Abstract
When mink kits were infected neonatally with a highly virulent strain of Aleutian disease virus (ADV), 100% of both Aleutian and non-Aleutian genotype mink died of interstitial pneumonia characterized by permissive ADV infection of alveolar type II cells. Treatment of infected kits with either mink anti-ADV gamma globulin or mouse monoclonal antibodies against ADV structural proteins reduced mortality by 50 to 75% and drastically reduced the severity of clinical signs. Interestingly, mink kits that survived the acute pulmonary disease all developed the chronic form of immune complex-mediated Aleutian disease. Thus, the antibodies directed against ADV structural proteins were capable of modulating the in vivo pathogenicity from an acute fulminant disease to a chronic immune complex-mediated disorder. The mechanism of this modulation was examined by strand-specific in situ hybridization. We found that the number of ADV-infected type II cells was the same in both untreated and antibody-treated kits. However, in the treated kits, viral replication and transcription were restricted at the cellular level. These data suggested that antibodies prevented acute viral pneumonia by restricting the intracellular level of viral replication and that the relevant antigenic determinants were contained within the viral structural proteins. The restricted levels of viral replication and transcription seen in antibody-treated mink kits resembled the levels observed in infected adult mink and suggested a role of antiviral antibodies in development of persistent infection and chronic immune complex disease.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aasted B. Aleutian disease of mink. Virology and immunology. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand Suppl. 1985;287:1–47. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aasted B. Purification and characterization of Aleutian disease virus. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1980 Dec;88(6):323–328. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1980.tb02650.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alexandersen S., Aasted B. Restricted heterogeneity of the early antibody response to Aleutian disease virus in mink kits. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand C. 1986 Aug;94(4):137–143. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1986.tb02103.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alexandersen S. Acute interstitial pneumonia in mink kits: experimental reproduction of the disease. Vet Pathol. 1986 Sep;23(5):579–588. doi: 10.1177/030098588602300506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alexandersen S., Bloom M. E. Studies on the sequential development of acute interstitial pneumonia caused by Aleutian disease virus in mink kits. J Virol. 1987 Jan;61(1):81–86. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.1.81-86.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alexandersen S., Bloom M. E., Wolfinbarger J. Evidence of restricted viral replication in adult mink infected with Aleutian disease of mink parvovirus. J Virol. 1988 May;62(5):1495–1507. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.5.1495-1507.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
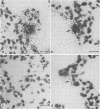
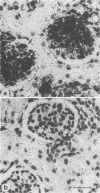
- Alexandersen S., Bloom M. E., Wolfinbarger J., Race R. E. In situ molecular hybridization for detection of Aleutian mink disease parvovirus DNA by using strand-specific probes: identification of target cells for viral replication in cell cultures and in mink kits with virus-induced interstitial pneumonia. J Virol. 1987 Aug;61(8):2407–2419. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.8.2407-2419.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alexandersen S., Hau J. Rocket line immunoelectrophoresis: an improved assay for simultaneous quantification of a mink parvovirus (Aleutian disease virus) antigen and antibody. J Virol Methods. 1985 Feb;10(2):145–151. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(85)90100-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alexandersen S., Uttenthal-Jensen A., Aasted B. Demonstration of non-degraded Aleutian disease virus (ADV) proteins in lung tissue from experimentally infected mink kits. Brief report. Arch Virol. 1986;87(1-2):127–133. doi: 10.1007/BF01310549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom M. E., Race R. E., Aasted B., Wolfinbarger J. B. Analysis of Aleutian disease virus infection in vitro and in vivo: demonstration of Aleutian disease virus DNA in tissues of infected mink. J Virol. 1985 Sep;55(3):696–703. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.3.696-703.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom M. E., Race R. E., Wolfinbarger J. B. Analysis of Aleutian disease of mink parvovirus infection using strand-specific hybridization probes. Intervirology. 1987;27(2):102–111. doi: 10.1159/000149727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom M. E., Race R. E., Wolfinbarger J. B. Characterization of Aleutian disease virus as a parvovirus. J Virol. 1980 Sep;35(3):836–843. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.3.836-843.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerny A., Sutter S., Bazin H., Hengartner H., Zinkernagel R. M. Clearance of lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus in antibody- and B-cell-deprived mice. J Virol. 1988 May;62(5):1803–1807. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.5.1803-1807.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesebro B., Bloom M., Hadlow W., Race R. Purification and ultrastructure of Aleutian disease virus of mink. Nature. 1975 Apr 3;254(5499):456–457. doi: 10.1038/254456a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cho H. J., Ingram D. G. Antigen and antibody in Aleutian disease in mink. I. Precipitation reaction by agar-gel electrophoresis. J Immunol. 1972 Feb;108(2):555–557. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dimmock N. J. Mechanisms of neutralization of animal viruses. J Gen Virol. 1984 Jun;65(Pt 6):1015–1022. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-65-6-1015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eklund C. M., Hadlow W. J., Kennedy R. C., Boyle C. C., Jackson T. A. Aleutian disease of mink: properties of the etiologic agent and the host responses. J Infect Dis. 1968 Dec;118(5):510–526. doi: 10.1093/infdis/118.5.510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujinami R. S., Oldstone M. B. Antiviral antibody reacting on the plasma membrane alters measles virus expression inside the cell. Nature. 1979 Jun 7;279(5713):529–530. doi: 10.1038/279529a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardiner E. M., Tattersall P. Evidence that developmentally regulated control of gene expression by a parvoviral allotropic determinant is particle mediated. J Virol. 1988 May;62(5):1713–1722. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.5.1713-1722.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gollins S. W., Porterfield J. S. A new mechanism for the neutralization of enveloped viruses by antiviral antibody. Nature. 1986 May 15;321(6067):244–246. doi: 10.1038/321244a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon Y. J., Johnson B., Romanowski E., Araullo-Cruz T. RNA complementary to herpes simplex virus type 1 ICP0 gene demonstrated in neurons of human trigeminal ganglia. J Virol. 1988 May;62(5):1832–1835. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.5.1832-1835.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas L., Löchelt M., Kaaden O. R. Detection of Aleutian disease virus DNA in tissues of naturally infected mink. J Gen Virol. 1988 Mar;69(Pt 3):705–710. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-3-705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haase A. T., Gantz D., Eble B., Walker D., Stowring L., Ventura P., Blum H., Wietgrefe S., Zupancic M., Tourtellotte W. Natural history of restricted synthesis and expression of measles virus genes in subacute sclerosing panencephalitis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):3020–3024. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.3020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haase A. T. The pathogenesis of slow virus infections: molecular analyses. J Infect Dis. 1986 Mar;153(3):441–447. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.3.441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadlow W. J., Race R. E., Kennedy R. C. Comparative pathogenicity of four strains of Aleutian disease virus for pastel and sapphire mink. Infect Immun. 1983 Sep;41(3):1016–1023. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.3.1016-1023.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper M. E., Marselle L. M., Gallo R. C., Wong-Staal F. Detection of lymphocytes expressing human T-lymphotropic virus type III in lymph nodes and peripheral blood from infected individuals by in situ hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(3):772–776. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.3.772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawgood S., Benson B. J., Schilling J., Damm D., Clements J. A., White R. T. Nucleotide and amino acid sequences of pulmonary surfactant protein SP 18 and evidence for cooperation between SP 18 and SP 28-36 in surfactant lipid adsorption. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(1):66–70. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.1.66. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy-Stoskopf S., Narayan O. Neutralizing antibodies to visna lentivirus: mechanism of action and possible role in virus persistence. J Virol. 1986 Jul;59(1):37–44. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.1.37-44.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen S., Alexandersen S., Lund E., Have P., Hansen M. Acute interstitial pneumonitis caused by Aleutian disease virus in mink kits. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand A. 1984 Sep;92(5):391–393. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1984.tb04419.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel B. The interaction of neutralized poliovirus with HeLa cells. I. Adsorption. Virology. 1967 Feb;31(2):238–247. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(67)90167-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter D. D., Larsen A. E., Porter H. G. Aleutian disease of mink. Adv Immunol. 1980;29:261–286. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60046-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter D. D., Larsen A. E., Porter H. G. Reduced severity of lesions in mink infected transplacentally with Aleutian disease virus. J Immunol. 1977 Sep;119(3):872–876. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter D. D., Larsen A. E., Porter H. G. The pathogenesis of Aleutian disease of mink. 3. Immune complex arteritis. Am J Pathol. 1973 May;71(2):331–344. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter D. D., Larsen A. E., Porter H. G. The pathogenesis of Aleutian disease of mink. I. In vivo viral replication and the host antibody response to viral antigen. J Exp Med. 1969 Sep 1;130(3):575–593. doi: 10.1084/jem.130.3.575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prieur D. J., Collier L. L. Animal model of human disease: Chédiak-Higashi syndrome. Am J Pathol. 1978 Feb;90(2):533–536. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prieur D. J., Collier L. L. Animal model of human disease: Chédiak-Higashi syndrome. Am J Pathol. 1978 Feb;90(2):533–536. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Race R. E., Chesebro B., Bloom M. E., Aasted B., Wolfinbarger J. Monoclonal antibodies against Aleutian disease virus distinguish virus strains and differentiate sites of virus replication from sites of viral antigen sequestration. J Virol. 1986 Jan;57(1):285–293. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.1.285-293.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid D. M., Reid T. M., Brown T., Rennie J. A., Eastmond C. J. Human parvovirus-associated arthritis: a clinical and laboratory description. Lancet. 1985 Feb 23;1(8426):422–425. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)91146-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth S., Kaaden O. R., van Dawen S., Moennig V. Aleutian disease virus in B and T lymphocytes from blood and spleen and in bone marrow cells from naturally infected mink. Intervirology. 1984;22(4):211–217. doi: 10.1159/000149553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shanley J. D., Jordan M. C., Stevens J. G. Modification by adoptive humoral immunity of murine cytomegalovirus infection. J Infect Dis. 1981 Feb;143(2):231–237. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.2.231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St George J. A., Cranz D. L., Zicker S. C., Etchison J. R., Dungworth D. L., Plopper C. G. An immunohistochemical characterization of rhesus monkey respiratory secretions using monoclonal antibodies. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1985 Sep;132(3):556–563. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1985.132.3.556. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiehm E. R., Ashida E., Kim K. S., Winston D. J., Haas A., Gale R. P. Intravenous immunoglobulins as therapeutic agents. Ann Intern Med. 1987 Sep;107(3):367–382. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-107-2-367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stolze B., Kaaden O. R. Apparent lack of neutralizing antibodies in Aleutian disease is due to masking of antigenic sites by phospholipids. Virology. 1987 May;158(1):174–180. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90251-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warr R. G., Hawgood S., Buckley D. I., Crisp T. M., Schilling J., Benson B. J., Ballard P. L., Clements J. A., White R. T. Low molecular weight human pulmonary surfactant protein (SP5): isolation, characterization, and cDNA and amino acid sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(22):7915–7919. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.22.7915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White D. G., Woolf A. D., Mortimer P. P., Cohen B. J., Blake D. R., Bacon P. A. Human parvovirus arthropathy. Lancet. 1985 Feb 23;1(8426):419–421. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)91145-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White R. T., Damm D., Miller J., Spratt K., Schilling J., Hawgood S., Benson B., Cordell B. Isolation and characterization of the human pulmonary surfactant apoprotein gene. 1985 Sep 26-Oct 2Nature. 317(6035):361–363. doi: 10.1038/317361a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]