Abstract
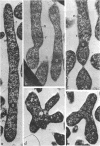
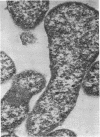
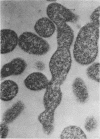
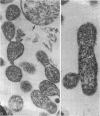
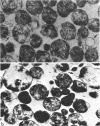
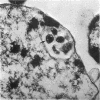
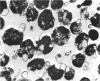
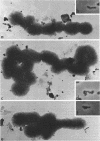
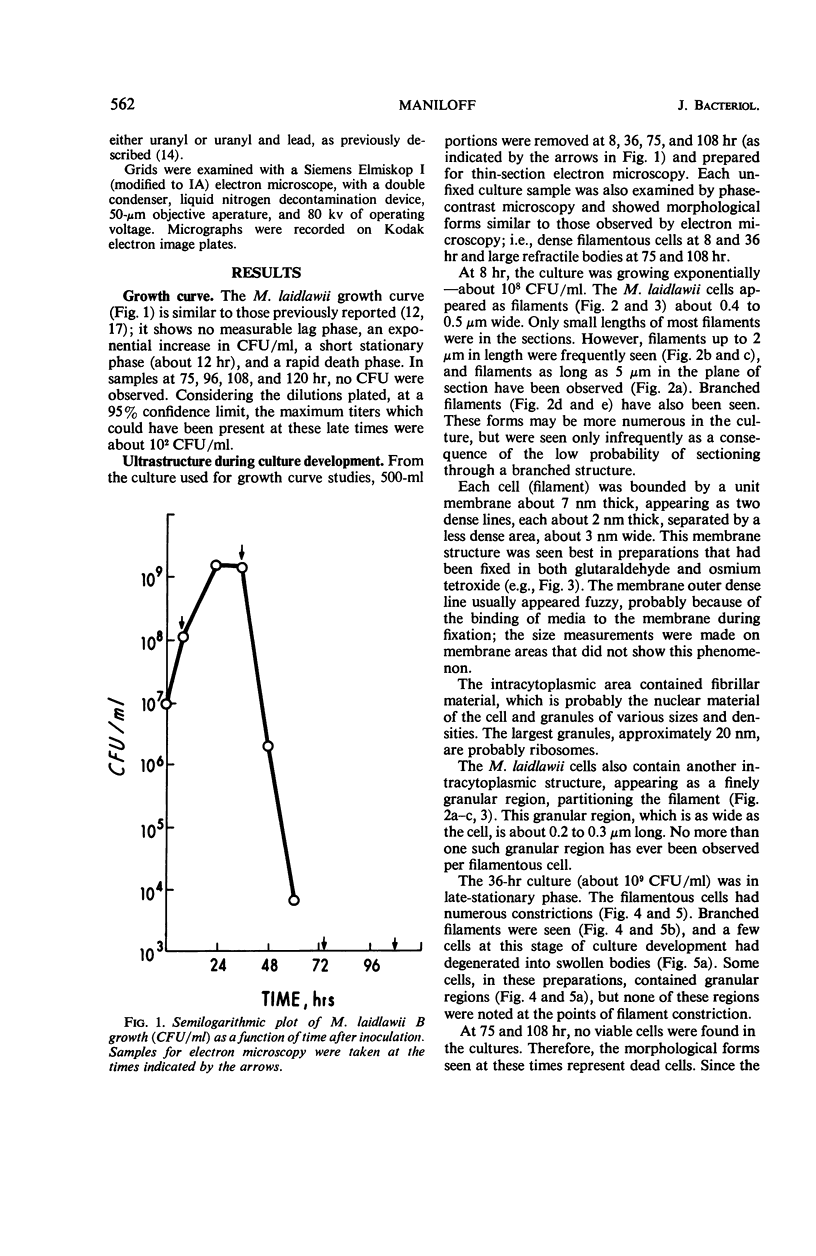
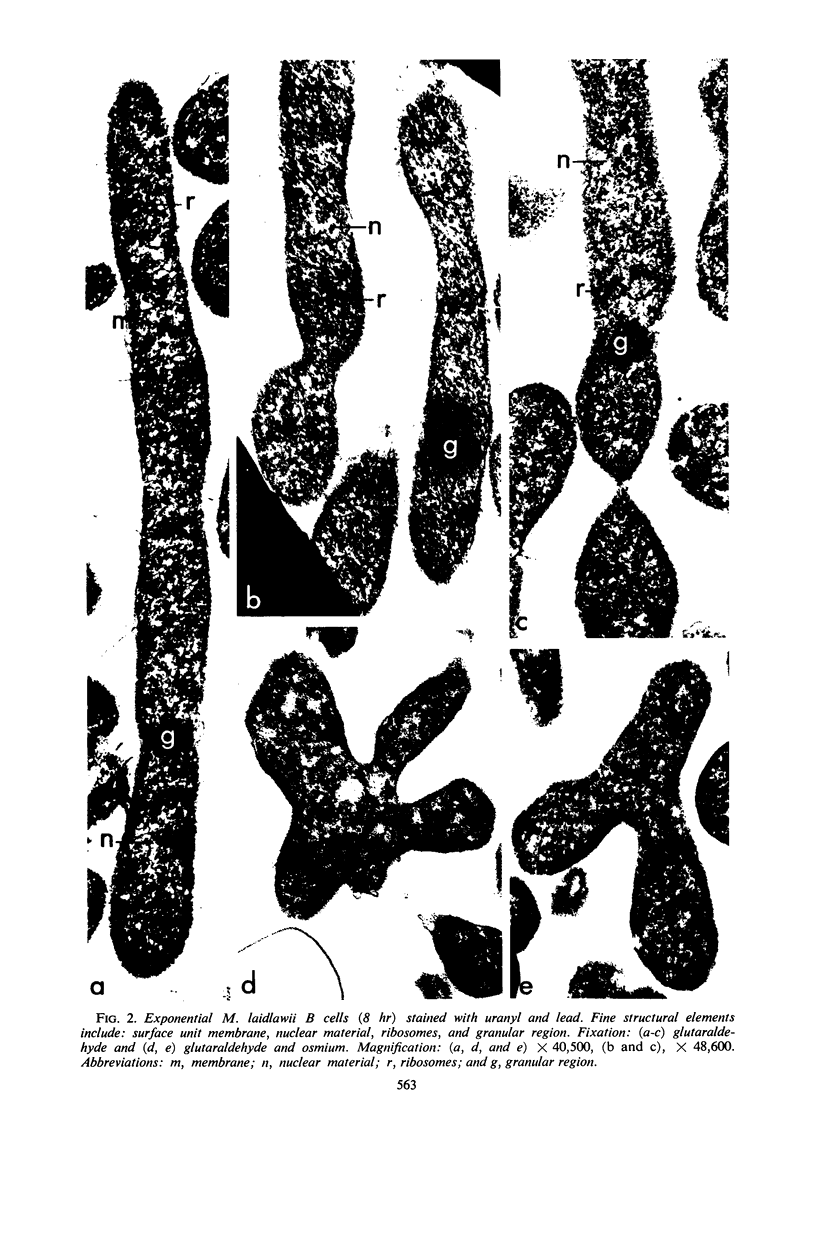
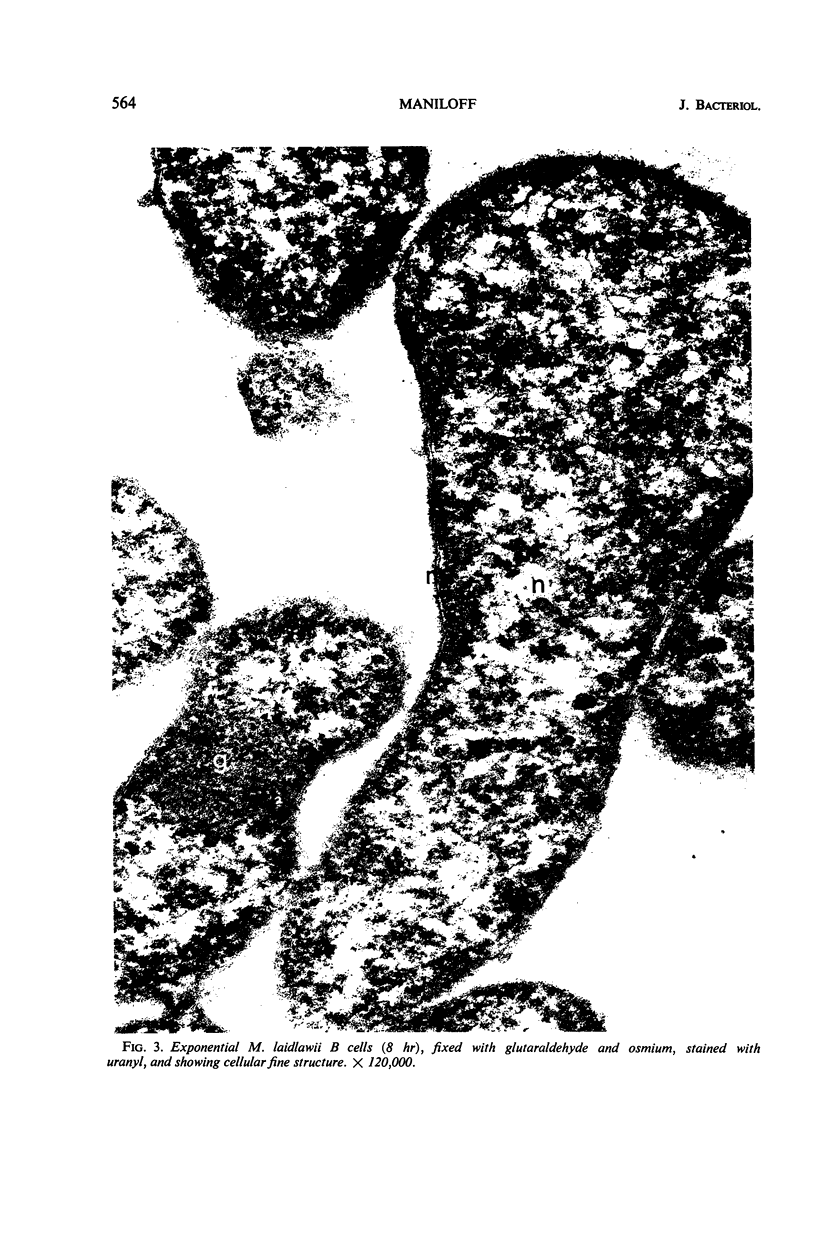
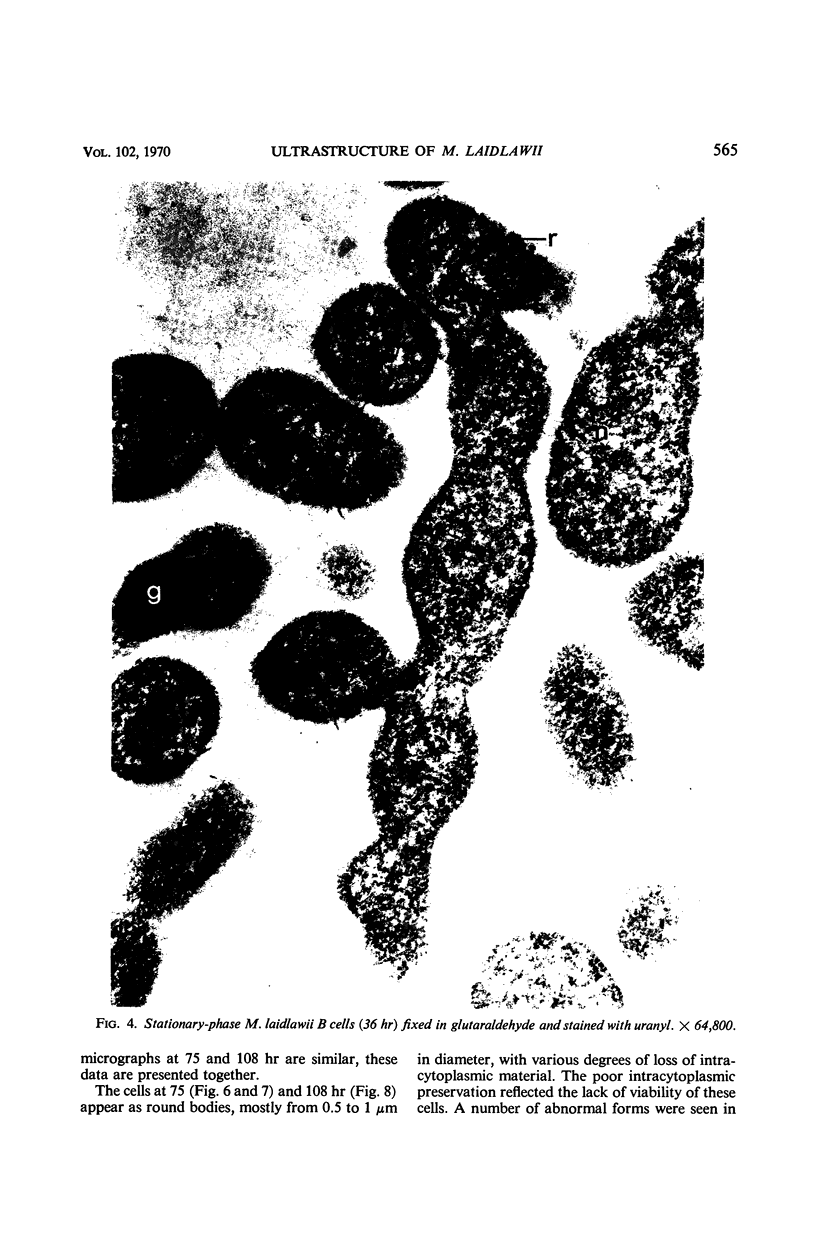
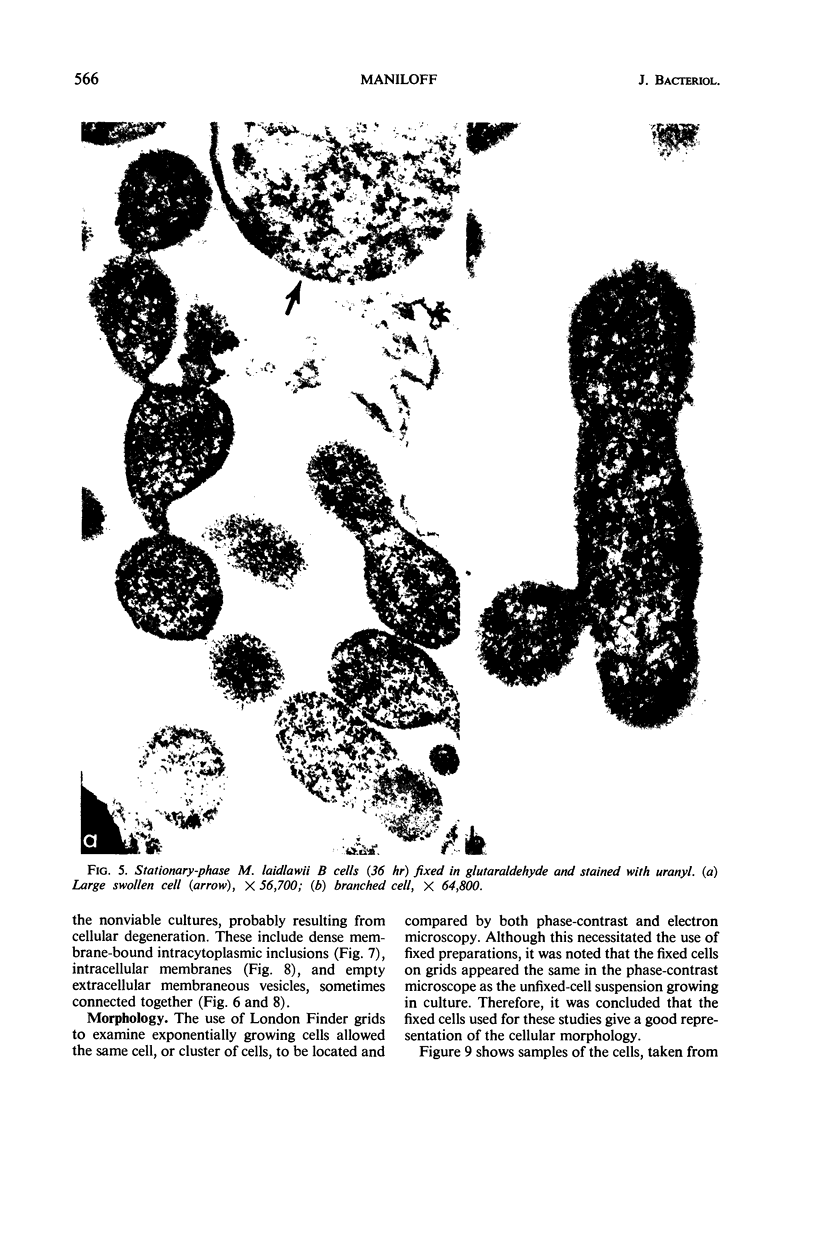
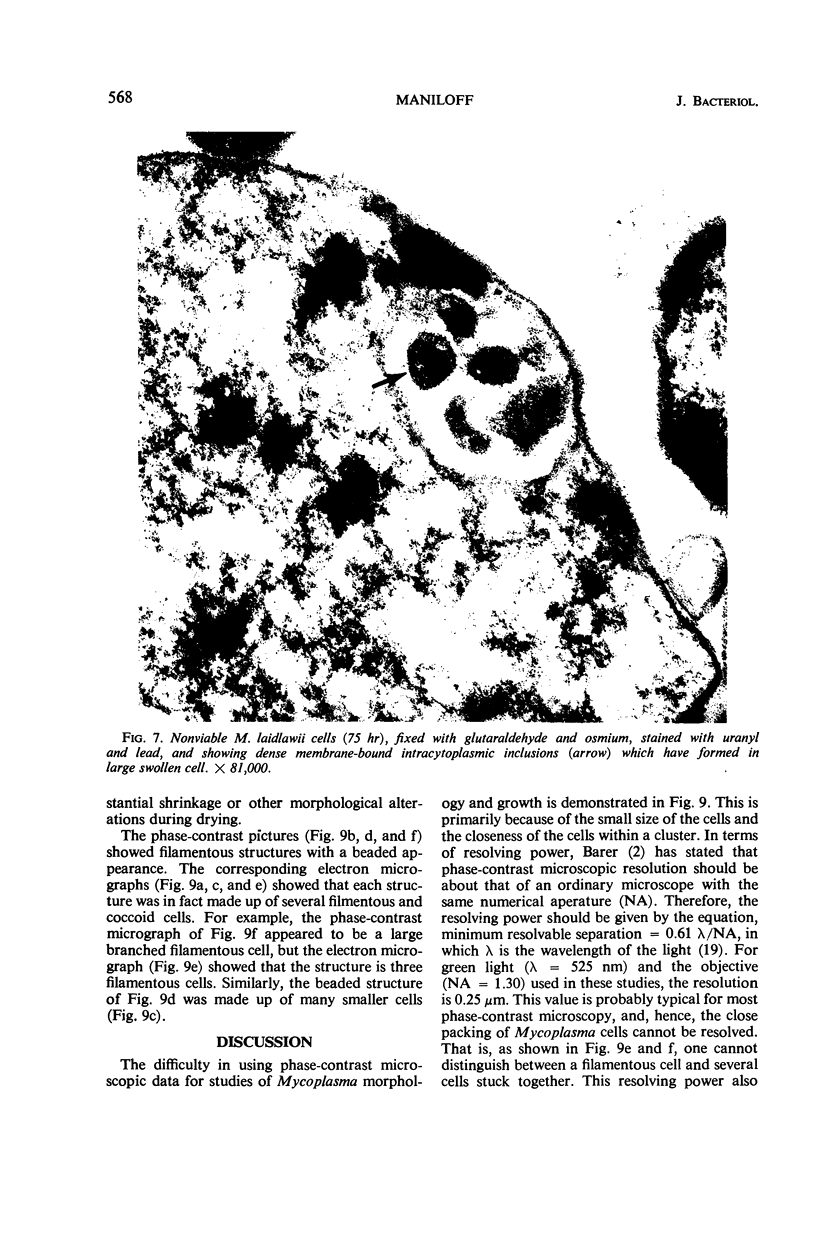
Mycoplasma laidlawii B has been studied by phase-contrast and electron microscopy (thin-section and negative staining). Exponential-phase cells are filaments with the following structures: surface unit membrane, nuclear material, ribosomes, and intracellular granular region. These cells appear to reproduce by binary fission. In stationary phase, the filamentous cells have numerous constrictions, giving them a beaded appearance. Nonviable death-phase cultures contain cellular debris: swollen cells, granular bodies, and other aberrant forms.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- DOMERMUTH C. H., NIELSEN M. H., FREUNDT E. A., BIRCH-ANDERSEN A. ULTRASTRUCTURE OF MYCOPLASMA SPECIES. J Bacteriol. 1964 Sep;88:727–744. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.3.727-744.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furness G. Analysis of the growth cycle of Mycoplasma orale by synchronized division and by ultraviolet irradiation. J Infect Dis. 1968 Oct;118(4):436–442. doi: 10.1093/infdis/118.4.436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furness G., Pipes F. J., McMurtrey M. J. Analysis of the life cycle of Mycoplasma pneumoniae by synchronized division and by ultraviolet and x irradiations. J Infect Dis. 1968 Feb;118(1):7–13. doi: 10.1093/infdis/118.1.7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLENBERGER E., RYTER A., SECHAUD J. Electron microscope study of DNA-containing plasms. II. Vegetative and mature phage DNA as compared with normal bacterial nucleoids in different physiological states. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1958 Nov 25;4(6):671–678. doi: 10.1083/jcb.4.6.671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELTON W. H. Growth-curve studies of pleuropneumonialike organisms. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1960 Jan 15;79:422–429. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1960.tb42707.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANILOFF J., MOROWITZ H. J., BARRNETT R. J. STUDIES OF THE ULTRASTRUCTURE AND RIBOSOMAL ARRANGEMENTS OF THE PLEUROPNEUMONIA-LIKE ORGANISM A5969. J Cell Biol. 1965 Apr;25:139–150. doi: 10.1083/jcb.25.1.139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniloff J. Electron microscopy of small cells: Mycoplasma hominis. J Bacteriol. 1969 Dec;100(3):1402–1408. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.3.1402-1408.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniloff J., Morowitz H. J., Barrnett R. J. Ultrastructure and Ribosomes of Mycoplasma gallisepticum. J Bacteriol. 1965 Jul;90(1):193–204. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.1.193-204.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniloff J., Morowitz H. J. Ultrastructure and life cycle of Mycoplasma gallisepticum A5969. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1967 Jul 28;143(1):59–65. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1967.tb27644.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morowitz H. J., Maniloff J. Analysis of the life cycle of Mycoplasma gallisepticum. J Bacteriol. 1966 Apr;91(4):1638–1644. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.4.1638-1644.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin S., Cosenza B. J. Growth phases of Mycoplasma in liquid media observed with phase-contrast microscope. J Bacteriol. 1966 Feb;91(2):858–869. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.2.858-869.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin S., Morowitz H. J., Terry T. M. Membrane subunits of Mycoplasma laidlawii and their assembly to membranelike structures. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Jul;54(1):219–225. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.1.219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]