Abstract
Oxidative stress and inflammation are implicated in the pathogenesis of many age-related diseases. Stress-induced overproduction of inflammatory cytokines, such as interleukin-8 (IL-8), is one of the early events of inflammation. The objective of this study was to elucidate mechanistic links between oxidative stress and overproduction of IL-8 in retinal pigment epithelial (RPE) cells. We found that exposure of RPE cells to H2O2, paraquat, or A2E-mediated photooxidation resulted in increased expression and secretion of IL-8. All of these oxidative stressors also inactivated the proteasome in RPE cells. In contrast, tert-butylhydroperoxide (TBH), a lipophilic oxidant that did not stimulate IL-8 production, also did not inactivate the proteasome. Moreover, prolonged treatment of RPE cells with proteasome-specific inhibitors recapitulated the stimulation of IL-8 production. These data suggest that oxidative inactivation of the proteasome is a potential mechanistic link between oxidative stress and up-regulation of the proinflammatory IL-8. The downstream signaling pathways that govern the production of IL-8 include NF-κB and p38 MAPK. Proteasome inhibition both attenuated the activation and delayed the turnoff of NF-κB, resulting in biphasic effects on the production of IL-8. Prolonged proteasome inhibition (>2 h) resulted in activation of p38 MAPK via activation of MKK3/6 and increased the production of IL-8. Chemically inhibiting the p38 MAPK blocked the proteasome inhibition-induced up-regulation of IL-8. Together, these data indicate that oxidative inactivation of the proteasome and the related activation of the p38 MAPK pathway provide a potential link between oxidative stress and overproduction of proinflammatory cytokines, such as IL-8.
Oxidative stress, which refers to cellular damage caused by reactive oxygen species, has been implicated in the onset and progression of many age-related diseases, including age-related macular degeneration (AMD),3 arthritis, atherosclerosis, and certain types of cancer (1–3). Inflammatory events are also known to participate in the pathogenesis of these age-related diseases. The activation of redox-sensitive transcription factors may be involved in triggering the expression of proinflammatory cytokines (2). However, the molecular links between oxidative stress and inflammation are not fully understood.
Retina has the highest metabolic rate and oxygen consumption in the body. The high metabolic rate and oxygen consumption is usually accompanied by generation of reactive oxygen species. Chronic exposure to light could also increase the production of reactive oxygen species (1, 4). Therefore, retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) is a primary target of oxidative stress.
Age-related accumulation of lipofuscin in RPE is another source of oxidative stress. Lipofuscin is a mixture of non-degradable protein-lipid aggregates derived from the ingestion of photoreceptor outer segments (5). A2E is the major fluorophore of lipofuscin and acts as a photosensitizer to generate reactive oxygen species inside the cells upon exposure to blue light (5–7). An increasing body of literature indicates that oxidative stress and dysfunction of RPE are associated with the pathogenesis of AMD (8–10), the leading cause of blindness in industrialized countries. Recent studies indicate that inflammation is an important component of AMD (9, 11, 12) and that oxidative stress in RPE can trigger the activation of the complement system (13). Moreover, complement activation is associated with enhanced expression of IL-8, an important inflammatory cytokine (14, 15). Increased expression of IL-8 was also reported when RPE were fed oxidized photoreceptor outer segments (16). The increased expression of IL-8 may account, at least in part, for the inflammatory reactions during development of AMD (16, 17). However, the molecular mechanisms that regulate IL-8 expression under these conditions remain to be elucidated.
The ubiquitin-proteasome pathway (UPP) is the major non-lysosomal proteolytic pathway within cells (18–20). Proteins destined for degradation are first conjugated with a polyubiquitin chain by the sequential action of three classes of enzymes: E1, E2, and E3. The ubiquitin-protein conjugates are then recognized and degraded by a large protease complex called the proteasome (19, 21). The UPP has been involved in a myriad of cellular processes (20, 22), including regulation of immune response and inflammation (23, 24). Dysfunction of the UPP has been implicated in the pathogenesis of many degenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer disease (25), Parkinson disease (26), diabetic retinopathy (27), and cataract (28–31).
Because the UPP is involved in the regulation of gene expression and because it can be inactivated by oxidative stress (32–37), we hypothesized that oxidative inactivation of the UPP is a molecular mechanism that links oxidative stress to inflammatory events during the development of many degenerative diseases. The results of this study show that exposing ARPE-19 cells to H2O2, paraquat, and A2E-mediated photooxidation resulted in the inactivation of the proteasome and a dramatic increase in the expression and secretion of IL-8. In contrast, TBH, a lipophilic oxidant that did not inactivate the proteasome, also failed to stimulate the production of IL-8. Furthermore, prolonged treatment of ARPE-19 cells with proteasome inhibitors delayed the turnoff of NF-κB, activated the p38 MAPK, and led to a dramatic up-regulation of IL-8. Moreover, inhibiting p38 MAPK abolished the up-regulation of IL-8 induced by proteasome inhibitors. These data support the hypothesis that oxidative inactivation of the proteasome is a mechanistic link between oxidative stress and IL-8 overproduction. Because overproduction of IL-8 was suggested to play a role in the development of AMD (16, 17, 38, 39), our data also suggest that oxidative impairment of the UPP in RPE is likely to contribute to the development of AMD, by increasing local production of proinflammatory chemokines, such as IL-8.
EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURES
Materials—Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium (DMEM) was obtained from Invitrogen. Fetal bovine serum (FBS) was purchased from HyClone (Logan, UT). MG132 and SB203580 were obtained from Calbiochem (La Jolla, CA). Epoxomicin was purchased from Boston Biochem (Cambridge, MA). Sodium orthovanadate, paraquat (1,1-dimethyl-4,4-bipyridinium dichloride), Bay 11-7082, and the monoclonal antibody against β-actin were obtained from Sigma. The nitrocellulose membrane for Western blot was obtained from Bio-Rad. Rabbit polyclonal antibodies against phosphorylated p38 MAPK and MKK3/6, total p38 MAPK, MKK3, and MKK6 were purchased from Cell Signaling Technology (Danvers, MA). Goat anti-rabbit IgG and sheep anti-mouse IgG were obtained from Jackson ImmunoResearch Laboratories (West Grove, PA). The Super-Signal chemiluminescent detection kit was purchased from Pierce. The DuoSet ELISA kit for IL-8 was obtained from R&D Systems (Minneapolis, MN). The NF-κB oligonucleotide was purchased from Promega (Madison, WI).
Cell Culture and Treatments—The retinal pigment epithelial cell line ARPE-19 (40) was obtained from ATCC. The cells were routinely maintained at 37 °C under 5% CO2 and cultured in DMEM supplemented with 10% FBS and containing 100 units/ml penicillin G and 100 μg/ml streptomycin. Before treatment, confluent cell monolayers were rinsed once with phosphate-buffered saline and fresh medium was added. For proteasome inhibition studies, MG132 and epoxomicin were prepared in DMSO at 10 mm and diluted to 10 (MG 132) and 5 μm (epoxomicin) in the cell medium immediately before use. Cells were incubated with proteasome inhibitors for different periods of time as indicated in the figure legends. The p38 MAPK inhibitor SB203580 was prepared in DMSO at 10 mm and then diluted to 10 μm in the cell medium immediately before use. The NF-κB inhibitor Bay 11-7082 was prepared in DMSO at 20 mm and then diluted to 10 μm in the cell medium immediately before use.
Exposure to H2O2, Paraquat, or Tert-Butylhydroperoxide (TBH)—Subconfluent ARPE-19 cells were incubated in serum-, pyruvate-, and phenol red-free DMEM containing 4.5 g/liter glucose in the presence of the indicated concentrations of H2O2, paraquat, or TBH for 1 h. The cells were then collected and proteasome activity was determined using a fluorogenic peptide as substrate. For IL-8 secretion studies, the cells were exposed to different concentrations of H2O2, paraquat, or TBH as described above. After a 1-h incubation, cells were rinsed with phosphate-buffered saline and allowed to recover for 8 h in DMEM containing 10% FBS, pyruvate, and phenol red.
Exposure to A2E and Blue Light—ARPE-19 cells devoid of endogenous lipofuscin were grown to confluence and then cultured in DMEM with 10% heat-inactivated fetal calf serum and 0.1 mm nonessential amino acid solution with or without 10 μm A2E for 2 weeks. The medium was changed twice a week. With this protocol, A2E accumulates in the lysosomal compartment of the cells (41). For blue light exposure, the medium was replaced with phosphate-buffered saline containing calcium, magnesium, and glucose and exposed to 430-nm light delivered from a tungsten halogen source (430 ± 20 nm for 15 min at 2.62 milliwatt/cm2). The cells were then cultured in DMEM with 1% fetal calf serum for another 6 h. The medium was collected to determine IL-8 levels and the cells were collected for proteasome activity assay. Controls included cultures that had neither accumulated A2E nor been exposed to blue light, cells that accumulated A2E only or that had only been exposed to blue light. All the control cells were cultured in the same way as the cells that had accumulated A2E and were exposed to blue light.
Proteasome Activity Assay—ARPE-19 cells were lysed in 25 mm Tris-HCl buffer, pH 7.6. The chymotrypsin-like activity of the proteasome was determined using the fluorogenic peptide succinyl-Leu-Leu-Val-Tyr-amidomethylcoumarin (LLVY-AMC) as a substrate (42). The mixture, containing 20 μl of cell supernatant in 25 mm Tris-HCl, pH 7.6, was incubated at 25 °C with the peptide substrate (LLVY-AMC at 25 μm) in a buffer containing 50 mm Tris-HCl, pH 8.0, 100 mm NaCl, 5 mm EDTA, 1 mm EGTA, 3 mm NaN3, and 0.04% CHAPS. The final volume of the assay was 200 μl. Rates of reactions were measured in a temperature-controlled microplate fluorometric reader. Excitation/emission wavelengths were 380/440 nm. Proteasome activity was defined as the portion of peptidase activity in the cell extracts that was inhibited by 20 μm MG132, a potent proteasome inhibitor.
Western Blot Analysis—Whole cell lysates were prepared for Western blot analysis. After treatment, cells were rinsed once with ice-cold phosphate-buffered saline supplemented with 2 mm sodium orthovanadate, a phosphatase inhibitor, and immediately collected in SDS loading buffer. Cell lysates were then denatured at 100 °C for 5 min. Equal amounts of protein (50 or 100 μg/lane) were resolved on 10–12% SDS-polyacrylamide gels and transferred to nitrocellulose membranes. Membranes were probed with rabbit polyclonal antibodies against phosphorylated p38 MAPK and MKK3/6, total p38 MAPK, MKK3, and MKK6, or mouse monoclonal antibody against β-actin. After incubation with the corresponding horseradish peroxidase-conjugated secondary antibodies, the specific bound antibody was visualized using Super Signal chemiluminescent detection kit.
Enzyme-linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)—Levels of IL-8 secreted into the medium by RPE were determined by ELISA. The medium was diluted 10 times to determine IL-8 levels. All ELISAs were performed according to the manufacturer's instructions.
Real Time RT-PCR—Total RNA extraction from ARPE-19 cells and real time RT-PCR analysis were performed as described (27). For IL-8, the forward primer was: 5′-AAACCACCGGAAGGAACCAT-3′ and the reverse primer was: 5′-CCTTCACACAGAGCTGCAGAAA-3′. Levels of GAPDH were used for normalization of the total amount of mRNA. For quantification of GAPDH mRNA, the forward primer was 5′-ATCACCATCTTCCAGGAGCGA-3′ and the reverse primer was 5′-CCTTCTCCATGGTGGTGAAGAC-3′.
Preparation of Nuclear Extracts and Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assays—Nuclear extract preparations and DNA-binding assays were performed as previously described (43). The NF-κB DNA-binding double-stranded oligonucleotide used was 5′-AGTTGAGGGGACTTTCCCAGGC-3′. Specific DNA binding complex of NF-κB was identified as the band that disappeared when a 50-fold excess of cold oligonucleotide competitor was added in binding assays.
Statistical Analyses—Statistical analysis was performed using Student's t test assuming equal variances for all data points.
RESULTS
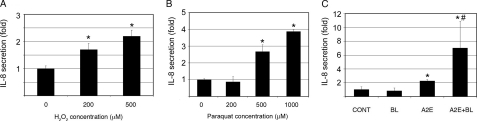
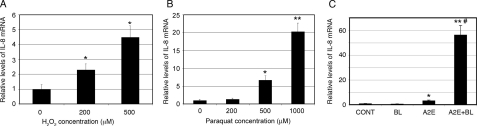
H2O2, Paraquat, or A2E-mediated Photooxidation Increases Production of IL-8 by RPE—A number of studies indicate that oxidative stress and inflammation are involved in the dysfunction of RPE and in the pathogenesis of AMD (1, 4). To investigate the potential link between oxidative stress and inflammation, we determined the effect of oxidative stress on secretion of IL-8, a proinflammatory cytokine. First, we assessed the effect of H2O2 exposure on the secretion of IL-8 by RPE. As shown in Fig. 1A, incubation of ARPE-19 cells with H2O2 increased secretion of IL-8 in a dose-dependent manner. Exposure of ARPE-19 cells to 500 μm H2O2 for 1 h resulted in a 2-fold increase in the secretion of IL-8 (Fig. 1A). We then determined the effect of paraquat, a superoxide generator (44), on the secretion of IL-8. The results show that exposure of ARPE-19 cells to 500 and 1000 μm paraquat for 1 h significantly increased the production of IL-8 (Fig. 1B), but exposure to lower concentrations of paraquat (<200 μm) had no detectable effect on IL-8 secretion (Fig. 1B). To further confirm the relationship between oxidative stress and up-regulation of IL-8, we evaluated the effect of A2E-mediated photooxidation on secretion of IL-8. Whereas exposure to blue light alone had little effect on IL-8 production, accumulation of A2E alone significantly increased IL-8 secretion as compared with the control (Fig. 1C). However, the combination of accumulation of A2E and blue light exposure further increased the secretion of IL-8 (Fig. 1C). Similar to the increase in IL-8 proteins in the medium, the mRNA levels of IL-8 in the cells also dramatically increased in response to these types of oxidative stress (Fig. 2). However, the extents to which IL-8 mRNA levels increased in response to oxidative stress were much greater than the increase in IL-8 proteins in the medium. Previous genomic and proteomic analyses found that for a substantial number of genes the absolute amount of protein in the cell is not strongly correlated to the amount of mRNA (45, 46). Whereas the levels of mRNA are mainly controlled by the transcription activity and mRNA stability, the levels of proteins reflect mRNA level, translation efficiency, and posttranslational modification and degradation. Secretion efficiency may also control the IL-8 levels in the medium. Taken together, these data suggest that physiologically relevant sources of oxidative stress lead to an up-regulation of IL-8 in RPE. These data are consistent with previous reports showing that oxidative stress stimulates IL-8 production in several cell types (47–50). Furthermore, the data show that accumulation of A2E alone also induced the secretion of IL-8, although it did not cause detectable oxidative damage, indicating that the expression and secretion of IL-8 are regulated by both oxidative and non-oxidative mechanisms.
FIGURE 1.
Oxidative stress increases IL-8 production by RPE. ARPE-19 cells were cultured in serum-, pyruvate-, and phenol red-free DMEM in the presence of different concentrations of H2O2 for 1 h (panel A), or in the presence of different concentrations of paraquat for 1 h (panel B) and allowed to recover for 8 h in DMEM containing 10% FBS, pyruvate, and phenol red. Alternatively, ARPE-19 cells were treated with blue light, A2E, or A2E plus blue light as indicated under “Experimental Procedures” (panel C). Levels of IL-8 in the medium were detected by ELISA and expressed as -fold changes in response to oxidative stress. The results are the mean ± S.D. of three independent experiments. *, p < 0.01 as compared with the control group; #, p < 0.01 as compared with blue light or A2E alone.
FIGURE 2.
Oxidative stress increases IL-8 mRNA levels. ARPE-19 cells were cultured in serum-, pyruvate-, and phenol red-free DMEM in the presence of different concentrations of H2O2 for 1 h (panel A), or in the presence of different concentrations of paraquat for 1 h (panel B) and allowed to recover for 8 h in DMEM containing 10% FBS, pyruvate, and phenol red. Alternatively, ARPE-19 cells were treated with blue light, A2E, or A2E plus blue light as indicated under “Experimental Procedures” (panel C). The cells were lysed in situ and total RNA was extracted. Levels of mRNA for IL-8 were assessed by real-time RT-PCR analysis. GAPDH mRNA was used as a control to normalize the total mRNA levels. The results are the mean ± S.D. of three independent experiments. Asterisk indicates p < 0.01 and double asterisk indicates p < 0.001 as compared with the control group; #, p < 0.001 as compared with blue light or A2E alone.
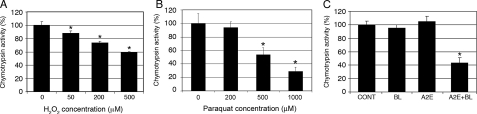
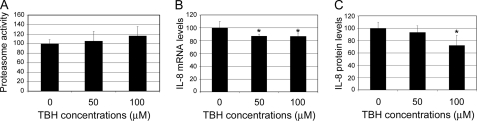
H2O2, Paraquat, or A2E-mediated Photooxidation Inactivates the Proteasome in RPE—The UPP plays important roles in the regulation of many transcription factors and gene expression in response to various stimuli. Previous studies showed that inhibition of the proteasome results in an increase in IL-8 production in other cell types (51–55) and that extensive oxidative stress can impair the function of the UPP (32–37, 56). To test whether oxidation-induced proteasome inactivation could be the potential mechanistic link between oxidative stress and the enhanced production of IL-8 by RPE cells, we determined the effect of oxidative stress on proteasome activity in ARPE-19 cells. As predicted, exposure of RPE cells to H2O2 resulted in a dose-dependent decrease in the proteasome activity (Fig. 2A). The proteasome in ARPE-19 cells was inhibited by H2O2 concentrations as low as 50 μm in the medium. The chymotrypsin activity of the proteasome was inhibited by 40% when the cells were exposed to 500 μm H2O2 for 1 h (Fig. 3A). Consistently, exposure of ARPE-19 cells to paraquat also resulted in a dose-dependent inhibition of the proteasome. The chymotrypsin activity of the proteasome was inhibited by 10, 50, and 70%, respectively, when the cells were exposed to 200, 500, and 1000 μm paraquat for 1 h (Fig. 3B). Furthermore, A2E-mediated photooxidation also led to inactivation of the proteasome. Accumulation of A2E alone or exposure to blue light alone had little effect on proteasome activity. However, exposure of A2E-loaded cells to blue light resulted in a 60% decrease in the chymotrypsin-like peptidase activity of the proteasome (Fig. 3C). The trypsin-like and peptidylglutamyl peptide hydrolase peptidase activities of the proteasome were also inhibited by these levels of oxidative stress (37). The correlation between oxidative inactivation of the proteasome and increased IL-8 production suggests that oxidative impairment of the UPP could be a potential link between oxidative stress and enhanced production of IL-8 by RPE cells. Consistent with this speculation, we found that treatment of the cells with TBH, a lipophilic oxidant, did not inactivate the proteasome, nor did it increase IL-8 production (Fig. 4). In fact, TBH treatment decreased the expression and secretion of IL-8 (Fig. 4, B and C). The decline in expression and secretion of IL-8 upon TBH treatment might be due to direct inhibition of the transcription machinery and the secretion system, because the mRNA and protein levels of other genes, such as vascular endothelial growth factor, also decreased upon treatment with TBH (data not shown).
FIGURE 3.
Oxidative stress impairs proteasome activity in RPE. ARPE-19 cells were cultured in serum-, pyruvate-, and phenol red-free DMEM in the presence of different concentrations of H2O2 for 1 h (panel A) or in the presence of different concentrations of paraquat for 1 h (panel B). Alternatively, ARPE-19 cells were treated with blue light, A2E, or A2E plus blue light as indicated under “Experimental Procedures” (panel C). Proteasome activity was determined using a fluorogenic peptide as a substrate as described under “Experimental Procedures.” The results are the mean ± S.D. of three independent experiments. p < 0.01 as compared with the control group.
FIGURE 4.
TBH does not inhibit the proteasome, nor does it stimulate IL-8 production. ARPE-19 cells were cultured in serum-, pyruvate-, and phenol red-free DMEM in the presence of different concentrations of TBH for 1 h. The chymotrypsin-like activity of the proteasome was determined (panel A). After recovery in normal medium for 8 h, levels of mRNA for IL-8 were assessed by real-time RT-PCR analysis (panel B) and IL-8 concentrations in the medium were determined by ELISA (panel C). The results are the mean ± S.D. of three independent experiments. Asterisk indicates p < 0.05.
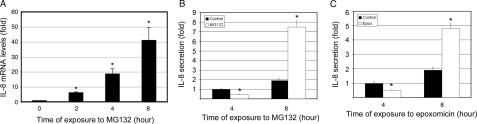
Inhibition of the UPP Alters IL-8 Production in a Biphasic Manner—The data above suggest that oxidative impairment of the UPP could be a mechanistic link between oxidative stress and enhanced production of IL-8 by RPE cells. To further corroborate this potential link, we directly tested the effect of proteasome inhibition on the production of IL-8 by RPE cells. As shown in Fig. 5A, IL-8 mRNA levels increased in a time-dependent manner after proteasome inhibition, starting as early as 2 h. In untreated cells, IL-8 levels in the medium increased in a time-dependent manner (Fig. 5B), indicating that RPE cells continuously secrete this chemokine, which accumulates in the medium. Unlike the effect on mRNA levels, the effect of proteasome inhibition on secretion of IL-8 was biphasic. Short-term (up to 4 h) inhibition of the proteasome reduced the secretion of IL-8. However, long-term (6 h or longer) proteasome inhibition stimulated the secretion of IL-8 by as much as 3-fold (Fig. 5B). Treatment of ARPE-19 cells with epoxomicin, another specific inhibitor of the proteasome, resulted in a similar effect on the secretion of IL-8 (Fig. 5C). To further confirm that impairment of the proteaseome is a trigger for the up-regulation of IL-8 secretion, we determined the dose-dependent relationship between proteasome inhibitors and IL-8 production. We found that when the proteasome was inhibited 40% or more by 1–10 μm MG132 or 0.5–5 μm epoxomicin for 8 h, there was a dose-dependent increase in IL-8 secretion (supplemental Fig. S1). However, when the cells were treated with 0.1 μm MG132 or 0.05 μm epoxomicin for 8 h, which resulted in 5–10% inhibition of the proteasome, there was no detectable effect on IL-8 secretion (supplemental Fig. S1). Furthermore, expression of K6W-ubiquitin, a dominant negative inhibitor of the UPP (57), in ARPE-19 cells also resulted in a 2-fold increase in IL-8 secretion (supplemental Fig. S2). These data indicate that inhibition of the proteasome, or impairment of the UPP, can affect the production of IL-8 at multiple levels, such as transcription, translation, and secretion, and therefore the net effect of proteasome inhibition on IL-8 production may vary, depending on the duration of proteasome inhibition.
FIGURE 5.
Proteasome inhibition differentially regulates IL-8 production in RPE. ARPE-19 cells were cultured in the presence of MG132 for 0, 2, 4, and 8 h (panels A and B) or in the presence of epoxomicin for 4 and 8(panel C). Levels of mRNA for IL-8 were assessed by real-time RT-PCR analysis (panel A). GAPDH mRNA was used as a control to normalize the total mRNA levels. Levels of IL-8 in the medium were detected by ELISA following incubation of ARPE-19 cells in the presence or absence of MG132 for 4 or 8 h (panel B) or in the presence or absence of epoxomicin (panel C) for 4 or 8 h. The results are the mean ± S.D. of three independent experiments. *, p < 0.001 as compared with the control.
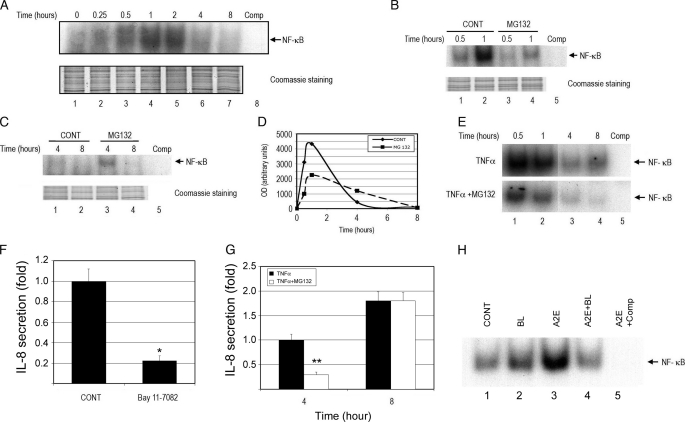
Differential Regulation of Signal Transduction Pathways by the UPP and Their Roles in Controlling the Production of IL-8—The expression of IL-8 is controlled by various transcription factors and signaling pathways, such as NF-κB, AP-1, and p38 MAPK (58–60), and many of these are regulated by the UPP (61, 62). To elucidate the molecular link between proteasome inhibition and altered secretion of IL-8, we first evaluated the effect of proteasome inhibition on NF-κB activation. As shown in Fig. 6A, NF-κB was activated by changing the medium and DNA-binding activity peaking between 1 and 2 h after addition of fresh medium. NF-κB DNA-binding activity was barely detectable 8 h after changing the medium (Fig. 6A). To study the effect of proteasome inhibition on NF-κB activation, we compared the NF-κB DNA-binding activity at 0.5-, 1-, 4-, and 8-h time points. When proteasome activity was inhibited by MG132, the NF-κB DNA-binding activity in the nuclei decreased by ∼50% as compared with control cells at 0.5 and 1 h after changing the medium (Fig. 6B, compare lanes 3 and 4 with lanes 1 and 2, respectively). NF-κB DNA-binding activity was barely detectable in the control cells 4 h after changing the medium (Fig. 6, C, lanes 1 and 2, and D). Surprisingly, the NF-κB DNA-binding activity lasted longer in the presence of a proteasome inhibitor and relatively higher DNA-binding activity of this transcription factor could still be detected in the nuclei 4 h after changing the medium (Fig. 6C, compare lane 3 with lane 1, and D). By 8 h after changing the medium NF-κB DNA-binding activity was undetectable both in the presence or absence of proteasome inhibitor (Fig. 6C).
FIGURE 6.
Proteasome inhibition alters NF-κB activation. ARPE-19 cells were cultured in fresh medium for 0, 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, 4, and 8 h to study the time course of NF-κB activation (panel A). To study the effect of proteasome inhibition on NF-κB activation, the cells were cultured in the presence or absence of MG132 for 30 and 60 min (panel B) or 4 and 8 h (panel C), nuclear extracts were prepared, and electrophoretic mobility gel shift assays were performed for NF-κB binding (panels A–C). Time 0 is when the medium was changed. The specific DNA binding complexes of NF-κB were identified as the band that disappeared in the presence of 50-fold excess of cold oligonucleotide competitor in the binding assay (panel A, lane 8, and panels B, C, E, and H, lane 5). The relative NF-κB binding activities in panels B and C were quantified by densitometry (panel D). The effects of TNFα and proteasome inhibition on NF-κB activity are shown in panel E. The effects of a NF-κB inhibitor (panel F) or a NF-κB activator (panel G) on IL-8 production was determined by ELISA. ARPE-19 cells were exposed to blue light alone, accumulated A2E alone, or accumulated A2E and exposed to blue light. After 3 h recovery in normal medium, NF-κB activity was determined in the nuclear extracts (panel H). The figure is representative of three independent experiments with similar results. *, p < 0.001 as compared with the control; **, p < 0.001 as compared between cells treated with TNFα alone and cells treated with TNFα plus MG132.
As shown in other types of cells, NF-κB DNA-binding activity increased significantly upon stimulation with TNFα (Fig. 6E, lanes 1 and 2). The signal decreased after 1 h of TNFα treatment, but it was still detectable by 8 h of incubation (Fig. 6E, lane 4). Treatment with a proteasome inhibitor substantially attenuated the TNFα-induced activation of NF-κB (Fig. 6E, compare upper panel with lower panel).
Because NF-κB can regulate IL-8 expression, we hypothesized that the attenuated activation of NF-κB by proteasome inhibition might account for the initial decline in the production of IL-8 observed under these conditions. To test this possibility, we first evaluated the effect of a NF-κB inhibitor on the expression of IL-8. Indeed, treatment of ARPE-19 cells with Bay 11-7082, an inhibitor of NF-κB activation, decreased the secretion of IL-8 by 70% (Fig. 6F). To further corroborate the involvement of NF-κB in the regulation of IL-8 production, we evaluated the effect of TNFα, a potent activator of NF-κB, on the secretion of IL-8. As predicted, levels of IL-8 in the medium increased dramatically upon incubation of ARPE-19 with TNFα (Fig. 6G). Even in the presence of TNFα, proteasome inhibition reduced the production of IL-8 during the first 4 h of treatment (Fig. 6G), which is consistent with the inhibition of NF-κB activation (Fig. 6E). However, after 8 h, the proteasome inhibitor was no longer able to reverse the effect of TNFα on IL-8 production (Fig. 6G), even though it still reduced TNFα-induced NF-κB DNA-binding activity (Fig. 6E).
As shown in Fig. 3C, although loading A2E alone did not inhibit the proteasome, it increased IL-8 expression and secretion moderately. To test whether the effect of A2E on IL-8 secretion was related to NF-κB activation, we determined the DNA-binding activity of NF-κB under these conditions. As predicted, exposure to blue light alone increased NF-κB DNA-binding activity slightly, whereas loading A2E alone significantly increased the DNA-binding activity of this transcription factor (Fig. 6H). However, when the cells were loaded with A2E and exposed to blue light, the NF-κB DNA-binding activity decreased (Fig. 6H). This may be due to oxidative inactivation of the proteasome (Fig. 3C).
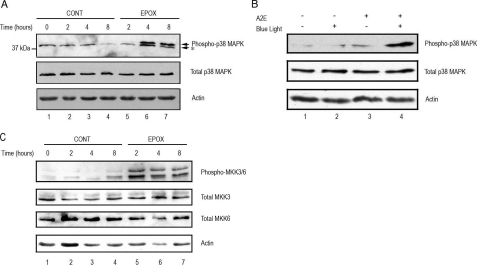
Proteasome Inhibition Activates p38 MAPK in RPE—The above data suggest that the impaired activation of NF-κB may contribute to the initial decrease in IL-8 production upon proteasome inhibition, but the sustained activation of this pathway could only partially explain the enhanced production of IL-8 upon prolonged inhibition of the UPP. To search for the alternative signal transduction pathways that account for the up-regulation of IL-8 upon prolonged proteasome inhibition, we examined the effect of proteasome inhibitors on activation of the p38 MAPK pathway. The p38 MAPK has been shown to regulate IL-8 gene expression by stabilizing its mRNA (58, 59, 63), and p38 MAPK could be activated upon various stresses, including proteasome inhibition (64–67). To investigate the signaling pathways involved in the up-regulation of IL-8 production, we determined the effects of proteasome inhibition on p38 MAPK activation. As shown in Fig. 7A, phosphorylated p38 was barely detectable in control cells. Short-term inhibition of the proteasome had no detectable effect on p38 MAPK phosphorylation. However, inhibiting the proteasome for 4 h or longer resulted in the accumulation of phosphorylated p38 MAPK (Fig. 7A, compare lanes 6 and 7 with lanes 3 and 4, respectively).
FIGURE 7.
Proteasome inhibition and photooxidation activate p38 MAPK and MKK3/6 in RPE. Panel A, ARPE-19 cells were cultured in the presence or absence of epoxomicin, a specific proteasome inhibitor, for 0, 2, 4, and 8 h. Levels of endogenous phospho-p38 MAPK, total p38 MAPK, and actin were detected by Western blot using polyclonal (to phosphorylated and total p38 MAPK) and monoclonal antibodies (to actin). Panel B, ARPE-19 cells were treated with blue light, A2E, or blue light plus A2E as indicated under “Experimental Procedures.” Levels of endogenous phospho-p38 MAPK, total p38 MAPK, and actin were detected by Western blot using polyclonal (to phosphorylated and total p38 MAPK) and monoclonal antibodies (to actin). Panel C, ARPE-19 cells were cultured in the absence or presence of the proteasome inhibitor MG132, for 0, 2, 4, and 8 h. Levels of endogenous phospho-MKK3/6, total MKK3, MKK6, and actin were detected by Western blot using polyclonal (to phosphorylated and total MKK3 and -6) and monoclonal antibodies (to actin). The figures are representative of three independent experiments with similar results.
To correlate the oxidative inactivation of the proteasome with p38 MAPK activation, we determined the effect of A2E-mediated photooxidation on the levels of phosphorylated p38 MAPK in ARPE-19 cells. Whereas accumulation of A2E alone or exposure to blue light alone had little effect on p38 MAPK phosphorylation (Fig. 7B, compare lanes 2 and 3 with lane 1), accumulation of A2E and exposure to blue light together dramatically increased the levels of phosphorylated p38 MAPK (Fig. 7B, compare lane 4 with lanes 1–3). In contrast, the total amount of p38 MAPK did not change in any of the experimental conditions. These data indicate that oxidative stress can lead to activation of p38 MAPK, probably via inactivation of the proteasome.
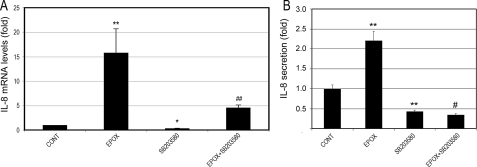
Inhibition of the p38 MAPK Blocks the Proteasome Inhibition-induced Up-regulation of IL-8—The data above suggest that long-term proteasome inhibition up-regulates IL-8 and activates p38 MAPK in RPE. To further test the causal relationship between p38 MAPK activation and up-regulation of IL-8 in response to long-term proteasome inhibition, we evaluated the effect of a p38 MAPK inhibitor on IL-8 production after 8 h of proteasome inhibition. As shown in Fig. 8A, proteasome inhibition up-regulated IL-8 gene expression by 15-fold. Remarkably, SB203580, a p38 MAPK inhibitor, was able to completely reverse the IL-8 mRNA up-regulation induced by proteasome inhibition. Even in control cells, SB203580 led to a decrease in IL-8 gene expression in RPE cells. Consistent with the effect on mRNA levels, proteasome inhibition dramatically increased secretion of IL-8 by RPE cells (Fig. 8B), and this effect was completely abolished in the presence of the p38 MAPK inhibitor. These data strongly suggest that the activation of p38 MAPK plays a major role in the up-regulation of IL-8 following long-term proteasome inhibition.
FIGURE 8.
Inhibition of p38 MAPK blocks proteasome inhibition-induced up-regulation of IL-8. ARPE-19 cells were cultured in the presence or absence of epoxomicin, SB203580, or epoxomicin plus SB203580 for 8 h. Levels of mRNA for IL-8 were assessed by real-time RT-PCR analysis (panel A). GAPDH mRNA was used as a control to normalize the total mRNA levels. IL-8 protein levels in the media were determined by ELISA (panel B). The results are the mean ± S.D. of three independent experiments. *, p < 0.05, and **, p < 0.01 as compared with the control; #, p < 0.001, and ##, p = 0.09 as compared with epoxomicin alone.
Proteasome Inhibition Activates MKK3/6 in RPE—To determine the upstream events that trigger the activation of p38 MAPK in response to long-term proteasome inhibition, we determined the effect of proteasome inhibition on the activation of MKK3 and MKK6, the upstream kinases involved in the activation of p38 MAPK (68–71). In control cells, the levels of phospho-MKK3/6 were barely detectable (Fig. 7C, lanes 1–4). Proteasome inhibition resulted in an increase in phospho-MKK3/6 levels, without significantly affecting the levels of total MKK3 or MKK6 (Fig. 7C, compare lanes 5–7 with lanes 2–4, respectively). These data indicate that proteasome-dependent activation of MKK3 and MKK6 are likely to be among the upstream events that lead to p38 activation and increased production of IL-8 in RPE cells.
DISCUSSION
Emerging evidence indicates that oxidative stress and inflammation play an important role in the pathogenesis of AMD and many other age-related degenerative diseases (1, 2, 12). Oxidative stress can trigger inflammation (13) and this can, in turn, exacerbate the generation of reactive oxygen species. IL-8 is a major inflammatory and angiogenic chemokine (58) and the up-regulation of IL-8 in response to oxidative stress may be an important link between oxidative stress and inflammation (47–50, 72, 73). Elucidation of the molecular mechanisms by which oxidative stress up-regulates IL-8 would help us to better understand the relationship between oxidative stress and inflammation.
Because the UPP is involved in regulating a number of signal transduction pathways and its activity can be compromised upon oxidative stress (32–37, 56), we hypothesized that oxidative inactivation of the UPP is a potential mechanistic link between oxidative stress and overexpression of IL-8 in RPE cells. The data presented in this paper support this hypothesis by showing that several physiologically relevant oxidative stressors inactivated the proteasome and increased the production of IL-8, whereas an oxidative stressor that did not inactivate the proteasome also failed to stimulate the production of IL-8. Moreover, prolonged inhibition of the proteasome also stimulated the production of IL-8. The differential regulation of NF-κB and p38 MAPK signal transduction pathways appears to be responsible for the altered expression of IL-8 upon proteasome inhibition. Whereas the inhibition of NF-κB activation may play a role in the decreased secretion of IL-8 upon short-term proteasome inhibition, p38 MAPK appears to be the major pathway involved in the enhanced IL-8 production in response to long-term proteasome inhibition, because inhibition of this pathway can completely block the up-regulation of IL-8 induced by proteasome inhibitors. This conclusion is consistent with previous reports that documented the activation of p38 MAPK in response to proteasome inhibitors in other types of cells (64–67). Furthermore, A2E-mediated photooxidation in RPE cells also activated p38 MAPK and enhanced production of IL-8 in a manner comparable with that observed upon proteasome inhibition. Thus, it is conceivable that physiologically relevant oxidative stress, such as photooxidation, may increase IL-8 by activating the p38 MAPK signaling pathway via inhibiting the proteasome. However, we cannot rule out the possibility of other pathways being involved in this up-regulation. For example, it has been shown that phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt is involved in the regulation of the IL-8 gene in various cell types (74–76), and that Akt can also be regulated by the UPP (66, 77–79).
We also found that proteasome inhibition activates MKK3 and MKK6, the upstream kinases for p38 MAPK. Consistent with our data, a previous report showed that proteasome inhibition results in the activation of MKK3/MKK6 (64). It is plausible that proteasome inhibition activates p38 MAPK via activation of MKK3/MKK6. However, proteasome inhibition may also activate p38 MAPK via a MAPKK-independent mechanism. Transforming growth factor-β-activated protein kinase 1 (TAK1)-binding protein 1 has also been reported to activate p38 MAPK (80) and TAK1 is regulated by the UPP (81, 82).
Previous reports on the effects of proteasome inhibition on IL-8 expression are controversial. Although some reports showed that proteasome inhibitors down-regulate IL-8 (83–85), others showed an increase in IL-8 expression and secretion (51–55). The present work reconciles these apparently conflicting reports by demonstrating that proteasome inhibition regulates IL-8 production in a time-dependent manner. That is, short-term inhibition of the proteasome reduces IL-8 secretion via inhibition of NF-κB activation, whereas long-term proteasome inhibition stimulates the production of IL-8 through activation of p38 MAPK. Therefore, the net effect of proteasome inhibition in the production of IL-8 depends on the duration of the proteasome inhibition. We also found that accumulation of A2E, the major fluorophore and photosensitizer of lipofuscin, in ARPE-19 cells stimulated the production of IL-8 in an oxidation-independent manner. It appears that activation of NF-κB pathway is one of the molecular mechanisms by which A2E promotes the expression and secretion of IL-8 (Fig. 6H).
This study provides, for the first time, a novel molecular link between oxidative stress and inflammation. Oxidative inactivation of the proteasome and the subsequent alterations in several signaling pathways, such as NF-κB and p38 MAPK, are plausible mechanisms that underlie the oxidative stress-induced up-regulation of IL-8, one of the most potent proinflammatory and proangiogenic chemokines. Given the function of the UPP in regulating IL-8, vascular endothelial growth factor and MCP-1 in RPE cells (27) and the roles of these chemokines and growth factor in the pathogenesis of AMD (38, 39, 86), impairment of the UPP in RPE could significantly contribute to the development of AMD. Thus, protecting the UPP from oxidative inactivation may become a valid therapeutic strategy for prevention of AMD and other age- and inflammation-related diseases.
Supplementary Material
This work was supported, in whole or in part, by National Institutes of Health Grants EY 11717 (to F. S.), EY 13250 (to A. T.), and EY12951 (to J. R. S.). This work was also supported by Portuguese Foundation for Science and Technology Grant POCI/SAU-OBS/57772/2004 (to P. P.) and United States Department of Agriculture Grant CRIS 1950-51000-060-01A. The costs of publication of this article were defrayed in part by the payment of page charges. This article must therefore be hereby marked “advertisement”in accordance with 18 U.S.C. Section 1734 solely to indicate this fact.
The on-line version of this article (available at http://www.jbc.org) contains supplemental Figs. S1 and S2.
Footnotes
The abbreviations used are: AMD, age-related macular degeneration; IL-8, interlukin-8; UPP, ubiquitin-proteasome pathway; RPE, retina pigment epithelial cells; A2E, pyridinium bisretinoid; TBH, t-butylhydroperoxide; CHAPS, 3-[(3-cholamidopropyl)dimethylammonio]-1-propanesulfonate; DMEM, Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium; FBS, fetal bovine serum; DMSO, dimethyl sulfoxide; ELISA, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; RT, reverse transcriptase; TNFα, tumor necrosis factor α; GAPDH, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; MKK, mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase.
References
- 1.Beatty, S., Koh, H., Phil, M., Henson, D., and Boulton, M. (2000) Surv. Ophthalmol. 45 115–134 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Chung, H. Y., Sung, B., Jung, K. J., Zou, Y., and Yu, B. P. (2006) Antioxid. Redox Signal. 8 572–581 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Lavrovsky, Y., Chatterjee, B., Clark, R. A., and Roy, A. K. (2000) Exp. Gerontol. 35 521–532 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Liang, F. Q., and Godley, B. F. (2003) Exp. Eye Res. 76 397–403 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Sparrow, J. R., and Boulton, M. (2005) Exp. Eye Res. 80 595–606 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Rozanowska, M., Jarvis-Evans, J., Korytowski, W., Boulton, M. E., Burke, J. M., and Sarna, T. (1995) J. Biol. Chem. 270 18825–18830 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Rozanowska, M., Wessels, J., Boulton, M., Burke, J. M., Rodgers, M. A., Truscott, T. G., and Sarna, T. (1998) Free Radic. Biol. Med. 24 1107–1112 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Boulton, M., Roanowska, M., and Wess, T. (2004) Graefe's Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 242 76–84 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Zarbin, M. A. (2004) Arch. Ophthalmol. 122 598–614 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Zhou, J., Cai, B., Jang, Y. P., Pachydaki, S., Schmidt, A. M., and Sparrow, J. R. (2005) Exp. Eye Res. 80 567–580 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Donoso, L. A., Kim, D., Frost, A., Callahan, A., and Hageman, G. (2006) Surv. Ophthalmol. 51 137–152 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.McGeer, E. G., Klegeris, A., and McGeer, P. L. (2005) Neurobiol. Aging 26 Suppl. 1, 94–97 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Zhou, J., Jang, Y. P., Kim, S. R., and Sparrow, J. R. (2006) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 103 16182–16187 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Fukuoka, Y., and Medof, E. M. (2001) Curr. Eye Res. 23 320–325 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Fukuoka, Y., Strainic, M., and Medof, M. E. (2003) Clin. Exp. Immunol. 131 248–253 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Higgins, G. T., Wang, J. H., Dockery, P., Cleary, P. E., and Redmond, H. P. (2003) Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 44 1775–1782 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Kalayoglu, M. V., Bula, D., Arroyo, J., Gragoudas, E. S., D'Amico, D., and Miller, J. W. (2005) Graefe's Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 243 1080–1090 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Ciechanover, A. (2003) Biochem. Soc. Trans. 31 474–481 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Glickman, M. H., and Ciechanover, A. (2002) Physiol. Rev. 82 373–428 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Shang, F., and Taylor, A. (2004) Exp. Eye Res. 78 1–14 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Pickart, C. M. (2001) Annu. Rev. Biochem. 70 503–533 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Welchman, R. L., Gordon, C., and Mayer, R. J. (2005) Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 6 599–609 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Qureshi, N., Vogel, S. N., Van Way, C., 3rd, Papasian, C. J., Qureshi, A. A., and Morrison, D. C. (2005) Immunol. Res. 31 243–260 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Kloetzel, P. M. (2004) Nat. Immunol. 5 661–669 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Hope, A. D., de Silva, R., Fischer, D. F., Hol, E. M., van Leeuwen, F. W., and Lees, A. J. (2003) J. Neurochem. 86 394–404 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Dawson, T. M., and Dawson, V. L. (2003) Science 302 819–822 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Fernandes, A. F., Guo, W., Zhang, X., Gallagher, M., Ivan, M., Taylor, A., Pereira, P., and Shang, F. (2006) Exp. Eye Res. 83 1472–1481 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Dudek, E. J., Shang, F., Valverde, P., Liu, Q., Hobbs, M., and Taylor, A. (2005) FASEB J. 19 1707–1709 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Jahngen-Hodge, J., Cyr, D., Laxman, E., and Taylor, A. (1992) Exp. Eye Res. 55 897–902 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Shang, F., Gong, X., Palmer, H. J., Nowell, T. R., Jr., and Taylor, A. (1997) Exp. Eye Res. 64 21–30 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Shang, F., Nowell, T. R., Jr., and Taylor, A. (2001) Exp. Eye Res. 73 229–238 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Caballero, M., Liton, P. B., Epstein, D. L., and Gonzalez, P. (2003) Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 308 346–352 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Conconi, M., Petropoulos, I., Emod, I., Turlin, E., Biville, F., and Friguet, B. (1998) Biochem. J. 333 407–415 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Ishii, T., Sakurai, T., Usami, H., and Uchida, K. (2005) Biochemistry 44 13893–13901 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Okada, K., Wangpoengtrakul, C., Osawa, T., Toyokuni, S., Tanaka, K., and Uchida, K. (1999) J. Biol. Chem. 274 23787–23793 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Obin, M., Shang, F., Gong, X., Handelman, G., Blumberg, J., and Taylor, A. (1998) FASEB J. 12 561–569 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Zhang, X., Zhou, J., Fernandes, A. F., Sparrow, J. R., Pereira, P., Taylor, A., and Shang, F. (2008) Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 49 in press [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 38.Ambati, J., Anand, A., Fernandez, S., Sakurai, E., Lynn, B. C., Kuziel, W. A., Rollins, B. J., and Ambati, B. K. (2003) Nat. Med. 9 1390–1397 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Yoshida, A., Yoshida, S., Khalil, A. K., Ishibashi, T., and Inomata, H. (1998) Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 39 1097–1106 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Dunn, K. C., Aotaki-Keen, A. E., Putkey, F. R., and Hjelmeland, L. M. (1996) Exp. Eye Res. 62 155–169 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Sparrow, J. R., Parish, C. A., Hashimoto, M., and Nakanishi, K. (1999) Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 40 2988–2995 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Bulteau, A. L., Lundberg, K. C., Humphries, K. M., Sadek, H. A., Szweda, P. A., Friguet, B., and Szweda, L. I. (2001) J. Biol. Chem. 276 30057–30063 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Dudek, E. J., Shang, F., and Taylor, A. (2001) Free Radic. Biol. Med. 31 651–658 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Cocheme, H. M., and Murphy, M. P. (2008) J. Biol. Chem. 283 1786–1798 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Nie, L., Wu, G., and Zhang, W. (2006) Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 339 603–610 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Tian, Q., Stepaniants, S. B., Mao, M., Weng, L., Feetham, M. C., Doyle, M. J., Yi, E. C., Dai, H., Thorsson, V., Eng, J., Goodlett, D., Berger, J. P., Gunter, B., Linseley, P. S., Stoughton, R. B., Aebersold, R., Collins, S. J., Hanlon, W. A., and Hood, L. E. (2004) Mol. Cell Proteomics 3 960–969 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Ito, K., Hanazawa, T., Tomita, K., Barnes, P. J., and Adcock, I. M. (2004) Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 315 240–245 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Tomita, K., Barnes, P. J., and Adcock, I. M. (2003) Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 301 572–577 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Verhasselt, V., Goldman, M., and Willems, F. (1998) Eur. J. Immunol. 28 3886–3890 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Yamamoto, K., Kushima, R., Kisaki, O., Fujiyama, Y., and Okabe, H. (2003) Inflammation 27 123–128 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Gerber, A., Heimburg, A., Reisenauer, A., Wille, A., Welte, T., and Buhling, F. (2004) Eur. Respir. J. 24 40–48 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Hipp, M. S., Urbich, C., Mayer, P., Wischhusen, J., Weller, M., Kracht, M., and Spyridopoulos, I. (2002) Eur. J. Immunol. 32 2208–2217 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Joshi-Barve, S., Barve, S. S., Butt, W., Klein, J., and McClain, C. J. (2003) Hepatology 38 1178–1187 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Wu, H. M., Chi, K. H., and Lin, W. W. (2002) FEBS Lett. 526 101–105 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Wu, H. M., Wen, H. C., and Lin, W. W. (2002) Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 27 234–243 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Jahngen-Hodge, J., Obin, M. S., Gong, X., Shang, F., Nowell, T. R., Jr., Gong, J., Abasi, H., Blumberg, J., and Taylor, A. (1997) J. Biol. Chem. 272 28218–28226 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Shang, F., Deng, G., Liu, Q., Guo, W., Haas, A. L., Crosas, B., Finley, D., and Taylor, A. (2005) J. Biol. Chem. 280 20365–20374 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Brat, D. J., Bellail, A. C., and Van Meir, E. G. (2005) Neuro-oncol. 7 122–133 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Hoffmann, E., Dittrich-Breiholz, O., Holtmann, H., and Kracht, M. (2002) J. Leukocyte Biol. 72 847–855 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Roebuck, K. A. (1999) J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 19 429–438 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Chen, Z. J. (2005) Nat. Cell Biol. 7 758–765 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Maniatis, T. (1999) Genes Dev. 13 505–510 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Kumar, S., Boehm, J., and Lee, J. C. (2003) Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2 717–726 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Ho, A. K., McNeil, L., Terriff, D., Price, D. M., and Chik, C. L. (2005) Biochem. Pharmacol. 70 1840–1850 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Meriin, A. B., Gabai, V. L., Yaglom, J., Shifrin, V. I., and Sherman, M. Y. (1998) J. Biol. Chem. 273 6373–6379 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Shi, Y. Y., Small, G. W., and Orlowski, R. Z. (2006) Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 100 33–47 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Wu, W. T., Chi, K. H., Ho, F. M., Tsao, W. C., and Lin, W. W. (2004) Biochem. J. 379 587–593 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Derijard, B., Raingeaud, J., Barrett, T., Wu, I. H., Han, J., Ulevitch, R. J., and Davis, R. J. (1995) Science 267 682–685 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Han, J., Lee, J. D., Jiang, Y., Li, Z., Feng, L., and Ulevitch, R. J. (1996) J. Biol. Chem. 271 2886–2891 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Kyriakis, J. M., and Avruch, J. (2001) Physiol. Rev. 81 807–869 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Raingeaud, J., Whitmarsh, A. J., Barrett, T., Derijard, B., and Davis, R. J. (1996) Mol. Cell Biol. 16 1247–1255 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Biagioli, M. C., Kaul, P., Singh, I., and Turner, R. B. (1999) Free Radic. Biol. Med. 26 454–462 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Gilmour, P. S., Rahman, I., Donaldson, K., and MacNee, W. (2003) Am. J. Physiol. 284 L533–L540 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Newcomb, D. C., Sajjan, U., Nanua, S., Jia, Y., Goldsmith, A. M., Bentley, J. K., and Hershenson, M. B. (2005) J. Biol. Chem. 280 36952–36961 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Osawa, Y., Nagaki, M., Banno, Y., Brenner, D. A., Asano, T., Nozawa, Y., Moriwaki, H., and Nakashima, S. (2002) Infect. Immun. 70 6294–6301 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Wen, X. F., Yang, G., Mao, W., Thornton, A., Liu, J., Bast, R. C., Jr., and Le, X. F. (2006) Oncogene 25 6986–6996 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Adachi, M., Katsumura, K. R., Fujii, K., Kobayashi, S., Aoki, H., and Matsuzaki, M. (2003) FEBS Lett. 554 77–80 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Medina, E. A., Afsari, R. R., Ravid, T., Castillo, S. S., Erickson, K. L., and Goldkorn, T. (2005) Endocrinology 146 2726–2735 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Yan, D., Guo, L., and Wang, Y. (2006) J. Cell Biol. 174 415–424 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Ge, B., Gram, H., Di Padova, F., Huang, B., New, L., Ulevitch, R. J., Luo, Y., and Han, J. (2002) Science 295 1291–1294 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Kaur, S., Wang, F., Venkatraman, M., and Arsura, M. (2005) J. Biol. Chem. 280 38599–38608 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Wang, C., Deng, L., Hong, M., Akkaraju, G. R., Inoue, J., and Chen, Z. J. (2001) Nature 412 346–351 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Cuschieri, J., Gourlay, D., Garcia, I., Jelacic, S., and Maier, R. V. (2004) Cell Immunol. 227 140–147 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Fiedler, M. A., Wernke-Dollries, K., and Stark, J. M. (1998) Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 19 259–268 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Kamat, A. M., Karashima, T., Davis, D. W., Lashinger, L., Bar-Eli, M., Millikan, R., Shen, Y., Dinney, C. P., and McConkey, D. J. (2004) Mol. Cancer Ther. 3 279–290 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Campochiaro, P. A., Soloway, P., Ryan, S. J., and Miller, J. W. (1999) Mol. Vis. 5 34. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.