Abstract
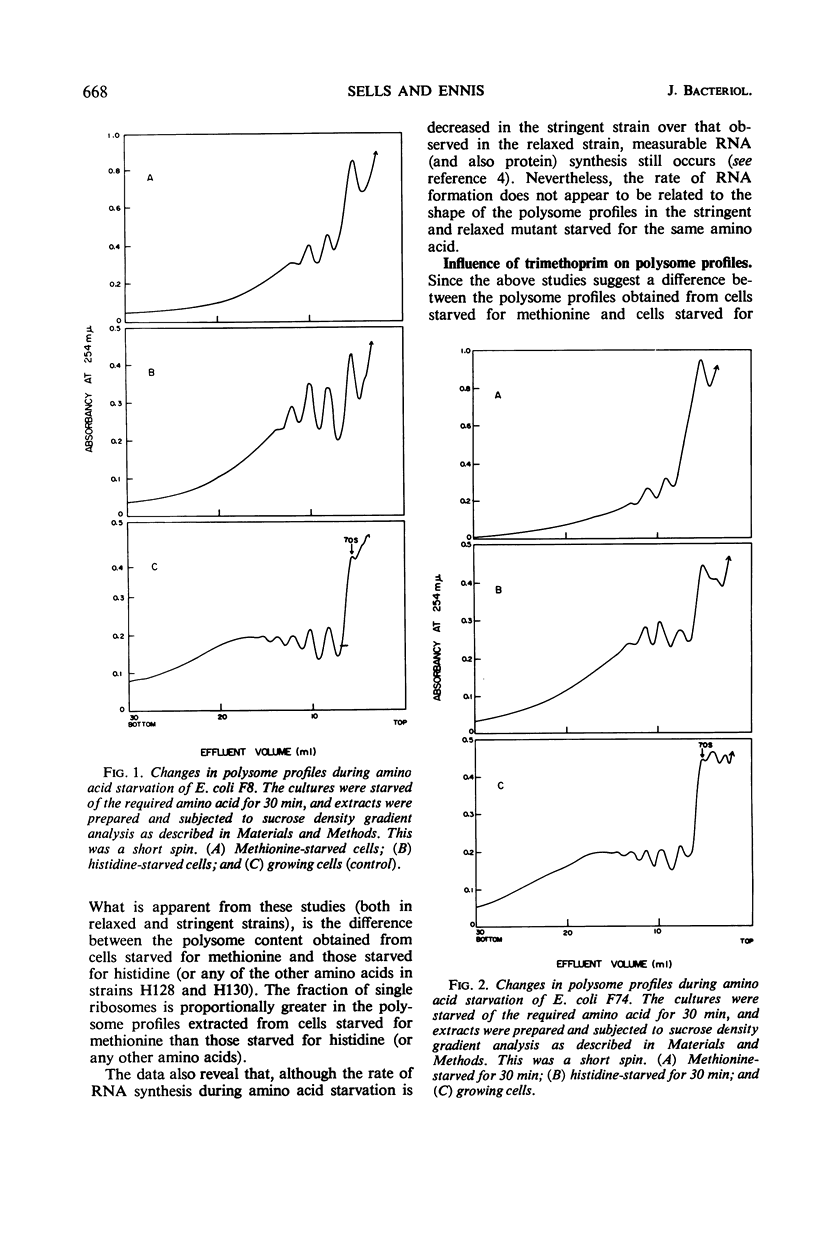
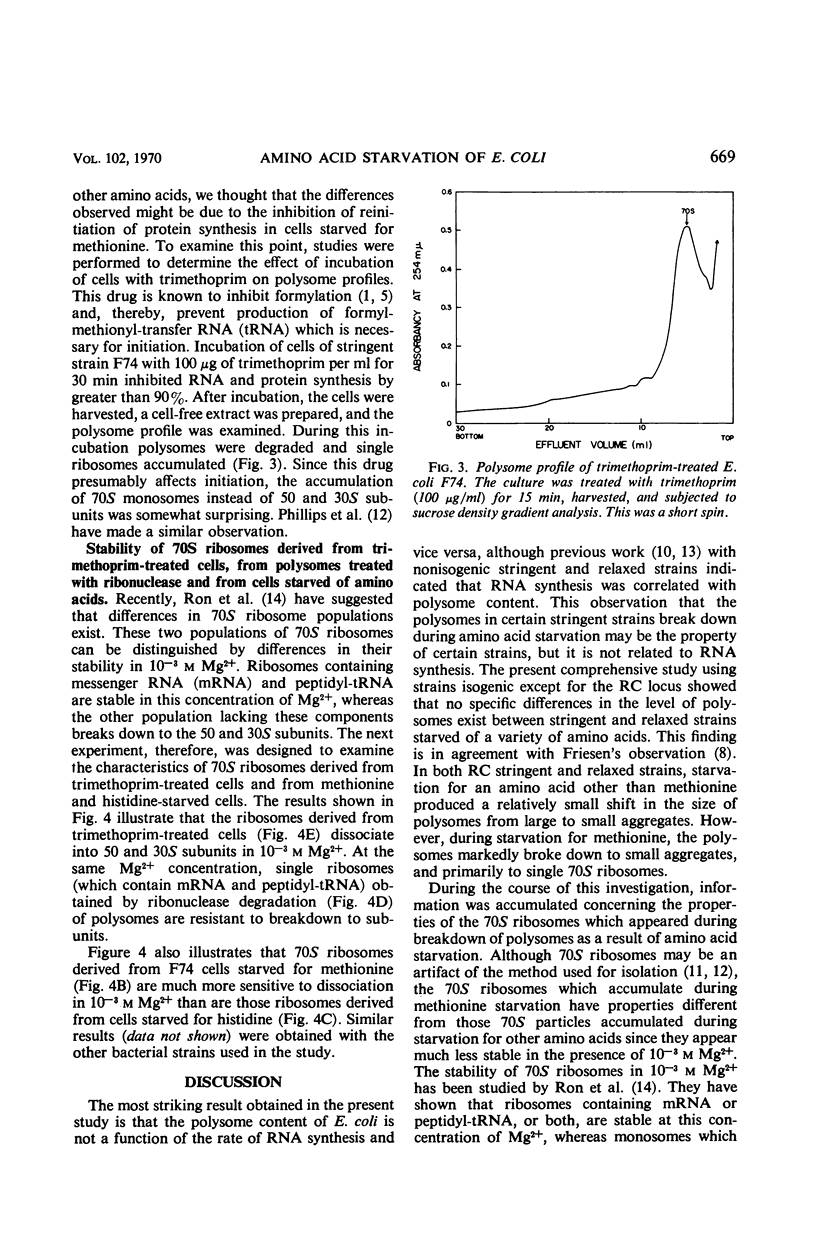
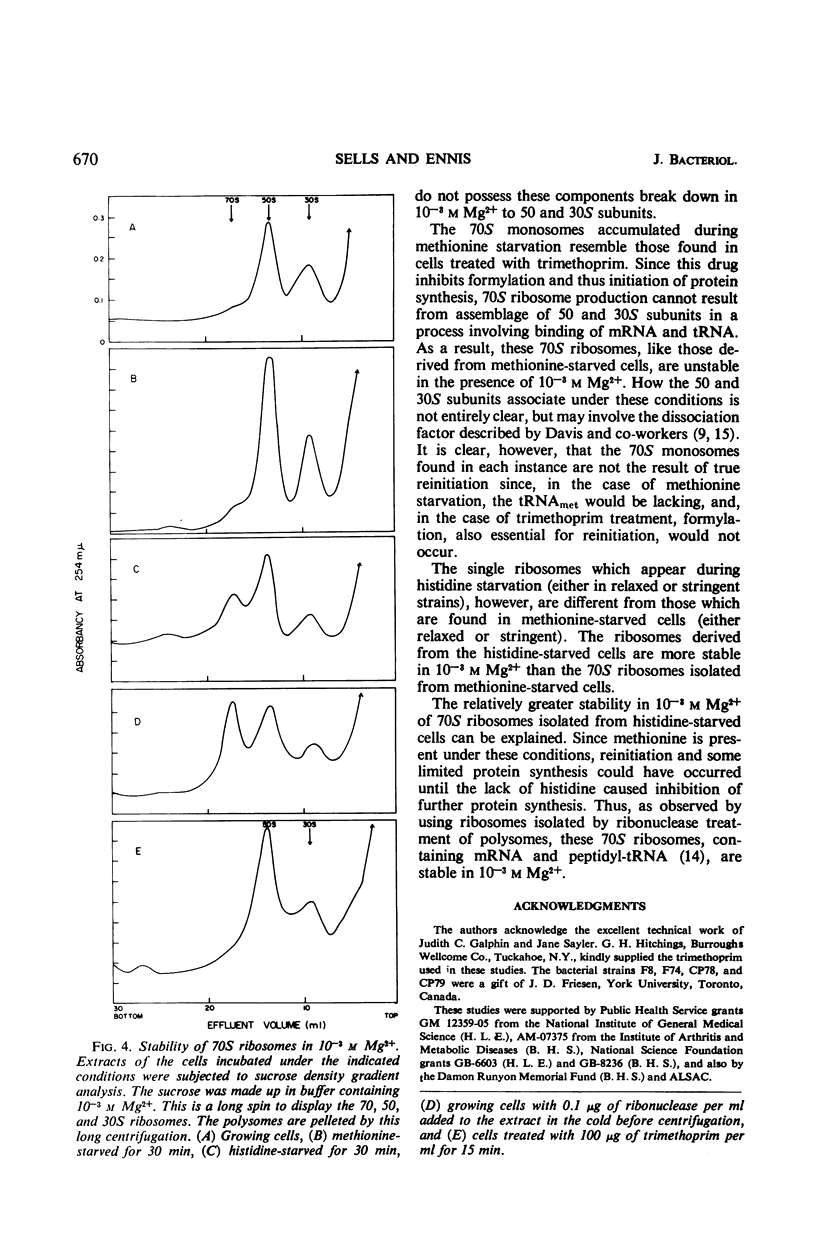
The influence of amino acid starvation on polysome content was examined in relaxed and stringent strains of Escherichia coli which were isogenic for the RC locus. No difference was observed between the polysome profiles obtained from two different sets of stringent and relaxed strains starved for the same amino acid. In both relaxed and stringent strains, starvation for amino acids other than methionine resulted in only a slight breakdown of polysomes with a concomitant increase of 70S ribosomes. However, starvation for methionine in both RC stringent and relaxed strains of E. coli resulted in a more extensive degradation of polysomes and accumulation of 70S ribosomes. The 70S ribosomes obtained as a result of methionine starvation were more sensitive to degradation to 50 and 30S subunits in 10−3m Mg2+ than 70S monomers obtained either by degradation of polysomes with ribonuclease or by starvation of cells for amino acids other than methionine. The 70S ribosomes from methionine starvation were similar (sensitivity to 10−3m Mg2+) to 70S ribosomes obtained from cells in which initiation of protein synthesis had been prevented by trimethoprim, an inhibitor of formylation. Since N-formyl-methionyl-transfer ribonucleic acid is required for initiation, the 70S ribosomes obtained in both methionine-starved and trimethoprim-treated cells must result from association of 50 and 30S subunits for reasons other than reinitiation. These results suggest that the level of ribonucleic acid synthesis does not influence the distribution of ribosomes in the polysome profile and vice versa.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burchall J. J., Hitchings G. H. Inhibitor binding analysis of dihydrofolate reductases from various species. Mol Pharmacol. 1965 Sep;1(2):126–136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P. S., Ennis H. L. The requirement for potassium for bacteriophage T4 protein and deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis. Virology. 1965 Nov;27(3):282–289. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(65)90107-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. D., MINGIOLI E. S. Mutants of Escherichia coli requiring methionine or vitamin B12. J Bacteriol. 1950 Jul;60(1):17–28. doi: 10.1128/jb.60.1.17-28.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edlin G., Stent G. S., Baker R. F., Yanofsky C. Synthesis of a specific messenger RNA during amino acid starvation of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1968 Oct 28;37(2):257–268. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90266-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenstadt J., Lengyel P. Formylmethionyl-tRNA dependence of amino acid incorporation in extracts of trimethoprim-treated Escherichia coli. Science. 1966 Oct 28;154(3748):524–527. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiil N., Friesen J. D. Isolation of "relaxed" mutants of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1968 Feb;95(2):729–731. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.2.729-731.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flessel C. P., Ralph P., Rich A. Polyribosomes of growing bacteria. Science. 1967 Nov 3;158(3801):658–660. doi: 10.1126/science.158.3801.658. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friesen J. D. A study of the relationship between polyribosomes and messenger RNA in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1968 Mar 14;32(2):183–200. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90003-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohler R. E., Ron E. Z., Davis B. D. Significance of the free 70 s ribosomes in Escherichia coli extracts. J Mol Biol. 1968 Aug 28;36(1):71–82. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90220-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris D. W., DeMoss J. A. Polysome transitions and the regulation of ribonucleic acid synthesis in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Jul;56(1):262–268. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.1.262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips L. A., Hotham-Iglewski B., Franklin R. M. Polyribosomes of Escherichia coli. I. Effects of monovalent cations on the distribution of polysomes, ribosomes and ribosomal subunits. J Mol Biol. 1969 Mar 14;40(2):279–288. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90475-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips L. A., Hotham-Iglewski B., Franklin R. M. Polyribosomes of Escherichia coli. II. Experiments to determine the in vivo distribution of polysomes, ribosomes and ribosomal subunits. J Mol Biol. 1969 Oct 14;45(1):23–38. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90207-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ron E. Z., Kohler R. E., Davis B. D. Increased stability of polysomes in an Escherichia coli mutant with relaxed control of RNA synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Aug;56(2):471–475. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.2.471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ron E. Z., Kohler R. E., Davis B. D. Magnesium ion dependence of free and polysomal ribosomes from Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1968 Aug 28;36(1):83–89. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90221-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subramanian A. R., Ron E. Z., Davis B. D. A factor required for ribosome dissociation in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Oct;61(2):761–767. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.2.761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


