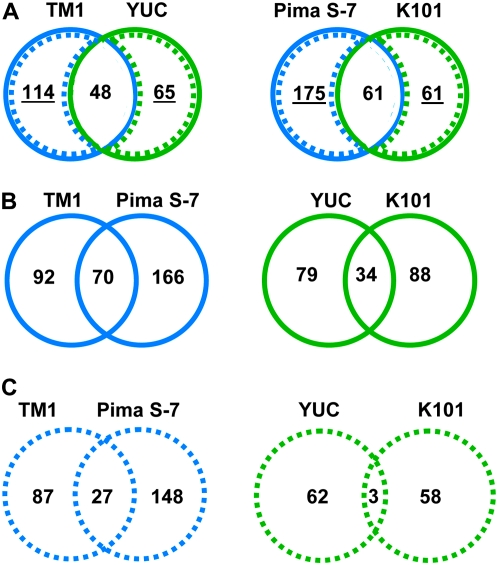
Figure 2.—
Comparisons of changes in homeolog expression bias during fiber development in wild and cultivated G. hirsutum (wild, Yuc; domesticated, TM1) and G. barbadense (wild, K101; domesticated, Pima S-7). To analyze changes in homeolog bias during development, a linear model that included only one effect (time point, with three levels 5, 10, and 20) and an error was used. The 1484 P-values from each comparison were converted to q-values using the method of Storey and Tibshirani (2003). These q-values were used to identify the number of differentially biased genes for a given comparison when controlling the false discovery rate (FDR) at various levels. For each accession shown, genes exhibiting changes in homeolog bias were concatenated into a single list. (A) Numbers of shared and nonshared changes in homeolog expression bias between wild and domesticated forms of G. hirsutum (left) and G. barbadense (right). (B) Number of shared and nonshared changes between two different domesticated (left) and wild (right) species. (C) Number of shared and nonshared changes using only those genes that changed homeolog bias during domestication (left) or in the wild (right).