Abstract
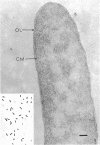
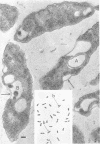
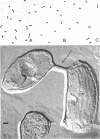
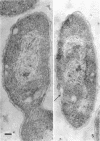
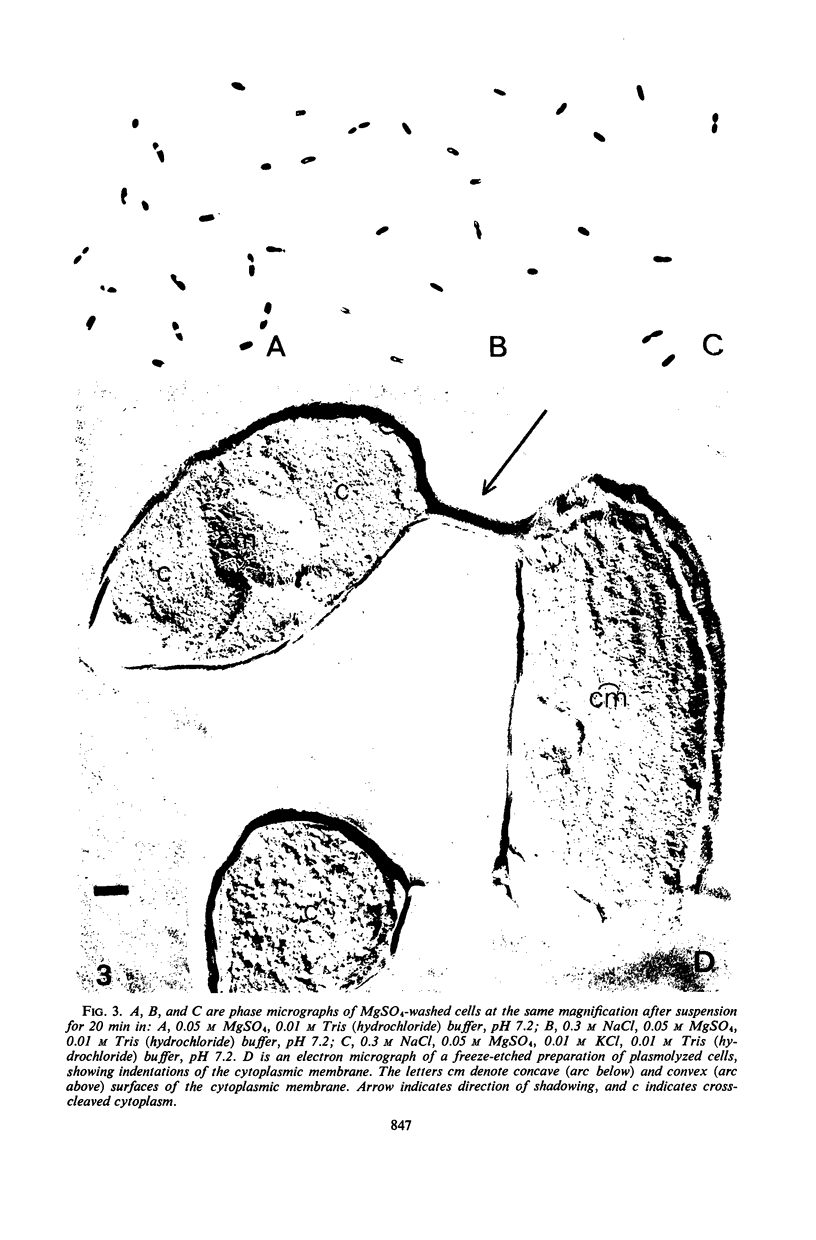
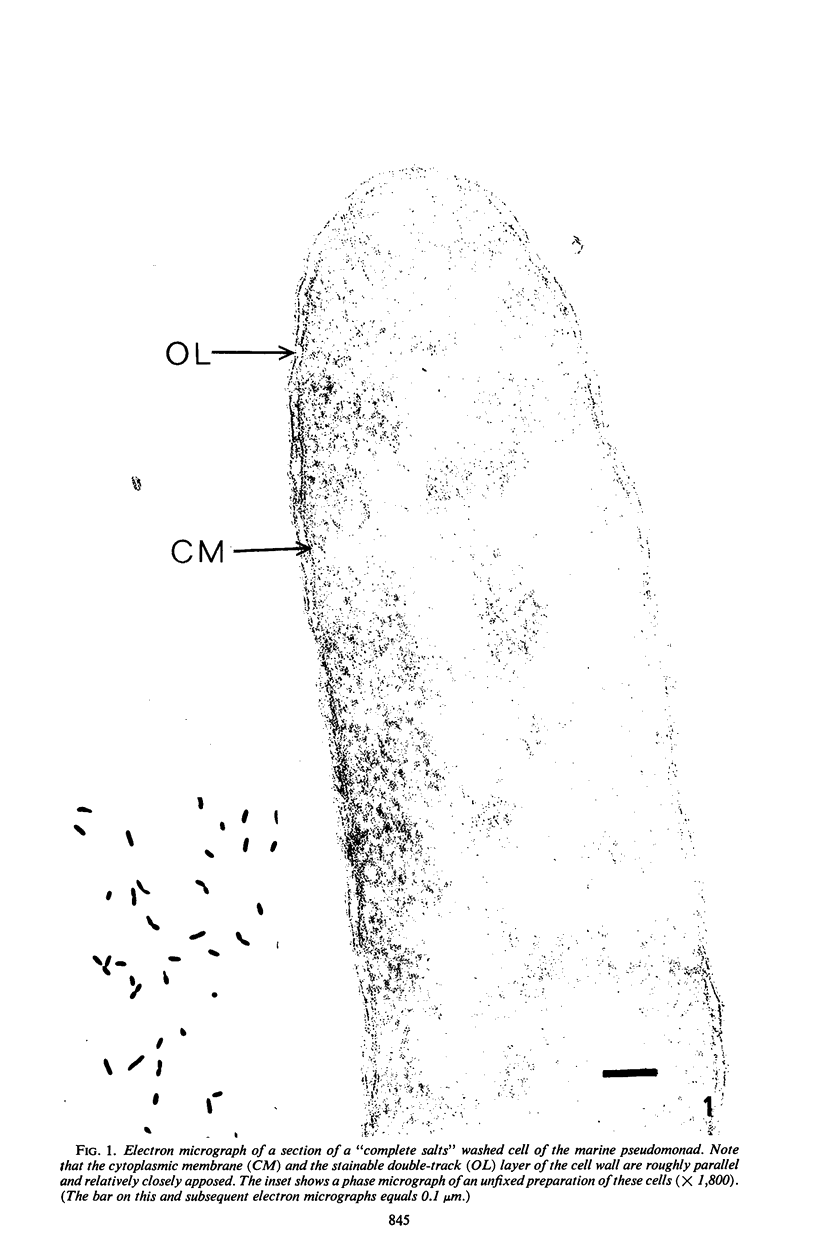
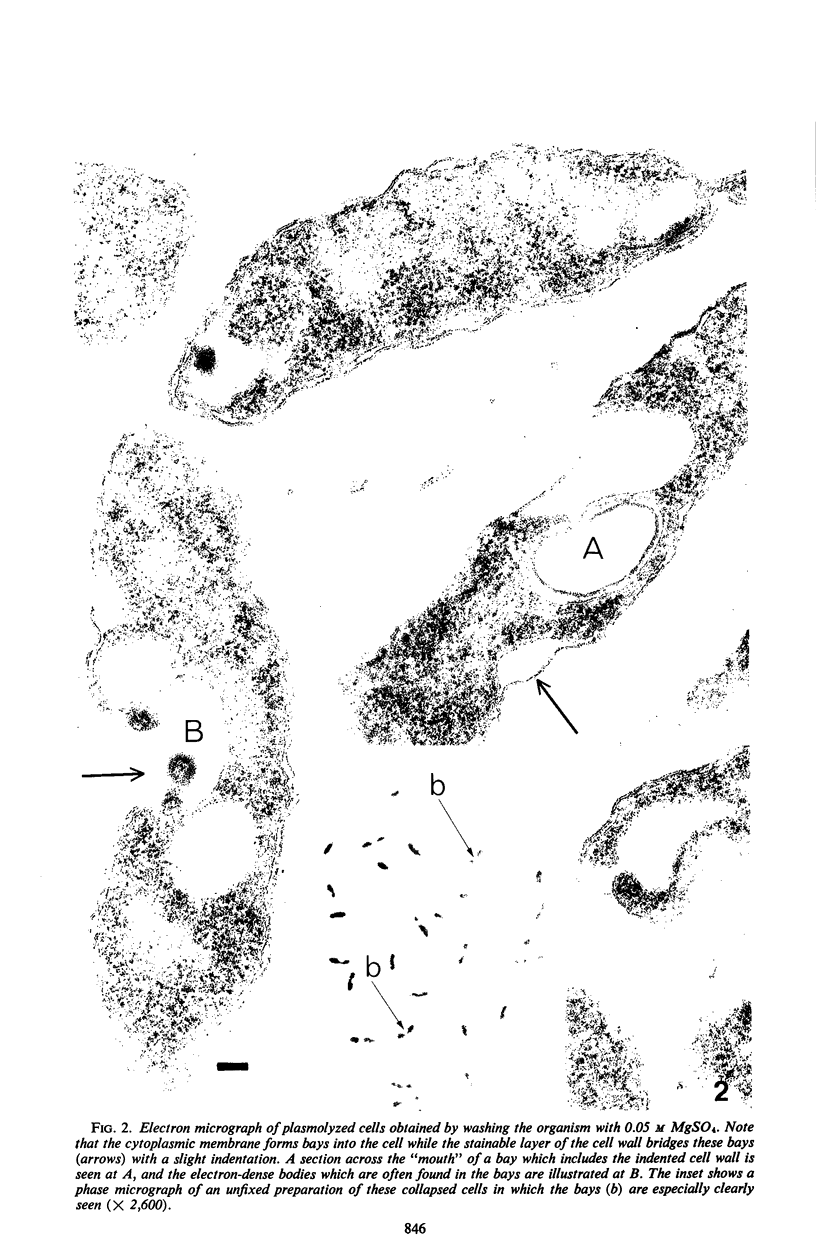
When cells of a marine pseudomonad were washed with a solution consisting of 0.3 m NaCl, 0.05 m MgSO4, and 0.01 m KCl (complete salts), they maintained their normal morphology. When washed with a solution of 0.05 m MgSO4, they became plasmolyzed as indicated by both phase and electron microscopy. Suspensions of cells washed with 0.05 m MgSO4 showed an increase in optical density (OD) when 0.3 m NaCl was added, and this was followed by a decrease in OD upon the further addition of 0.01 m KCl. Salts of other monovalent cations were not effective in replacing K+ in producing the OD decrease. Phase-contrast microscopy revealed that the increase in OD was accompanied by a decrease in cell size, and the decrease in OD, by an increase in the cell size. Both phase and electron microscopy showed that the K+-dependent decrease in OD was accompanied by deplasmolysis of the cells. Na+ was required in the suspending medium in addition to K+ to obtain deplasmolysis. The intracellular K+ concentration in cells which had been washed with complete salts and which had retained their normal morphology was found to be 0.290 m. In cells plasmolyzed by washing with 0.05 m MgSO4, the intracellular K+ concentration was 0.004 m. Deplasmolyzed cells contained 0.330 m K+. The membrane profile of plasmolyzed cells was retained when protoplasts were formed. The protoplasts became spherical if incubated in a solution permitting the deplasmolysis of the parent cells. The evidence obtained indicates that plasmolysis and deplasmolysis under the conditions described was due to the loss and gain, respectively, of K+ by the cells. The effect of Na+ could be ascribed to its capacity to control the porosity of the cytoplasmic membrane of this organism.
Full text
PDF


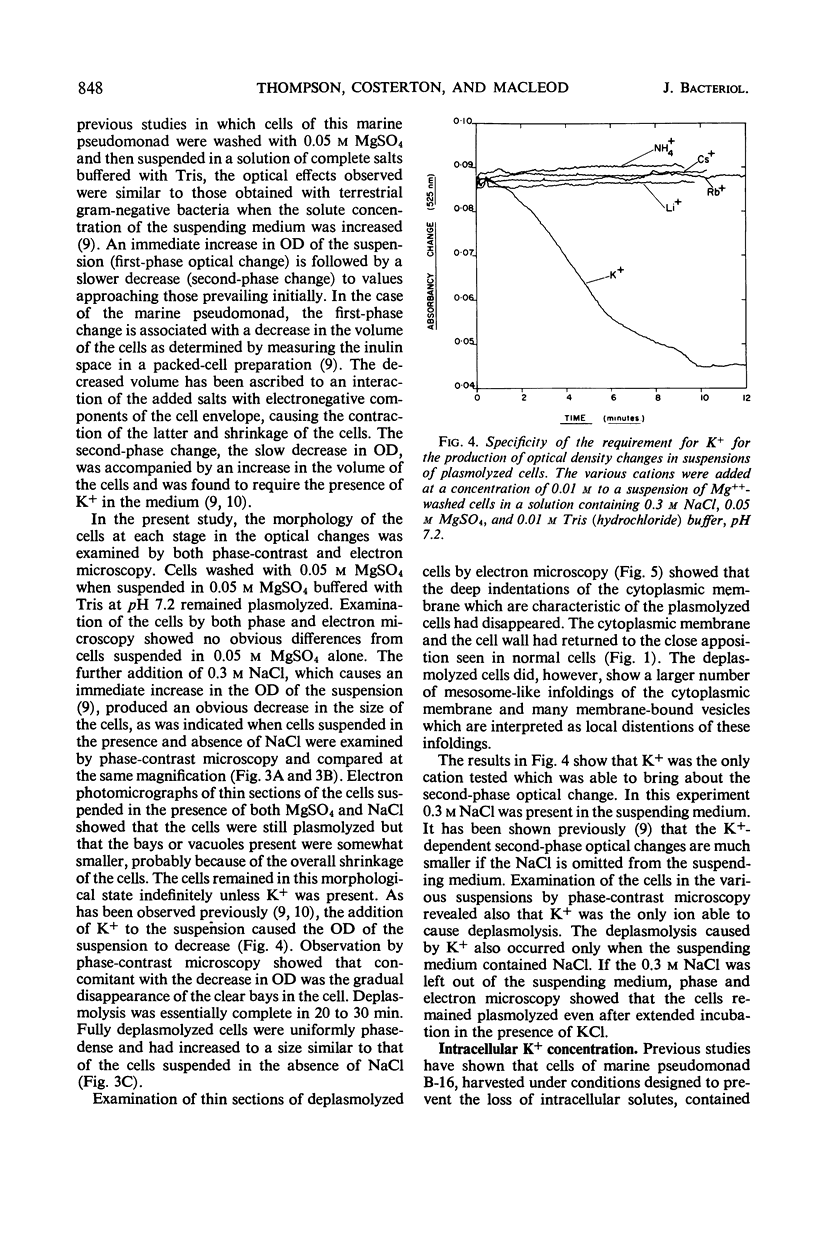
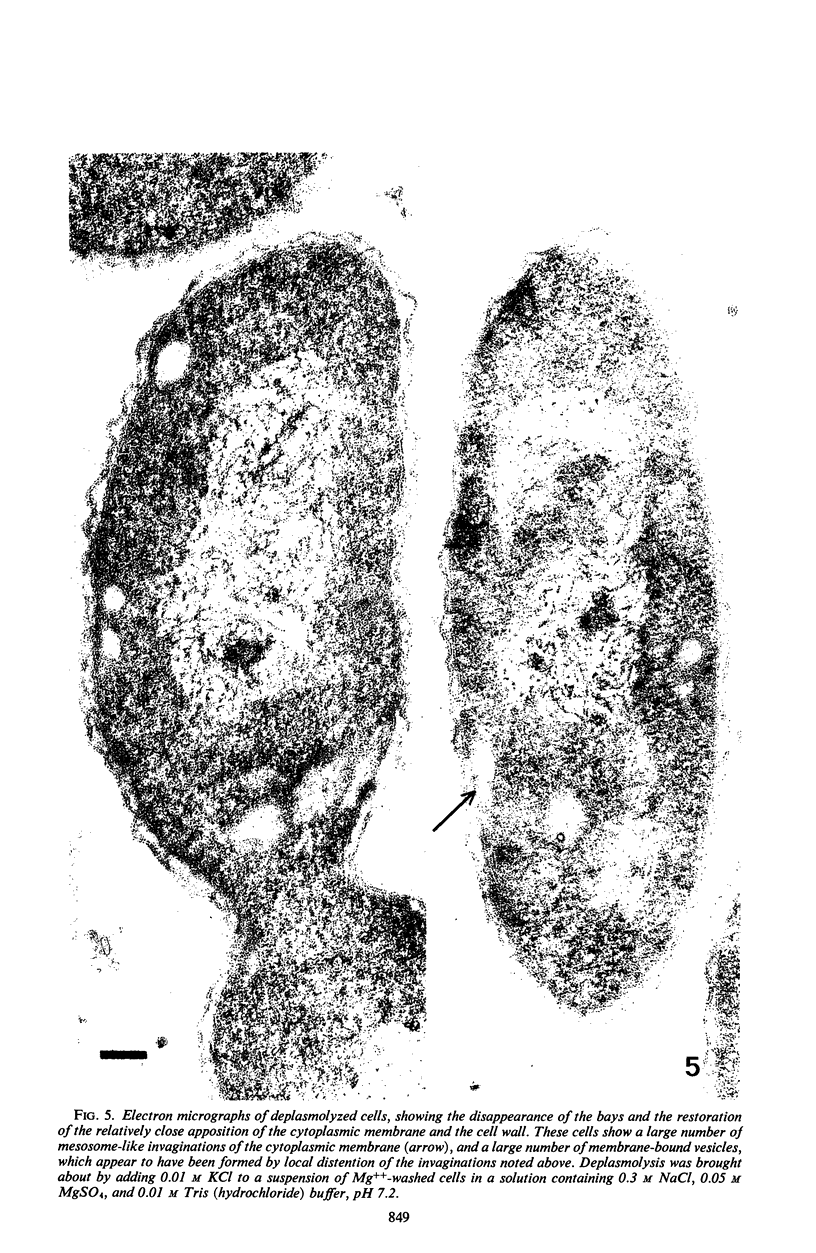

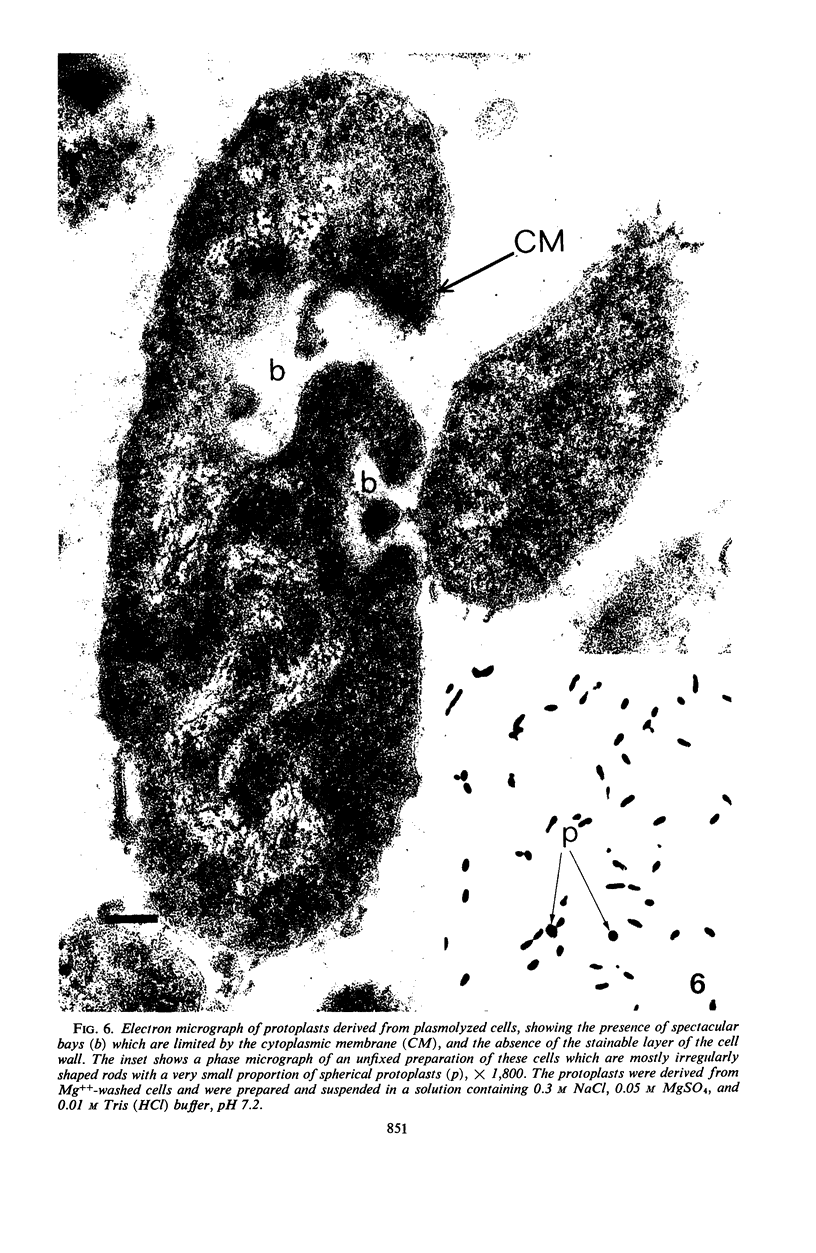
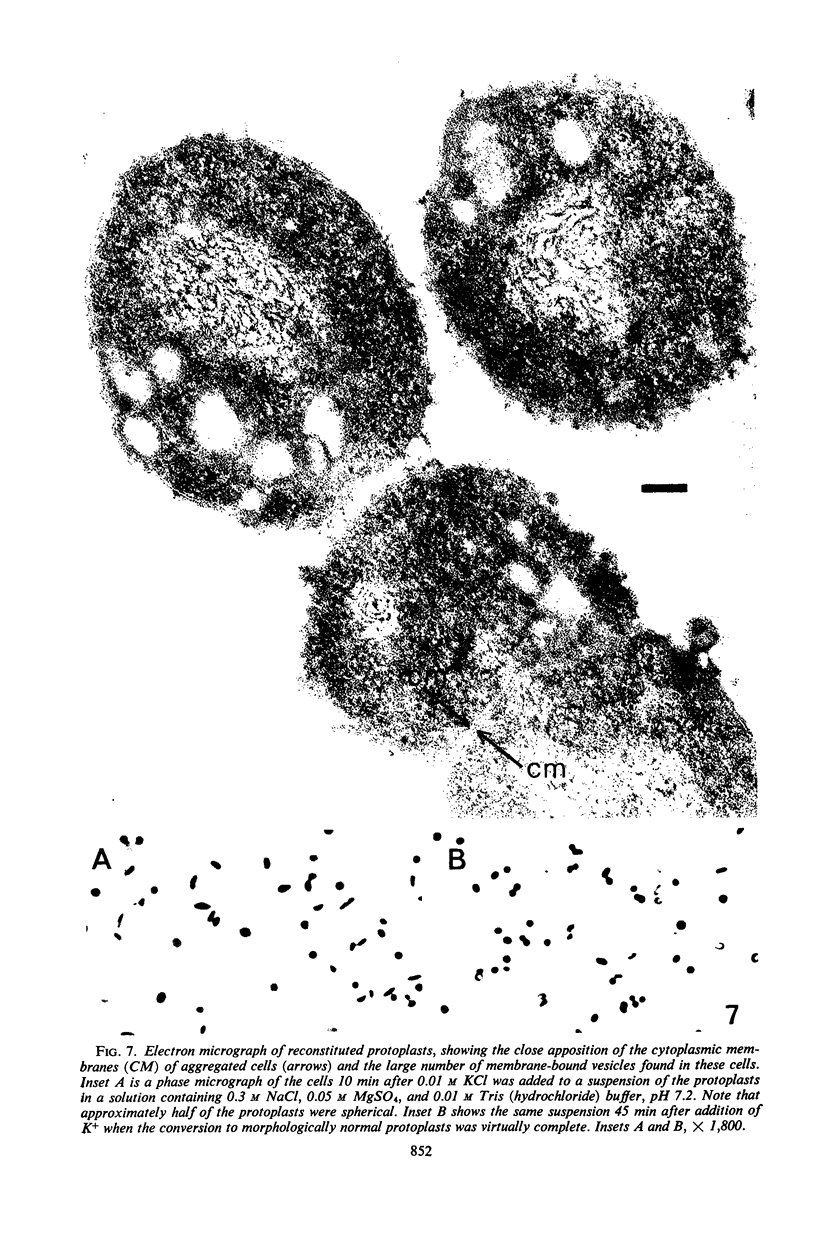


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bayer M. E. Areas of adhesion between wall and membrane of Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1968 Oct;53(3):395–404. doi: 10.1099/00221287-53-3-395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHRISTIAN J. H., WALTHO J. A. The sodium and potassium content of non-halophilic bacteria in relation to salt tolerance. J Gen Microbiol. 1961 May;25:97–102. doi: 10.1099/00221287-25-1-97. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COTA-ROBLES E. H. ELECTRON MICROSCOPY OF PLASMOLYSIS IN ESCHERICHIA COLI. J Bacteriol. 1963 Mar;85:499–503. doi: 10.1128/jb.85.3.499-503.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costerton J. W., Forsberg C., Matula T. I., Buckmire F. L., MacLeod R. A. Nutrition and metabolism of marine bacteria. XVI. Formation of protoplasts, spheroplasts, and related forms from a gram-negative marine bacterium. J Bacteriol. 1967 Nov;94(5):1764–1777. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.5.1764-1777.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Voe I. W., Thompson J., Costerton J. W., MacLeod R. A. Stability and comparative transport capacity of cells, mureinoplasts, and true protoplasts of a gram-negative bacterium. J Bacteriol. 1970 Mar;101(3):1014–1026. doi: 10.1128/jb.101.3.1014-1026.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOCH A. L. Some calculations on the turbidity of mitochondria and bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1961 Aug 19;51:429–441. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(61)90599-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MURRAY R. G., STEED P., ELSON H. E. THE LOCATION OF THE MUCOPEPTIDE IN SECTIONS OF THE CELL WALL OF ESCHERICHIA COLI AND OTHER GRAM-NEGATIVE BACTERIA. Can J Microbiol. 1965 Jun;11:547–560. doi: 10.1139/m65-072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matula T. I., MacLeod R. A. Mechanism of optical effects in suspensions of a marine pseudomonad. J Bacteriol. 1969 Oct;100(1):403–410. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.1.403-410.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matula T. I., Srivastava V. S., Wong P., MacLeod R. A. Transport and retention of K+ and other metabolites in a marine pseudomonad and their relation to the mechanism of optical effects. J Bacteriol. 1970 Jun;102(3):790–796. doi: 10.1128/jb.102.3.790-796.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS E. S. The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:208–212. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheie P. O. Plasmolysis of Escherichia coli B-r with sucrose. J Bacteriol. 1969 May;98(2):335–340. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.2.335-340.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholander P. F. Osmotic mechanism and negative pressure. Science. 1967 Apr 7;156(3771):67–69. doi: 10.1126/science.156.3771.67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson I. L. The cytological effects of myxin on Escherichia coli. Can J Microbiol. 1969 Jul;15(7):707–711. doi: 10.1139/m69-125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong P. T., Thompson J., MacLeod R. A. Nutrition and metabolism of marine bacteria. XVII. Ion-dependent retention of alpha-aminoisobutyric acid and its relation to Na+ dependent transport in a marine pseudomonad. J Biol Chem. 1969 Feb 10;244(3):1016–1025. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]