951 Aug;5(3):576–586. doi: 10.1099/00221287-5-3-576. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edward D. G., Freundt E. A., Chanock R. M., Fabricant J., Hayflick L., Lemcke R. M., Rezin S., Somerson N. L., Wittler R. G. Recommendations on nomenclature of the order Mycoplasmatales. Science. 1967 Mar 31;155(3770):1694–1696. doi: 10.1126/science.155.3770.1694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurzepa H., Flinton L., VanDemark P. J. Growth of parasitic Mycoplasma without serum of serum fraction. J Bacteriol. 1969 Sep;99(3):908–909. doi: 10.1128/jb.99.3.908-909.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund P. G., Shorb M. S. Growth of Mycoplasma gallisepticum strain J without serum. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1966 Apr;121(4):1070–1075. doi: 10.3181/00379727-121-30969. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAZIN S., COHEN A. Nutritional requirements and metabolism of Mycoplasma laidlawii. J Gen Microbiol. 1963 Jan;30:141–154. doi: 10.1099/00221287-30-1-141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAZIN S., ROTTEM S. FATTY ACID REQUIREMENTS OF MYCOPLASMA LAIDLAWII. J Gen Microbiol. 1963 Dec;33:459–470. doi: 10.1099/00221287-33-3-459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RODWELL A. W., ABBOT A. The function of glycerol, cholesterol and long-chain fatty acids in the nutrition of Mycoplasma mycoides. J Gen Microbiol. 1961 Jun;25:201–214. doi: 10.1099/00221287-25-2-201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RODWELL A. W. Nutrition and metabolism of Mycoplasma mycoides var. mycoides. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1960 Jan 15;79:499–507. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1960.tb42716.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROTTEM S., RAZIN S. LIPASE ACTIVITY OF MYCOPLASMA. J Gen Microbiol. 1964 Oct;37:123–134. doi: 10.1099/00221287-37-1-123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin S., Shafer Z. Incorporation of cholesterol by membranes of bacterial L-phase variants with an appendix on the determination of the L-phase parentage by the electrophoretic patterns of cell proteins. J Gen Microbiol. 1969 Nov;58(3):327–339. doi: 10.1099/00221287-58-3-327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin S. Structure and function in mycoplasma. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1969;23:317–356. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.23.100169.001533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin S. The cell membrane of mycoplasma. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1967 Jul 28;143(1):115–129. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1967.tb27651.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodwell A. W. The nutrition and metabolism of mycoplasma: Progress and problems. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1967 Jul 28;143(1):88–109. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1967.tb27649.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodwell A. W. The supply of cholesterol and fatty acids for the growth of mycoplasmas. J Gen Microbiol. 1969 Sep;58(1):29–37. doi: 10.1099/00221287-58-1-29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH P. F., LECCE J. G., LYNN R. J. A lipoprotein as a growth factor for cortain pleuropneumonialike organisms. J Bacteriol. 1954 Nov;68(5):627–633. doi: 10.1128/jb.68.5.627-633.1954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. F., Boughton J. E. ROLE OF PROTEIN AND PHOSPHOLIPID IN THE GROWTH OF PLEUROPNEUMONIA-LIKE ORGANISMS. J Bacteriol. 1960 Dec;80(6):851–860. doi: 10.1128/jb.80.6.851-860.1960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tully J. G., Razin S. Characteristics of a new sterol-nonrequiring Mycoplasma. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jun;98(3):970–978. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.3.970-978.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tully J. G., Razin S. Physiological and serological comparisons among strains of Mycoplasma granularum and Mycoplasma laidlawii. J Bacteriol. 1968 May;95(5):1504–1512. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.5.1504-1512.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


