Abstract
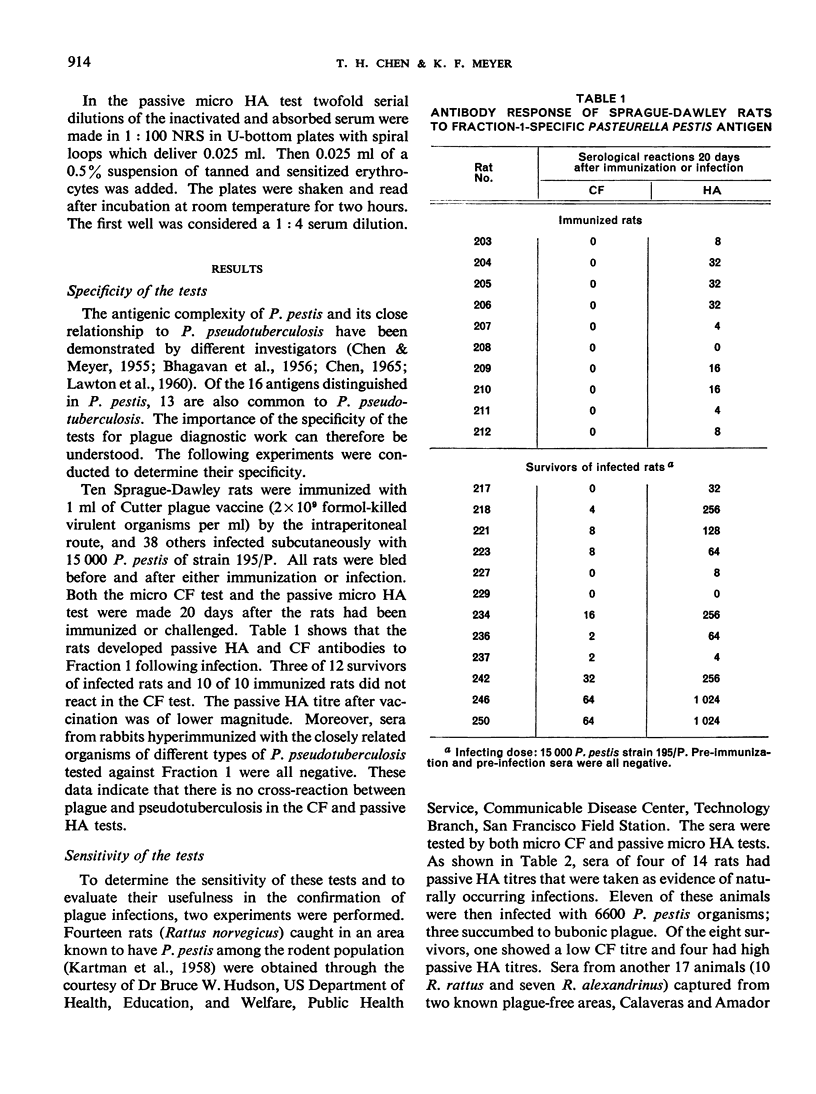
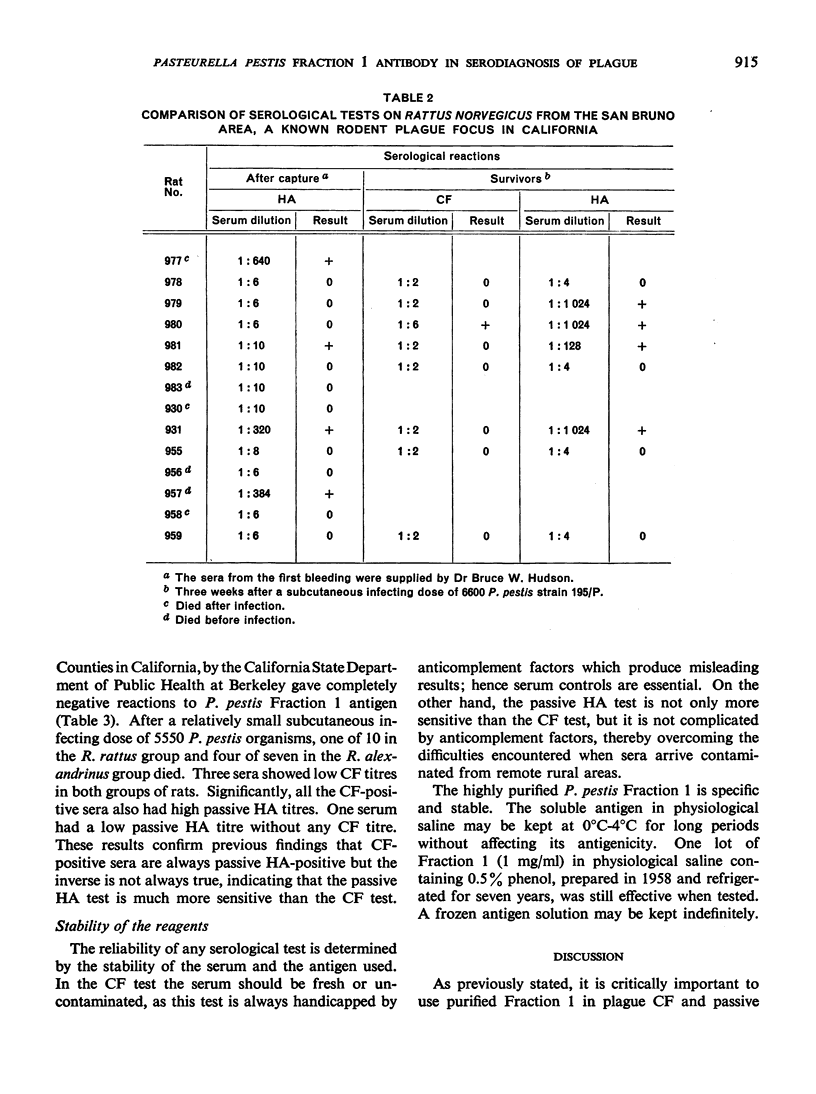
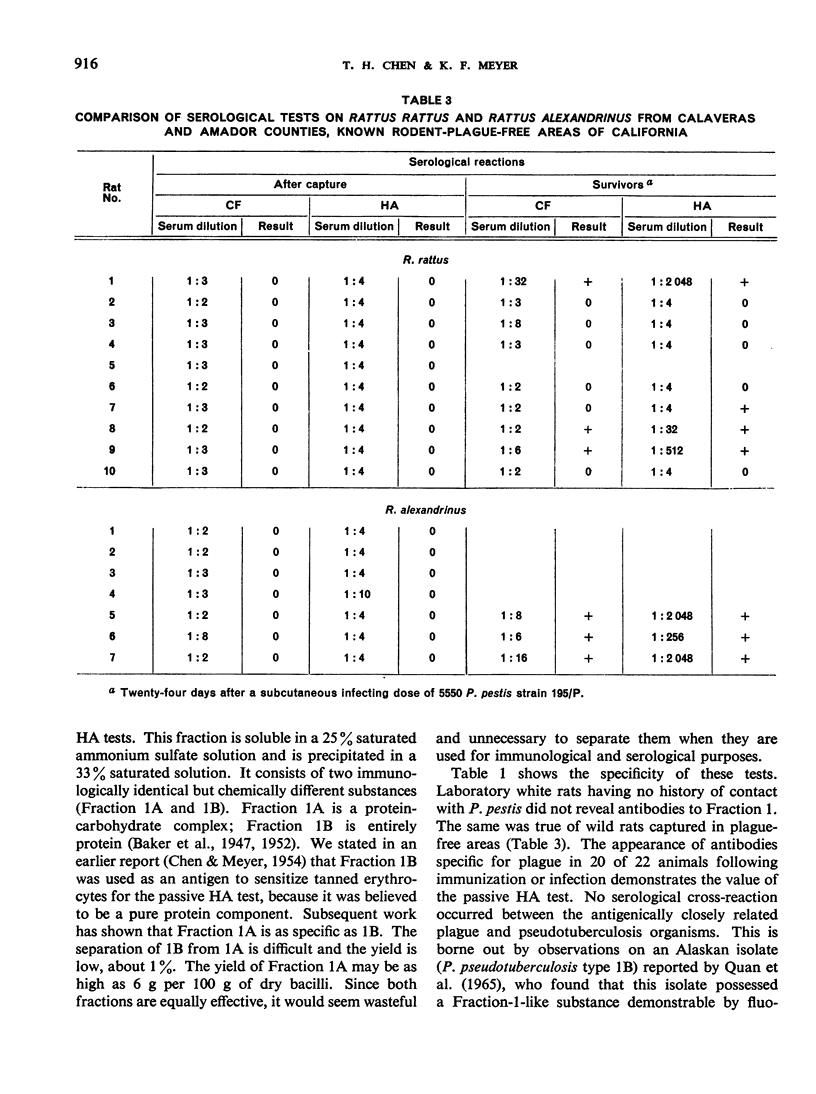
Owing to the relatively long duration of specific serum plague antibodies in the host, the serological diagnosis of plague has substantial advantages over the conventional method of isolation of the causative agent. For the performance of both the complement-fixation (CF) and passive haemagglutination (HA) tests, the use of highly purified, specific Fraction 1 antigen is essential, and its preparation is discussed in this paper. Although both tests measure the same antibodies, the passive HA test is the more sensitive and constitutes the most effective means of detecting recovery from plague infection in nature. The CF test is nevertheless invaluable for such purposes as determining the antibody content of sera from immunized or infected hosts, indicating the amount of Fraction 1 developed by strains of Pasteurella pestis in cultures and therefore present in a vaccine, or detecting and estimating the amount of Fraction 1 antigen in extracts prepared from infected animal tissues and therefore for the field diagnosis of wild rodent plague after contamination or decomposition of rodents' carcasses.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BAKER E. E., SOMMER H., FOSTER L. E., MEYER E., MEYER K. F. Studies on immunization against plague. I. The isolation and characterization of the soluble antigen of Pasteurella pestis. J Immunol. 1952 Feb;68(2):131–145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BHAGAVAN N. V., CHEN T. H., MEYER K. F. Further studies of antigenic structure of Pasteurella pestis in gels. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1956 Mar;91(3):353–356. doi: 10.3181/00379727-91-22260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAVANAUGH D. C., THORPE B. D., BUSHMAN J. B., NICHOLES P. S., RUST J. H., Jr DETECTION OF AN ENZOOTIC PLAGUE FOCUS BY SEROLOGICAL METHODS. Bull World Health Organ. 1965;32:197–203. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHEN T. H., LARSON A., MEYER K. F. STUDIES ON IMMUNIZATION AGAINST PLAGUE. XVII. EXPERIMENTAL STUDIES ON THE EFFECTIVENESS OF ALUMINUM-HYDROXIDE-ADSORBED FORMALIN-KILLED PASTEURELLA PESTIS. J Immunol. 1964 Oct;93:668–676. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHEN T. H., MEYER K. F. Studies on immunization against plague. VII. A hemagglutination test with the protein fraction of Pasteurella pestis: a serologic comparison of virulent and avirulent strains with observations on the structure of the bacterial cells and its relationship to infection and immunity. J Immunol. 1954 Apr;72(4):282–298. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHEN T. H., MEYER K. F. Studies on immunization against plague. X. Specific precipitation of Pasteurella pestis antigens and antibodies in gels. J Immunol. 1955 Jun;74(6):501–507. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHEN T. H., QUAN S. F., MEYER K. F. Studies on immunization against plague. II. The complement-fixation test. J Immunol. 1952 Feb;68(2):147–158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHEN T. H. THE ANTIGENIC STRUCTURE OF PASTEURELLA PESTIS AND ITS RELATIONSHIP TO VIRULENCE AND IMMUNITY. Acta Trop. 1965;22:97–117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUDSON B. W., QUAN S. F., GOLDENBERG M. I. SERUM ANTIBODY RESPONSES IN A POPULATION OF MICROTUS CALIFORNICUS AND ASSOCIATED RODENT SPECIES DURING AND AFTER PASTEURELLA PESTIS EPIZOOTICS IN THE SAN FRANCISCO BAY AREA. Zoonoses Res. 1964 Apr;3:15–29. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KARTMAN L., MILES V. I., PRINCE F. M. Ecological studies of wild rodent plague in the San Francisco bay area of California. I. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1958 Jan;7(1):112–124. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1958.7.112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAWTON W. D., FUKUI G. M., SURGALLA M. J. Studies on the antigens of Pasteurella pestis and Pasteurella pseudotuberculosis. J Immunol. 1960 May;84:475–479. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- QUAN S. F., KNAPP W., GOLDENBERG M. I., HUDSON B. W., LAWTON W. D., CHEN T. H., KARTMAN L. ISOLATION OF A STRAIN OF PASTEURELLA PSEUDOTUBERCULOSIS FROM ALASKA IDENTIFIED AS PASTEURELLA PESTIS: AN IMMUNOFLUORESCENT FALSE POSITIVE. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1965 May;14:424–432. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1965.14.424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEVER J. L. Application of a microtechnique to viral serological investigations. J Immunol. 1962 Mar;88:320–329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


