Abstract
A mutant of Escherichia coli resembles its parent in taking up actinomycin after treatment with ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid but differs in that it survives this uptake and excretes actinomycin at an increased rate.
Full text
PDF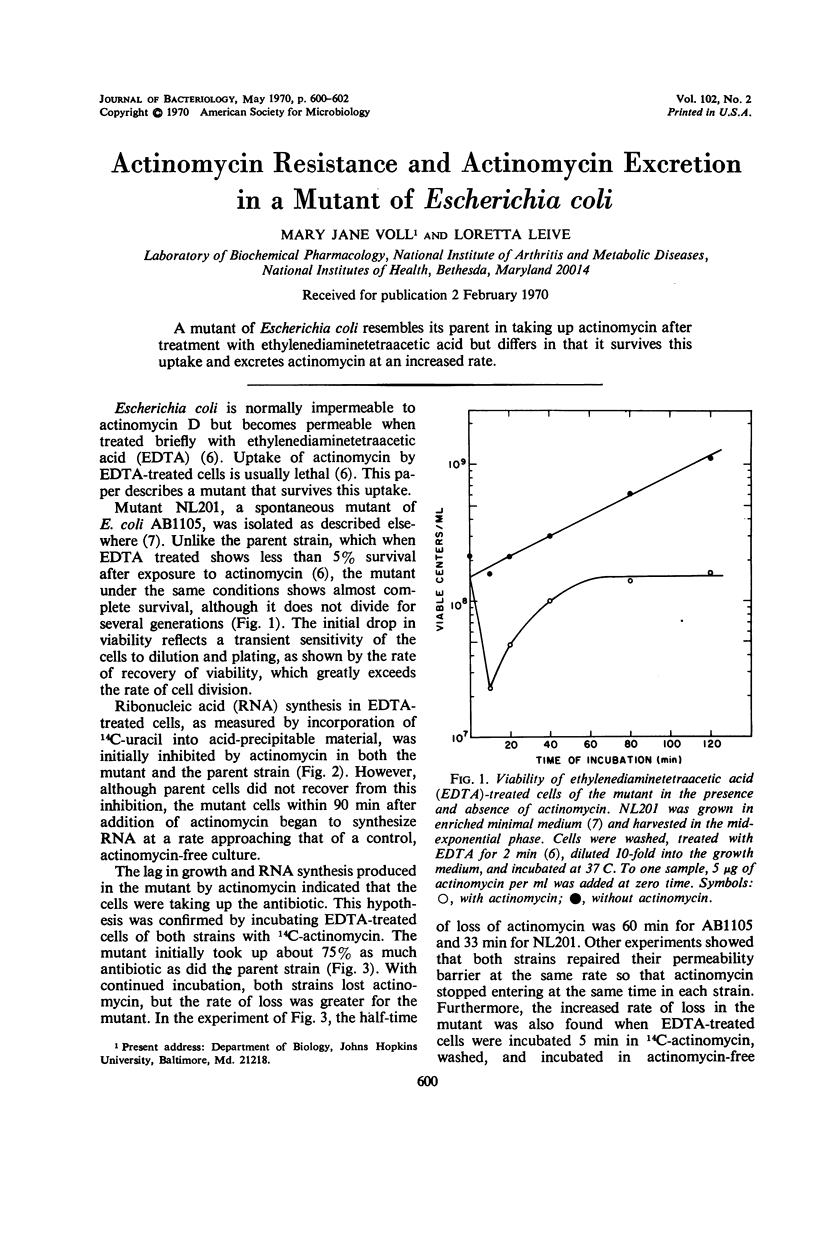

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- GELLERT M., SMITH C. E., NEVILLE D., FELSENFELD G. ACTINOMYCIN BINDING TO DNA: MECHANISM AND SPECIFICITY. J Mol Biol. 1965 Mar;11:445–457. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80001-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATZ E., WEISSBACH H. Incorporation of C14-labeled amino acids into actinomycin and protein by Streptomyces antibioticus. J Biol Chem. 1963 Feb;238:666–675. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz E., Mauger A. B., Weissbach H. Biosynthesis of highly labeled actinomycins. Mol Pharmacol. 1965 Jul;1(1):107–109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kushner D. J., Khan S. R. Proflavine Uptake and Release in Sensitive and Resistant Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1968 Oct;96(4):1103–1114. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.4.1103-1114.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leive L. Studies on the permeability change produced in coliform bacteria by ethylenediaminetetraacetate. J Biol Chem. 1968 May 10;243(9):2373–2380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voll M. J., Leive L. Release of lipopolysaccharide in Escherichia coli resistant to the permeability increase induced by ethylenediaminetetraacetate. J Biol Chem. 1970 Mar 10;245(5):1108–1114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


