Abstract
A total of 60 patients in Madras with haemorrhagic and non-haemorrhagic clinical forms of smallpox were investigated by a variety of bleeding and coagulation studies in an attempt to reveal specific haematological defects that might account for the haemorrhagic diathesis in certain cases of smallpox.
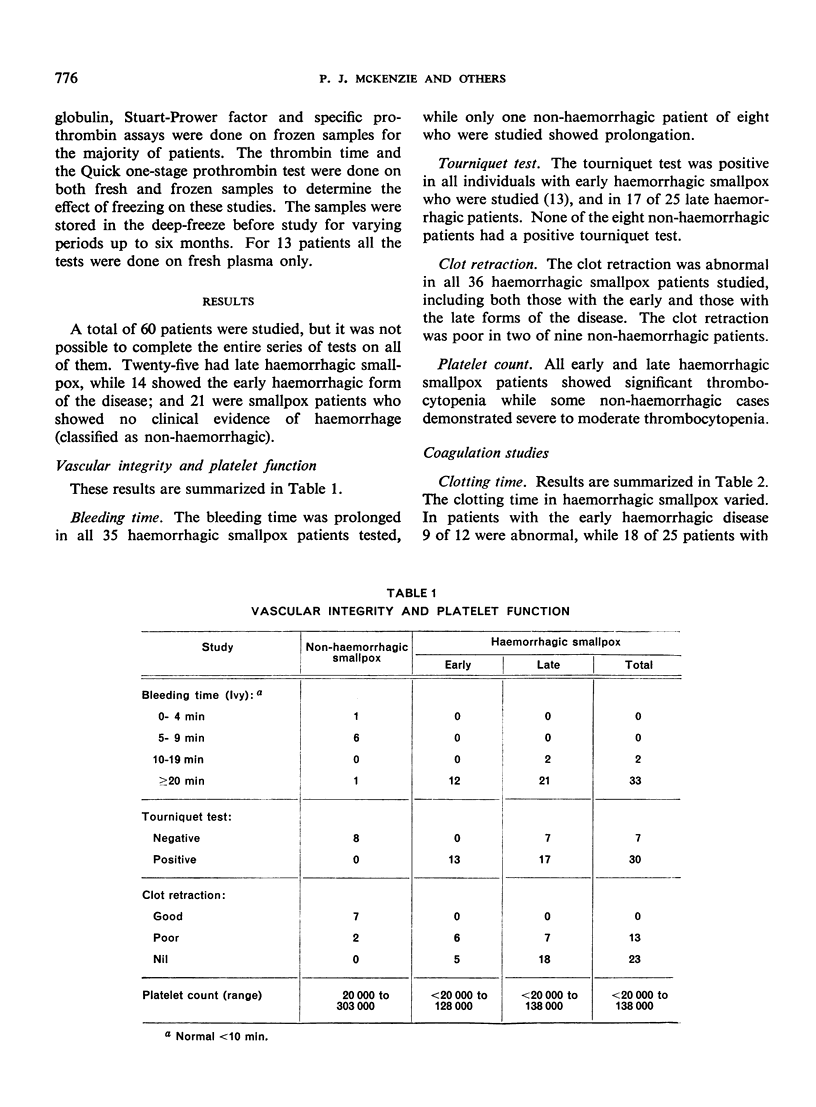
The non-haemorrhagic smallpox patients had no coagulation abnormalities, although some had thrombocytopenia.
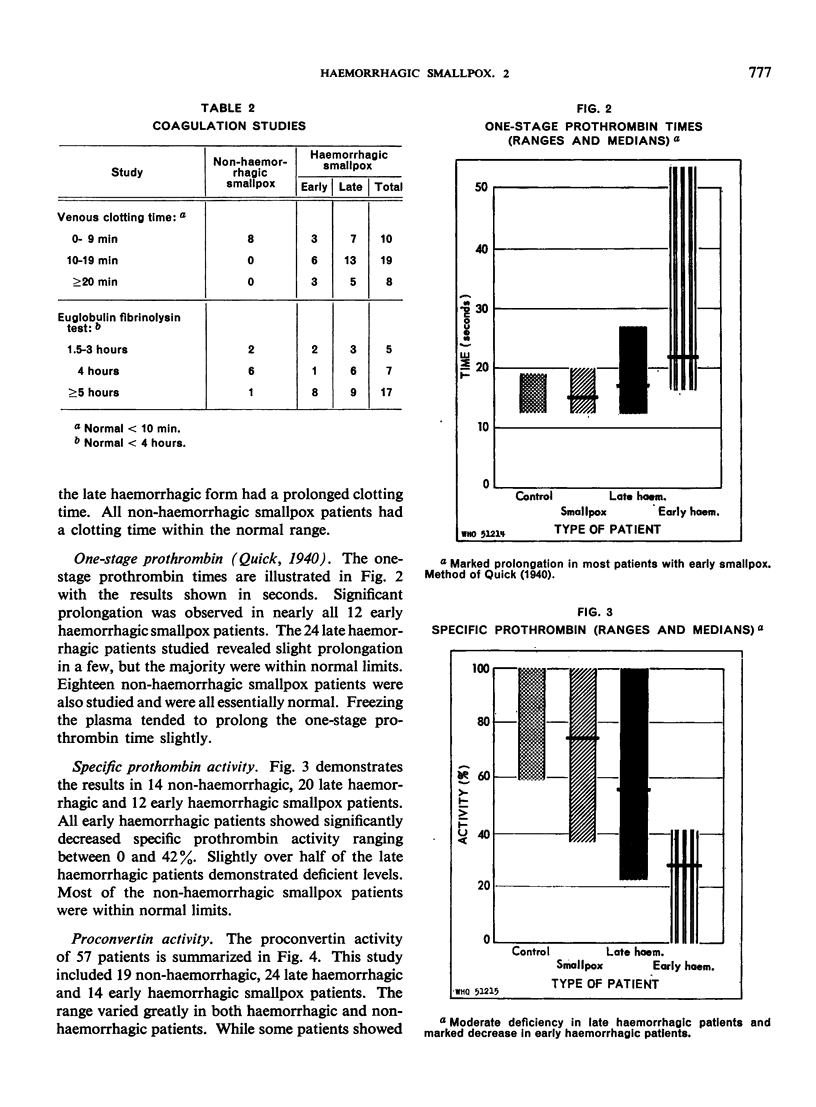
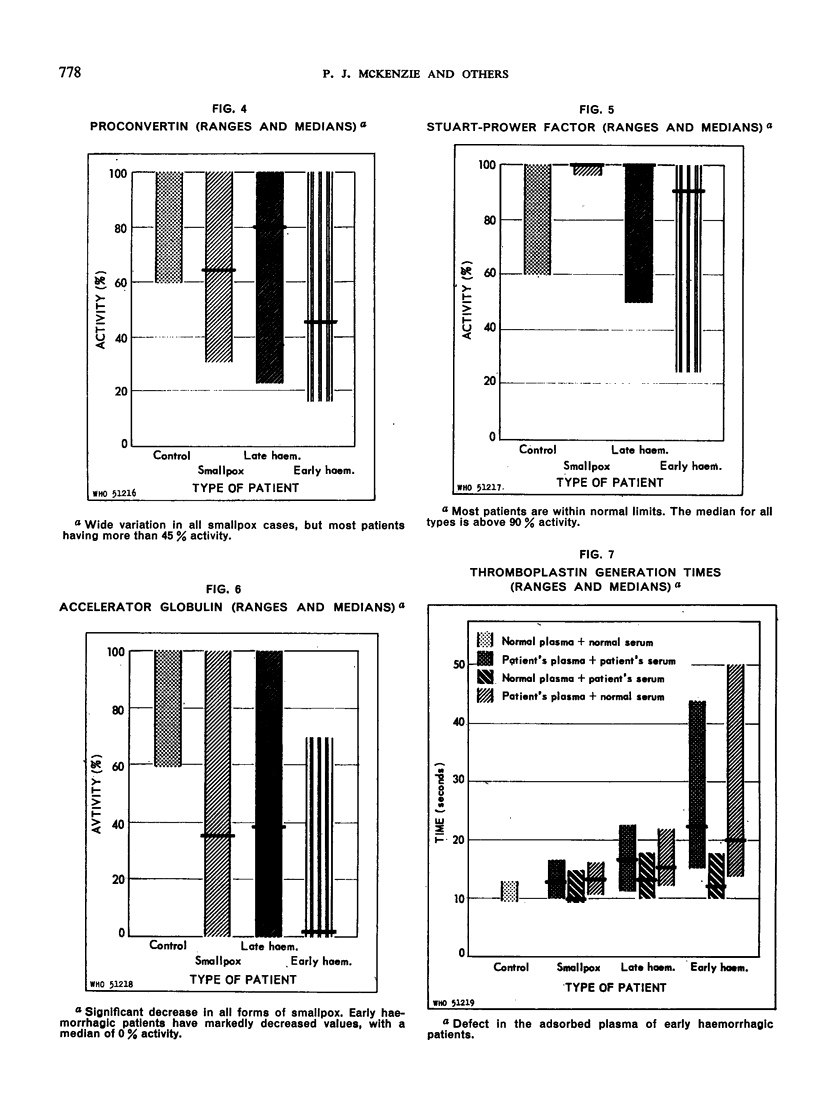
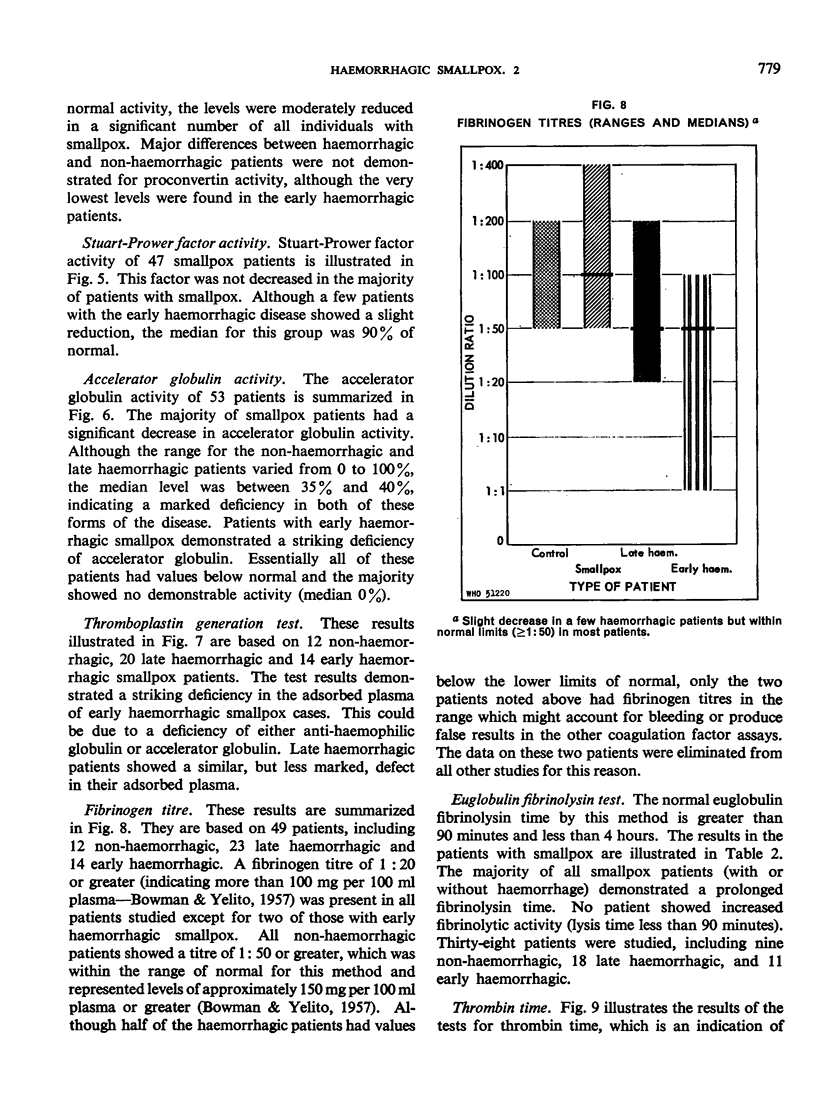
The early haemorrhagic patients showed a deficiency of platelets, prothrombin and accelerator globulin, and increased circulating antithrombin. Patients with the late form of haemorrhagic smallpox showed significant thrombocytopenia and less severe deficiencies of the same coagulation factors; a few also had increased antithrombin.
The authors suggest that therapy with fresh, frozen or lyophilized plasma should be tried; fresh, platelet-rich plasma should offer the greatest benefit.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BACHMANN F., DUCKERT F., KOLLER F. The Stuart-Prower factor assay and its clinical significance. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1958 May 1;2(1-2):24–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BORCHGREVINK C. F., POOL J. G., STORMORKEN H. A new assay for factor V (proaccelerin-accelerin) using Russell's viper venom. J Lab Clin Med. 1960 Apr;55:625–632. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOWMAN H. S., YELITO M. B. A method for determining the plasma fibrinogen titer. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1957 Sep;74(3):670–673. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(57)90526-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COPLEY A. L., NIEWIAROWSKI S., MARECHAL J. A micromethod of euglobulin fibrinolysis in plasma of human subjects and small laboratory animals. J Lab Clin Med. 1959 Mar;53(3):468–473. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MIALE J. B., WILSON M. P. Studies on the thromboplastin generation test. I. Method and clinical applications. Am J Clin Pathol. 1956 Sep;26(9):969–983. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/26.9.969. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OWREN P. A., AAS K. The control of dicumarol therapy and the quantitative determination of prothrombin and proconvertin. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1951;3(3):201–208. doi: 10.3109/00365515109060600. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts J. F., Coffee G., Creel S. M., Gaal A., Githens J. H., Rao A. R., Sundara Babu B. V., Kempe C. H. Haemorrhagic smallpox. I. Preliminary haematological studies. Bull World Health Organ. 1965;33(5):607–613. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SKIRMONT E., MARKS E. K., JACOBSON L. O. A modified technique for counting blood platelets. Am J Med Technol. 1949 Mar;15(2):86–86. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


